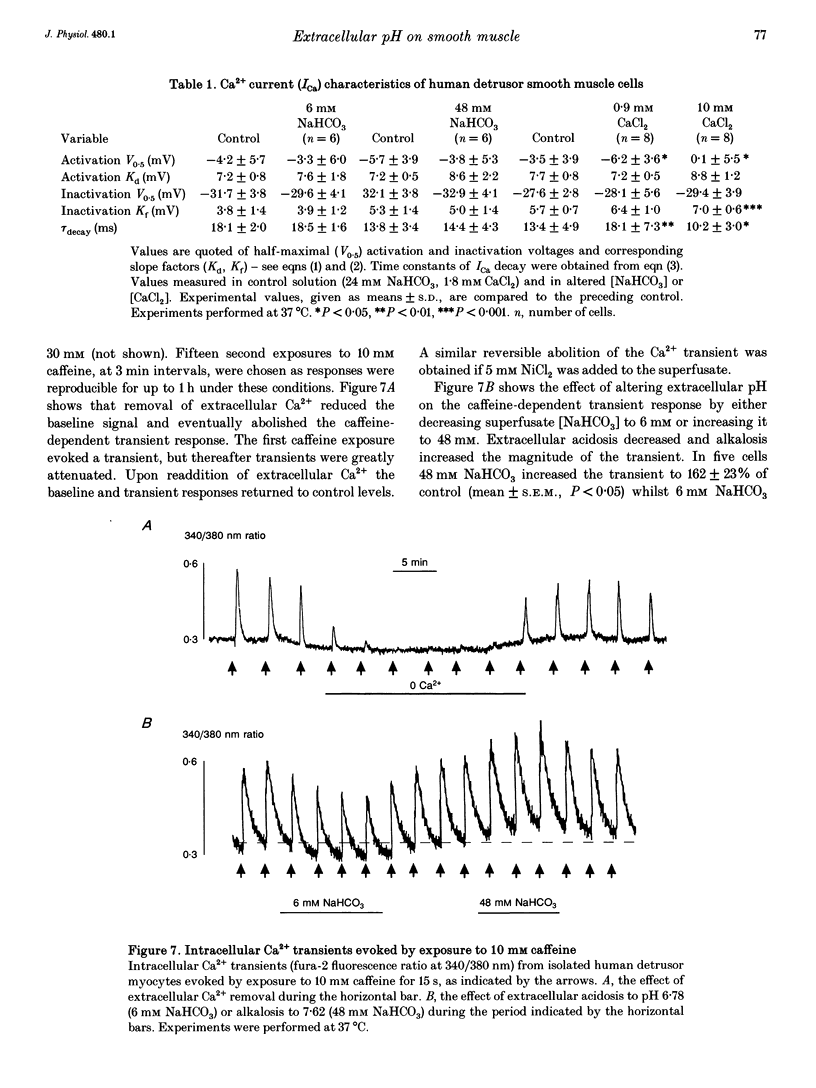
Abstract
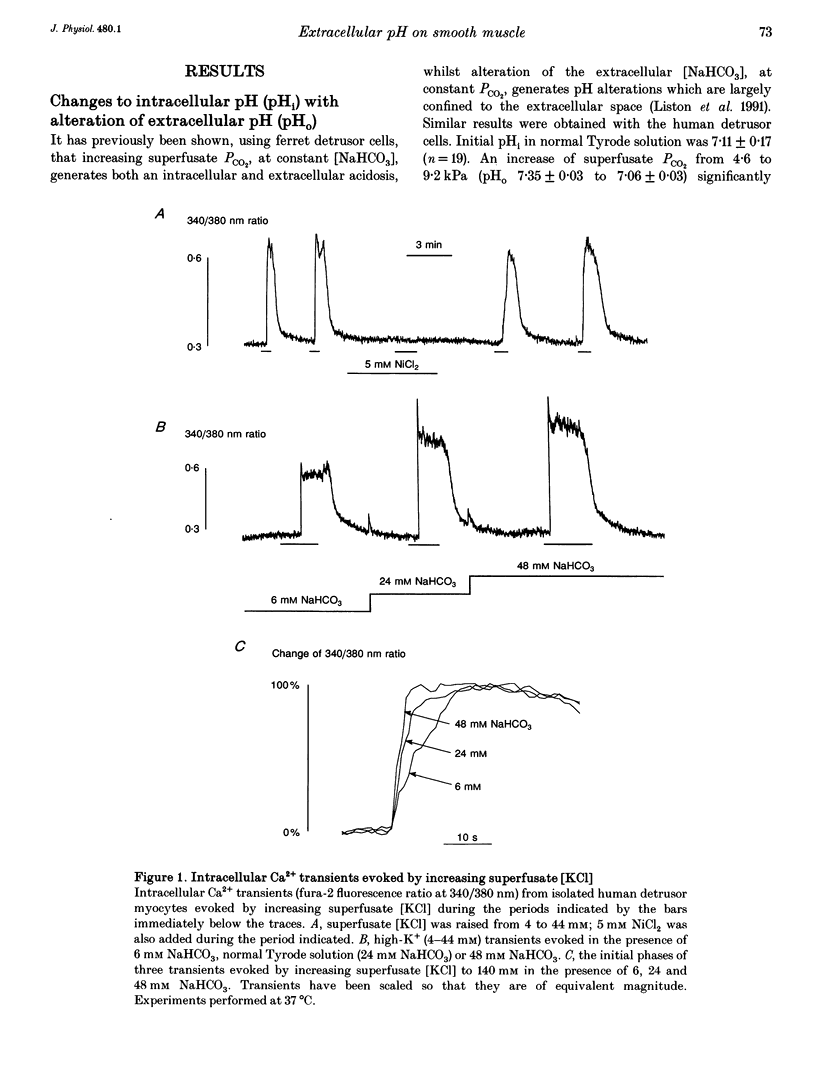
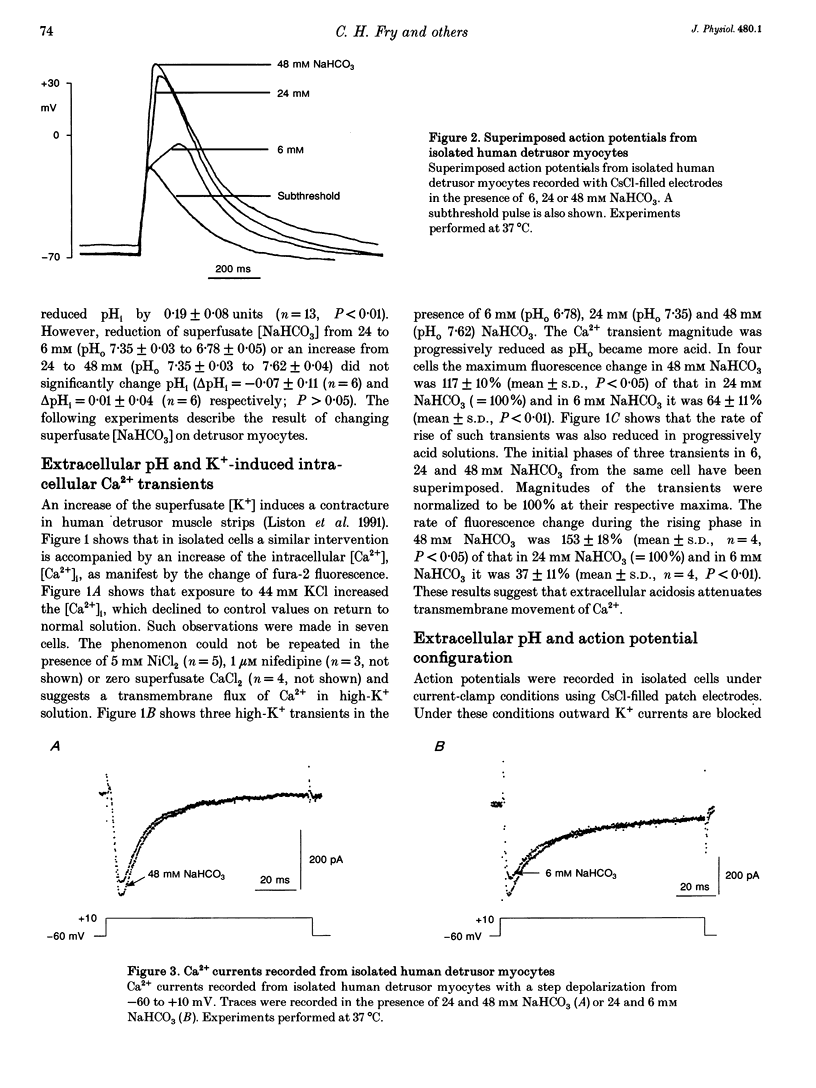
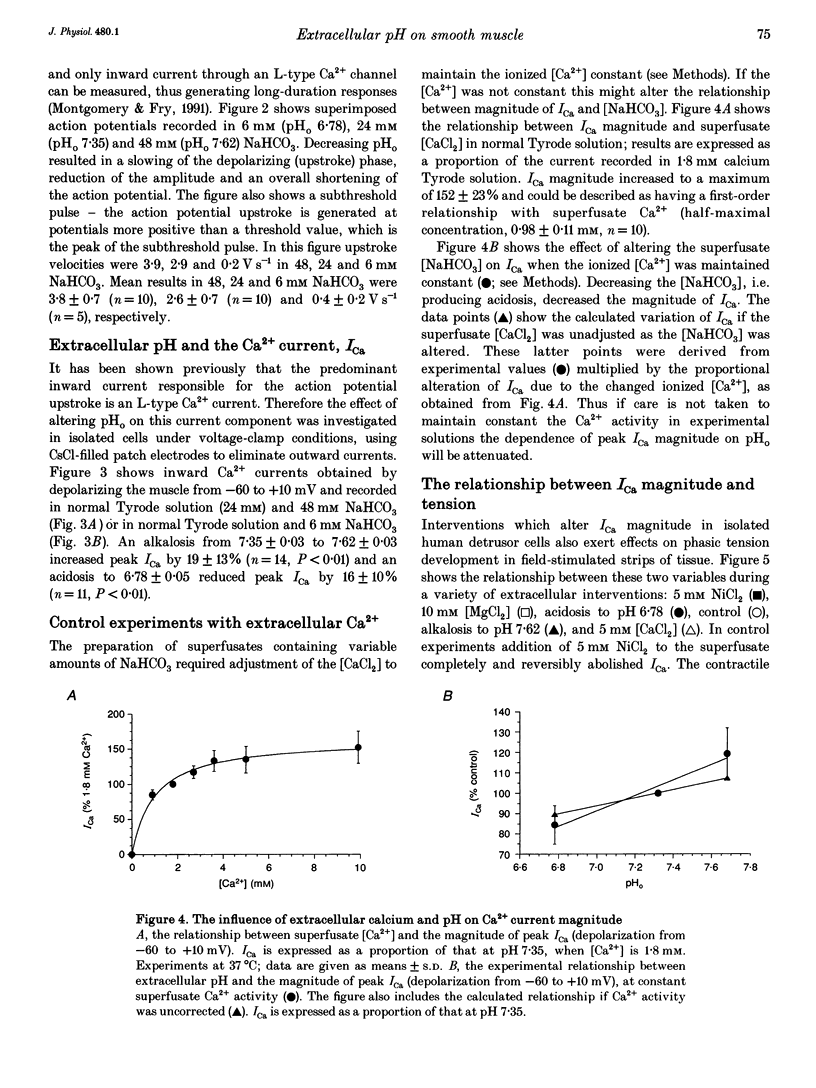
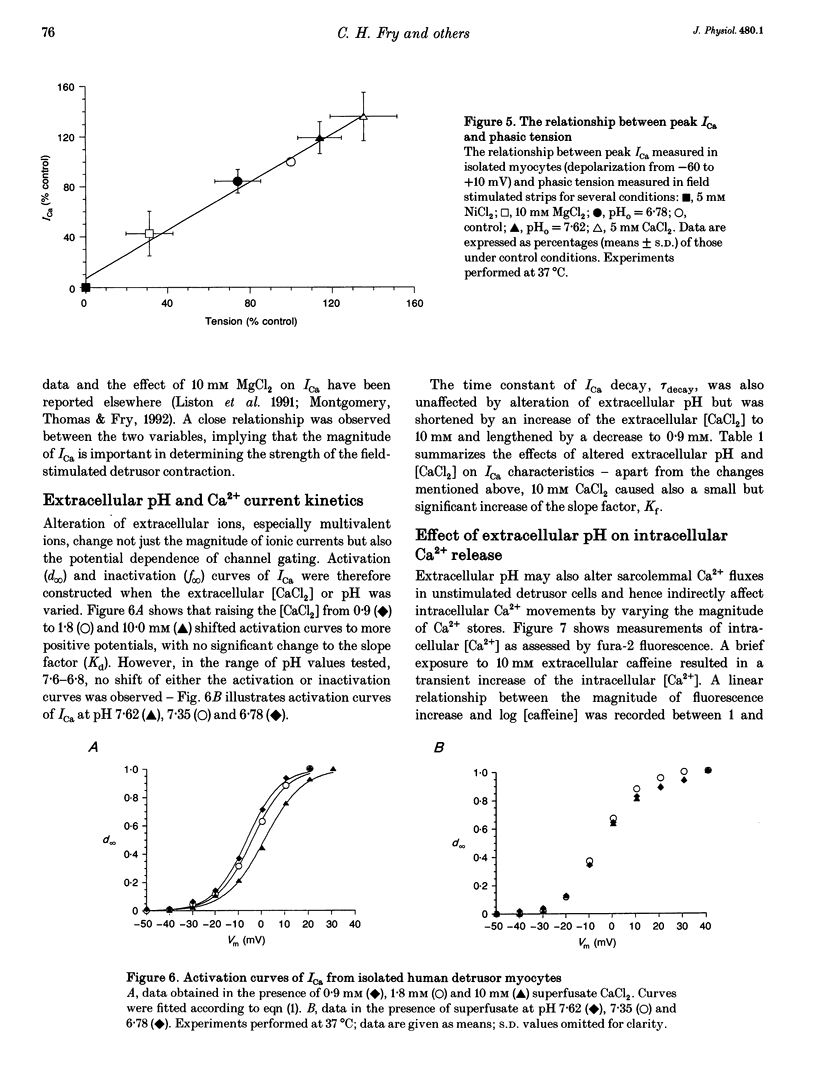
1. The influence of extracellular pH changes on intracellular pH and [Ca2+], as well as on L-type Ca2+ currents, has been investigated in isolated human detrusor smooth muscle cells. 2. Alteration of extracellular pH by changing superfusate PCO2 also changed intracellular pH. A change of superfusate pH made by altering the [NaHCO3] at constant PCO2 was not reflected in a change in intracellular pH. 3. Extracellular acidosis attenuated the magnitude and rate of change of intracellular [Ca2+] evoked by raising the extracellular [KCl]. 4. Extracellular acidosis attenuated the rate of rise and amplitude of the action potential, as well as the magnitude of the L-type Ca2+ current. In the pH range 6.78-7.62 no alteration to the voltage dependence of Ca2+ current activation or inactivation was recorded. 5. A close proportional relationship between tension generated by multicellular strips and the magnitude of peak inward Ca2+ current in isolated cells was noted over a wide range of the two variables using a number of interventions, including alteration to extracellular pH, [Ca2+] and [Mg2+]. 6. Extracellular acidosis attenuated the magnitude of caffeine-dependent intracellular Ca2+ transients and the resting [Ca2+]i between transients. Acidosis was without effect on the rise of [Ca2+]i induced by carbachol. 7. The results suggest that the negative inotropic effect of extracellular acidosis can be accounted for by attenuation of the L-type Ca2+ current. The results also imply that intracellular stores are influenced by transmembrane Ca2+ fluxes at rest and that such fluxes are also attenuated by extracellular H+.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aickin C. C., Brading A. F. The effect of loop diuretics on Cl- transport in smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens and taenia from the caecum. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:33–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisner D. A., Nichols C. G., O'Neill S. C., Smith G. L., Valdeolmillos M. The effects of metabolic inhibition on intracellular calcium and pH in isolated rat ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:393–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldrup J., Thorup J., Nielsen S. L., Hald T., Hainau B. Permeability and ultrastructure of human bladder epithelium. Br J Urol. 1983 Oct;55(5):488–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1983.tb03354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry C. H., Poole-Wilson P. A. Effects of acid-base changes on excitation--contraction coupling in guinea-pig and rabbit cardiac ventricular muscle. J Physiol. 1981;313:141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich V Y. a., Isenberg G. Depolarization-mediated intracellular calcium transients in isolated smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:187–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Isenberg G. Caffeine-induced release and reuptake of Ca2+ by Ca2+ stores in myocytes from guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:99–117. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich V. Y., Isenberg G. Contribution of Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release to the [Ca2+]i transients in myocytes from guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:119–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam F. R., 3rd, Rivas P. A., Wendt D. J., Starmer C. F., Grant A. O. Extracellular pH modulates block of both sodium and calcium channels by nicardipine. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1178–H1184. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iijima T., Ciani S., Hagiwara S. Effects of the external pH on Ca channels: experimental studies and theoretical considerations using a two-site, two-ion model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):654–658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kass R. S., Krafte D. S. Negative surface charge density near heart calcium channels. Relevance to block by dihydropyridines. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Apr;89(4):629–644. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Role of G-proteins in muscarinic receptor inward and outward currents in rabbit jejunal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:395–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafte D. S., Kass R. S. Hydrogen ion modulation of Ca channel current in cardiac ventricular cells. Evidence for multiple mechanisms. J Gen Physiol. 1988 May;91(5):641–657. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liston T. G., Palfrey E. L., Raimbach S. J., Fry C. H. The effects of pH changes on human and ferret detrusor muscle function. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery B. S., Fry C. H. The action potential and net membrane currents in isolated human detrusor smooth muscle cells. J Urol. 1992 Jan;147(1):176–184. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)37192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery B. S., Thomas P. J., Fry C. H. The actions of extracellular magnesium on isolated human detrusor muscle function. Br J Urol. 1992 Sep;70(3):262–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1992.tb15728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTS R. F., AYER J. L., SCHIESS W. A. The renal regulation of acid-base balance in man; the reabsorption and excretion of bicarbonate. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey E. L., Fry C. H., Shuttleworth K. E. A new in vitro microsuperfusion technique for investigation of human detrusor muscle. Br J Urol. 1984 Dec;56(6):635–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1984.tb06134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prod'hom B., Pietrobon D., Hess P. Interactions of protons with single open L-type calcium channels. Location of protonation site and dependence of proton-induced current fluctuations on concentration and species of permeant ion. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):23–42. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Ozaki H., Karaki H. Multiple effects of caffeine on contraction and cytosolic free Ca2+ levels in vascular smooth muscle of rat aorta. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;338(4):443–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00172125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh H., Seyama I. On the mechanism by which changes in extracellular pH affect the electrical activity of the rabbit sino-atrial node. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:181–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethia K. K., Smith J. C. The effect of pH and lignocaine on detrusor instability. Br J Urol. 1987 Dec;60(6):516–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1987.tb05032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuringer D., Diarra A., Sauvé R. Modulation by extracellular pH of bradykinin-evoked activation of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):H656–H666. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.3.H656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


