Abstract
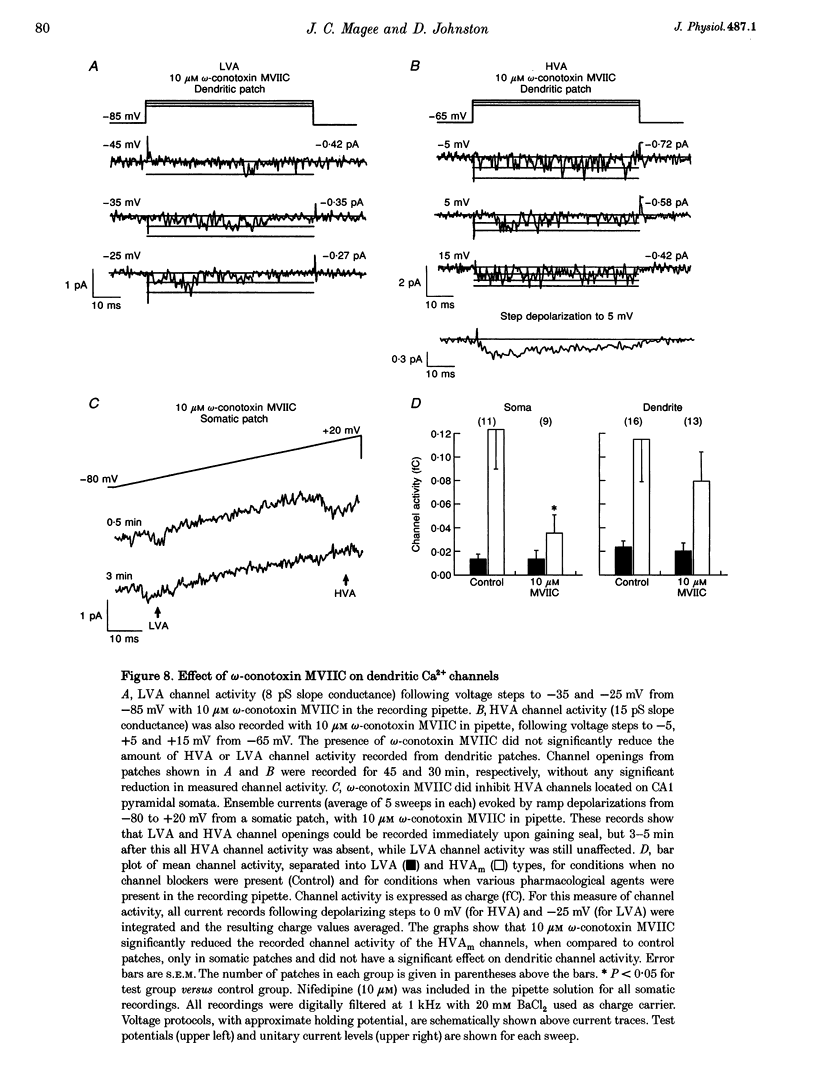
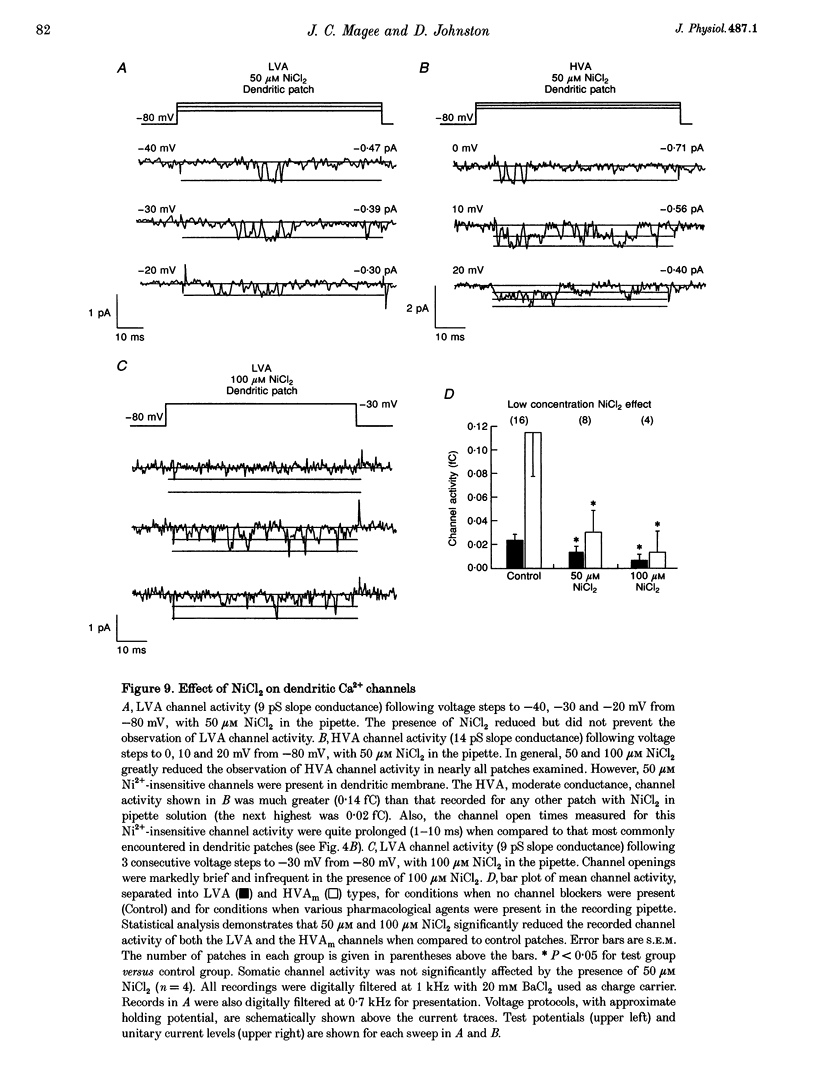
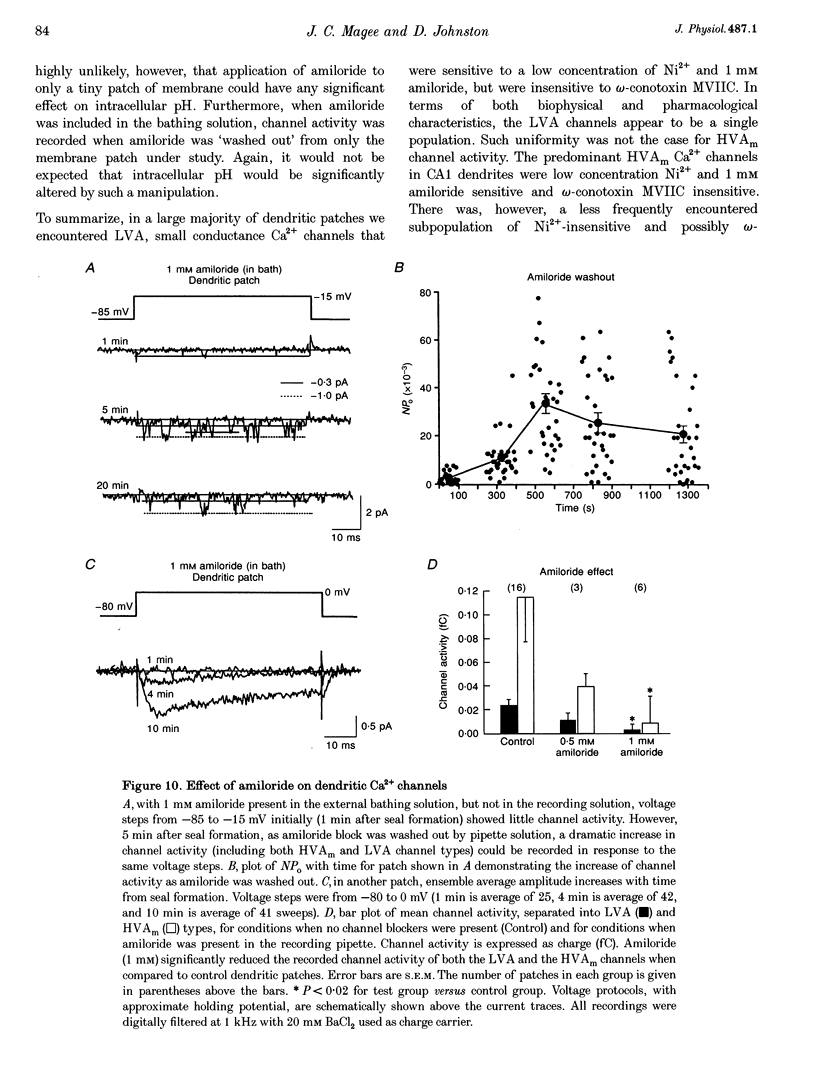
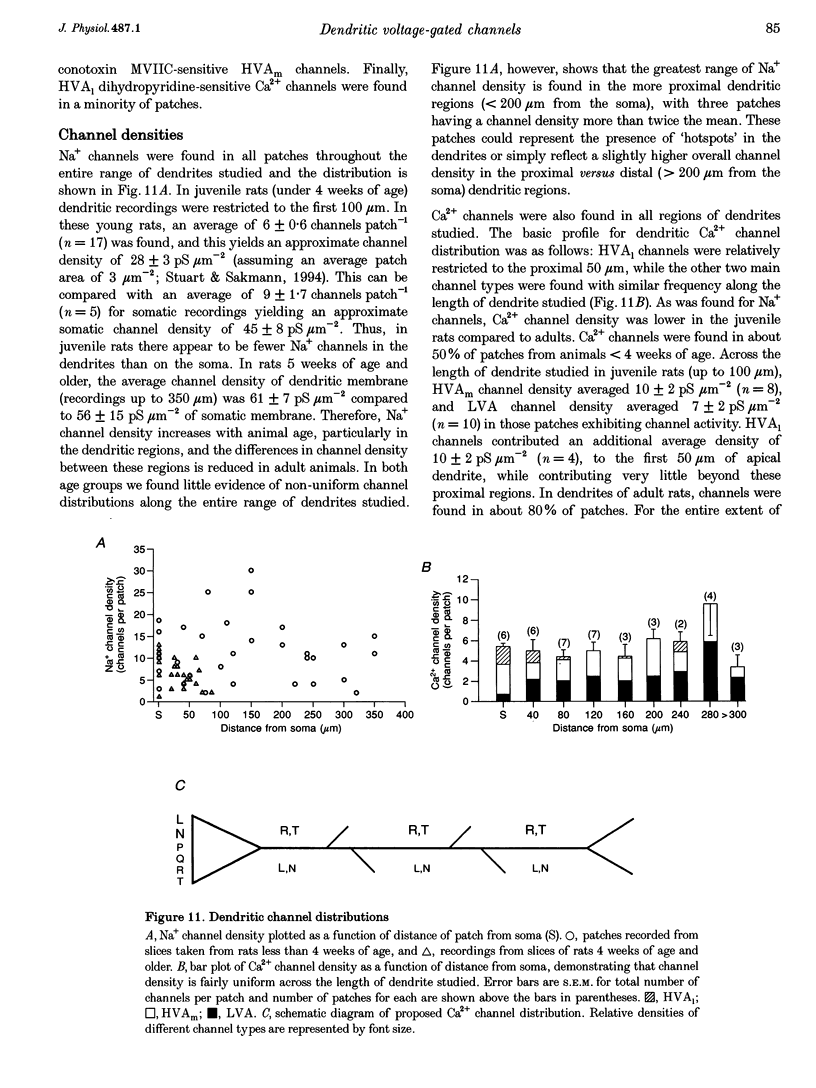
1. We have used dendrite-attached patch-clamp techniques to record single Na+ and Ca2+ channel activity from the apical dendrites (up to 350 microns away from soma) of CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat hippocampal slices (ages: 2-8 weeks). 2. Na+ channels were found in every patch examined (range: 2 to > 20 channels per patch). Channel openings, which had a slope conductance of 15 +/- 0.3 pS (mean +/- S.E.M.), began with test commands to around -50 mV and consisted of both early transient channel activity and also later occurring prolonged openings of 5-15 ms. All Na+ channel activity was suppressed by inclusion of TTX (1 microM) in the recording pipette. 3. Ca2+ channel activity was recorded in about 80% of the patches examined (range: 1 to > 10 channels per patch). Several types of channel behaviour were observed in these patches. Single channel recordings in 110 mM BaCl2, revealed an approximately 10 pS channel of small unitary current amplitude (-0.5 pA at -20 mV). These channels began activating at relatively hyperpolarized potentials (-50 mV) and ensemble averages of this low voltage-activated (LVA) channel activity showed rapid inactivation. 4. A somewhat heterogeneous population of high voltage-activated, moderate conductance (HVAm; approximately 17 pS), Ca2+ channel activity was also encountered. These channels exhibited a relatively large unitary amplitude (-0.8 pA at 0 mV) and ensemble averages demonstrated moderate inactivation. The HVAm population of channels could be tentatively subdivided into two separate groups based upon mean channel open times. 5. Less frequently, HVA, large conductance (27 pS) Ca2+ channel activity (HVA1) was also observed. This large unitary amplitude (-1.5 pA at 0 mV) channel activity began with steps to approximately 0 mV and ensemble averages did not show any time-dependent inactivation. The dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel agonist Bay K 8644 (0.5 or 1 microM) was found to characteristically prolong these channel openings. 6. omega-Conotoxin MVIIC (10 microM), did not significantly reduce the amount of channel activity recorded from the LVA, HVAm or HVA1 channel types in dendritic patches. In patches from somata, omega-conotoxin MVIIC was effective in eliminating a significant amount of HVAm Ca2+ channel activity. Inclusion of 50 or 100 microM NiCl2 to the recording solution significantly reduced the amount of channel activity recorded from LVA and HVAm channel types in dendritic patches. A subpopulation of HVAm channels was, however, found to be Ni2+ insensitive. Dendritic HVA, channel activity was unaffected by these low concentrations of Ni2+.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



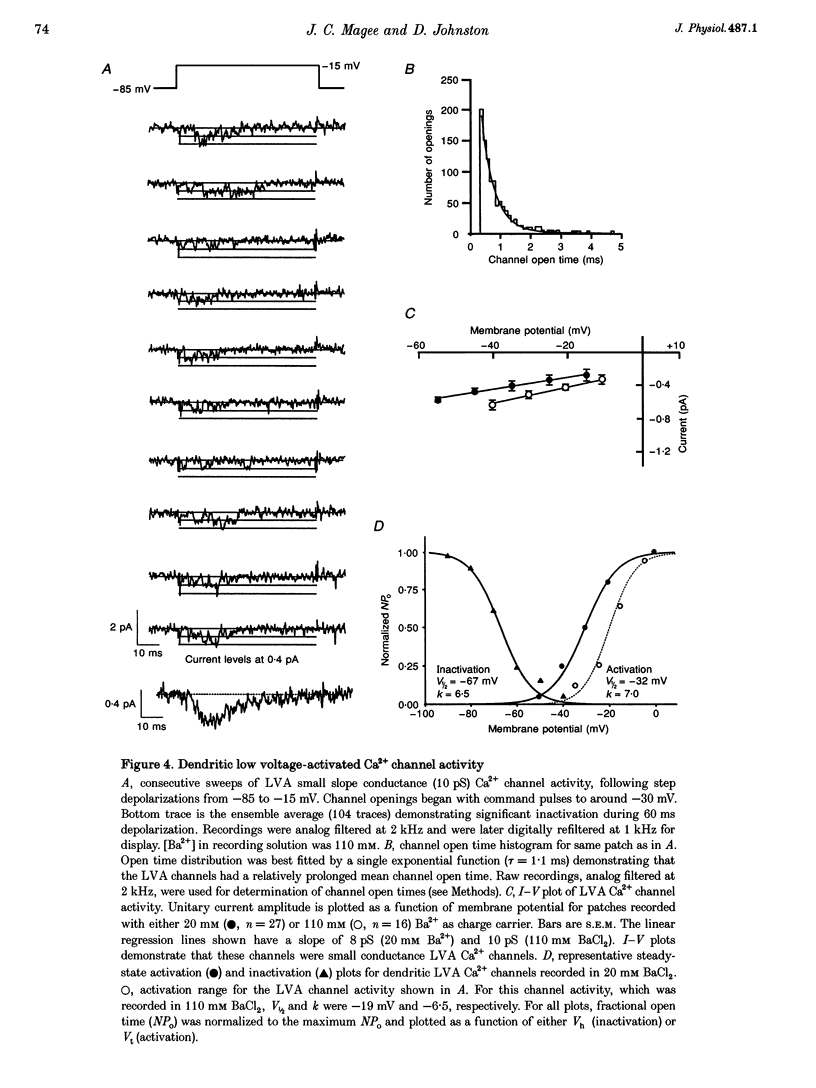
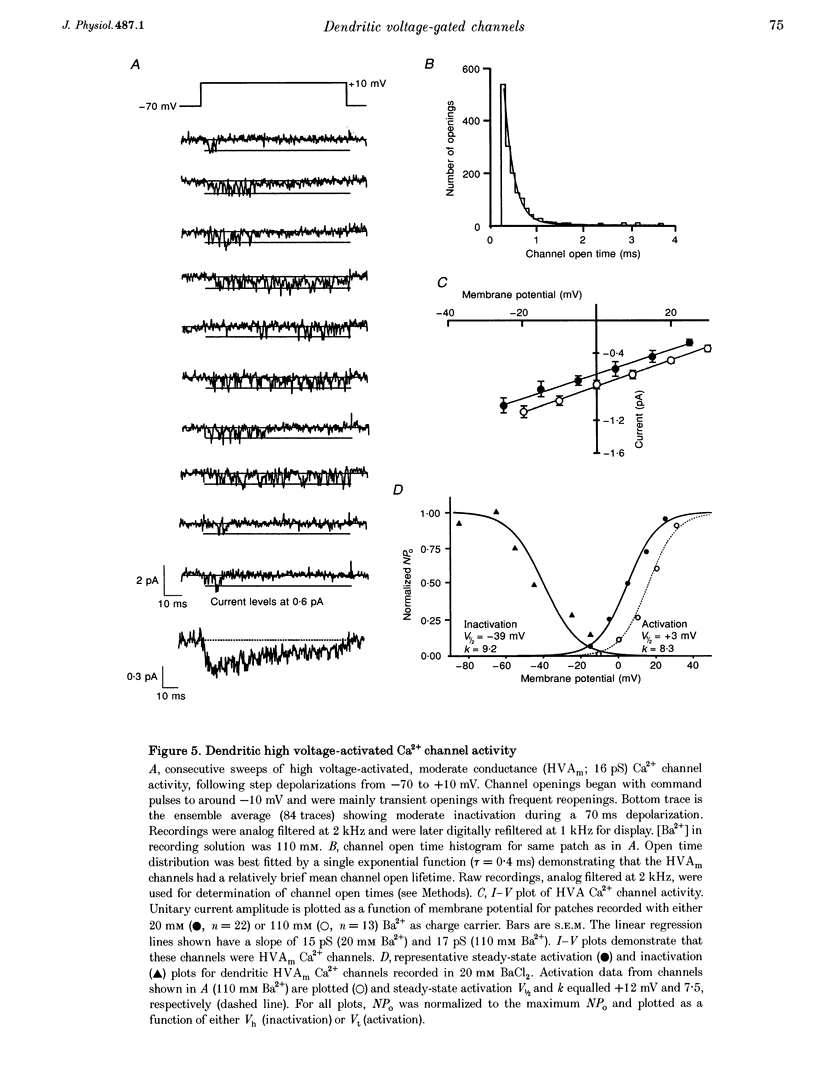

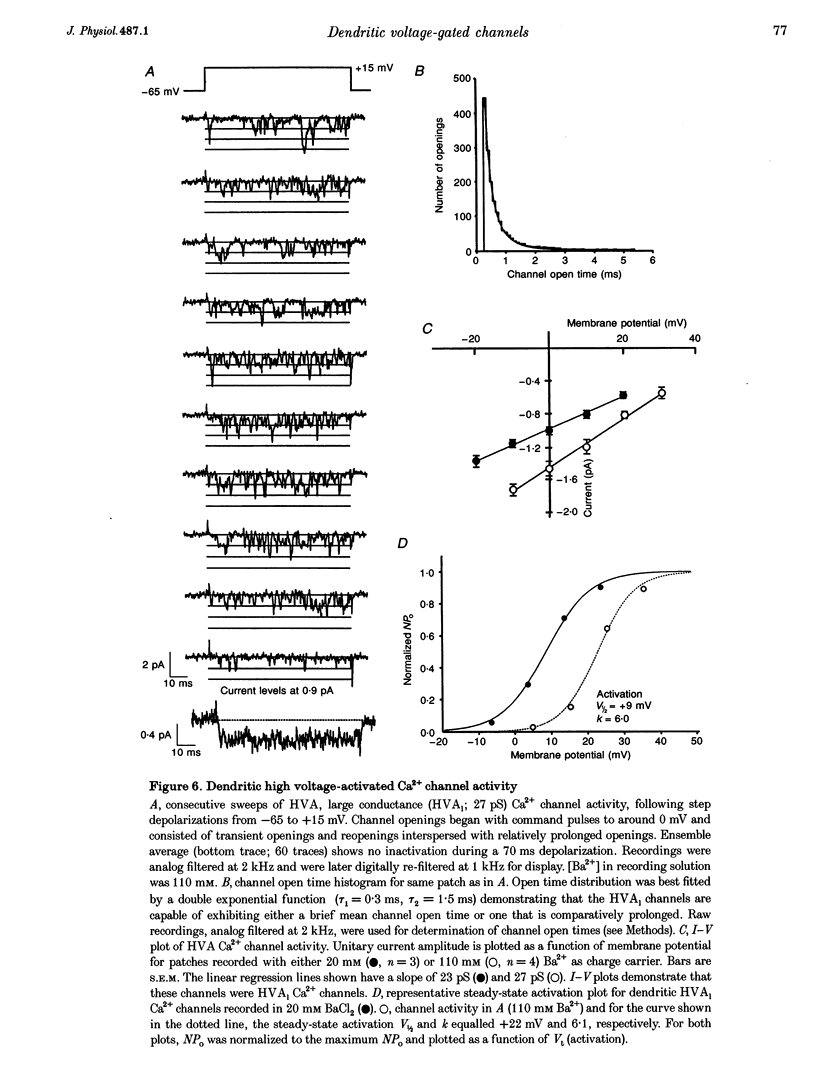
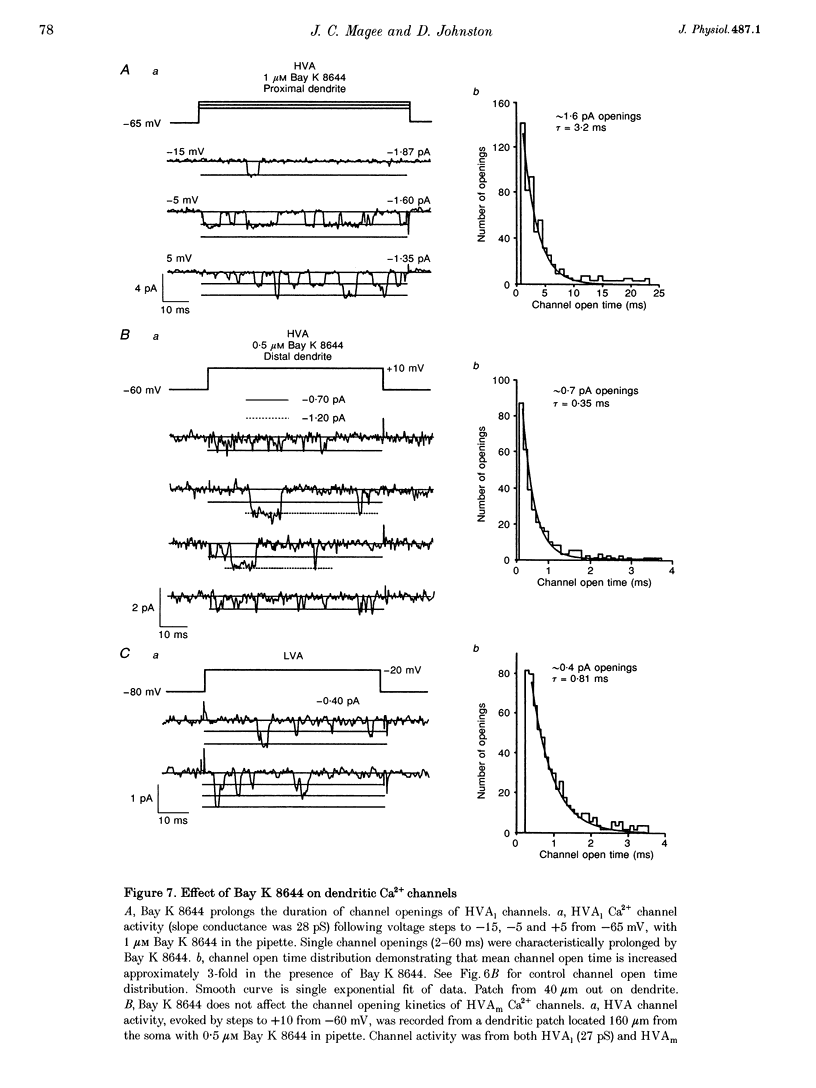








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alzheimer C., Schwindt P. C., Crill W. E. Modal gating of Na+ channels as a mechanism of persistent Na+ current in pyramidal neurons from rat and cat sensorimotor cortex. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):660–673. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00660.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Raastad M., Storm J. F. Excitatory synaptic integration in hippocampal pyramids and dentate granule cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:81–86. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Storm J., Wheal H. V. Thresholds of action potentials evoked by synapses on the dendrites of pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:509–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie B. R., Eliot L. S., Ito K., Miyakawa H., Johnston D. Different Ca2+ channels in soma and dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons mediate spike-induced Ca2+ influx. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Jun;73(6):2553–2557. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.6.2553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colling S. B., Wheal H. V. Fast sodium action potentials are generated in the distal apical dendrites of rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Neurosci Lett. 1994 May 19;172(1-2):73–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Tsien R. W. Altered prevalence of gating modes in neurotransmitter inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):980–984. doi: 10.1126/science.8094902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliot L. S., Johnston D. Multiple components of calcium current in acutely dissociated dentate gyrus granule neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Aug;72(2):762–777. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.2.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor P. T., Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Zhou M., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W., Horne W. A. Functional expression of a rapidly inactivating neuronal calcium channel. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):455–458. doi: 10.1038/363455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor P. T., Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Zhou M., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W., Horne W. A. Functional expression of a rapidly inactivating neuronal calcium channel. Nature. 1993 Jun 3;363(6428):455–458. doi: 10.1038/363455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Kammermeier P. J., Jones S. W. Reevaluation of Ca2+ channel types and their modulation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. E., Gray R., Johnston D. Properties and distribution of single voltage-gated calcium channels in adult hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Jul;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Johnston D. Differential modulation of single voltage-gated calcium channels by cholinergic and adrenergic agonists in adult hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Oct;64(4):1291–1302. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.4.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:149–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. P., Nowycky M. C., Tsien R. W. Single-channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:173–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herreras O. Propagating dendritic action potential mediates synaptic transmission in CA1 pyramidal cells in situ. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Nov;64(5):1429–1441. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.5.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Calcium channel selectivity for divalent and monovalent cations. Voltage and concentration dependence of single channel current in ventricular heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):293–319. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard D. R., Monje V. D., Mintz I. M., Bean B. P., Nadasdi L., Ramachandran J., Miljanich G., Azimi-Zoonooz A., McIntosh J. M., Cruz L. J. A new Conus peptide ligand for mammalian presynaptic Ca2+ channels. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe D. B., Johnston D., Lasser-Ross N., Lisman J. E., Miyakawa H., Ross W. N. The spread of Na+ spikes determines the pattern of dendritic Ca2+ entry into hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):244–246. doi: 10.1038/357244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe D. B., Ross W. N., Lisman J. E., Lasser-Ross N., Miyakawa H., Johnston D. A model for dendritic Ca2+ accumulation in hippocampal pyramidal neurons based on fluorescence imaging measurements. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Mar;71(3):1065–1077. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.71.3.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D., Williams S., Jaffe D., Gray R. NMDA-receptor-independent long-term potentiation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:489–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. R., Wong R. K. Calcium current activation kinetics in isolated pyramidal neurones of the Ca1 region of the mature guinea-pig hippocampus. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:603–616. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Kinetic properties of single sodium channels in rat heart and rat brain. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jan;93(1):85–99. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden D. J. Long-term synaptic depression in the mammalian brain. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):457–472. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Hillman D. E., Cherksey B. Distribution and functional significance of the P-type, voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in the mammalian central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90053-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee J. C., Johnston D. Synaptic activation of voltage-gated channels in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):301–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7716525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A., Zucker R. S., Nicoll R. A. Postsynaptic calcium is sufficient for potentiation of hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2845577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D. H., Cruz L. J., Olivera B. M., Tsien R. W., Yoshikami D. Omega-conotoxin: direct and persistent blockade of specific types of calcium channels in neurons but not muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills L. R., Niesen C. E., So A. P., Carlen P. L., Spigelman I., Jones O. T. N-type Ca2+ channels are located on somata, dendrites, and a subpopulation of dendritic spines on live hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 2):6815–6824. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06815.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Adams M. E., Bean B. P. P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90223-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa H., Kato H. Active properties of dendritic membrane examined by current source density analysis in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 10;399(2):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa H., Ross W. N., Jaffe D., Callaway J. C., Lasser-Ross N., Lisman J. E., Johnston D. Synaptically activated increases in Ca2+ concentration in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells are primarily due to voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1163–1173. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90074-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogul D. J., Fox A. P. Evidence for multiple types of Ca2+ channels in acutely isolated hippocampal CA3 neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:259–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Long-opening mode of gating of neuronal calcium channels and its promotion by the dihydropyridine calcium agonist Bay K 8644. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):115–118. doi: 10.1126/science.1656525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell T. J., Alger B. E. Single calcium channels in rat and guinea-pig hippocampal neurons. J Physiol. 1991 May;436:739–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Tatebayashi H. Sodium current kinetics in freshly isolated neostriatal neurones of the adult guinea pig. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jul;416(5):594–603. doi: 10.1007/BF00382695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongrácz F., Poolos N. P., Kocsis J. D., Shepherd G. M. A model of NMDA receptor-mediated activity in dendrites of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Dec;68(6):2248–2259. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.6.2248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Holmes W. R., Jack J. J., Redman S. J., Segev I. Matching dendritic neuron models to experimental data. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S159–S186. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall A., Tsien R. W. Pharmacological dissection of multiple types of Ca2+ channel currents in rat cerebellar granule neurons. J Neurosci. 1995 Apr;15(4):2995–3012. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-04-02995.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regehr W. G., Tank D. W. Calcium concentration dynamics produced by synaptic activation of CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurosci. 1992 Nov;12(11):4202–4223. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-11-04202.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson T. L., Turner R. W., Miller J. J. Action-potential discharge in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: current source-density analysis. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Nov;58(5):981–996. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.5.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sah P., Gibb A. J., Gage P. W. The sodium current underlying action potentials in guinea pig hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Mar;91(3):373–398. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Zhang J. F., Mori Y., Adams M. E., Tsien R. W. Distinctive biophysical and pharmacological properties of class A (BI) calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90185-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. The variance of sodium current fluctuations at the node of Ranvier. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:97–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soong T. W., Stea A., Hodson C. D., Dubel S. J., Vincent S. R., Snutch T. P. Structure and functional expression of a member of the low voltage-activated calcium channel family. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1133–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.8388125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruston N., Jaffe D. B., Johnston D. Dendritic attenuation of synaptic potentials and currents: the role of passive membrane properties. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Apr;17(4):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spruston N., Schiller Y., Stuart G., Sakmann B. Activity-dependent action potential invasion and calcium influx into hippocampal CA1 dendrites. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):297–300. doi: 10.1126/science.7716524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhäuser C., Tennigkeit M., Matthies H., Gündel J. Properties of the fast sodium channels in pyramidal neurones isolated from the CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus of postnatal rats. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Mar;415(6):756–761. doi: 10.1007/BF02584017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. J., Dodt H. U., Sakmann B. Patch-clamp recordings from the soma and dendrites of neurons in brain slices using infrared video microscopy. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Jun;423(5-6):511–518. doi: 10.1007/BF00374949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. J., Sakmann B. Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):69–72. doi: 10.1038/367069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Presser F., Morad M. Amiloride selectively blocks the low threshold (T) calcium channel. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2451291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. P. Na+ currents that fail to inactivate. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Nov;16(11):455–460. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90077-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Wong R. K. Development of calcium current subtypes in isolated rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:671–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub R. D., Miles R., Jefferys J. G. Synaptic and intrinsic conductances shape picrotoxin-induced synchronized after-discharges in the guinea-pig hippocampal slice. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:525–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. W., Meyers D. E., Barker J. L. Fast pre-potential generation in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuroscience. 1993 Apr;53(4):949–959. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. W., Meyers D. E., Barker J. L. Localization of tetrodotoxin-sensitive field potentials of CA1 pyramidal cells in the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1989 Dec;62(6):1375–1387. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.62.6.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. W., Meyers D. E., Richardson T. L., Barker J. L. The site for initiation of action potential discharge over the somatodendritic axis of rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):2270–2280. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-02270.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Sugimori M., Cherksey B., Llinás R. P-type calcium channels in the somata and dendrites of adult cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1185–1199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90076-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Ahlijanian M. K., Catterall W. A. Clustering of L-type Ca2+ channels at the base of major dendrites in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):281–284. doi: 10.1038/347281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Hell J. W., Warner C., Dubel S. J., Snutch T. P., Catterall W. A. Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of an N-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1099–1115. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90069-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Merrick D. K., Catterall W. A. Differential subcellular localization of the RI and RII Na+ channel subtypes in central neurons. Neuron. 1989 Dec;3(6):695–704. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G., Levy W. B., Steward O. Spatial overlap between populations of synapses determines the extent of their associative interaction during the induction of long-term potentiation and depression. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Oct;64(4):1186–1198. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.4.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegar B. D., Kelly R., Lansman J. B. Block of current through single calcium channels by Fe, Co, and Ni. Location of the transition metal binding site in the pore. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Feb;97(2):351–367. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. K., Prince D. A., Basbaum A. I. Intradendritic recordings from hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. F., Randall A. D., Ellinor P. T., Horne W. A., Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Schwarz T. L., Tsien R. W. Distinctive pharmacology and kinetics of cloned neuronal Ca2+ channels and their possible counterparts in mammalian CNS neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1075–1088. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90003-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]