Abstract
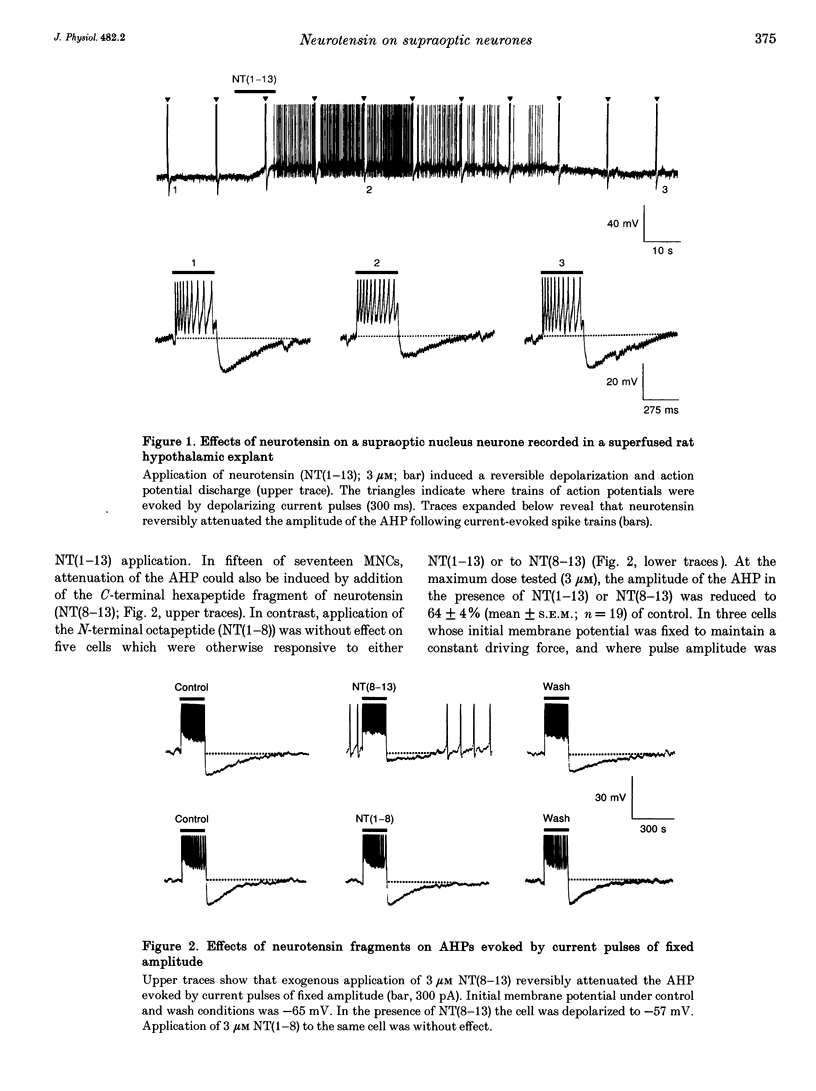
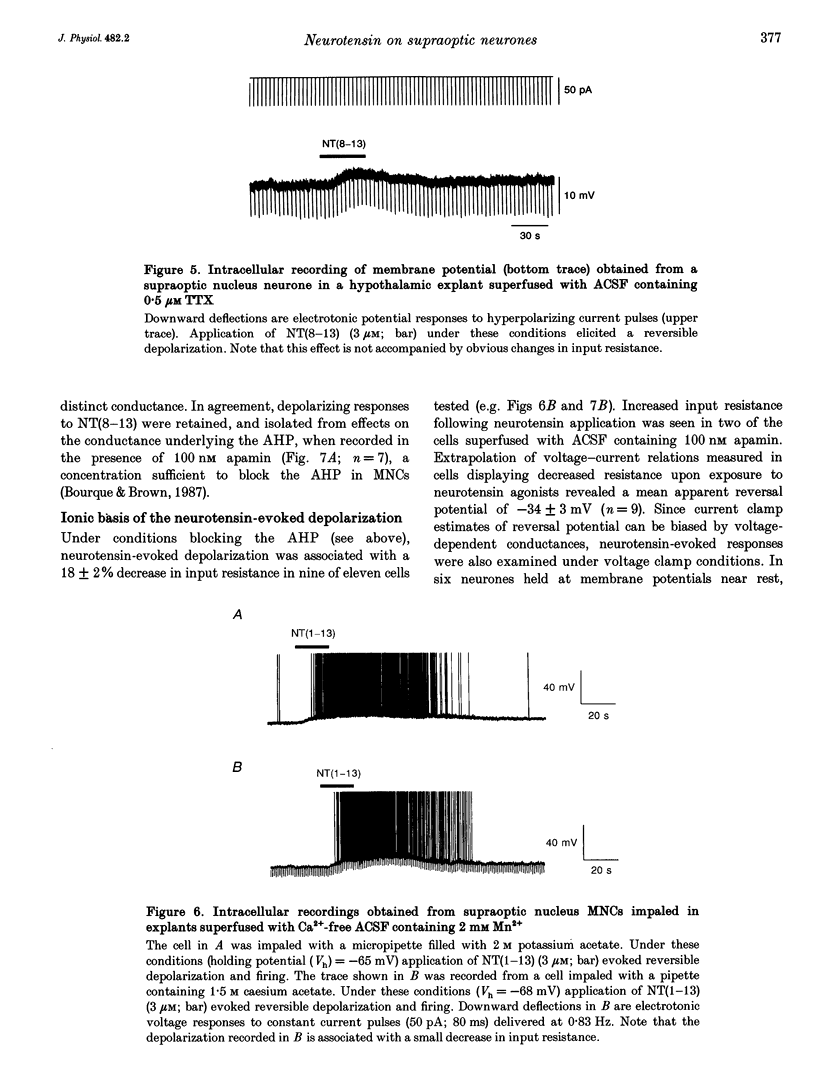
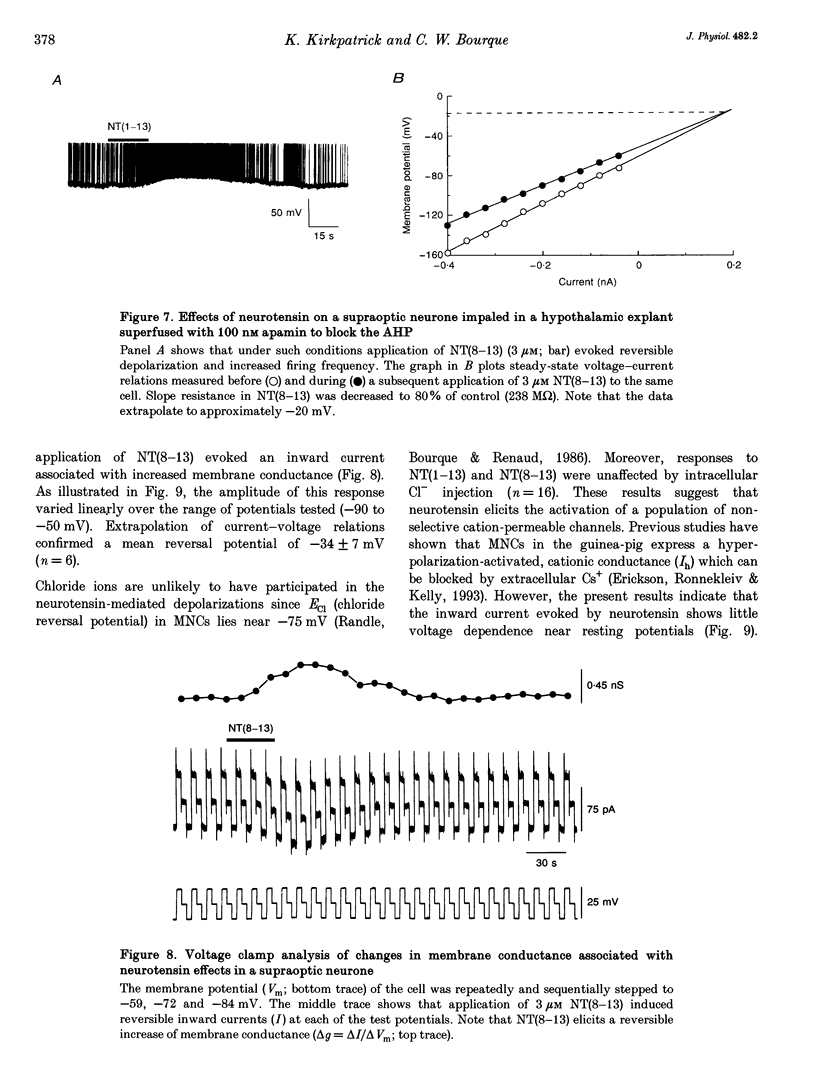
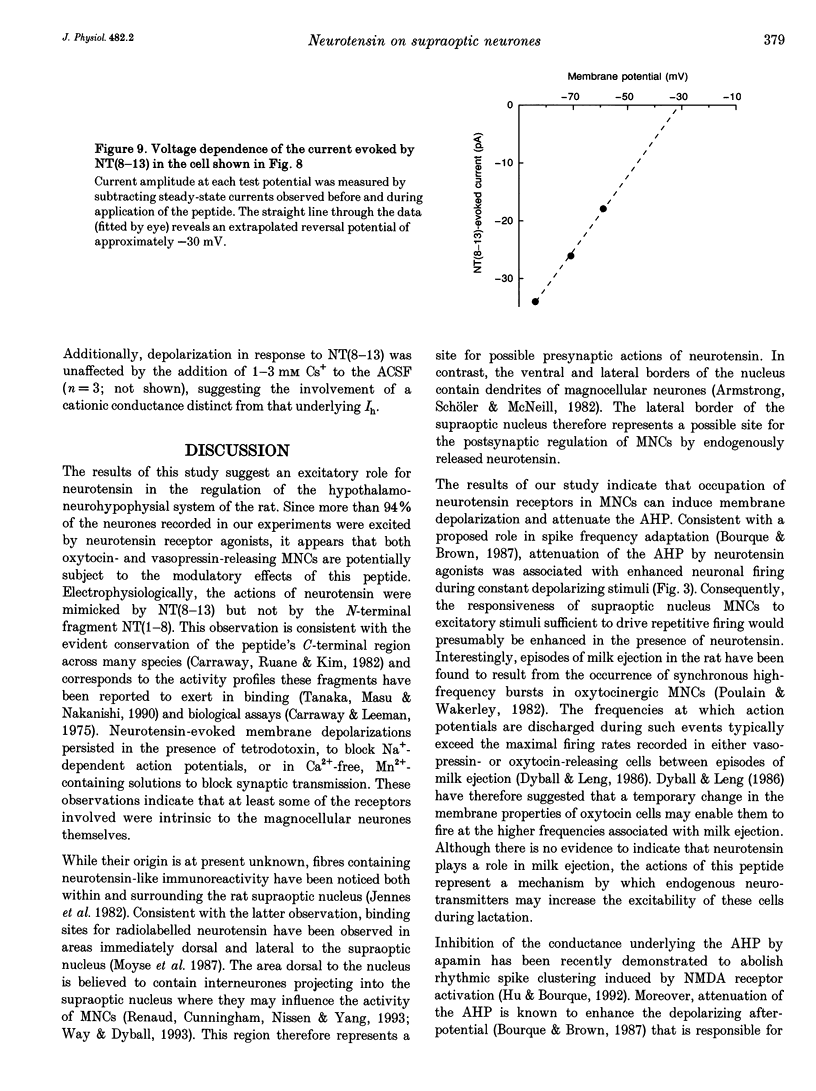
1. The electrophysiological actions of neurotensin on magnocellular neurosecretory cells (MNCs) were examined during intracellular recording from seventy-three supraoptic nucleus neurones in superfused explants of rat hypothalamus. 2. Application of neurotensin tridecapeptide (NT(1-13); 1 nM to 3 microM) caused a membrane depolarization and reversibly attenuated the after-hyperpolarization (AHP) which followed current-evoked spike trains. This effect was accompanied by increased firing frequency during depolarizing current pulses evoked from a fixed potential. 3. The effects of neurotensin could be mimicked by the C-terminal fragment, NT(8-13), but not by the N-terminal fragment, NT(1-8). 4. Depolarizing responses to NT(1-13) or NT(8-13), retained during K+ channel blockade with internal Cs+, were accompanied by increased membrane conductance. Current- and voltage-clamp analyses revealed that neurotensin-evoked depolarizations result partly from the activation of a non-selective cationic conductance reversing near -34 mV. 5. Depolarizing responses to neurotensin were retained in the presence of TTX or in Ca(2+)-free solutions, indicating the involvement of receptors located on the plasma membrane of MNCs themselves. 6. Through these effects endogenously released neurotensin may modulate excitability, activity patterns and secretion from the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial axis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E. Burst discharge in mammalian neuroendocrine cells involves an intrinsic regenerative mechanism. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1050–1052. doi: 10.1126/science.6879204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E. Intrinsic inhibition in magnocellular neuroendocrine cells of rat hypothalamus. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:171–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew R. D., Dudek F. E. Spike broadening in magnocellular neuroendocrine cells of rat hypothalamic slices. Brain Res. 1985 May 13;334(1):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90583-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong W. E., Schöler J., McNeill T. H. Immunocytochemical, Golgi and electron microscopic characterization of putative dendrites in the ventral glial lamina of the rat supraoptic nucleus. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):679–694. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audinat E., Hermel J. M., Crépel F. Neurotensin-induced excitation of neurons of the rat's frontal cortex studied intracellularly in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1989;78(2):358–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00228907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell R. J. Optimizing release from peptide hormone secretory nerve terminals. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:51–65. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Brown D. A. Apamin and d-tubocurarine block the afterhyperpolarization of rat supraoptic neurosecretory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Nov 23;82(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90127-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Randle J. C., Renaud L. P. Calcium-dependent potassium conductance in rat supraoptic nucleus neurosecretory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Dec;54(6):1375–1382. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.6.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. Activity dependence of action potential duration in rat supraoptic neurosecretory neurones recorded in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:429–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. Membrane properties of rat magnocellular neuroendocrine cells in vivo. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 1;540(1-2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90535-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Kitabgi P., Leeman S. E. The amino acid sequence of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin from bovine intestine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):7996–7998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Ruane S. E., Kim H. R. Distribution and immunochemical character of neurotensin-like material in representative vertebrates and invertebrates: apparent conservation of the COOH-terminal region during evolution. Peptides. 1982 Mar-Apr;3(2):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christinck F., Daniel E. E., Fox-Threlkeld J. E. Inhibitory and excitatory mechanisms of neurotensin action in canine intestinal circular muscle in vitro. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;70(10):1423–1431. doi: 10.1139/y92-200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyball R. E., Leng G. Regulation of the milk ejection reflex in the rat. J Physiol. 1986 Nov;380:239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson K. R., Ronnekleiv O. K., Kelly M. J. Electrophysiology of guinea-pig supraoptic neurones: role of a hyperpolarization-activated cation current in phasic firing. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:407–425. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas R. H., Nakajima S., Nakajima Y. Neurotensin excites basal forebrain cholinergic neurons: ionic and signal-transduction mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu B., Bourque C. W. NMDA receptor-mediated rhythmic bursting activity in rat supraoptic nucleus neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:667–687. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro-Toro J. P., Zhu Y. X. Neurotensin receptors on the ileum of the guinea-pig: evidence for the coexistence of inhibitory and excitatory receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 13;102(2):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennes L., Stumpf W. E., Kalivas P. W. Neurotensin: topographical distribution in rat brain by immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Sep 20;210(3):211–224. doi: 10.1002/cne.902100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Z. G., Pessia M., North R. A. Neurotensin excitation of rat ventral tegmental neurones. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 1;474(1):119–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullak A., Donoso M. V., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Extracellular calcium dependence of the neurotensin-induced relaxation of intestinal smooth muscles: studies with calcium channel blockers and BAY K-8644. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 31;135(3):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90678-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyse E., Rostène W., Vial M., Leonard K., Mazella J., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P., Beaudet A. Distribution of neurotensin binding sites in rat brain: a light microscopic radioautographic study using monoiodo [125I]Tyr3-neurotensin. Neuroscience. 1987 Aug;22(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulè F., Postorino A., Geraci A., Serio R. Neurotensin: dual effect on the motor activity of rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 3;212(2-3):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain D. A., Wakerley J. B. Electrophysiology of hypothalamic magnocellular neurones secreting oxytocin and vasopressin. Neuroscience. 1982 Apr;7(4):773–808. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randle J. C., Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. Characterization of spontaneous and evoked inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in rat supraoptic neurosecretory neurons in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Dec;56(6):1703–1717. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.6.1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud L. P., Cunningham J. T., Nissen R., Yang C. R. Electrophysiology of central pathways controlling release of neurohypophysial hormones. Focus on the lamina terminalis and diagonal band inputs to the supraoptic nucleus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jul 22;689:122–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb55542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowe Z. N., Nemeroff C. B. The electrophysiological actions of neurotensin in the central nervous system. Life Sci. 1991;49(14):987–1002. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90300-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way S. A., Dyball R. E. Interaction between magnocellular neurons and cells of the perinuclear zone involves NMDA receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jul 22;689:683–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb55628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. R., Bourque C. W., Renaud L. P. Dopamine D2 receptor activation depolarizes rat supraoptic neurones in hypothalamic explants. J Physiol. 1991 Nov;443:405–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


