Abstract
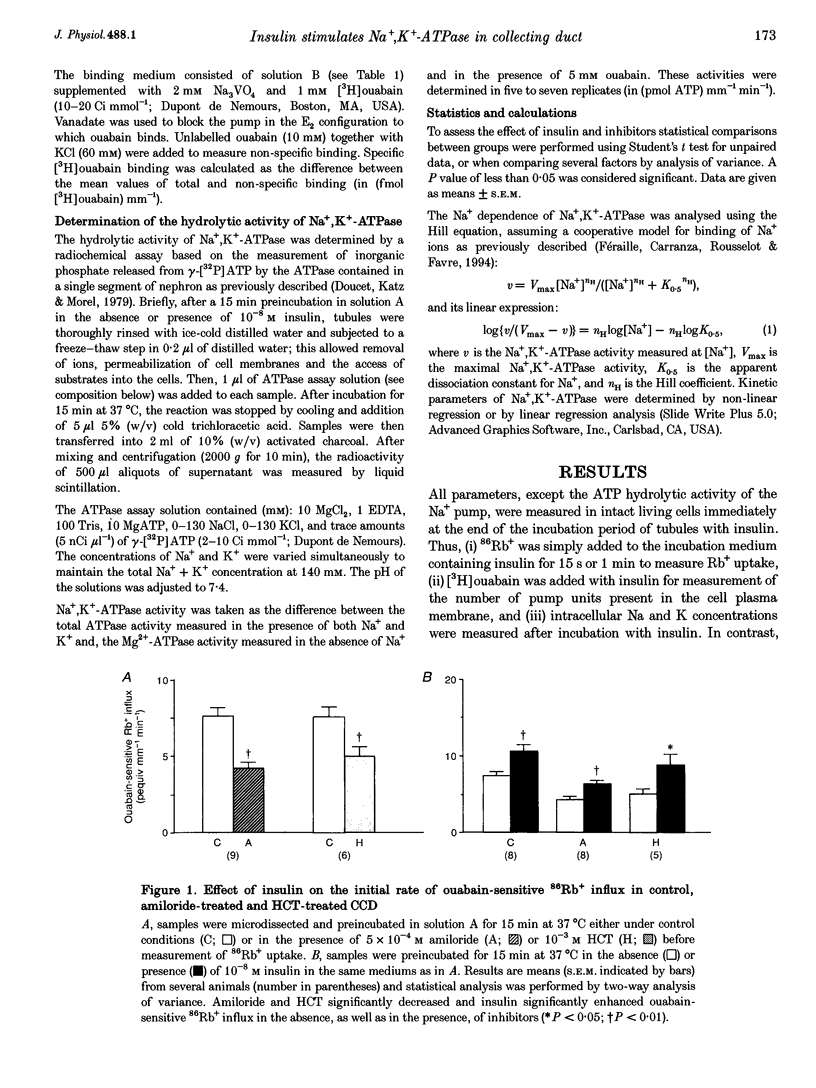
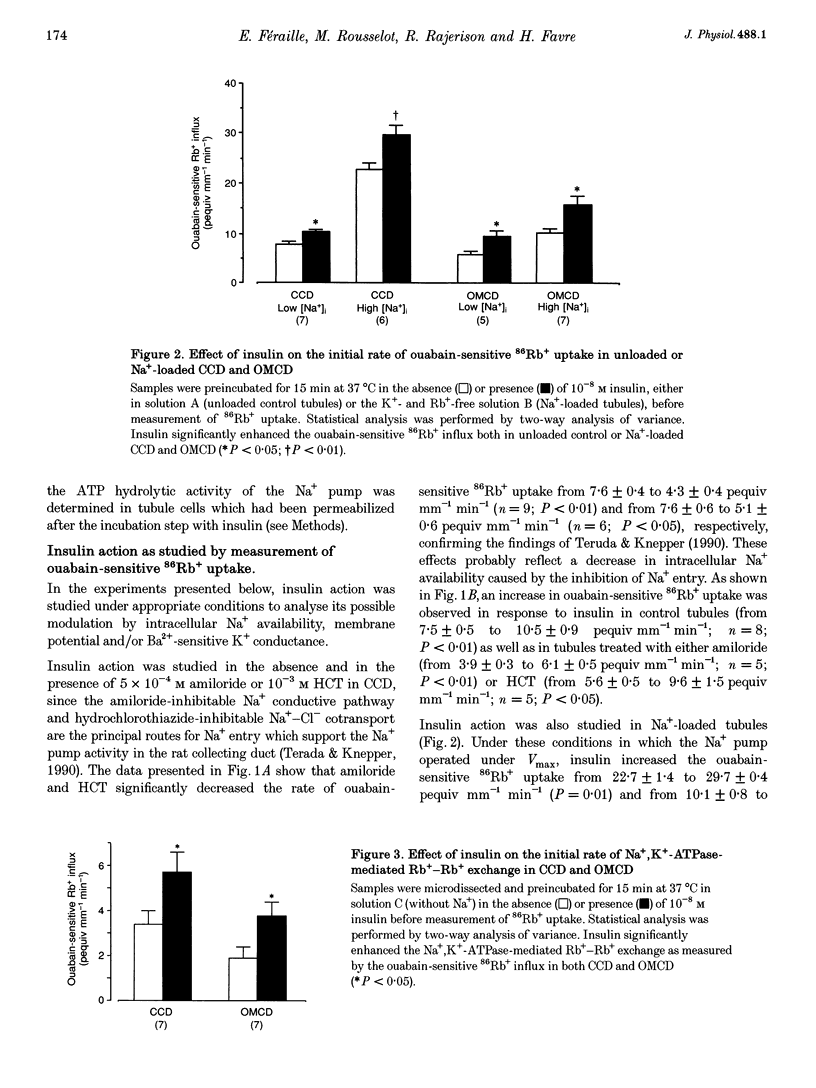
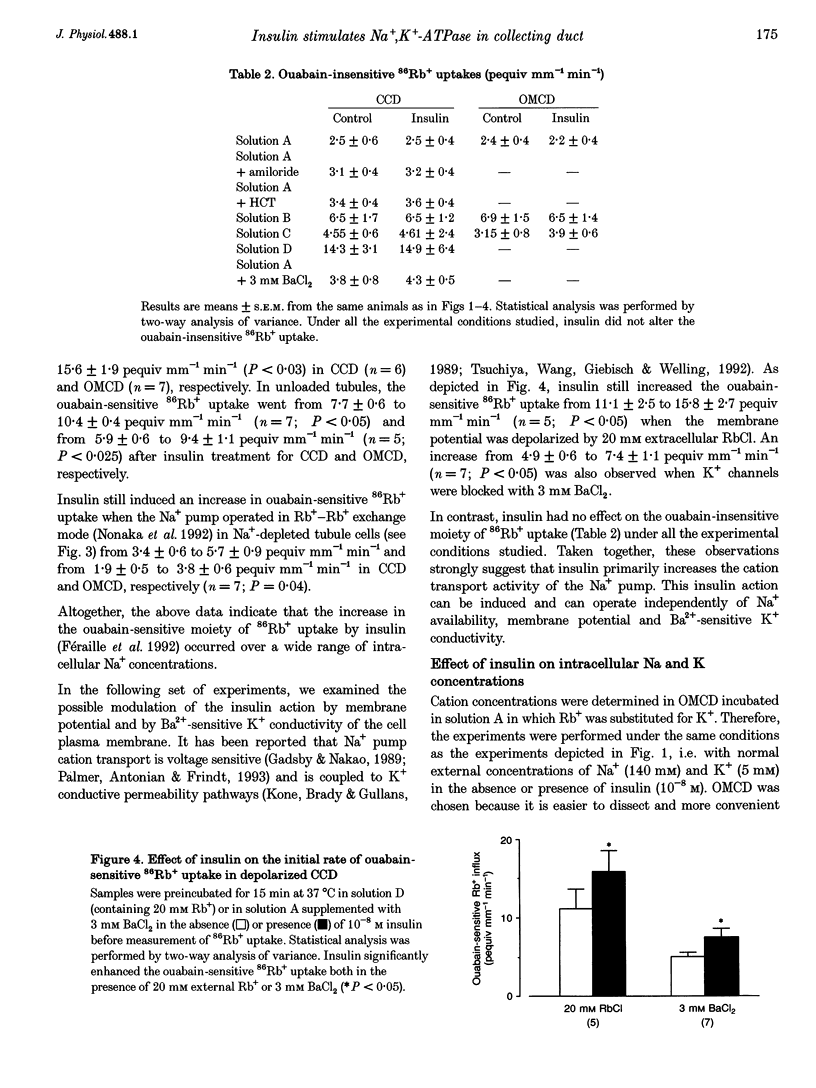
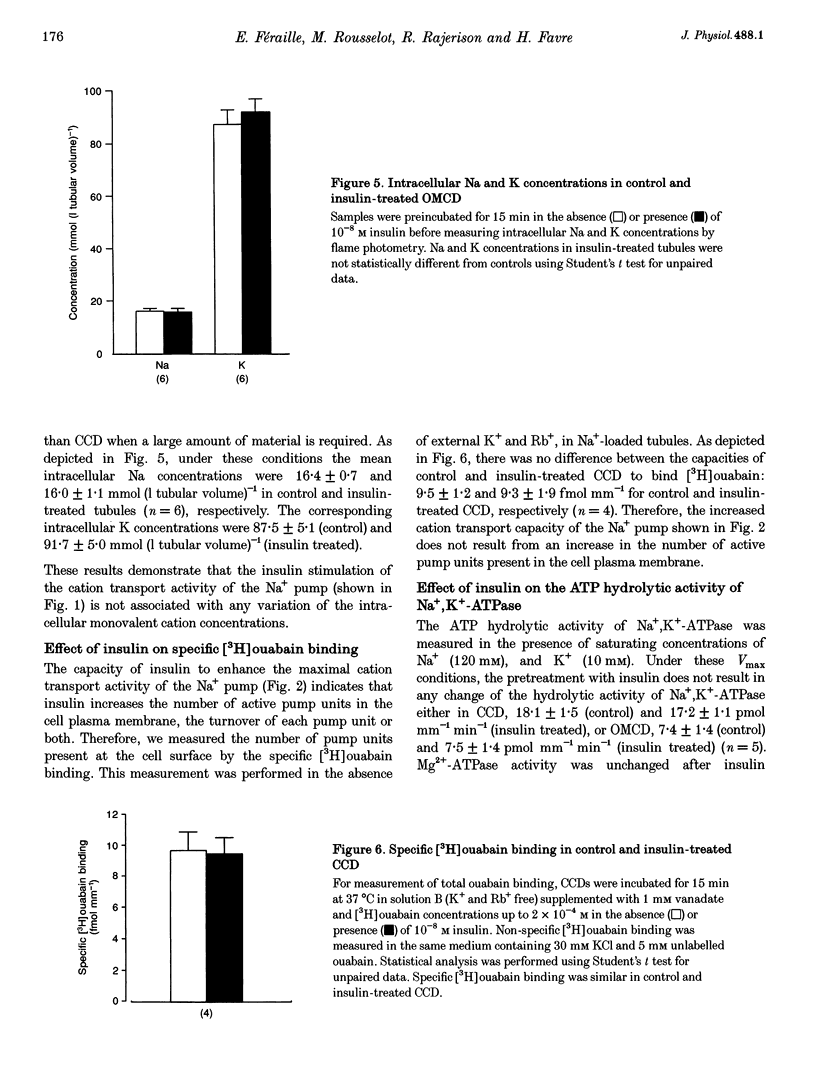
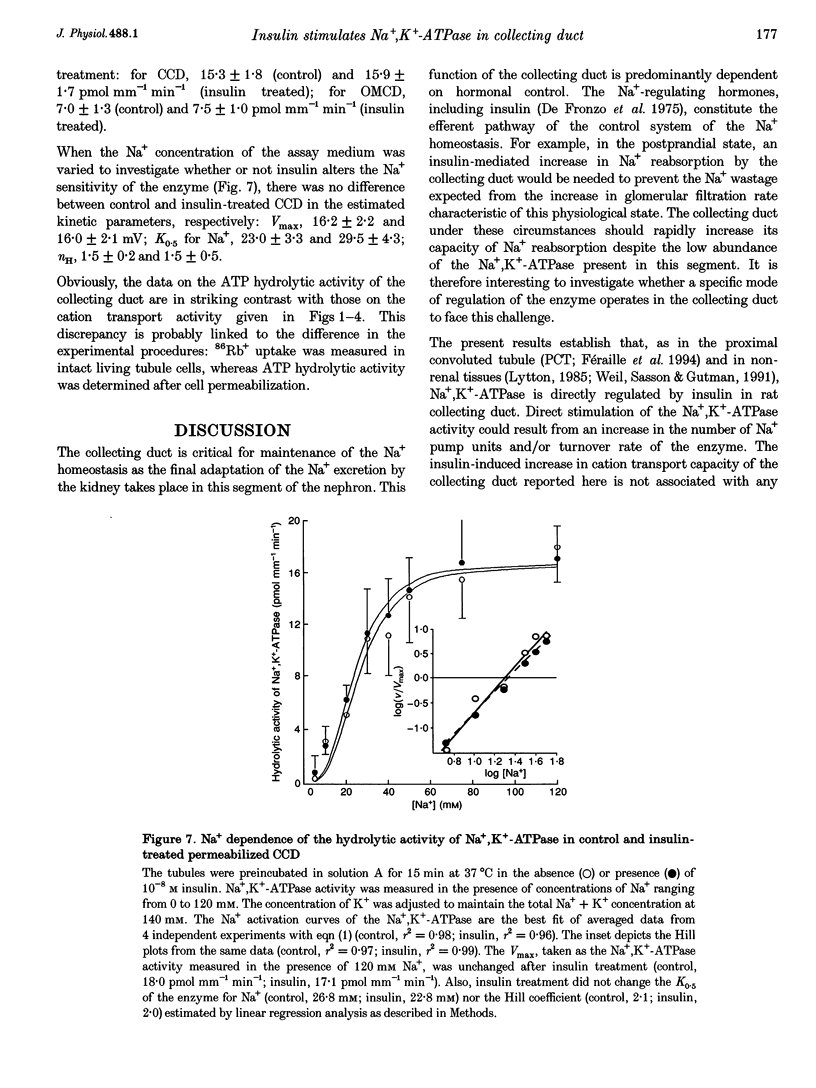
1. The collecting duct is involved in the whole antinatriuretic effect of insulin, as indicated in vitro by the stimulatory effect of the hormone on ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake. Since Na+,K(+)-ATPase drives Na+ reabsorption, the contribution of the Na+ pump to the effect of insulin was investigated in rat isolated cortical and outer medullary collecting duct. 2. Insulin enhanced ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake in the absence, as well as in the presence, of either 5 x 10(-4) M amiloride or 10(-3) M hydrochlorothiazide (HCT). Maximal ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake, measured in Na(+)-loaded tubules, was also enhanced by insulin. The insulin effect persisted both in the absence of external Na+, when the Na+,K(+)-ATPase operates in a Rb(+)-Rb+ exchange mode, and in tubules depolarized by a high external concentration (20 mM) of Rb+ or by addition of 3 mM Ba2+. 3. Insulin treatment did not alter the intracellular Na and K concentrations, the specific binding of [3H]ouabain measured in intact tubules, or the hydrolytic activity of Na+,K(+)-ATPase measured after permeabilization of the tubule cells. 4. In conclusion, in the rat collecting duct, insulin increased Na+,K(+)-ATPase-mediated cation transport independently of Na+ availability, membrane potential and recruitment of pump units. The effect of insulin was lost after cell permeabilization, suggesting the presence of a cytosolic factor which controls the turnover of Na+,K(+)-ATPase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlet-Bas C., Arystarkhova E., Cheval L., Marsy S., Sweadner K., Modyanov N., Doucet A. Are there several isoforms of Na,K-ATPase alpha subunit in the rabbit kidney? J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11512–11515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlet-Bas C., Cheval L., Khadouri C., Marsy S., Doucet A. Difference in the Na affinity of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase along the rabbit nephron: modulation by K. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):F246–F250. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlet-Bas C., Khadouri C., Marsy S., Doucet A. Enhanced intracellular sodium concentration in kidney cells recruits a latent pool of Na-K-ATPase whose size is modulated by corticosteroids. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7799–7803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum M. Insulin stimulates volume absorption in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1104–1109. doi: 10.1172/JCI112925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. S., Laprade R., Lapointe J. Y. Coupling between transepithelial Na transport and basolateral K conductance in renal proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1994 Apr;266(4 Pt 2):F517–F527. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.4.F517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot-Chabaud M., Jaisser F., Gingold M., Bonvalet J. P., Farman N. Na+-K+-ATPase-dependent sodium flux in cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F605–F613. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot-Chabaud M., Wanstok F., Bonvalet J. P., Farman N. Cell sodium-induced recruitment of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase pumps in rabbit cortical collecting tubules is aldosterone-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11676–11681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Yang C. P., Brown J. A., Jr, Scott W. N. Insulin-stimulated sodium transport in toad urinary bladder. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. J., McCarthy D. M., Stoff J. S. Direct hemodynamic effect of insulin in the isolated perfused kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):F580–F585. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.4.F580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Cooke C. R., Andres R., Faloona G. R., Davis P. J. The effect of insulin on renal handling of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):845–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI107996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Goldberg M., Agus Z. S. The effects of glucose and insulin on renal electrolyte transport. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):83–90. doi: 10.1172/JCI108463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Barlet C. Evidence for differences in the sensitivity to ouabain of NaK-ATPase along the nephrons of rabbit kidney. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):993–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet A., Katz A. I., Morel F. Determination of Na-K-ATPase activity in single segments of the mammalian nephron. Am J Physiol. 1979 Aug;237(2):F105–F113. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.2.F105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Mernissi G., Doucet A. Quantitation of [3H]ouabain binding and turnover of Na-K-ATPase along the rabbit nephron. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F158–F167. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlij D., De Smet P., Van Driessche W. Effect of insulin on area and Na+ channel density of apical membrane of cultured toad kidney cells. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 15;481(Pt 3):533–542. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidelman M. L., May J. M., Biber T. U., Watlington C. O. Insulin stimulation of Na+ transport and glucose metabolism in cultured kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C121–C123. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya H., Tabei K., Muto S., Asano Y. Effect of insulin on potassium secretion in rabbit cortical collecting ducts. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 2):F30–F35. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.1.F30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féraille E., Barlet-Bas C., Cheval L., Rousselot M., Carranza M. L., Dreher D., Arystarkhova E., Doucet A., Favre H. Presence of two isoforms of Na, K-ATPase with different pharmacological and immunological properties in the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Jun;430(2):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00374651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féraille E., Carranza M. L., Buffin-Meyer B., Rousselot M., Doucet A., Favre H. Protein kinase C-dependent stimulation of Na(+)-K(+)-ATP epsilon in rat proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1995 May;268(5 Pt 1):C1277–C1283. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.5.C1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féraille E., Carranza M. L., Rousselot M., Favre H. Insulin enhances sodium sensitivity of Na-K-ATPase in isolated rat proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jul;267(1 Pt 2):F55–F62. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.1.F55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féraille E., Marsy S., Cheval L., Barlet-Bas C., Khadouri C., Favre H., Doucet A. Sites of antinatriuretic action of insulin along rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):F175–F179. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.1.F175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Féraille E., Vogt B., Rousselot M., Barlet-Bas C., Cheval L., Doucet A., Favre H. Mechanism of enhanced Na-K-ATPase activity in cortical collecting duct from rats with nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1295–1300. doi: 10.1172/JCI116328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Nakao M. Steady-state current-voltage relationship of the Na/K pump in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):511–537. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesek F. A., Schoolwerth A. C. Insulin increases Na(+)-H+ exchange activity in proximal tubules from normotensive and hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 2):F695–F703. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.5.F695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner K. A. Insulin increases loop segment chloride reabsorption in the euglycemic rat. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1206–F1213. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kone B. C., Brady H. R., Gullans S. R. Coordinated regulation of intracellular K+ in the proximal tubule: Ba2+ blockade down-regulates the Na+,K+-ATPase and up-regulates two K+ permeability pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6431–6435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J. Insulin affects the sodium affinity of the rat adipocyte (Na+,K+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10075–10080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandon B., Siga E., Chabardes D., Firsov D., Roinel N., De Rouffignac C. Insulin stimulates Na+, Cl-, Ca2+, and Mg2+ transports in TAL of mouse nephron: cross-potentiation with AVP. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):F361–F369. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.3.F361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marunaka Y., Hagiwara N., Tohda H. Insulin activates single amiloride-blockable Na channels in a distal nephron cell line (A6). Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):F392–F400. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.3.F392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill D. L. Characterization of the adipocyte ghost (Na+,K+) pump. Insights into the insulin regulation of the adipocyte (Na+,K+) pump. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15817–15823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizet A., Lefebvre P., Crabbé J. Control by insulin of sodium potassium and water excretion by the isolated dog kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1971;323(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00586561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka T., Warden D. H., Stokes J. B. Analysis of K+ transport by rabbit CCD: conductive pathways and K(+)-K+ exchange by Na(+)-K+ pump. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 2):F86–F97. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.1.F86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. G., Antonian L., Frindt G. Regulation of the Na-K pump of the rat cortical collecting tubule by aldosterone. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jul;102(1):43–57. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Quantitation and characterization of the (Na+,K+)-adenosine triphosphatase in the rat adipocyte plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11946–11952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo J., Morel F. Na+ and K+ cell concentrations in collagenase-treated rat kidney tubules incubated at various temperatures. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 1):C407–C414. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.5.C407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Knepper M. A. Thiazide-sensitive NaCl absorption in rat cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):F519–F528. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.3.F519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Wang W., Giebisch G., Welling P. A. ATP is a coupling modulator of parallel Na,K-ATPase-K-channel activity in the renal proximal tubule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6418–6422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil E., Sasson S., Gutman Y. Mechanism of insulin-induced activation of Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase in isolated rat soleus muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C224–C230. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]