Abstract
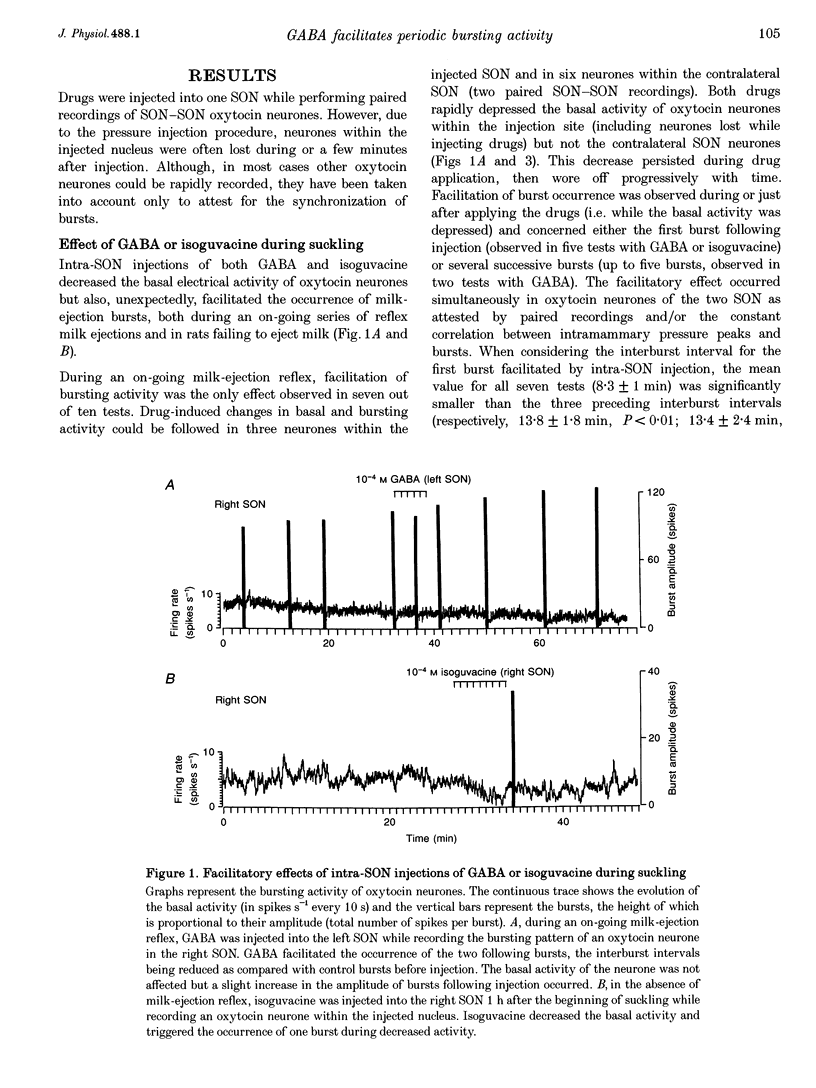
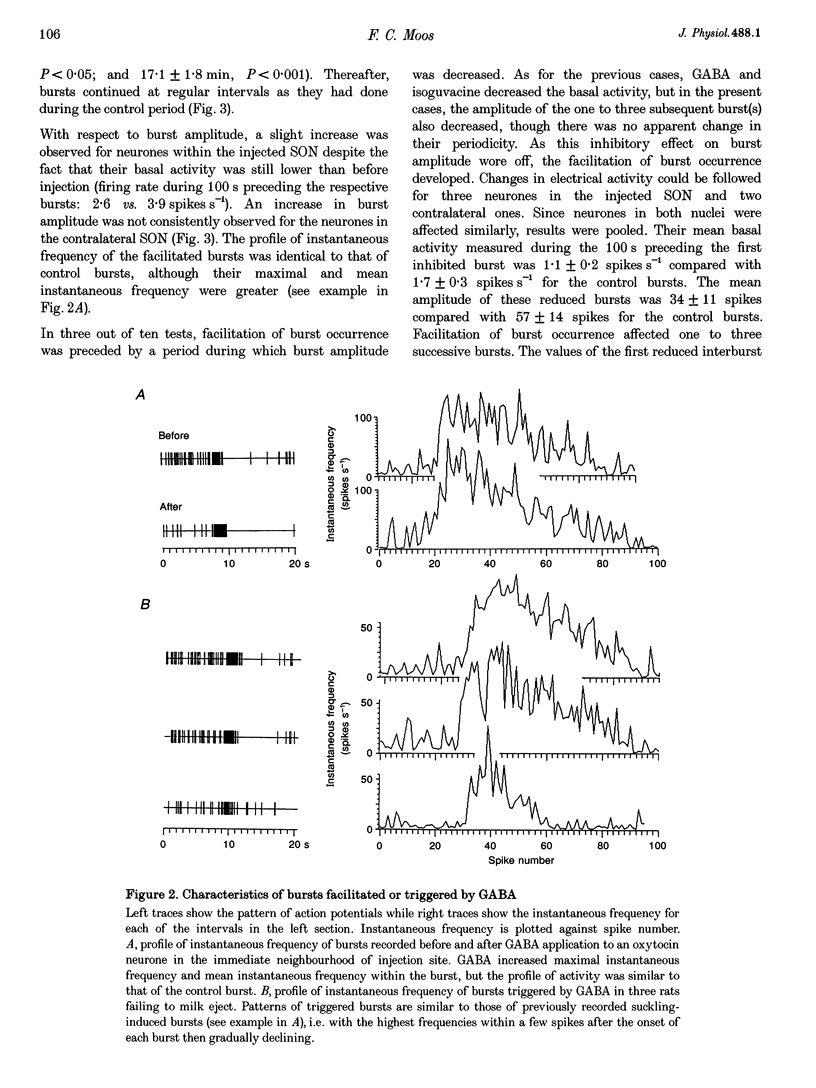
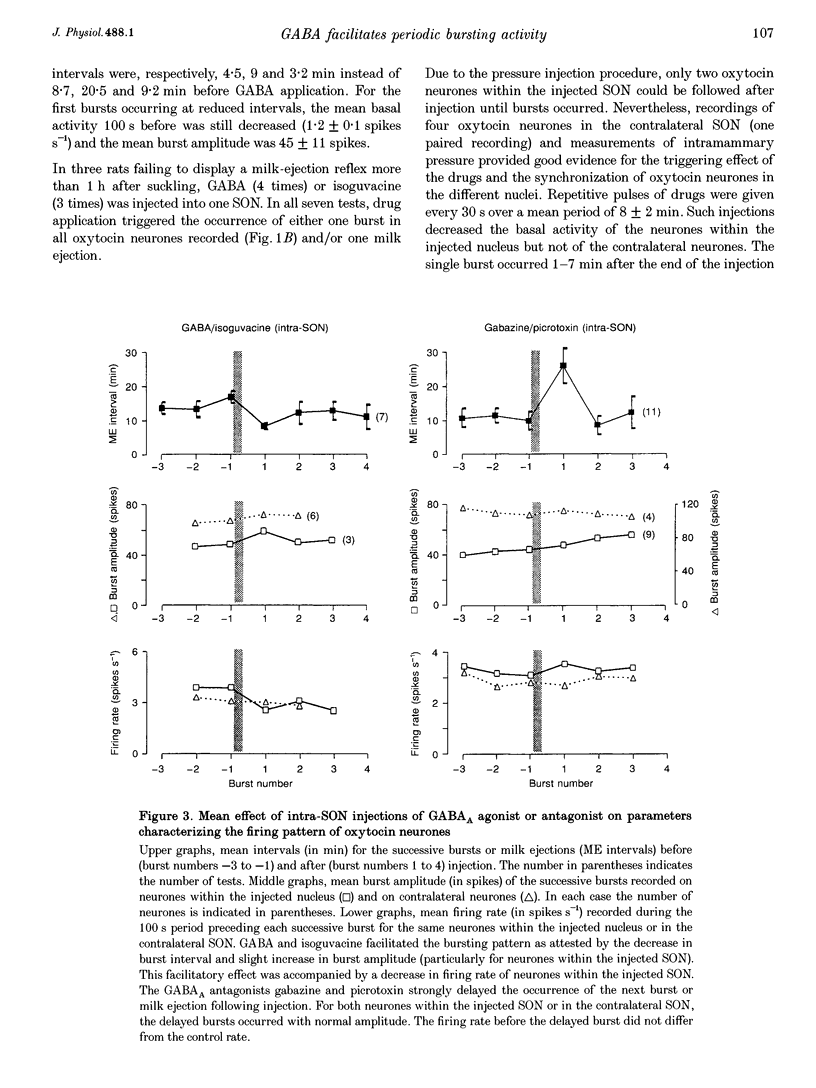
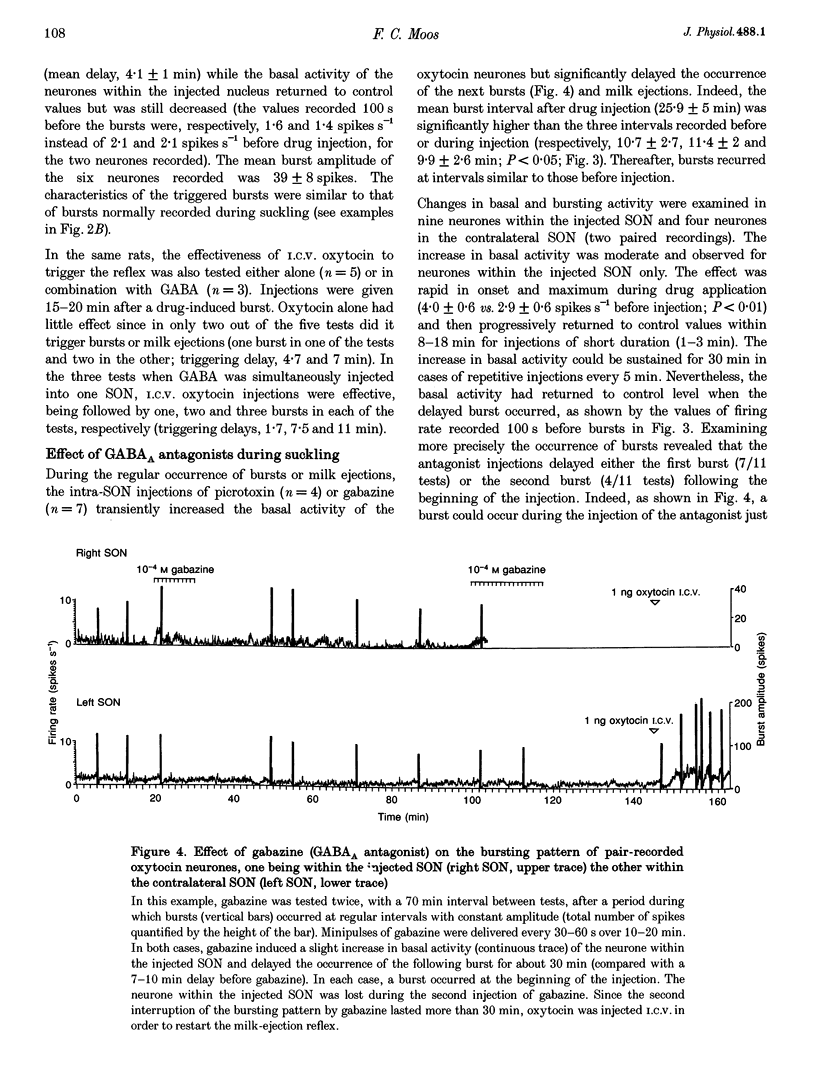
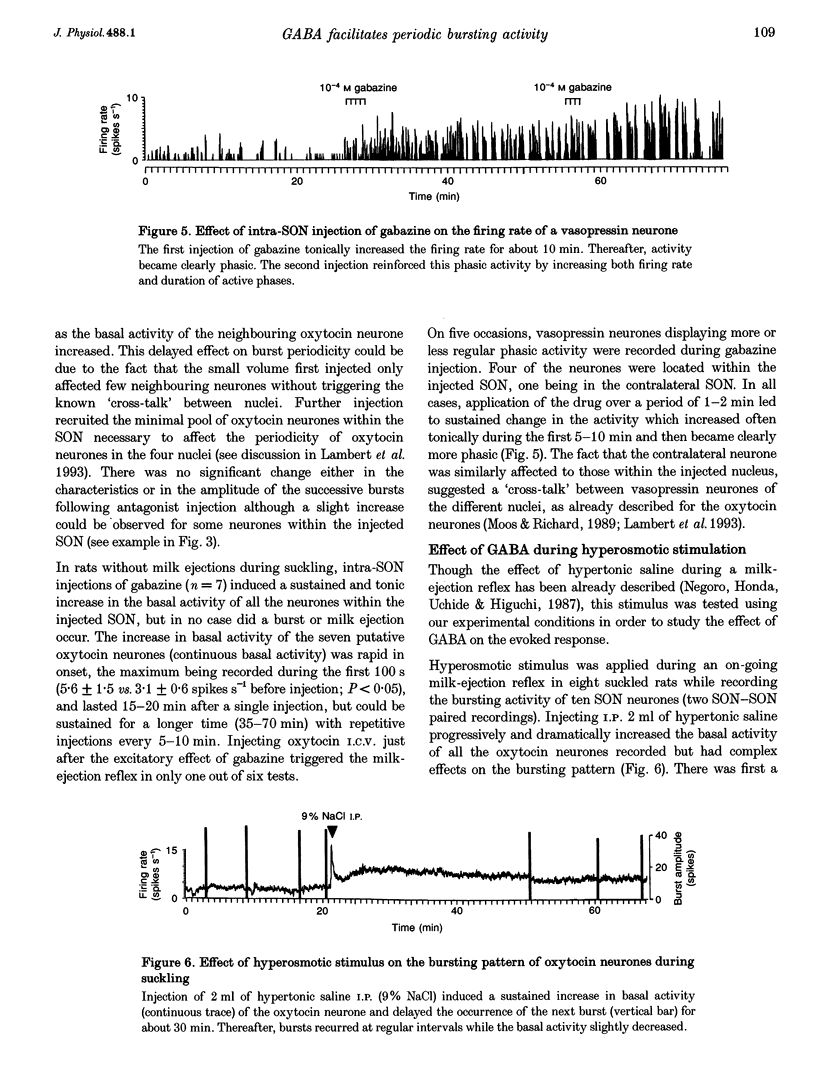
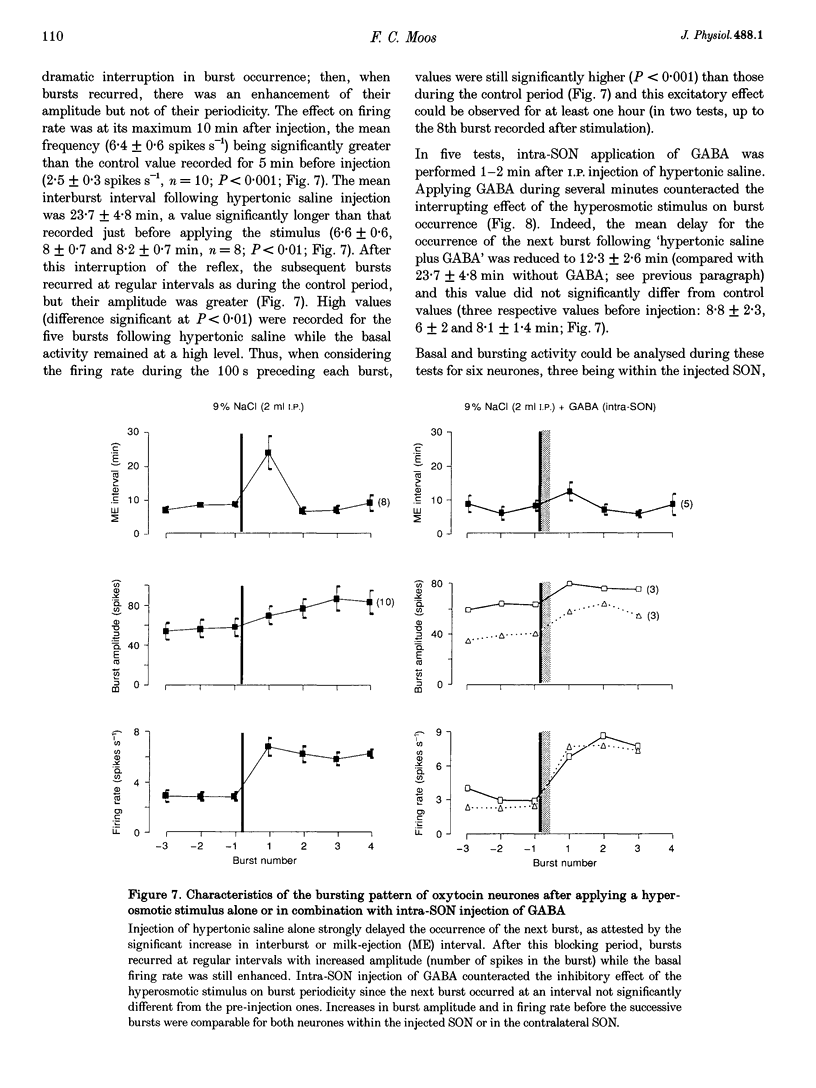
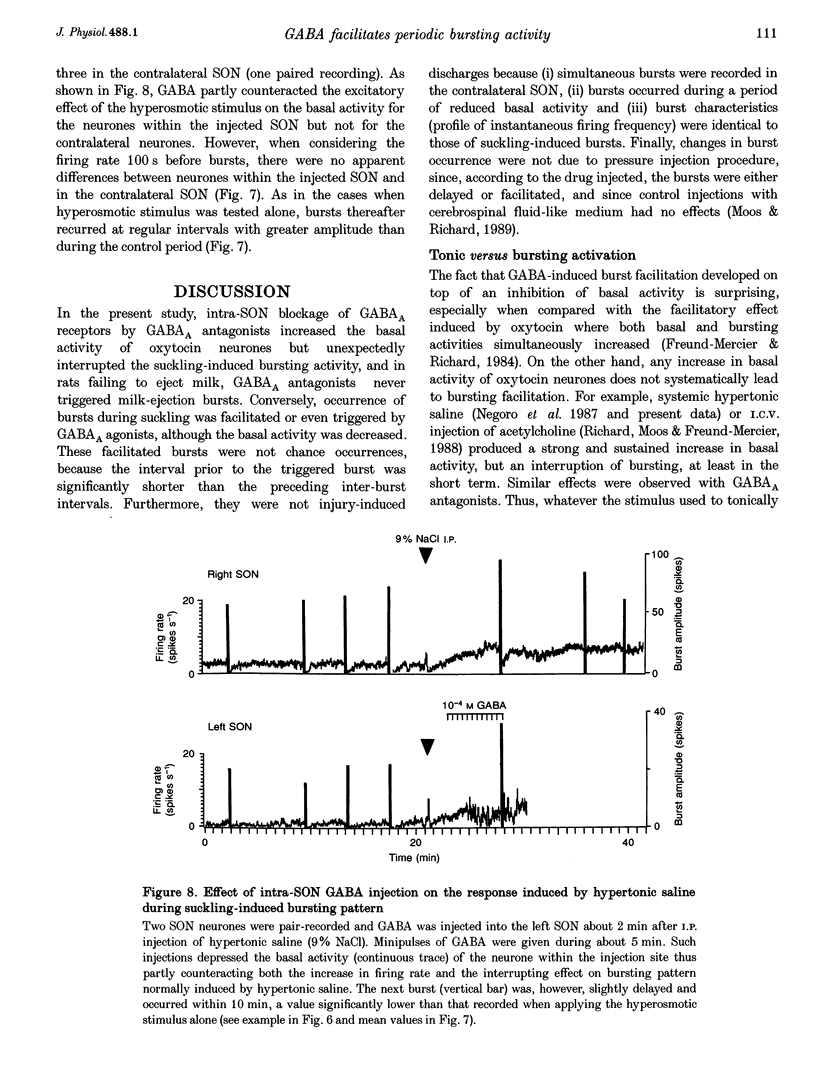
1. GABAergic innervation of oxytocin neurones is particularly abundant during lactation, but little is known about its functional role. In this study, the role of GABAA receptors in the suckling-induced bursting activity of oxytocin neurones was investigated in lactating rats. GABAA agonists or antagonists were applied by pressure injection into the immediate neighbourhood of recorded neurones while simultaneous recordings were made from oxytocin neurones in the contralateral supraoptic nucleus. 2. GABA and the GABA agonist isoguvacine decreased the basal electrical activity while application of GABAA antagonists (picrotoxin and gabazine) increased the basal electrical activity. However, in marked and unexpected contrast, application of GABA and isoguvacine facilitated or triggered milk-ejection reflex bursting activity whereas GABAA antagonists interrupted this reflex activity. 3. Systemic injection of hypertonic saline is known to increase the firing rate of neurones in the supraoptic nucleus and temporarily to interrupt suckling-induced bursting activity. Application of GABA into one supraoptic nucleus counteracted this inhibitory effect on milk ejection. 4. These observations can be explained if the role of the important GABAergic innervation of oxytocin neurones during lactation is to favour the expression of the stereotyped suckling-induced bursting activity. It might do this by attenuating inputs unrelated to suckling which are incompatible with bursts.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belin V., Moos F., Richard P. Synchronization of oxytocin cells in the hypothalamic paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in suckled rats: direct proof with paired extracellular recordings. Exp Brain Res. 1984;57(1):201–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00231147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisset G. W., Chowdrey H. S., Fairhall K. M., Gunn L. K. Central inhibition by gamma-aminobutyric acid and muscimol of the release of vasopressin and oxytocin by an osmotic stimulus in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):529–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12963.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimble M. J., Dyball R. E. Characterization of the responses of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones in the supraoptic nucleus to osmotic stimulation. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;271(1):253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decavel C., Van den Pol A. N. GABA: a dominant neurotransmitter in the hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Dec 22;302(4):1019–1037. doi: 10.1002/cne.903020423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund-Mercier M. J., Richard P. Electrophysiological evidence for facilitatory control of oxytocin neurones by oxytocin during suckling in the rat. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:447–466. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gies U., Theodosis D. T. Synaptic plasticity in the rat supraoptic nucleus during lactation involves GABA innervation and oxytocin neurons: a quantitative immunocytochemical analysis. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 1):2861–2869. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-02861.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman R. D., Rosella-Dampman L. M., Summy-Long J. Y. Endogenous opioid peptides inhibit oxytocin release in the lactating rat after dehydration and urethane. Endocrinology. 1987 Aug;121(2):536–543. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-2-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbison A. E. Immunocytochemical evidence for oestrogen receptors within GABA neurones located in the perinuclear zone of the supraoptic nucleus and GABAA receptor beta 2/beta 3 subunits on supraoptic oxytocin neurones. J Neuroendocrinol. 1994 Feb;6(1):5–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1994.tb00547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi T., Honda K., Takano S., Negoro H. Reduced oxytocin response to osmotic stimulus and immobilization stress in lactating rats. J Endocrinol. 1988 Feb;116(2):225–230. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1160225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert R. C., Moos F. C., Richard P. Action of endogenous oxytocin within the paraventricular or supraoptic nuclei: a powerful link in the regulation of the bursting pattern of oxytocin neurons during the milk-ejection reflex in rats. Neuroscience. 1993 Dec;57(4):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90046-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. T., Poulain D., Cobbett P. gamma-Aminobutyric acid as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the rat supraoptic nucleus: intracellular recordings in the hypothalamic slice. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 27;73(3):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90255-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos F., Richard P. Paraventricular and supraoptic bursting oxytocin cells in rat are locally regulated by oxytocin and functionally related. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:1–18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro H., Honda K., Uchide K., Higuchi T. Facilitation of milk ejection-related activation of oxytocin-secreting neurones by osmotic stimulation in the rat. Exp Brain Res. 1987;65(2):312–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00236303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B., Dyball R. E. Electrophysiological differentiation of oxytocin- and vasopressin-secreting neurones. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Apr;196(1125):367–384. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle J. C., Renaud L. P. Actions of gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat supraoptic nucleus neurosecretory neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:629–647. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P., Bourque C. W. Neurophysiology and neuropharmacology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurons secreting vasopressin and oxytocin. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(2):131–169. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summy-Long J. Y., Neumann I., Terrell M. L., Koehler E., Gestl S., Landgraf R., Kadekaro M. Crosstalk in the magnocellular system during osmotic stimulation of one supraoptic nucleus. Brain Res Bull. 1994;33(6):645–654. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasker J. G., Dudek F. E. Local inhibitory synaptic inputs to neurones of the paraventricular nucleus in slices of rat hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1993 Sep;469:179–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thellier D., Moos F., Richard P., Stoeckel M. E. Evidence for connections between a discrete hypothalamic dorsochiasmatic area and the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. Brain Res Bull. 1994;34(3):261–274. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thellier D., Moos F., Richard P., Stoeckel M. E. Evidence for reciprocal connections between the dorsochiasmatic area and the hypothalamo neurohypophyseal system and some related extrahypothalamic structures. Brain Res Bull. 1994;35(4):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(94)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisin D. L., Chapman C., Poulain D. A., Herbison A. E. Extracellular GABA concentrations in rat supraoptic nucleus during lactation and following haemodynamic changes: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neuroscience. 1994 Nov;63(2):547–558. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisin D. L., Herbison A. E., Poulain D. A. Central inhibitory effects of muscimol and bicuculline on the milk ejection reflex in the anaesthetized rat. J Physiol. 1995 Feb 15;483(Pt 1):211–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakerley J. B., Lincoln D. W. The milk-ejection reflex of the rat: a 20- to 40-fold acceleration in the firing of paraventricular neurones during oxytocin release. J Endocrinol. 1973 Jun;57(3):477–493. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0570477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Barnes E. M., Jr, Hablitz J. J. Whole-cell and single-channel recordings of GABA-gated currents in cultured chick cerebral neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Feb;59(2):495–513. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.2.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuarin J. P., Dudek F. E. Patch-clamp analysis of spontaneous synaptic currents in supraoptic neuroendocrine cells of the rat hypothalamus. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2323–2331. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02323.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


