Abstract
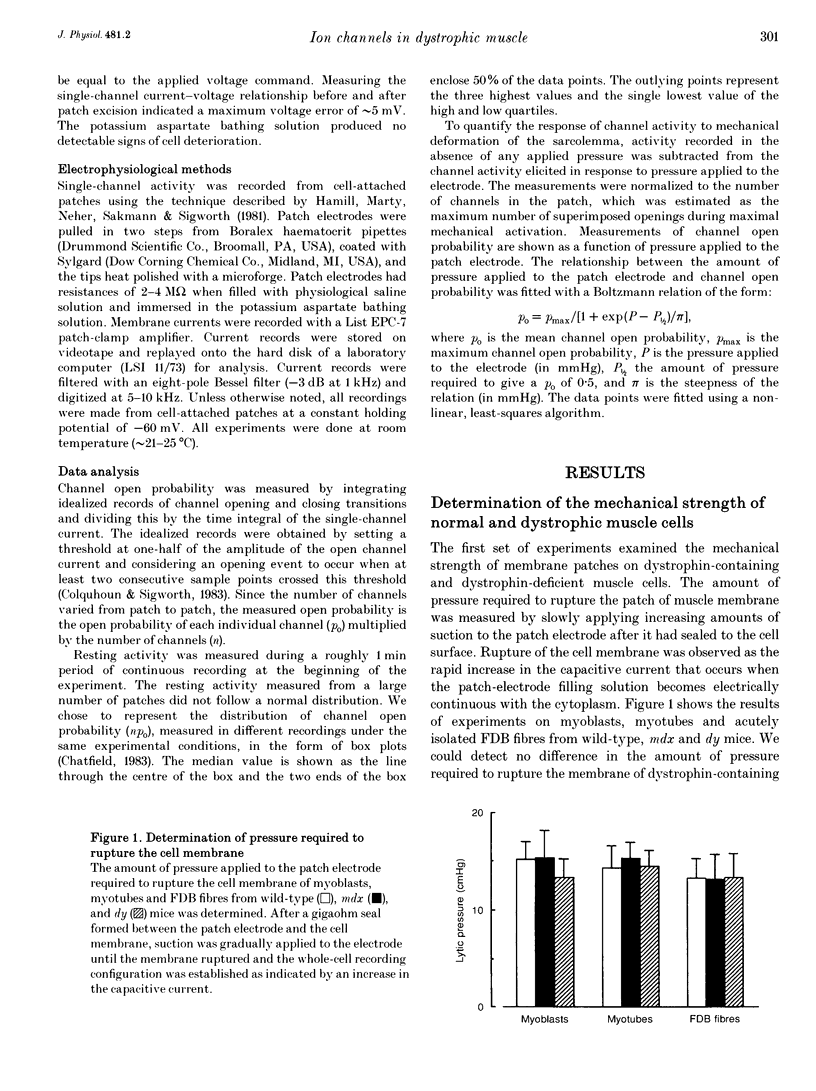
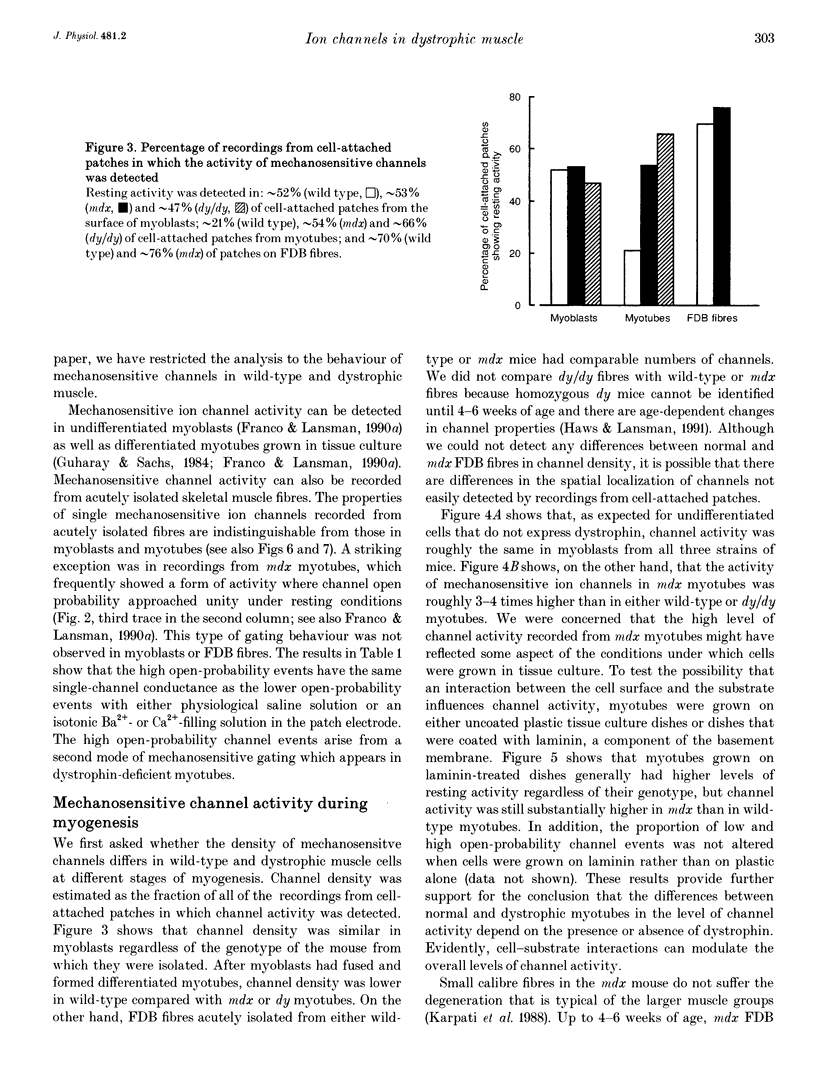
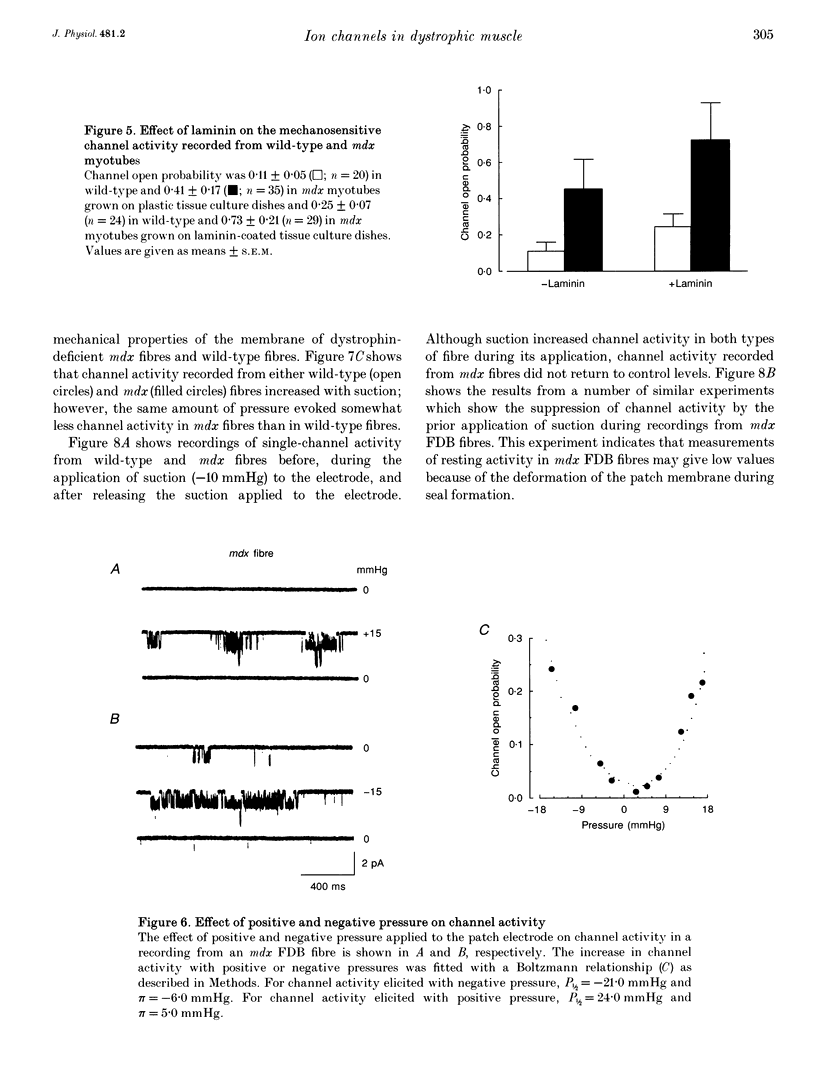
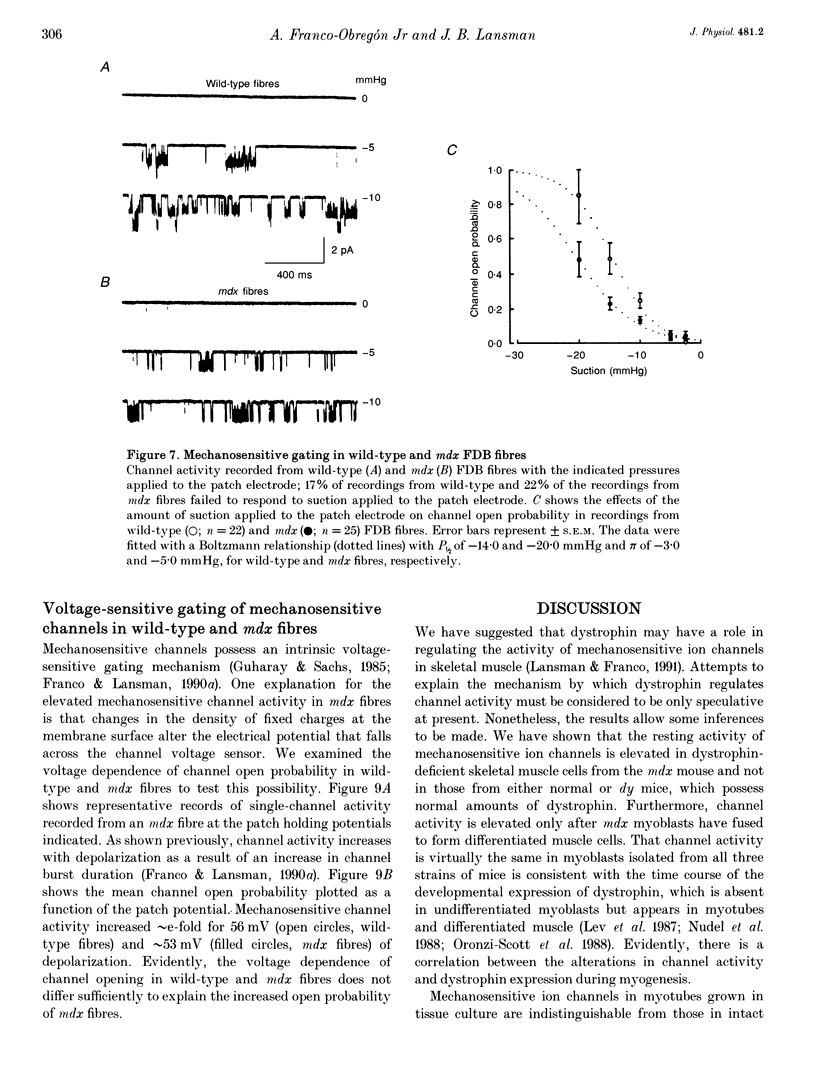
1. We examined the activity of single mechanosensitive ion channels in recordings from cell-attached patches on myoblasts, differentiated myotubes and acutely isolated skeletal muscle fibres from wild-type and mdx and dy mutant mice. The experiments were concerned with the role of these channels in the pathophysiology of muscular dystrophy. 2. The predominant form of channel activity recorded with physiological saline in the patch electrode arose from an approximately 25 pS mechanosensitive ion channel. Channel activity was similar in undifferentiated myoblasts isolated from all three strains of mice. By contrast, channel activity in mdx myotubes was approximately 3-4 times greater than in either wild-type or dy myotubes and arose from a novel mode of mechanosensitive gating. 3. Single mechanosensitive channels in acutely isolated flexor digitorum brevis fibres had properties indistinguishable from those of muscle cells grown in tissue culture. The channel open probability in mdx fibres was approximately 2 times greater than the activity recorded from wild-type fibres. The overall level of activity in fibres, however, was roughly an order of magnitude smaller than in myoblasts or myotubes. 4. Histological examination of the flexor digitorum brevis fibres from mdx mice showed no evidence of myonecrosis or regenerating fibres, suggesting that the elevated channel activity in dystrophin-deficient muscle precedes the onset of fibre degeneration. 5. An early step in the dystrophic process of the mdx mouse, which leads to pathophysiological Ca2+ entry, may be an alteration in the mechanisms that regulate mechanosensitive ion channel activity.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekoff A., Betz W. J. Physiological properties of dissociated muscle fibres obtained from innervated and denervated adult rat muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):25–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla E., Samitt C. E., Miranda A. F., Hays A. P., Salviati G., DiMauro S., Kunkel L. M., Hoffman E. P., Rowland L. P. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: deficiency of dystrophin at the muscle cell surface. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangain J., Vrbová G. Response of a fast muscle from normal and dystrophic (dy2j) mice to a local decrease in extracellular Ca2+ induced at different stages of postnatal life. J Neurol Sci. 1990 Mar;95(3):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90074-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervasti J. M., Campbell K. P. Dystrophin and the membrane skeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):82–87. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervasti J. M., Campbell K. P. Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1121–1131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90035-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervasti J. M., Ohlendieck K., Kahl S. D., Gaver M. G., Campbell K. P. Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):315–319. doi: 10.1038/345315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong P. Y., Turner P. R., Denetclaw W. F., Steinhardt R. A. Increased activity of calcium leak channels in myotubes of Duchenne human and mdx mouse origin. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):673–676. doi: 10.1126/science.2173137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A., Jr, Lansman J. B. Calcium entry through stretch-inactivated ion channels in mdx myotubes. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):670–673. doi: 10.1038/344670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco A., Jr, Lansman J. B. Stretch-sensitive channels in developing muscle cells from a mouse cell line. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:361–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guharay F., Sachs F. Mechanotransducer ion channels in chick skeletal muscle: the effects of extracellular pH. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:119–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guharay F., Sachs F. Stretch-activated single ion channel currents in tissue-cultured embryonic chick skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:685–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbiner B. M. Proteins associated with the cytoplasmic surface of adhesion molecules. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):551–564. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haws C. M., Lansman J. B. Developmental regulation of mechanosensitive calcium channels in skeletal muscle from normal and mdx mice. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Sep 23;245(1314):173–177. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter O. F., Burton F. L., Bovell D. L. Mechanical properties of normal and mdx mouse sarcolemma: bearing on function of dystrophin. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Dec;12(6):585–589. doi: 10.1007/BF01738447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. B. Spontaneous openings of the acetylcholine receptor channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3901–3904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Carpenter S., Prescott S. Small-caliber skeletal muscle fibers do not suffer necrosis in mdx mouse dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1988 Aug;11(8):795–803. doi: 10.1002/mus.880110802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Franco A., Jr What does dystrophin do in normal muscle? J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1991 Oct;12(5):409–411. doi: 10.1007/BF01738325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev A. A., Feener C. C., Kunkel L. M., Brown R. H., Jr Expression of the Duchenne's muscular dystrophy gene in cultured muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15817–15820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Calcium regulation in muscle diseases; the influence of innervation and activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 31;991(2):155–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura K., Ervasti J. M., Ohlendieck K., Kahl S. D., Campbell K. P. Association of dystrophin-related protein with dystrophin-associated proteins in mdx mouse muscle. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):588–591. doi: 10.1038/360588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier H., Southard J. L. Muscular dystrophy in the mouse caused by an allele at the dy-locus. Life Sci. 1970 Feb 8;9(3):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(70)90306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menke A., Jockusch H. Decreased osmotic stability of dystrophin-less muscle cells from the mdx mouse. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):69–71. doi: 10.1038/349069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Robzyk K., Yaffe D. Expression of the putative Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in differentiated myogenic cell cultures and in the brain. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):635–638. doi: 10.1038/331635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocalan M., Goodman S. L., Kühl U., Hauschka S. D., von der Mark K. Laminin alters cell shape and stimulates motility and proliferation of murine skeletal myoblasts. Dev Biol. 1988 Jan;125(1):158–167. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendieck K., Campbell K. P. Dystrophin-associated proteins are greatly reduced in skeletal muscle from mdx mice. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1685–1694. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlendieck K., Ervasti J. M., Matsumura K., Kahl S. D., Leveille C. J., Campbell K. P. Dystrophin-related protein is localized to neuromuscular junctions of adult skeletal muscle. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):499–508. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90301-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrof B. J., Shrager J. B., Stedman H. H., Kelly A. M., Sweeney H. L. Dystrophin protects the sarcolemma from stresses developed during muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3710–3714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. O., Sylvester J. E., Heiman-Patterson T., Shi Y. J., Fieles W., Stedman H., Burghes A., Ray P., Worton R., Fischbeck K. H. Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene expression in normal and diseased human muscle. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.2450401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinsley J. M., Blake D. J., Roche A., Fairbrother U., Riss J., Byth B. C., Knight A. E., Kendrick-Jones J., Suthers G. K., Love D. R. Primary structure of dystrophin-related protein. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):591–593. doi: 10.1038/360591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Head S. I., Bakker A. J., Stephenson D. G. Resting calcium concentrations in isolated skeletal muscle fibres of dystrophic mice. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:243–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


