Abstract
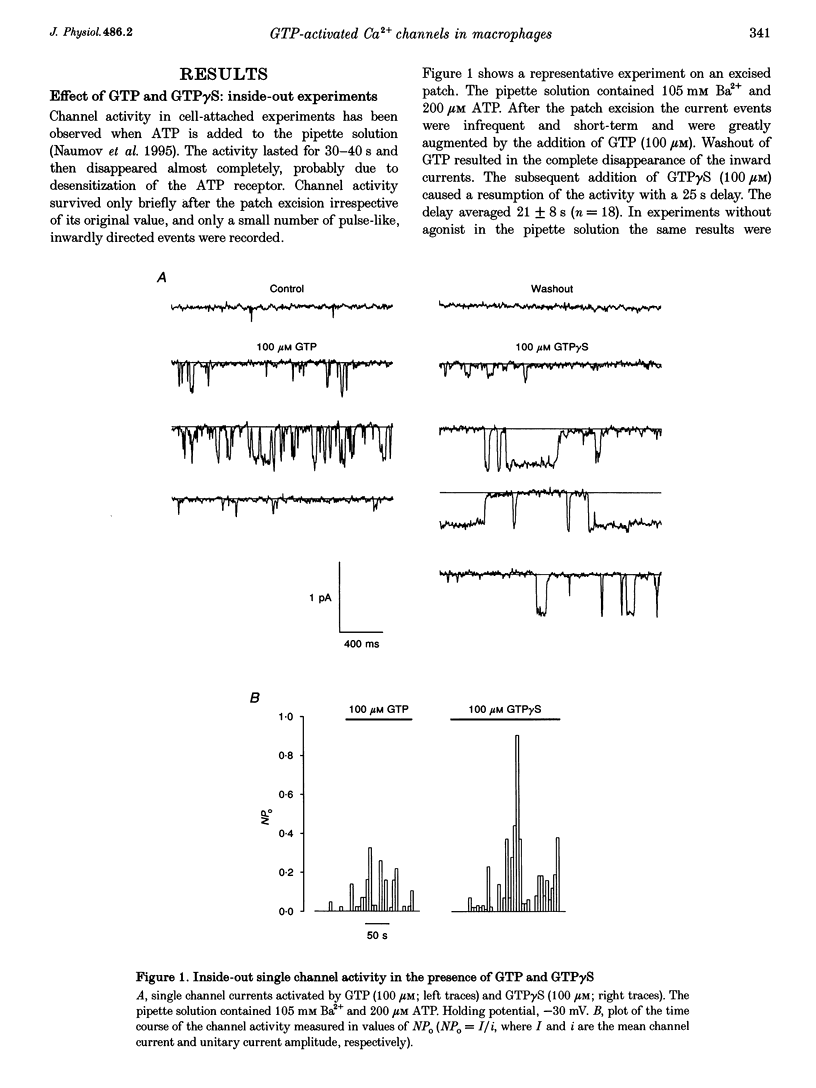
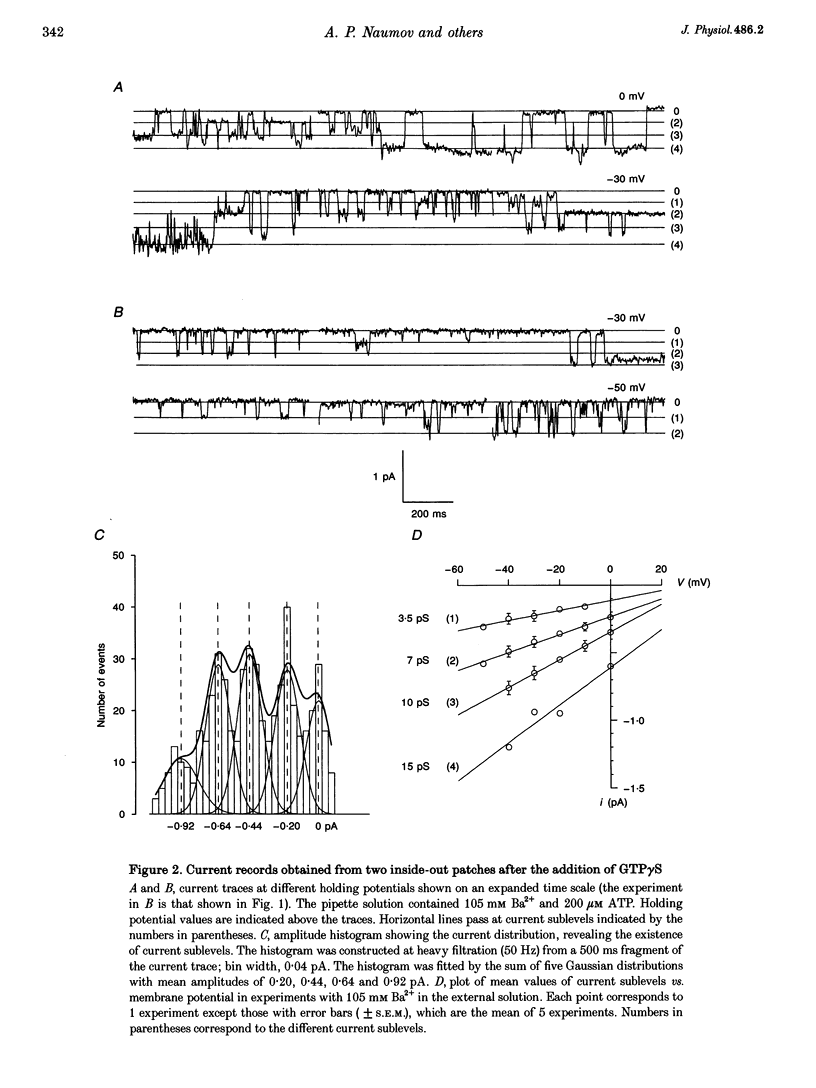
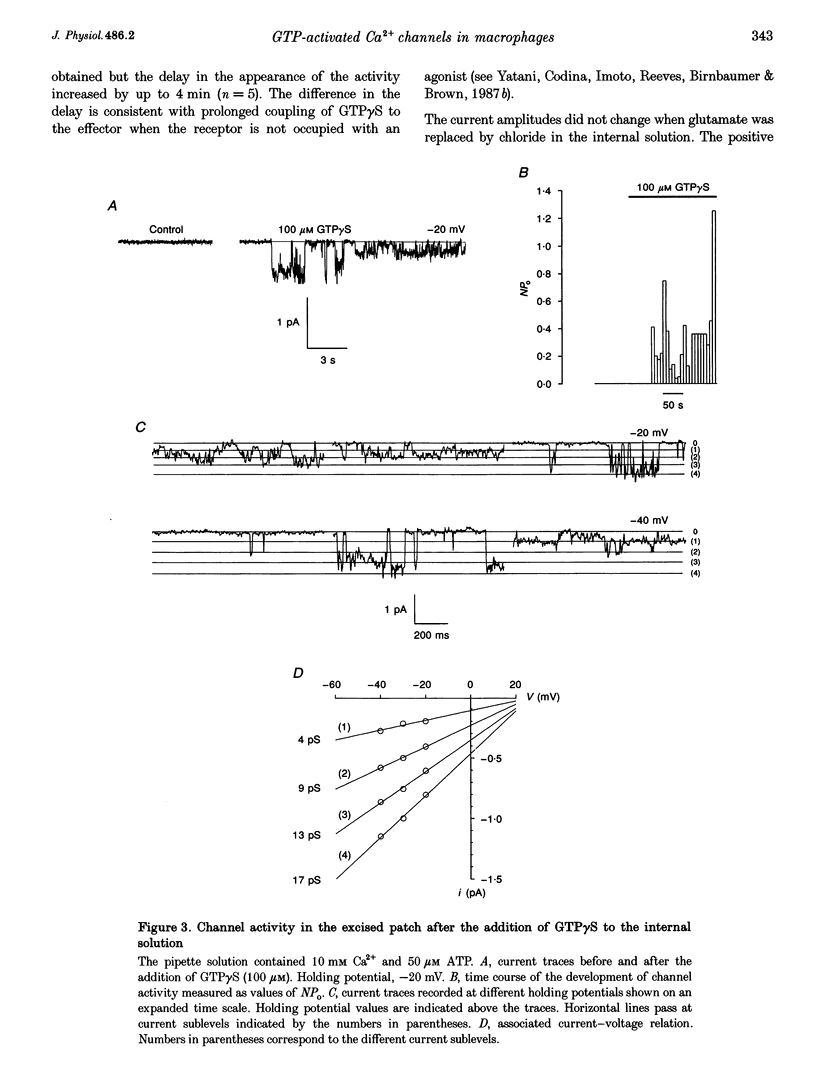
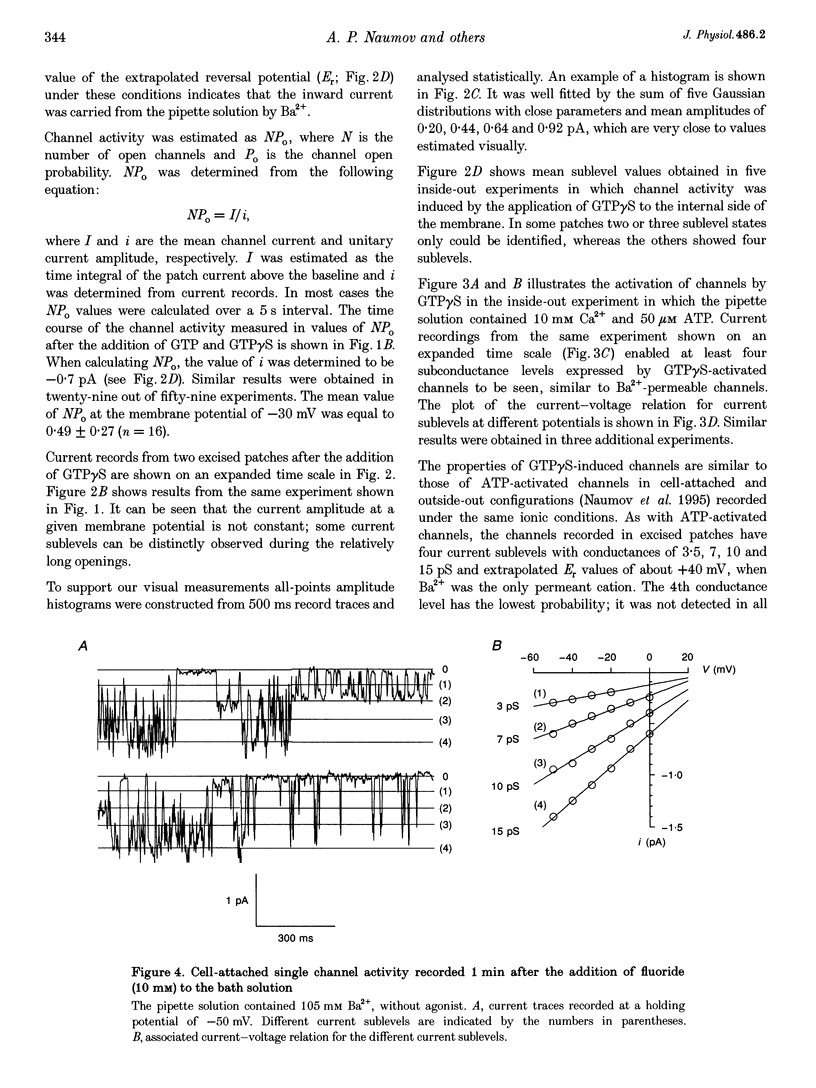
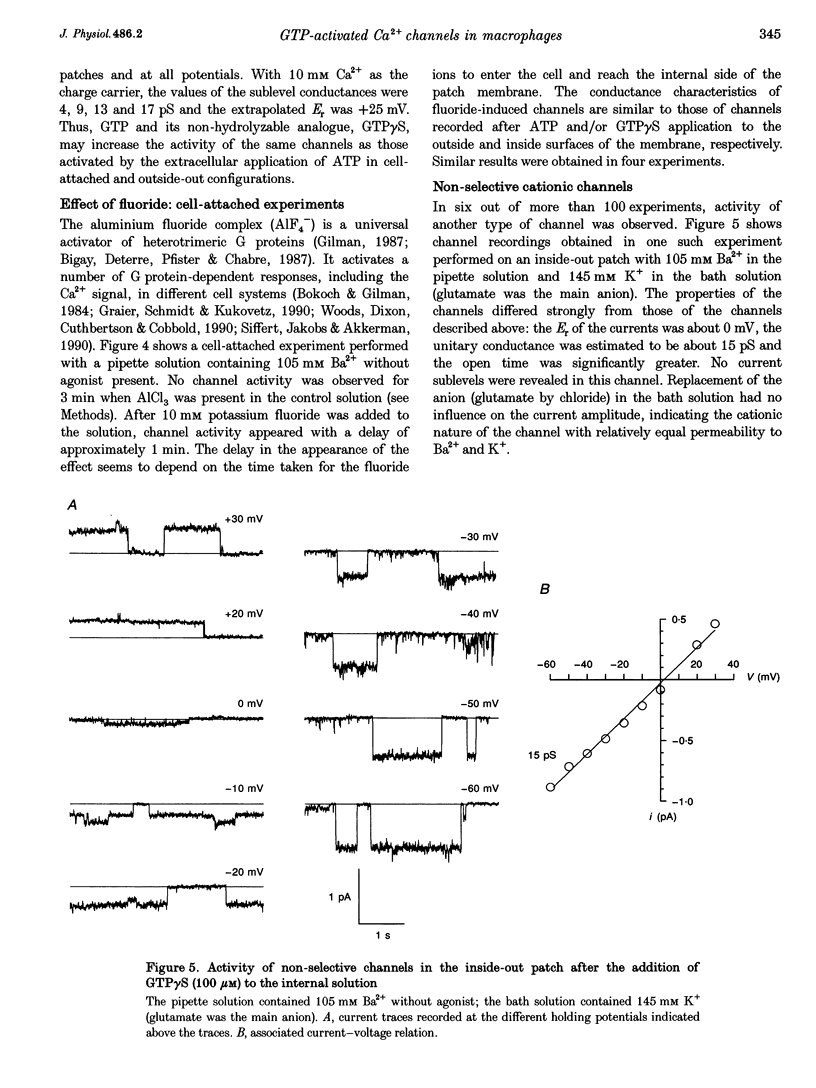
1. To elucidate the possible involvement of a G protein in ATP-evoked Ca(2+)-permeable channel activity, membrane currents of rat peritoneal macrophages were recorded using inside-out and cell-attached configurations of the patch clamp technique. 2. In inside-out experiments with a pipette solution containing 105 mM Ba2+, application of 100 microM GTP or GTP gamma S to the internal surface of the membrane elicited a rise in channel activity. This effect was observed in 49% of the patches investigated (n = 69). The mean value of NPo (N, number of open channels; Po, channel open probability) was equal to 0.49 +/- 0.27 (mean +/- S.E.M.; n = 16). The delay in the activity development was 21 +/- 8 s (n = 18) with 200 microM ATP added to the pipette solution and about 4 min (n = 5) without agonist in the pipette. Similar results were obtained with 10 mM Ca2+ as the only permeant cation. 3. Properties of GTP gamma S-evoked channels were identical to those of channels activated by extracellular application of ATP. The channels exhibited at least four conductance sublevels, the 4th one being the least frequent. With 105 mM Ba2+ as a permeant cation, sublevel conductances were 3.5, 7, 10 and 15 pS. Corresponding values for 10 mM Ca2+ were about 4, 9, 13 and 17 pS. Extrapolated reversal potential (Er) values were about +40 and +25 mV for Ba2+ and Ca2+, respectively. 4. The activity of channels with similar characteristics could be induced by the extracellular application of fluoride in cell-attached experiments without any agonist in the pipette solution.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoride complexes of aluminium or beryllium act on G-proteins as reversibly bound analogues of the gamma phosphate of GTP. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Two ATP-activated conductances in bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):1–27. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graier W. F., Schmidt K., Kukovetz W. R. Effect of sodium fluoride on cytosolic free Ca2(+)-concentrations and cGMP-levels in endothelial cells. Cell Signal. 1990;2(4):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90067-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Gardner P. Ion channels activated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in plasma membrane of human T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):301–304. doi: 10.1038/326301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Goronzy J., Weyand C. M., Gardner P. Single-channel and whole-cell recordings of mitogen-regulated inward currents in human cloned helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):269–273. doi: 10.1038/323269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Nakajima T., Sugimoto T. On the mechanism of activation of muscarinic K+ channels by adenosine in isolated atrial cells: involvement of GTP-binding proteins. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Sep;407(3):264–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00585301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuryshev Y. A., Naumov A. P., Avdonin P. V., Mozhayeva G. N. Evidence for involvement of a GTP-binding protein in activation of Ca2+ influx by epidermal growth factor in A431 cells: effects of fluoride and bacterial toxins. Cell Signal. 1993 Sep;5(5):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90051-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut-Smith M. P., Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Receptor-activated single channels in intact human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10479–10483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathie A., Bernheim L., Hille B. Inhibition of N- and L-type calcium channels by muscarinic receptor activation in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90205-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga H., Nishimoto I., Kojima I., Yamashita N., Kurokawa K., Ogata E. Activation of a calcium-permeable cation channel by insulin-like growth factor II in BALB/c 3T3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):C442–C446. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.4.C442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Lechleiter J. D., Cantley L. C., Talamo B. R. Extracellular ATP increases free cytosolic calcium in rat parotid acinar cells. Differences from phospholipase C-linked receptor agonists. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):291–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan R. A., Dvorak H. F., Dvorak A. M. Ultrastructural localization of nonspecific esterase activity in guinea pig and human monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes. Blood. 1981 Dec;58(6):1089–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozhayeva G. N., Naumov A. P., Kuryshev YuA Epidermal growth factor activates calcium-permeable channels in A 431 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 10;1011(2-3):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozhayeva G. N., Naumov A. P., Kuryshev YuA Variety of Ca(2+)-permeable channels in human carcinoma A431 cells. J Membr Biol. 1991 Nov;124(2):113–126. doi: 10.1007/BF01870456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Matsuki N. Adenosine triphosphate-activated inward current in isolated smooth muscle cells from rat vas deferens. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):644–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00584668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov A. P., Kiselyov K. I., Mamin A. G., Kaznacheyeva E. V., Kuryshev Y. A., Mozhayeva G. N. ATP-operated calcium-permeable channels activated via a guanine nucleotide-dependent mechanism in rat macrophages. J Physiol. 1995 Jul 15;486(Pt 2):339–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov A. P., Kuryshev Y. A., Kaznacheyeva E. V., Mozhayeva G. N. ATP-activated Ca(2+)-permeable channels in rat peritoneal macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 30;313(3):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81210-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus R., Reber B. F., Reuter H. Regulation of bradykinin- and ATP-activated Ca(2+)-permeable channels in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3984–3990. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppelenbosch M. P., Tertoolen L. G., den Hertog J., de Laat S. W. Epidermal growth factor activates calcium channels by phospholipase A2/5-lipoxygenase-mediated leukotriene C4 production. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90410-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Gallacher D. V. Extracellular ATP activates receptor-operated cation channels in mouse lacrimal acinar cells to promote calcium influx in the absence of phosphoinositide metabolism. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 7;264(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80782-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Gallacher D. V. The ATP-induced inward current in mouse lacrimal acinar cells is potentiated by isoprenaline and GTP. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:103–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siffert W., Jakobs K. H., Akkerman J. W. Sodium fluoride prevents receptor- and protein kinase C-mediated activation of the human platelet Na+/H+ exchanger without inhibiting its basic pHi-regulating activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15441–15448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P. Cationic channels sensitive to extracellular ATP in rat lacrimal cells. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:313–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Dixon C. J., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Fluoroaluminate mimics agonist application in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):613–615. doi: 10.1042/bj2650613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Chen G., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Permeability and Mg2+ blockade of histamine-operated cation channel in endothelial cells of rat intrapulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:395–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


