Abstract
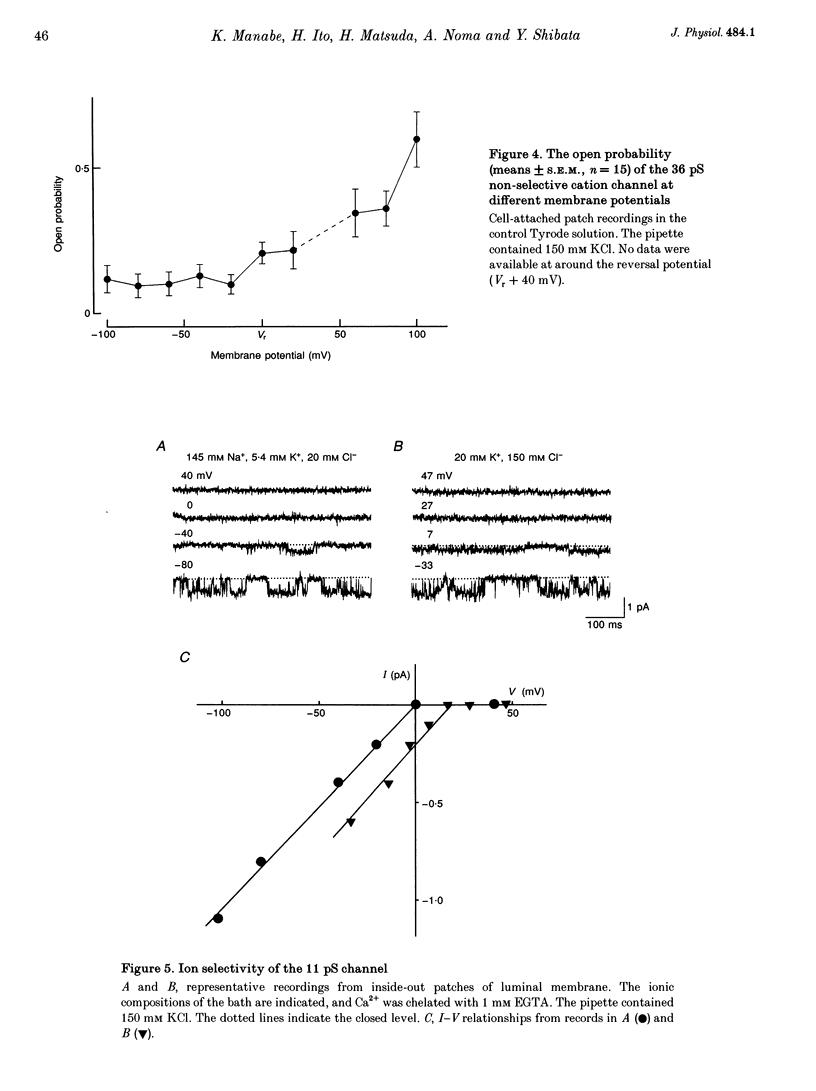
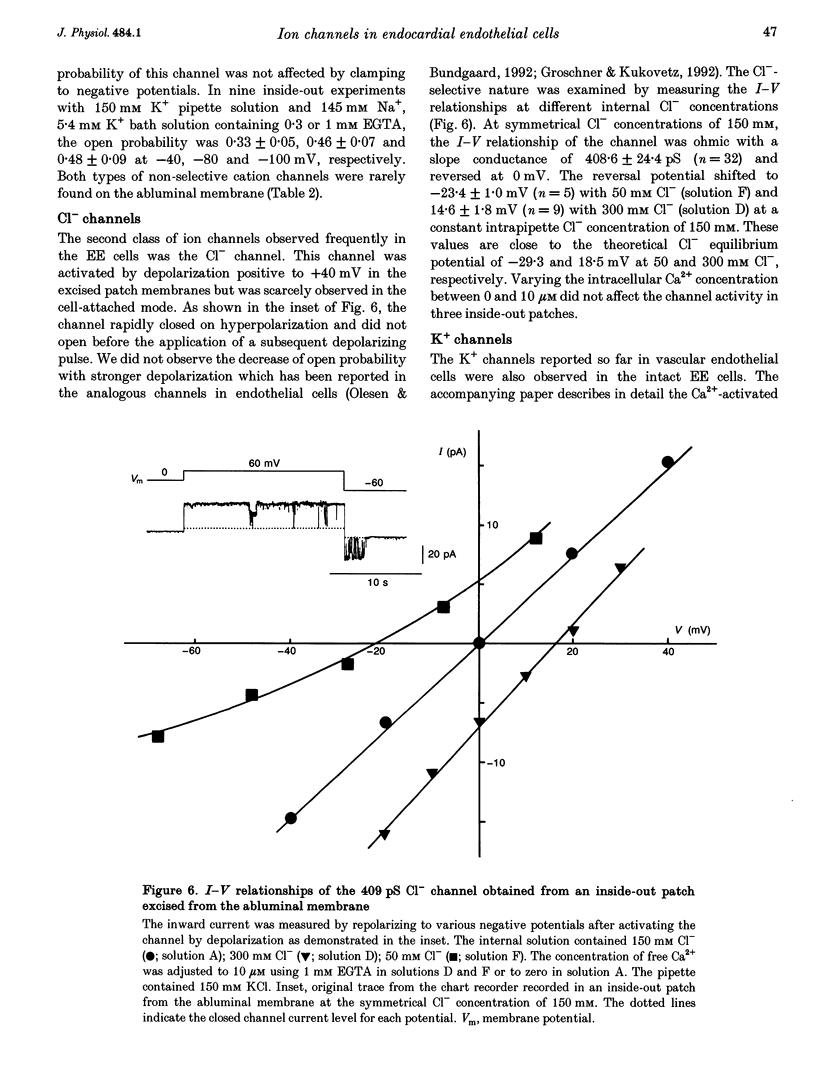
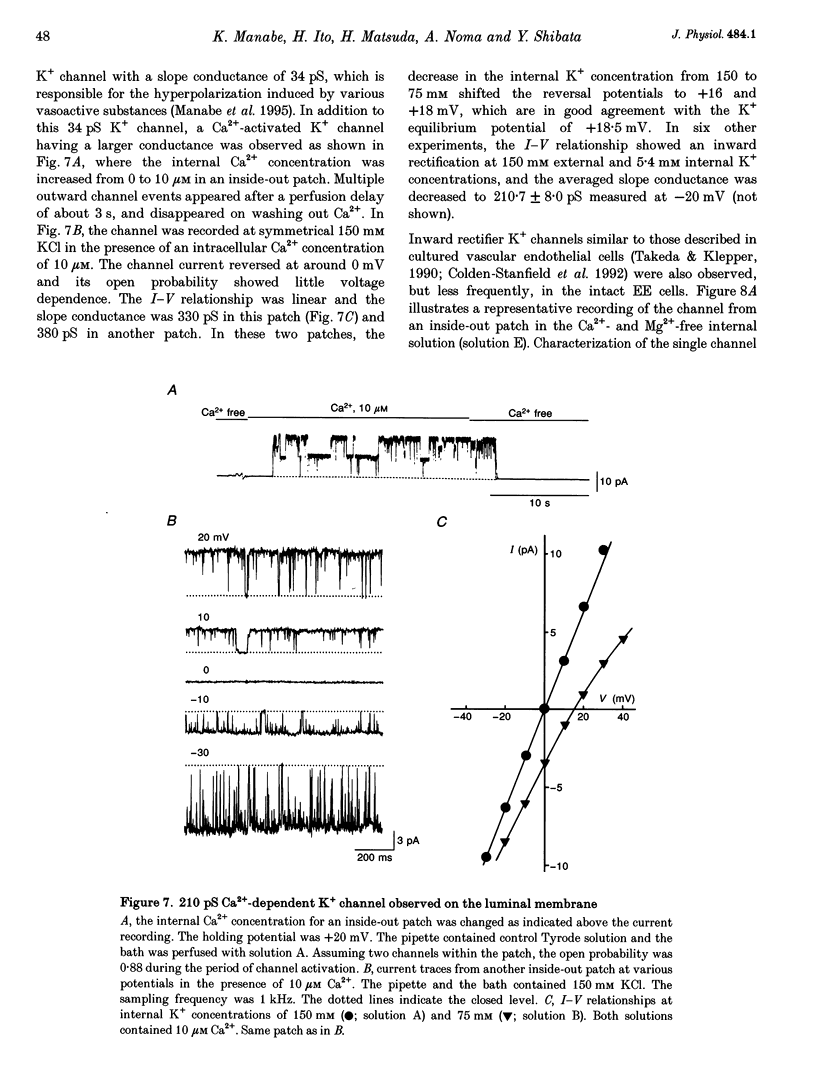
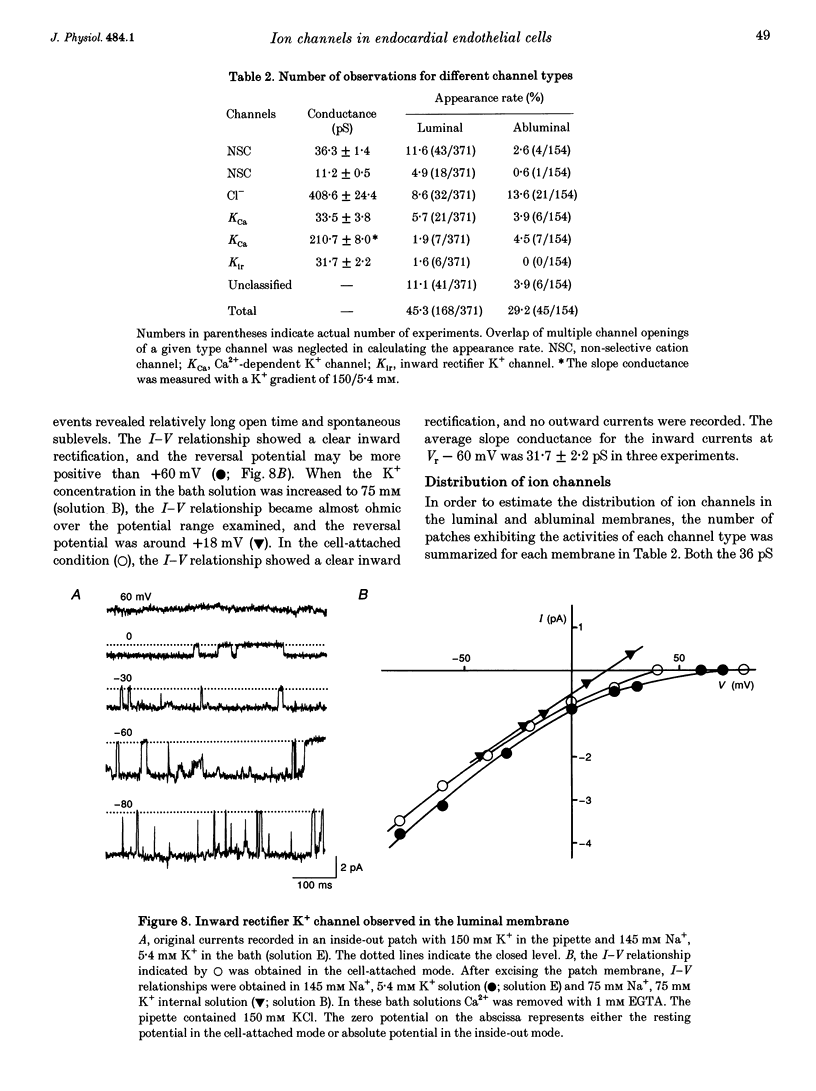
1. The ion channels on both the luminal and abluminal membranes of endocardial endothelial (EE) cells were separately recorded using the patch clamp technique in the guinea-pig heart. 2. The major population consisted of two types of non-selective cation channels, which showed open probabilities of 0.21 and 0.33 at the resting potential, and conductances of 36 and 11 pS, respectively. 3. The next major class was Cl- channels with an ohmic conductance of 409 pS. The channel was quiescent in the cell-attached mode but was activated by strong depolarization after excising the patch membrane. 4. The channels activated by intracellular Ca2+ were mainly K+ channels showing a 34 pS slope conductance and, less frequently, Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels having a large conductance (210 pS). The inward rectifier K+ channel (32 pS) was also observed. 5. The non-selective cation channels were recorded on the luminal membrane, but scarcely on the abluminal membrane, suggesting an active transport of K+ and Na+ across the endocardium. 6. The resting membrane conductance of the EE cells may be provided mostly by non-selective cation channels and 34 pS Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channels.
Full text
PDF
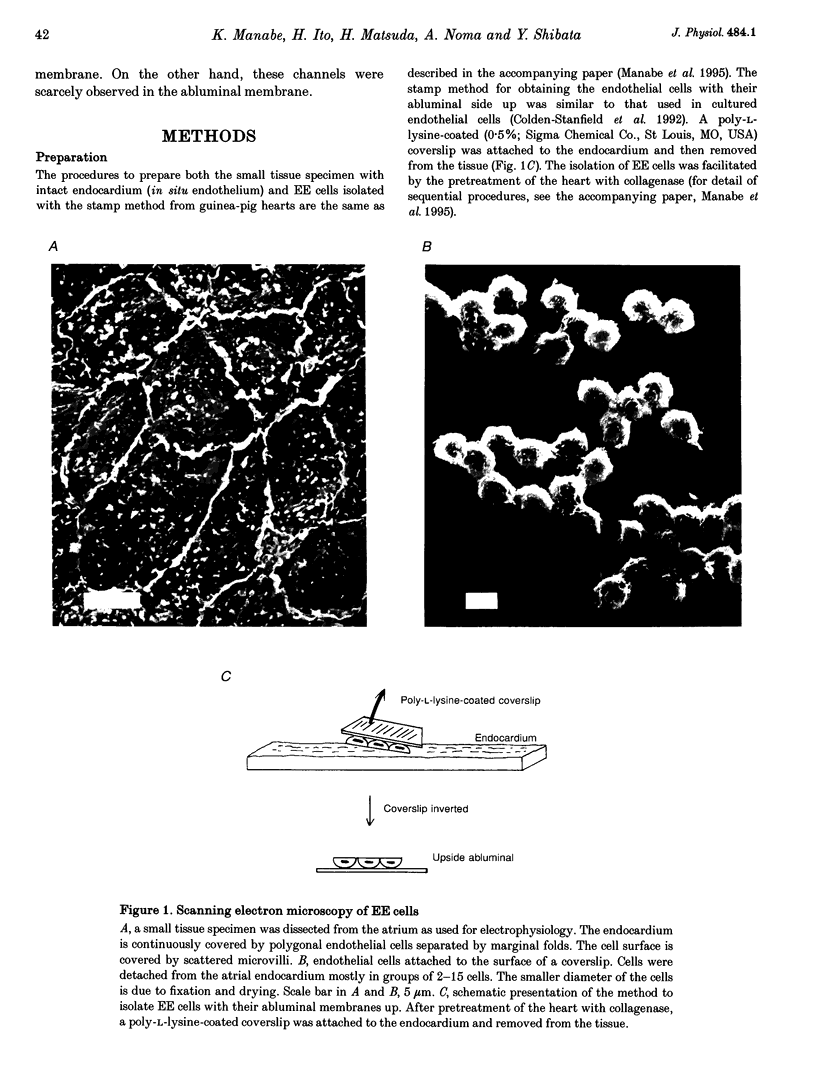

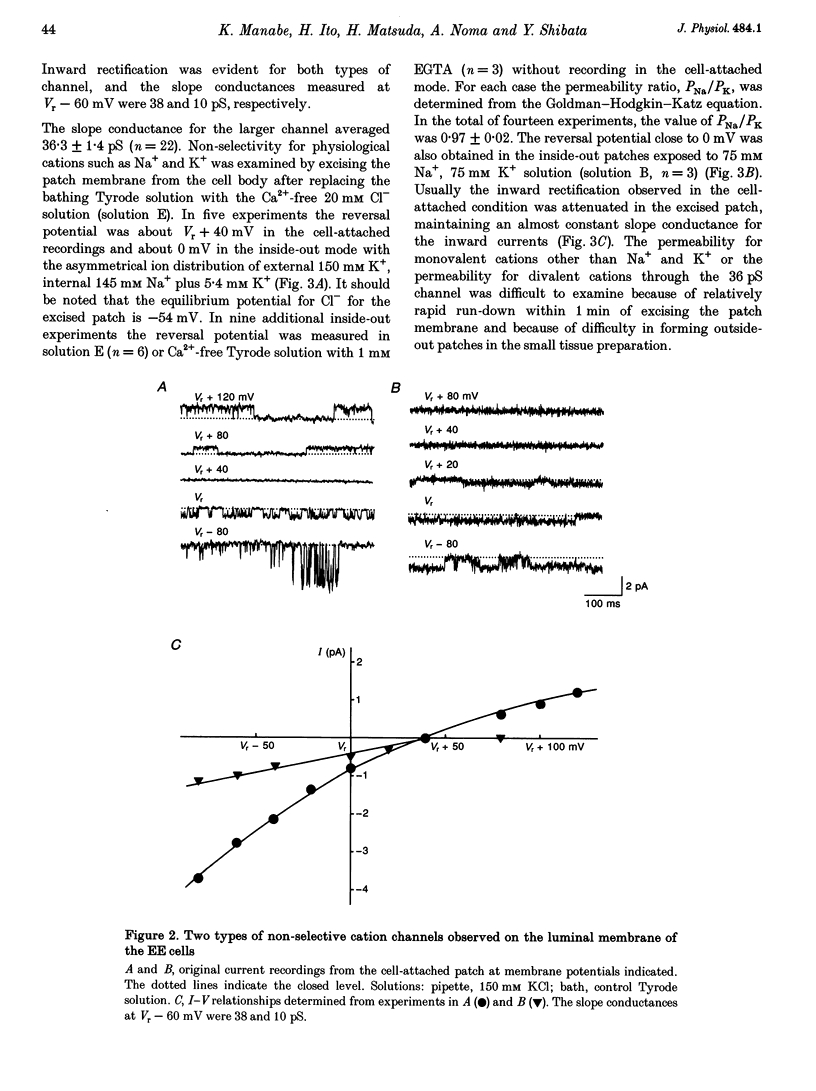
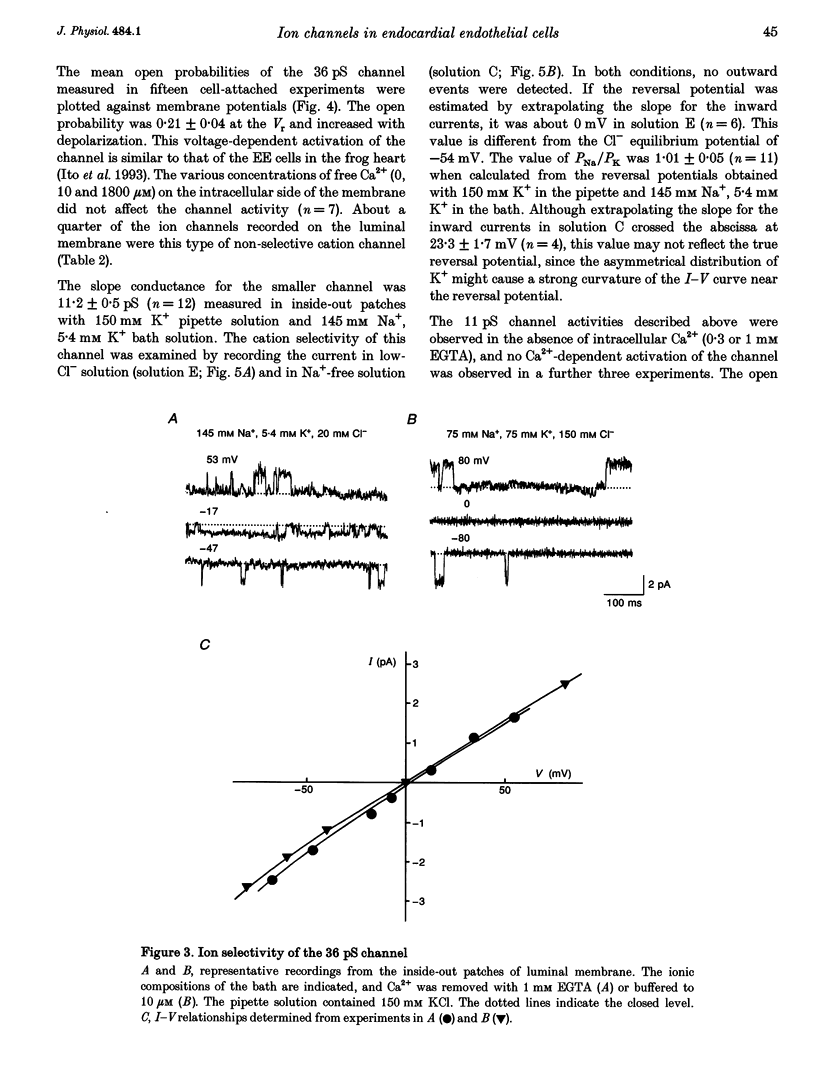



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Barakeh J., Laskey R., Van Breemen C. Ion channels and regulation of intracellular calcium in vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2389–2400. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2477294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Firth J. A., Goldstein G. W. Polarity of the blood-brain barrier: distribution of enzymes between the luminal and antiluminal membranes of brain capillary endothelial cells. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 16;192(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Goldstein G. W. Specialized properties and solute transport in brain capillaries. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:241–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregestovski P., Bakhramov A., Danilov S., Moldobaeva A., Takeda K. Histamine-induced inward currents in cultured endothelial cells from human umbilical vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert D. L., Andries L. J. The endocardial endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):H985–1002. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.4.H985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert D. L. The endocardium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:263–273. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Sage S. O. Bradykinin-evoked changes in cytosolic calcium and membrane currents in cultured bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:555–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colden-Stanfield M., Cramer E. B., Gallin E. K. Comparison of apical and basal surfaces of confluent endothelial cells: patch-clamp and viral studies. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):C573–C583. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.3.C573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRenzis F. A., Schechtman A. Staining by neutral red and trypan blue in sequence for assaying vital and nonvital cultured cells. Stain Technol. 1973 May;48(3):135–136. doi: 10.3109/10520297309116602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Mills J. W. Distribution of Na+-pump sites in transporting epithelia. Fed Proc. 1979 Feb;38(2):134–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtner H., Fröbe U., Busse R., Kohlhardt M. Single nonselective cation channels and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in aortic endothelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1987;98(2):125–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01872125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geibel J., Zweifach A., White S., Wang W. H., Giebisch G. K+ channels of the mammalian collecting duct. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1990 Jan-Apr;13(1-2):59–69. doi: 10.1159/000173348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groschner K., Kukovetz W. R. Voltage-sensitive chloride channels of large conductance in the membrane of pig aortic endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Jun;421(2-3):209–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00374829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Matsuda H., Noma A. Ion channels in the luminal membrane of endothelial cells of the bull-frog heart. Jpn J Physiol. 1993;43(2):191–206. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.43.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Single stretch-activated ion channels in vascular endothelial cells as mechanotransducers? 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):811–813. doi: 10.1038/325811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. E., Adams D. J., Johns A., Rubanyi G. M., van Breemen C. Membrane potential and Na(+)-K+ pump activity modulate resting and bradykinin-stimulated changes in cytosolic free calcium in cultured endothelial cells from bovine atria. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2613–2619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manabe K., Ito H., Matsuda H., Noma A. Hyperpolarization induced by vasoactive substances in intact guinea-pig endocardial endothelial cells. J Physiol. 1995 Apr 1;484(Pt 1):25–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelowitz D., Bacal K., Kunze D. L. Bradykinin-activated calcium influx pathway in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):H942–H948. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.4.H942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Distribution of potassium conductance in mammalian Müller (glial) cells: a comparative study. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2423–2432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Droogmans G., Gericke M., Schwarz G. Nonselective ion pathways in human endothelial cells. EXS. 1993;66:269–280. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7327-7_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B. Permeation properties of a non-selective cation channel in human vascular endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jul;416(5):609–611. doi: 10.1007/BF00382697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilius B., Riemann D. Ion channels in human endothelial cells. Gen Physiol Biophys. 1990 Apr;9(2):89–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen S. P., Bundgaard M. Chloride-selective channels of large conductance in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Feb;144(2):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. B. Sodium channel subconductance levels measured with a new variance-mean analysis. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):413–430. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp R., Hoyer J., Meyer J., Galla H. J., Gögelein H. Stretch-activated non-selective cation channels in the antiluminal membrane of porcine cerebral capillaries. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:435–449. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusko J., Tanzi F., van Breemen C., Adams D. J. Calcium-activated potassium channels in native endothelial cells from rabbit aorta: conductance, Ca2+ sensitivity and block. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:601–621. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Klepper M. Voltage-dependent and agonist-activated ionic currents in vascular endothelial cells: a review. Blood Vessels. 1990;27(2-5):169–183. doi: 10.1159/000158808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):623–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Chen G., Miwa K., Suzuki H. Permeability and Mg2+ blockade of histamine-operated cation channel in endothelial cells of rat intrapulmonary artery. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:395–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]