Abstract
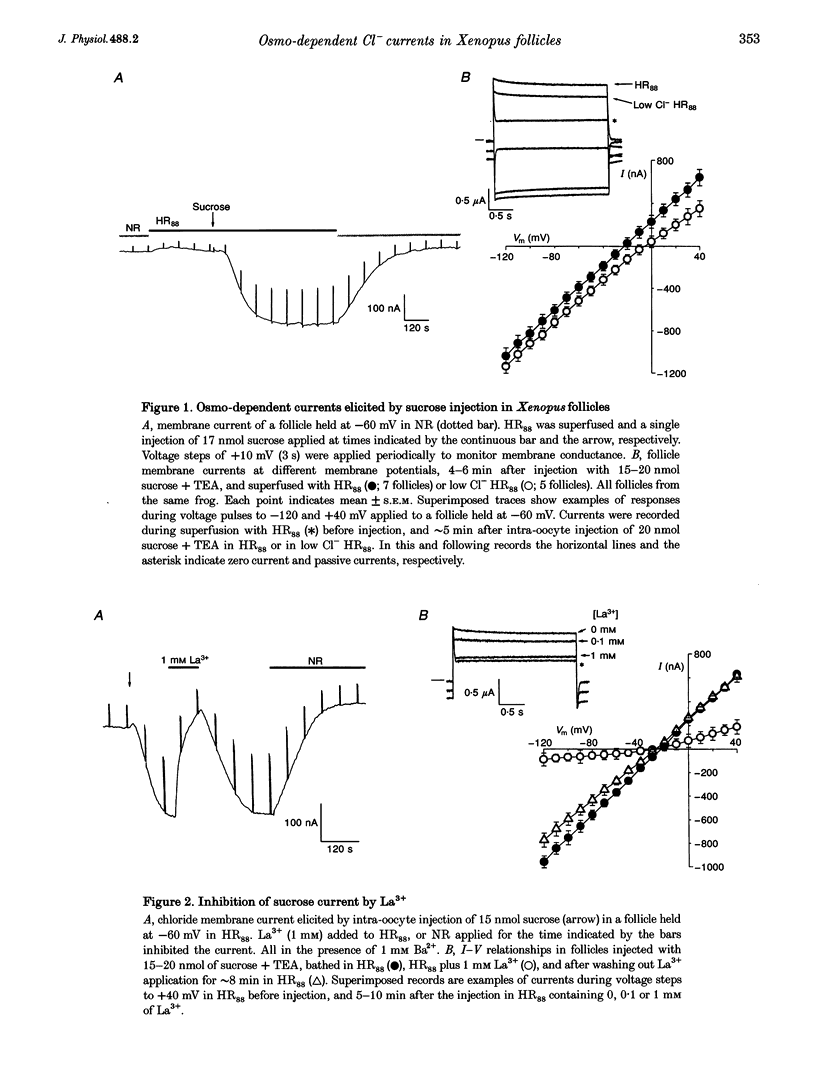
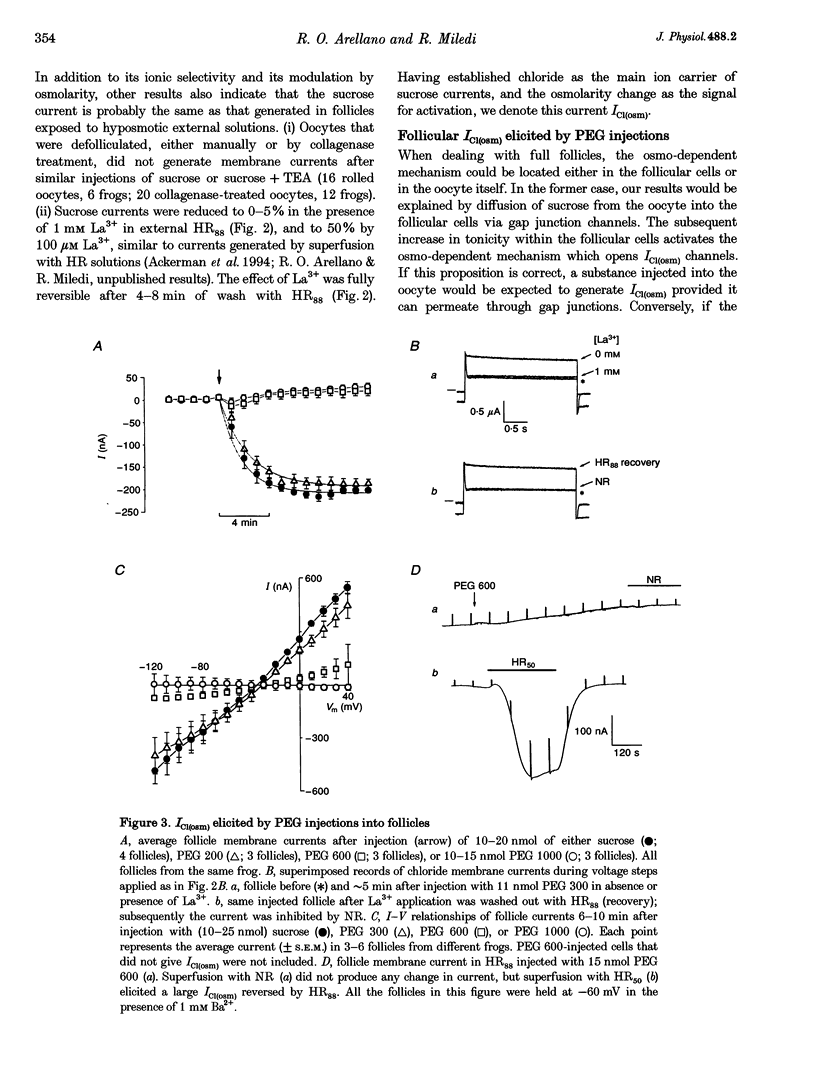
1. Osmolarity-dependent (osmo-dependent) ionic currents from follicle-enclosed Xenopus oocytes (follicles) were studied using the two-microelectrode voltage-clamp technique, combined with intra-oocyte pressure injection of sucrose or polyethylene glycols (PEGs). 2. Intra-oocyte injections of sucrose or PEG (3-25 nmol) generated inward membrane currents (follicles held at -60 mV) associated with an increase in membrane conductance. These currents were carried mainly by chloride ions (ICl(osm)), and were strongly attenuated by increasing the tonicity of the external medium, or by external application of La3+ (0.1-1 mM). 3. The ability to generate ICl(osm) depended on the molecular weight of the injected PEG. Injections of PEG 200 or 300 generated ICl(osm) in 95% of the follicles tested, PEG 600 generated comparable currents in only 20% of the follicles, while similar injections of PEG 1000 did not elicit ICl(osm). 4. Octanol (1-1.5 mM), a gap junction channel blocker, reversibly inhibited 50-90% of the ICl(osm) generated by injections of sucrose or PEG 300. Moreover, sucrose or PEG injections did not elicit ICl(osm) in defolliculated oocytes. 5. It is concluded that an increase in the internal osmolarity of the follicular cells activates a mechanism, probably involving cellular swelling, which leads to the opening of ICl(osm) channels most probably located in the follicular cell membrane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman M. J., Wickman K. D., Clapham D. E. Hypotonicity activates a native chloride current in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Feb;103(2):153–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.103.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arellano R. O., Miledi R. Novel Cl- currents elicited by follicle stimulating hormone and acetylcholine in follicle-enclosed Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Nov;102(5):833–857. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.5.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arellano R. O., Miledi R. Osmo-dependent Cl- currents activated by cyclic AMP in follicle-enclosed Xenopus oocytes. Proc Biol Sci. 1994 Dec 22;258(1353):229–235. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1994.0167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne C. L., Wiley H. S., Dumont J. N. Oocyte-follicle cell gap junctions in Xenopus laevis and the effects of gonadotropin on their permeability. Science. 1979 Jan 12;203(4376):182–183. doi: 10.1126/science.569364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gründer S., Thiemann A., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. Regions involved in the opening of CIC-2 chloride channel by voltage and cell volume. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):759–762. doi: 10.1038/360759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara N., Masuda H., Shoda M., Irisawa H. Stretch-activated anion currents of rabbit cardiac myocytes. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:285–302. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. F., Simon S. A., Ramón F. Interaction of anaesthetics with electrical synapses. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):498–500. doi: 10.1038/286498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapivinsky G. B., Ackerman M. J., Gordon E. A., Krapivinsky L. D., Clapham D. E. Molecular characterization of a swelling-induced chloride conductance regulatory protein, pICln. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Cholinergic and catecholaminergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:143–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. A calcium-dependent transient outward current in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jul 22;215(1201):491–497. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Woodward R. M. Effects of defolliculation on membrane current responses of Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:601–621. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Bor M., Ji H., Markwick A., Millan M. A., Catt K. J. Angiotensin II-induced calcium mobilization in oocytes by signal transfer through gap junctions. Science. 1990 Jul 20;249(4966):298–301. doi: 10.1126/science.2374929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supplisson S., Kado R. T., Bergman C. A possible Na/Ca exchange in the follicle cells of Xenopus oocyte. Dev Biol. 1991 Jun;145(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90122-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward R. M., Miledi R. Hormonal activation of ionic currents in follicle-enclosed Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


