Abstract
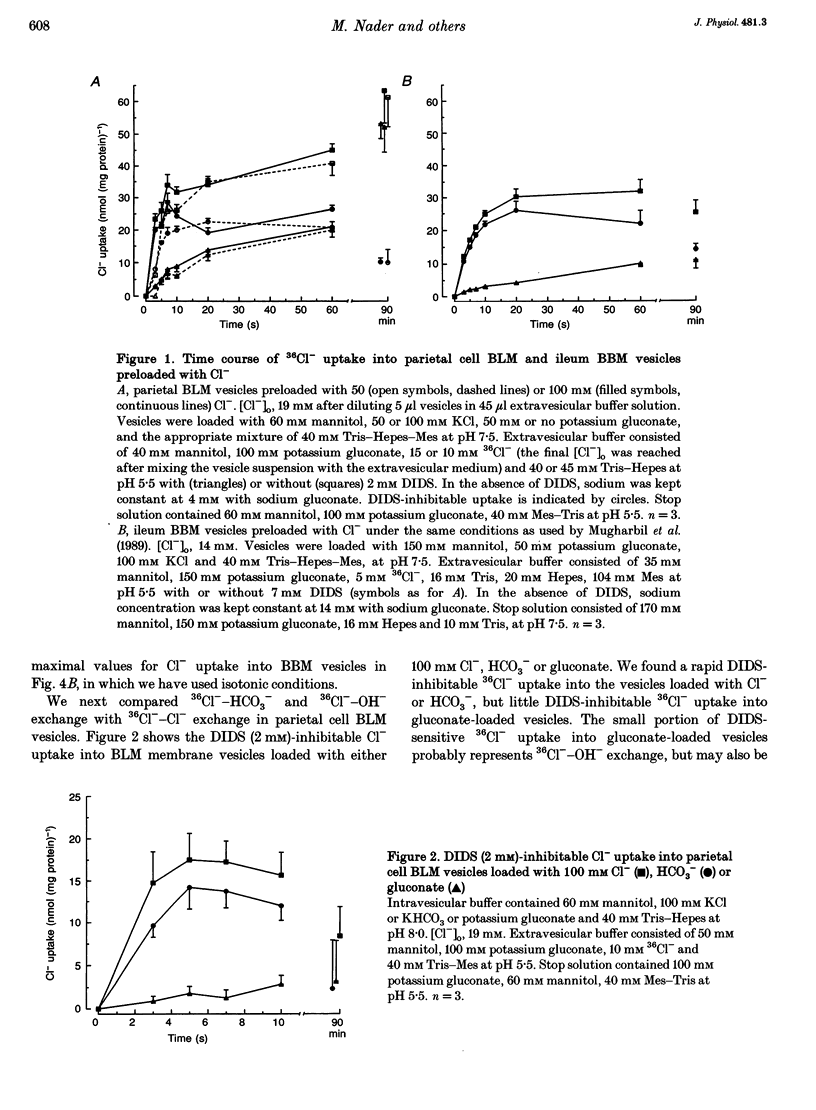
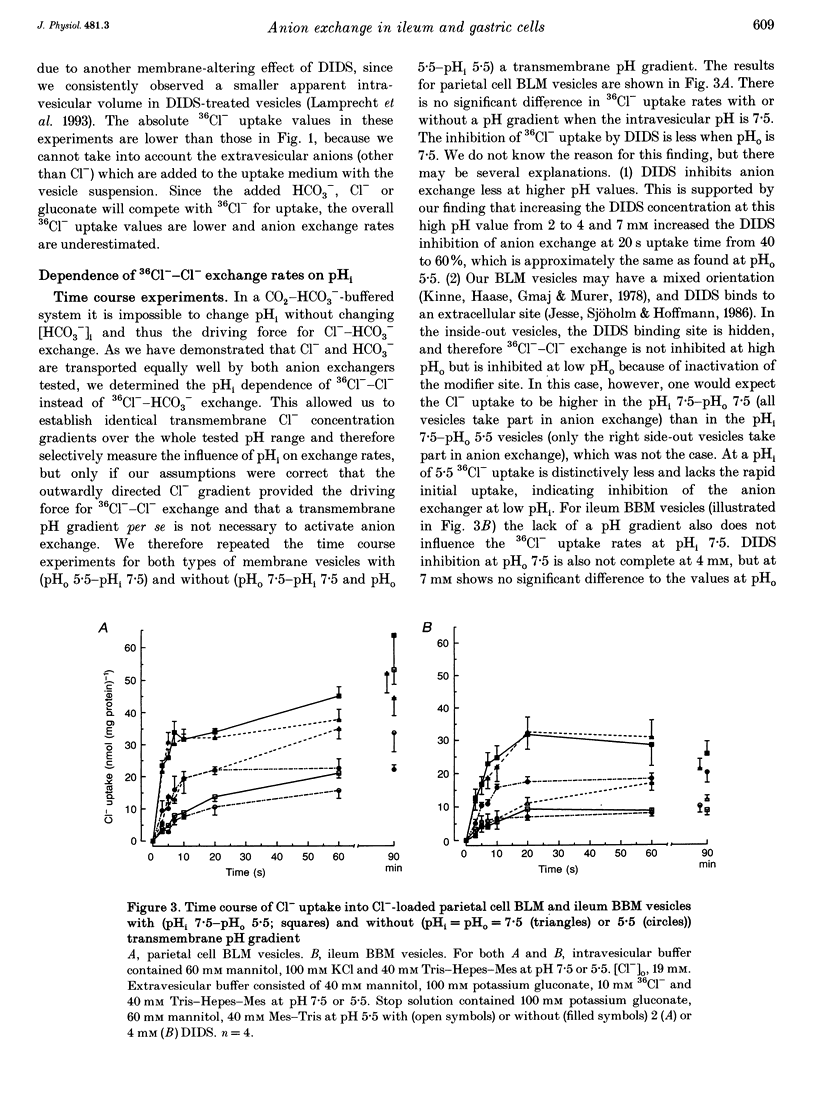
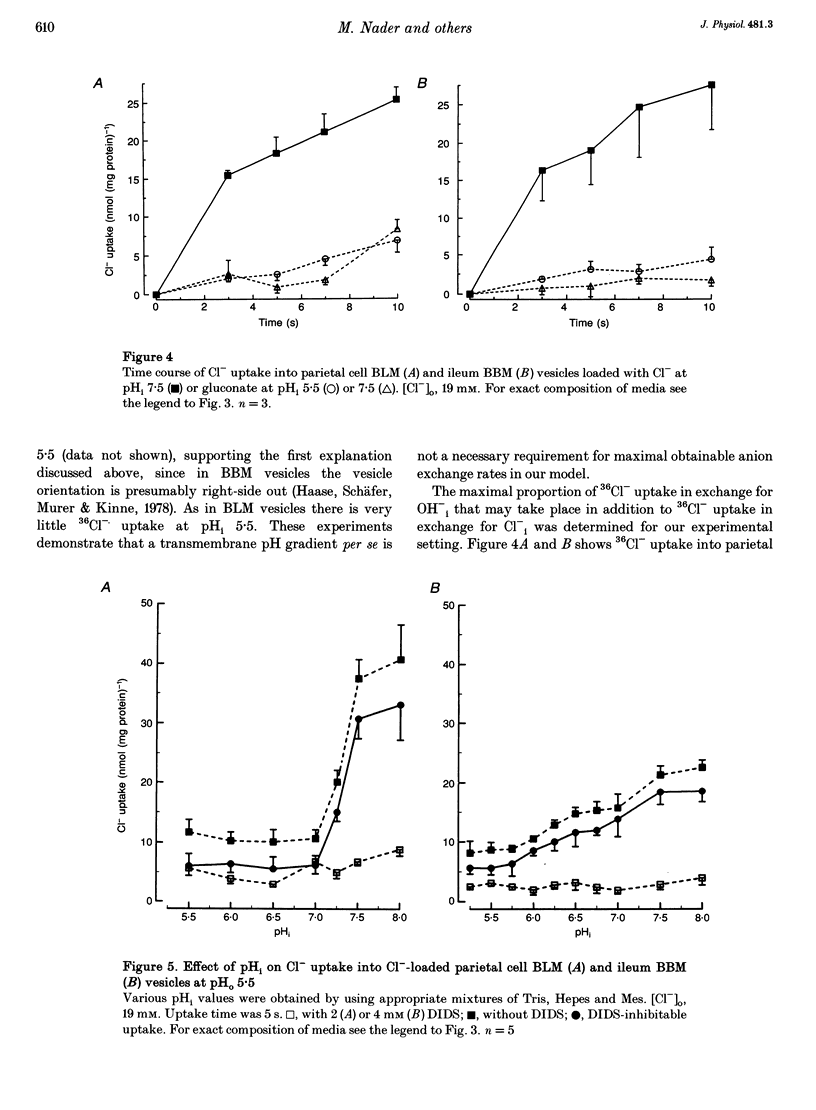
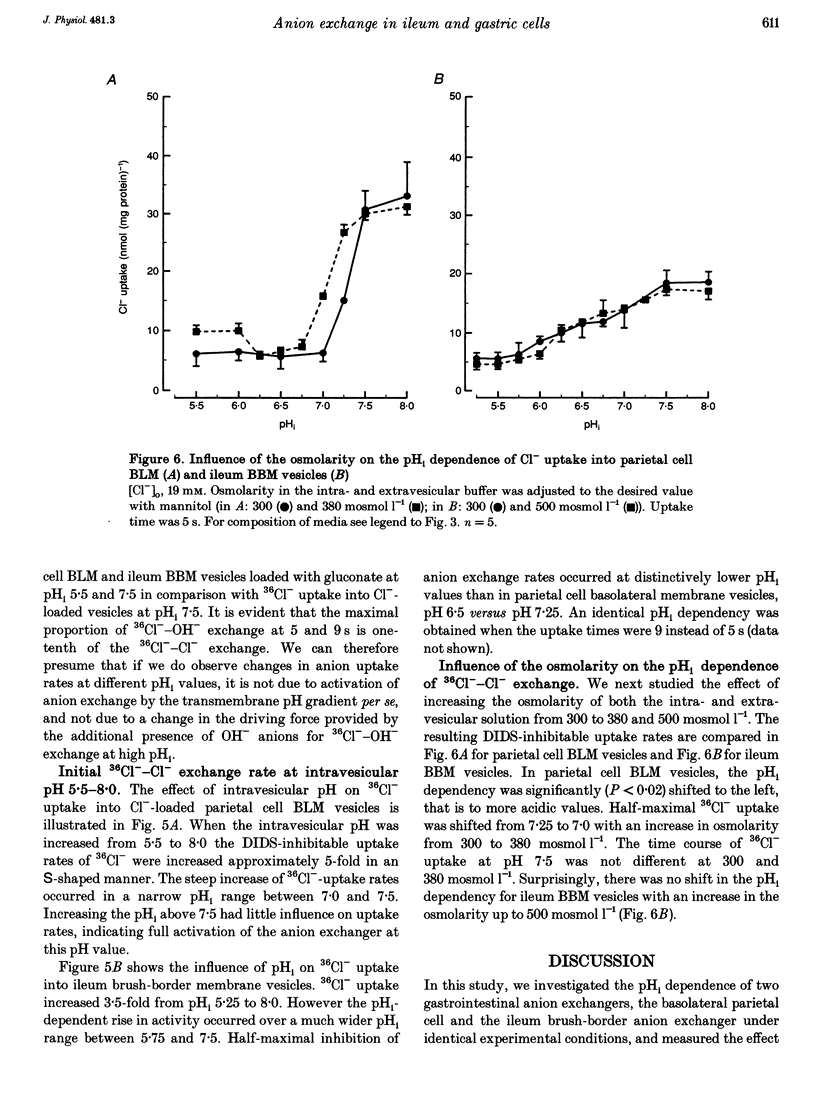
1. The purpose of this study was to look for evidence of a pH-sensitive modifier site on the parietal cell basolateral anion exchanger, determine the pH range in which allosteric regulation takes place, investigate the effect of the osmolarity on internal pH (pHi) dependence and compare it with that of the ileum brush-border anion exchanger. 2. When the pHi in parietal cell basolateral membrane (BLM) vesicles was increased, the rate of Cl(-)-gradient-driven 36Cl- uptake increased from 6.03 +/- 2.24 to 38.09 +/- 3.33 nmol (mg protein)-1 with the steep increase in anion exchange rates occurring within a narrow pH range between pHi 7.0 and 7.5. This was due to allosteric activation by internal OH- and not due to a change in driving force, since the driving force for maximal exchange rates was provided by the outwardly directed Cl- gradient. 3. The pHi dependency curve of parietal cell BLM anion exchange rates was shifted to the left by 0.25 pH units by increasing the osmolarity of the intra- and extravesicular solutions from 300 to 380 mosmol l-1. Thus cell shrinking may activate the parietal cell anion exchanger without a change in pHi and without phosphorylation of the anion exchanger protein. 4. In ileum brush-border membranes, the pHi-dependent increase in the rate of Cl(-)-gradient-driven 36Cl- uptake was more gradual and the half-maximal anion exchange rate was attained at lower pHi (pH 6.5). Increasing the osmolarity from 300 to 500 mosmol l-1 had no effect on pH dependence. 5. We conclude that the parietal cell basolateral and ileum brush-border anion exchangers possess an internal modifier site for allosteric activation by OH-, but the pH range in which allosteric regulation occurs differs between the two exchangers, as does the effect of an increase in osmolarity. Since current evidence suggests that both the parietal cell basolateral and the ileum brush-border anion exchanger are encoded by the AE2 gene, the differences in pHi dependence between the two may be due to alternative splicing, post-transcriptional modification, or the different membrane environment. 6. The pHi range for allosteric activation found in this study would suggest that for both the ileum and the parietal cell anion exchanger, but especially for the latter, a potentiating effect of the allosteric activation and the HCO3- availability occurs within the physiological pHi range and can cause dramatic increases in maximal anion exchange rates with increasing pHi.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chow A., Dobbins J. W., Aronson P. S., Igarashi P. cDNA cloning and localization of a band 3-related protein from ileum. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):G345–G352. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.3.G345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debellis L., Curci S., Frömter E. Microelectrode determination of oxyntic cell pH in intact frog gastric mucosa. Effect of histamine. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Dec;422(3):253–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00376210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E. B. Increase of intracellular pH in secreting frog gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 15;632(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd Assay of Na,K-ATPase in plasma membrane preparations: increasing the permeability of membrane vesicles using sodium dodecyl sulfate buffered with bovine serum albumin. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Yamaguchi D. T., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Cytosolic pH regulation in osteoblasts. Regulation of anion exchange by intracellular pH and Ca2+ ions. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Jan;95(1):121–145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase W., Schäfer A., Murer H., Kinne R. Studies on the orientation of brush-border membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):57–62. doi: 10.1042/bj1720057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna S. D., Mircheff A. K., Wright E. M. Alkaline phosphatase of basal lateral and brush border plasma membranes from intestinal epithelium. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(4):451–466. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey S. J. Intracellular pH measurements in gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jul;237(1):E82–E89. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.1.E82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst B. H., Forte J. G. Redistribution and characterization of (H+ + K+)-ATPase membranes from resting and stimulated gastric parietal cells. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):641–649. doi: 10.1042/bj2310641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann E. K., Simonsen L. O. Membrane mechanisms in volume and pH regulation in vertebrate cells. Physiol Rev. 1989 Apr;69(2):315–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessen F., Sjøholm C., Hoffmann E. K. Identification of the anion exchange protein of Ehrlich cells: a kinetic analysis of the inhibitory effects of 4,4'-diisothiocyano-2,2'-stilbene-disulfonic acid (DIDS) and labeling of membrane proteins with 3H-DIDS. J Membr Biol. 1986;92(3):195–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01869388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knickelbein R., Aronson P. S., Schron C. M., Seifter J., Dobbins J. W. Sodium and chloride transport across rabbit ileal brush border. II. Evidence for Cl-HCO3 exchange and mechanism of coupling. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 1):G236–G245. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.2.G236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopito R. R. Molecular biology of the anion exchanger gene family. Int Rev Cytol. 1990;123:177–199. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60674-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudrycki K. E., Newman P. R., Shull G. E. cDNA cloning and tissue distribution of mRNAs for two proteins that are related to the band 3 Cl-/HCO3- exchanger. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):462–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert R. W., Bradley M. E., Mircheff A. K. pH-sensitive anion exchanger in rat lacrimal acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):G517–G523. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.3.G517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamprecht G., Seidler U., Classen M. Intracellular pH-regulating ion transport mechanisms in parietal cell basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):G903–G910. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.265.5.G903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. Y., Ahluwalia M., Gruenstein E. An alkaline pH-activated Cl(-)-anion exchanger regulates pH homeostasis in fibroblasts. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C132–C139. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason M. J., Smith J. D., Garcia-Soto J. J., Grinstein S. Internal pH-sensitive site couples Cl-(-)HCO3- exchange to Na+-H+ antiport in lymphocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):C428–C433. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.2.C428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelangeli F. Acid secretion and intracellular pH in isolated oxyntic cells. J Membr Biol. 1978 Jan 12;38(1-2):31–50. doi: 10.1007/BF01875161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muallem S., Blissard D., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Sachs G. Activation of the Na+/H+ and Cl-/HCO3- exchange by stimulation of acid secretion in the parietal cell. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14703–14711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugharbil A., Knickelbein R. G., Aronson P. S., Dobbins J. W. Rabbit ileal brush-border membrane Cl-HCO3 exchanger is activated by an internal pH-sensitive modifier site. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):G666–G670. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.4.G666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Tønnessen T. I., Ludt J., Sandvig K. Effect of intracellular pH on the rate of chloride uptake and efflux in different mammalian cell lines. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2778–2785. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Tønnessen T. I., Sandvig K. pH-regulated anion antiport in nucleated mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):967–971. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso A. M., Townsley M. C., Wenzl E., Machen T. E. Regulation of intracellular pH in resting and in stimulated parietal cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C554–C561. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm W. S., Sanders S. S. Implications of the neutral carrier Cl-HCO3- exchange mechanism in gastric mucosa. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:442–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stieger B., Murer H. Heterogeneity of brush-border-membrane vesicles from rat small intestine prepared by a precipitation method using Mg/EGTA. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. A., Machen T. E. Regulation of Cl/HCO3 exchange in gastric parietal cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Sep;2(9):727–737. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.9.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. A., Machen T. E., Smolka A., Baron R., Kopito R. R. Identification of a 185-kDa band 3-related polypeptide in oxyntic cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C537–C544. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzl E., Machen T. E. Intracellular pH dependence of buffer capacity and anion exchange in the parietal cell. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 1):G741–G747. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.257.5.G741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanaka A., Carter K. J., Lee H. H., Silen W. Influence of Cl- on pH(i) in oxynticopeptic cells of in vitro frog gastric mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):G815–G824. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.5.G815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Adelsberg J. S., Edwards J. C., al-Awqati Q. The apical Cl/HCO3 exchanger of beta intercalated cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11283–11289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


