Abstract
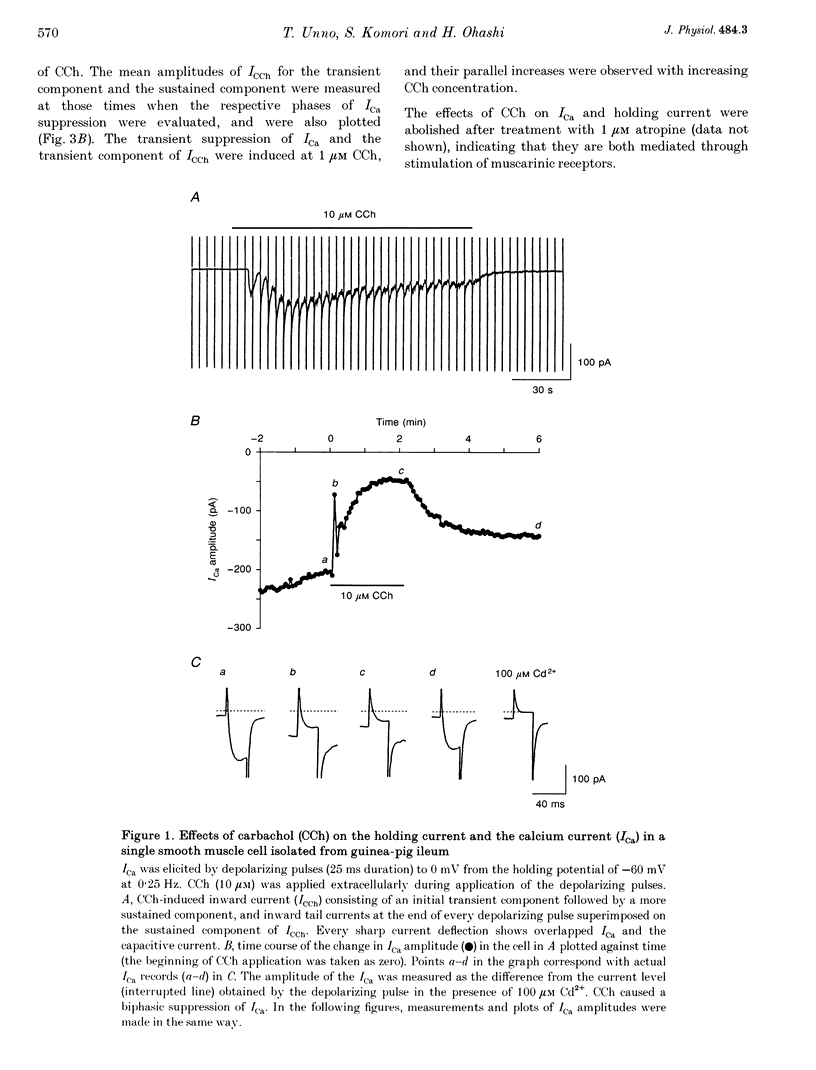
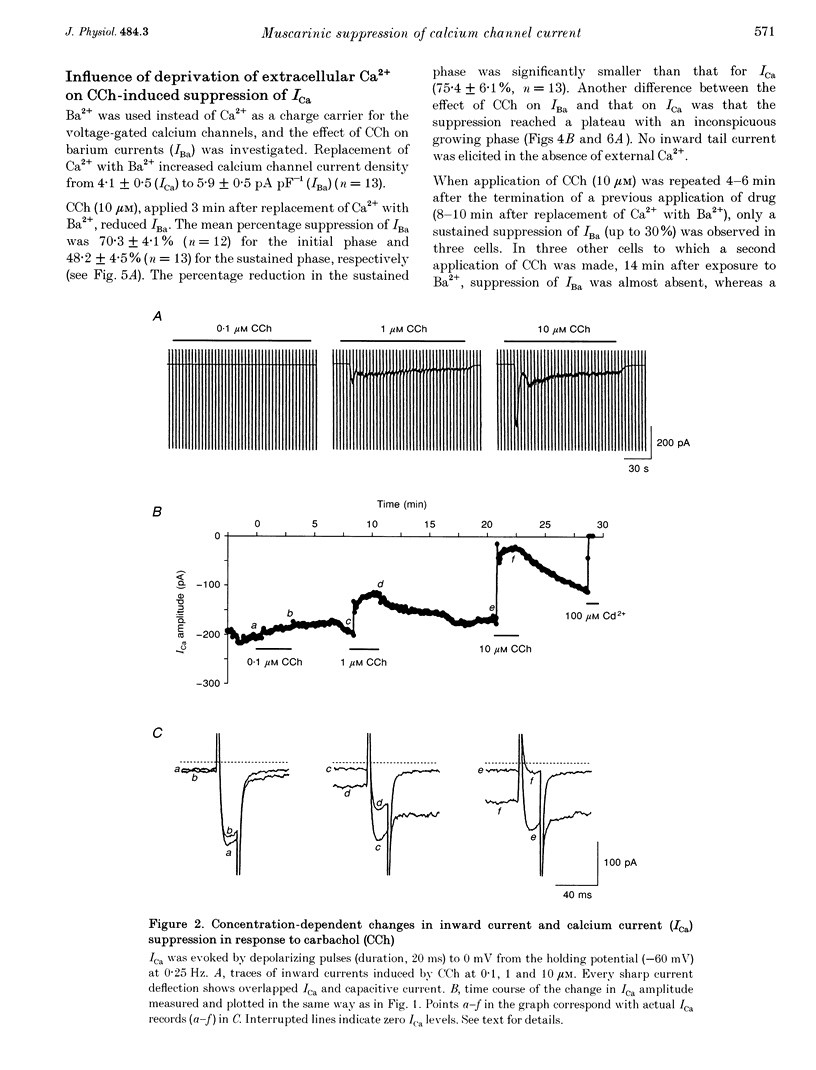
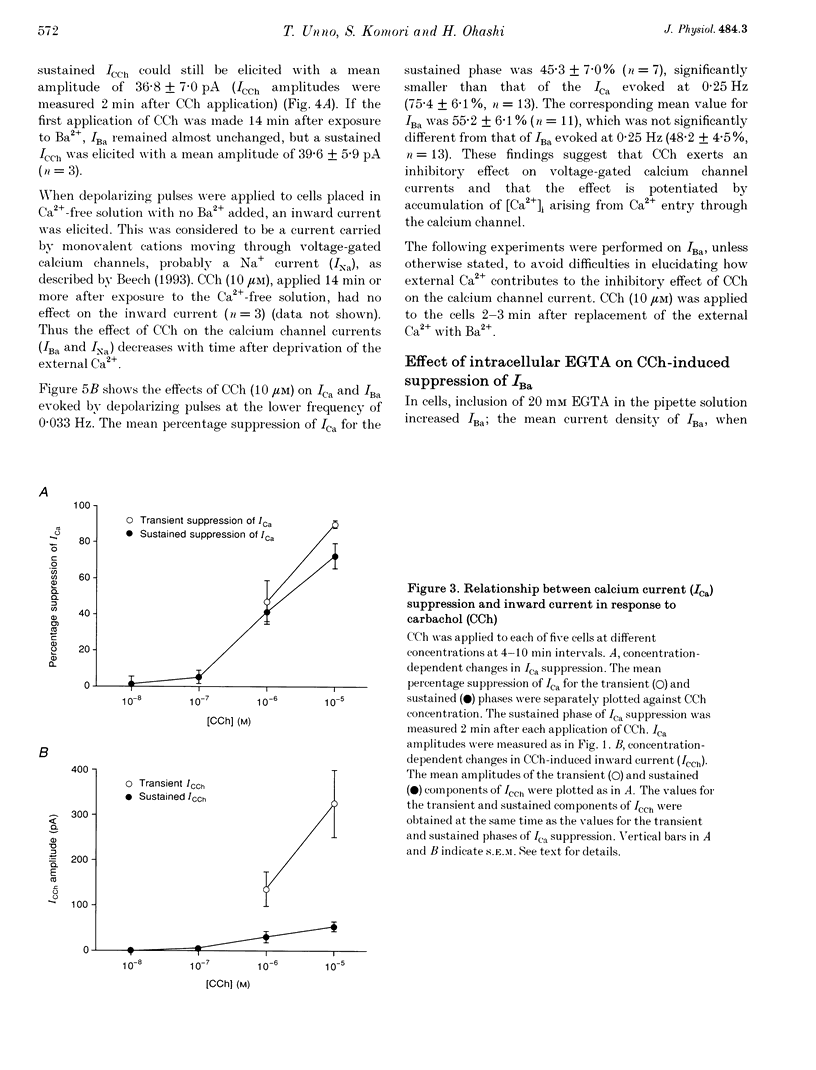
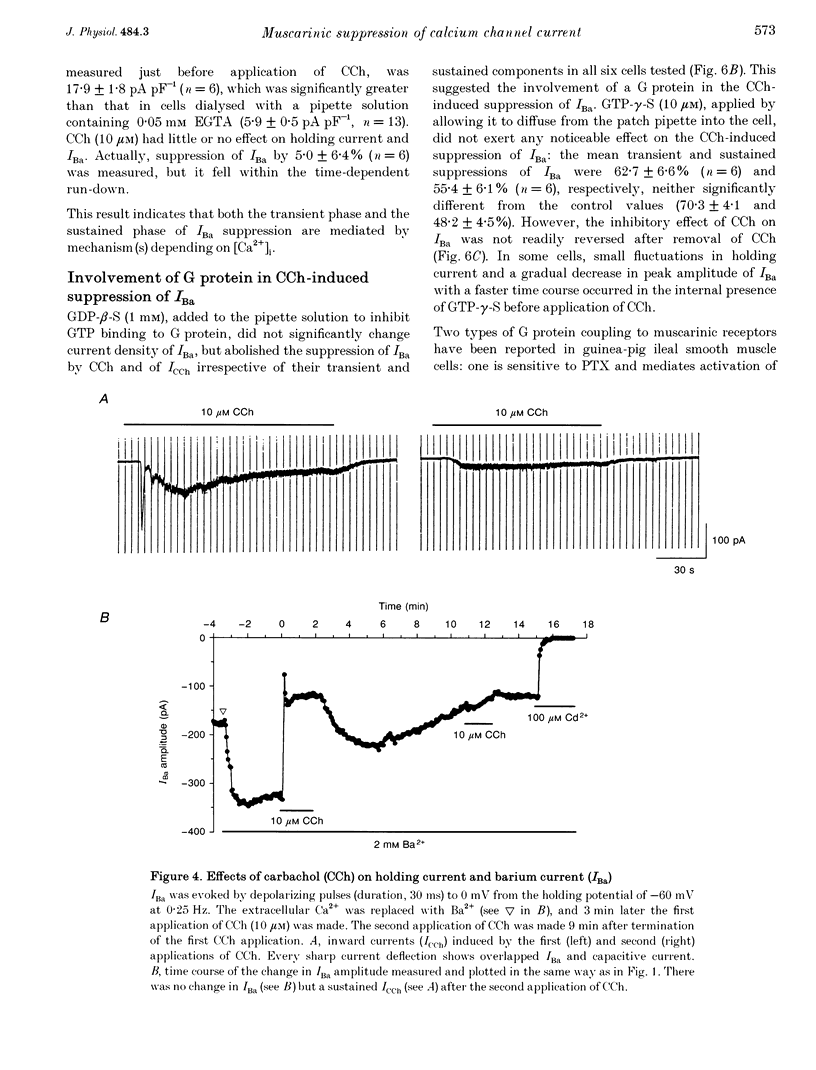
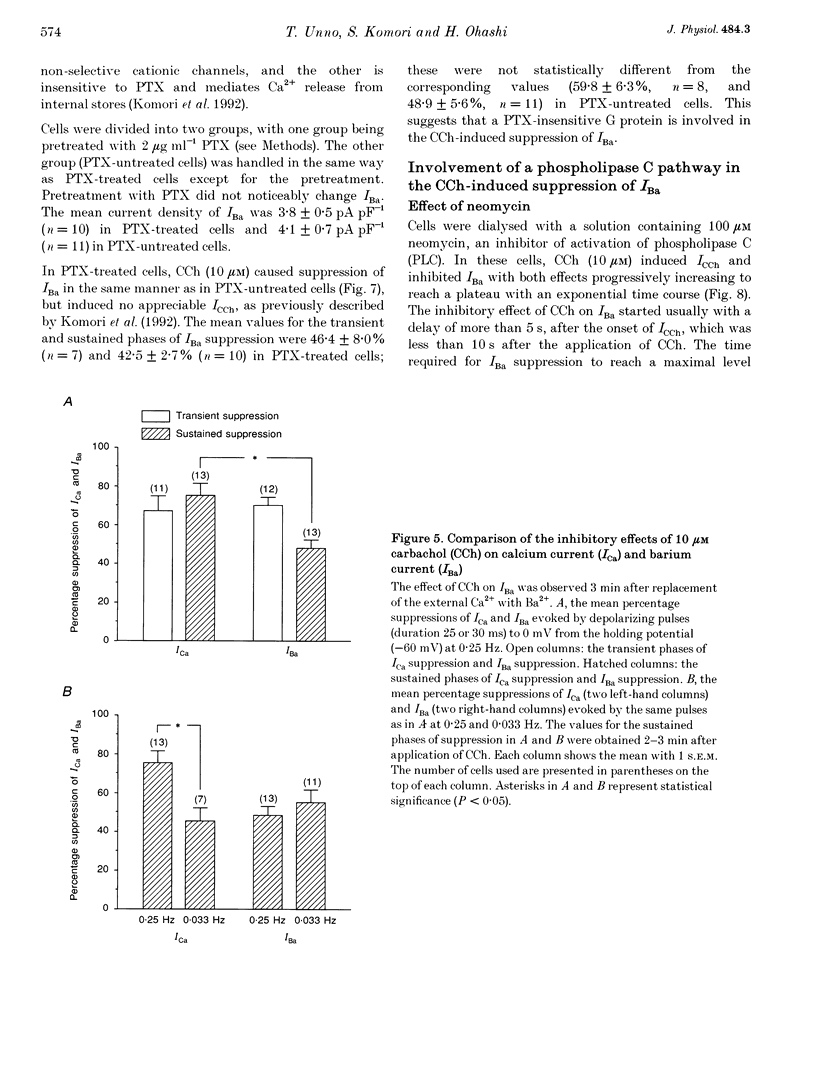
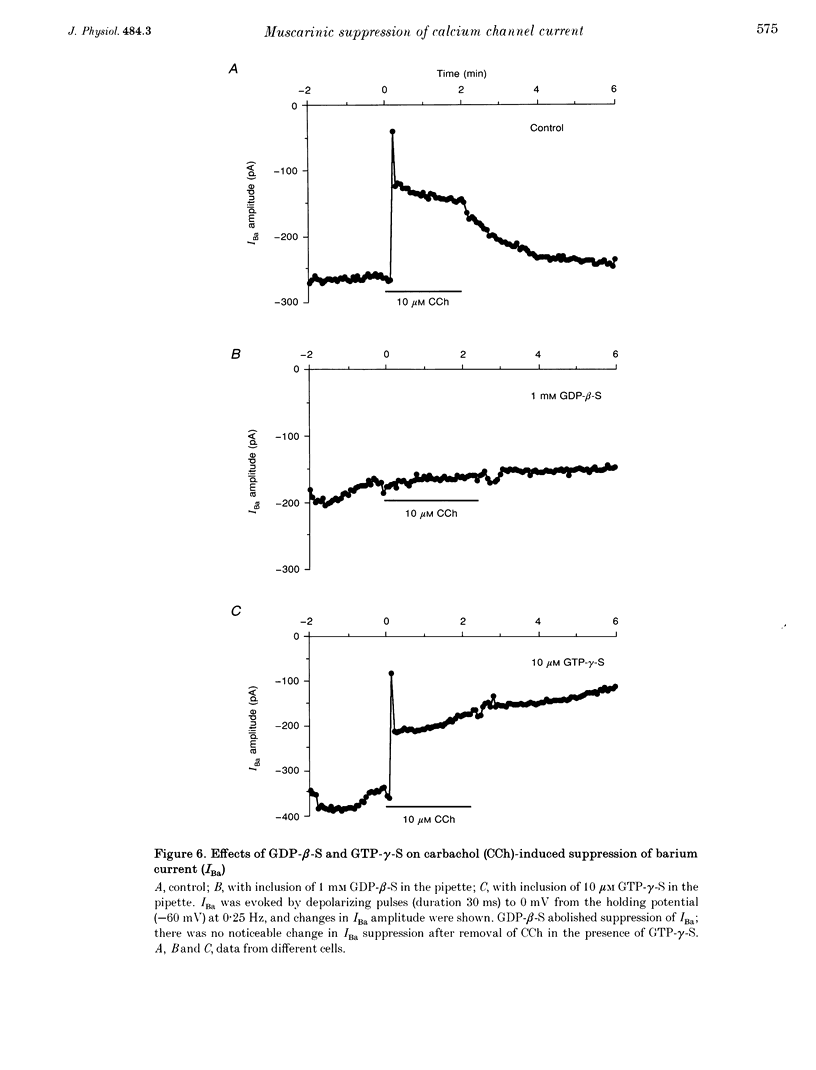
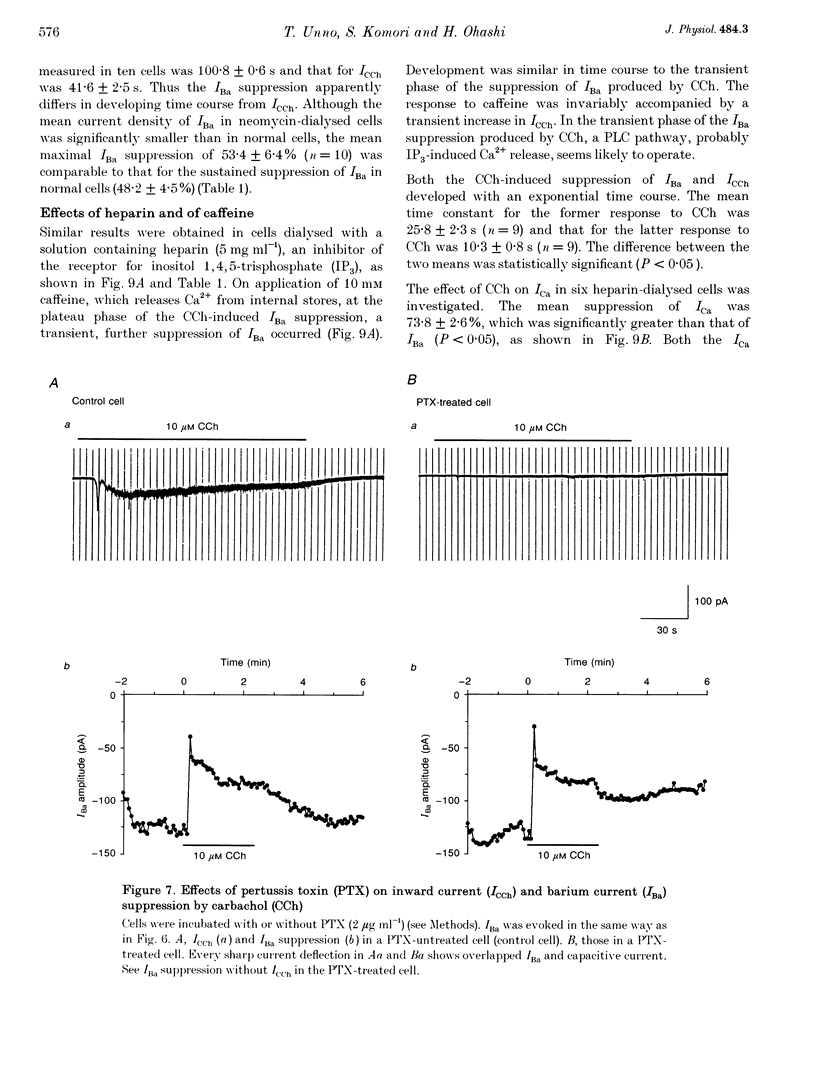
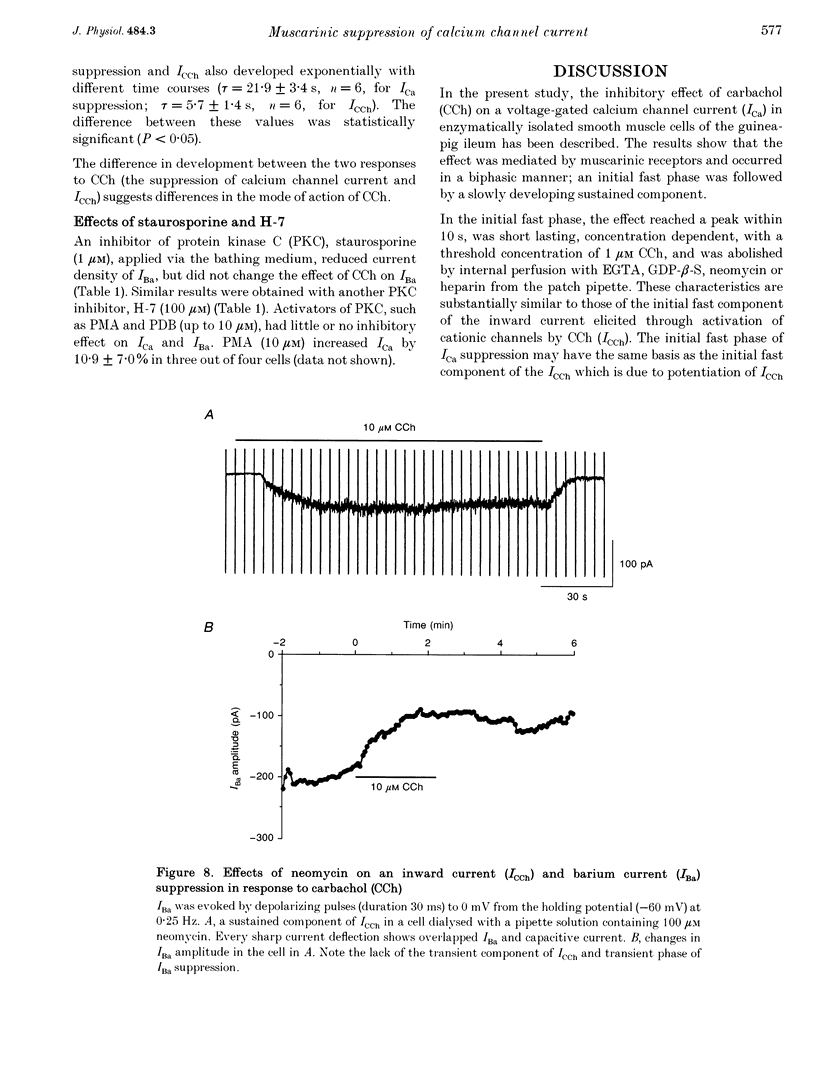
1. The effect of muscarinic receptor stimulation on voltage-gated calcium channel currents was examined in whole-cell voltage-clamped smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig ileum. 2. In cells voltage clamped at -60 mV and in which calcium channel currents (ICa) were elicited repeatedly by depolarizing pulses (25 ms duration, 0.25 Hz frequency) to 0 mV, carbachol (CCh, 10 microM) induced an inward current (ICCh) and were suppressed ICa, in a biphasic manner; an initial transient component was followed by a more sustained one. 3. A calcium channel current (IBa), when Ba2+ was used as a charge carrier, was also suppressed by CCh in a biphasic manner, as with ICa. The sustained phase of the IBa suppression was significantly smaller than that of the ICa suppression, suggesting that Ca2+ entry exerts a potentiating effect on the current suppression. 4. CCh had little or no effect on calcium channel currents (ICa and IBa) in cells dialysed with a pipette solution containing EGTA (20 mM). 5. Inclusion of GDP-beta-S (1 mM) in the pipette solution abolished ICCh and the suppression of IBa. With GTP-gamma-S (10 microM) in the pipette, the sustained phase of the IBa suppression remained almost unchanged even after removal of CCh. 6. Pretreatment with 2 micrograms ml-1 pertussis toxin (PTX), which abolished ICCh, did not change noticeably the initial transient and sustained phases of IBa suppression. 7. Neomycin (100 microM) or heparin (5 mg ml-1) in the pipette each abolished the initial transient component of ICCh as well as the initial transient phase of IBa suppression. 8. The biphasic effect of CCh on IBa was observed in the presence of either staurosporine (1 microM) or 1-(5-isoquinolinesulphonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (100 microM). Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (up to 10 microM) had no inhibitory effect on ICa and IBa. 9. The results suggest that stimulation of the muscarinic receptor causes a biphasic suppression of the voltage-gated calcium channel currents through a PTX-insensitive G protein in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle cells. The initial transient phase may be brought about by the release of Ca2+ from internal storage sites, and the sustained phase by a Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism which is independent of the phosphatidylinositol pathway.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 and arachidonic acid release in signal transduction. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Aug;18(4):503–507. doi: 10.1042/bst0180503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J. Inhibitory effects of histamine and bradykinin on calcium current in smooth muscle cells isolated from guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:565–583. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:385–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim L., Beech D. J., Hille B. A diffusible second messenger mediates one of the pathways coupling receptors to calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90226-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bkaily G., Peyrow M., Yamamoto T., Sculptoreanu A., Jacques D., Sperelakis N. Macroscopic Ca2+ -Na+ and K+ currents in single heart and aortic cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Mar-Apr;80(1-2):59–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00231004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Lim S. P. Properties of calcium stores and transient outward currents in single smooth muscle cells of rabbit intestine. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:385–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. The depolarizing action of acetylcholine or carbachol in intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):647–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp L. H., Vivaudou M. B., Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Acetylcholine increases voltage-activated Ca2+ current in freshly dissociated smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2092–2096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droogmans G., Callewaert G. Ca2+-channel current and its modification by the dihydropyridine agonist BAY k 8644 in isolated smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Mar;406(3):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00640911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich VYa, Shuba M. F., Smirnov S. V. Calcium-dependent inactivation of potential-dependent calcium inward current in an isolated guinea-pig smooth muscle cell. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:431–449. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Kameyama M., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of muscarinic inhibition of the cardiac Ca current. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):182–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00580674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Lazdunski M. Calcium channels: molecular pharmacology, structure and regulation. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(2):81–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01870922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Effect of membrane potential on acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:57–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Intracellular calcium ions modulate acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:73–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Acetylcholine activates single sodium channels in smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00581898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Weiss G. B. Calcium channels in smooth muscle. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):960–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith R. A., Burkman A. M., Sokoloski T. D., Fertel R. H. Nitroglycerin tolerance and cyclic GMP generation in the longitudinal smooth muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Apr;225(1):29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Calcium release induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in single rabbit intestinal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:495–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Inositol trisphosphate releases stored calcium to block voltage-dependent calcium channels in single smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Jun;418(5):437–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00497770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Bolton T. B. Role of G-proteins in muscarinic receptor inward and outward currents in rabbit jejunal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:395–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Takewaki T., Ohashi H. GTP-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:105–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. P., Bolton T. B. A calcium-dependent rather than a G-protein mechanism is involved in the inward current evoked by muscarinic receptor stimulation in dialysed single smooth muscle cells of small intestine. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):325–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui M., Karaki H. Dual effects of carbachol on cytosolic Ca2+ and contraction in intestinal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C787–C793. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muraki K., Bolton T. B., Imaizumi Y., Watanabe M. Effect of isoprenaline on Ca2+ channel current in single smooth muscle cells isolated from taenia of the guinea-pig caecum. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:563–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima T., Wu S., Irisawa H., Giles W. Mechanism of acetylcholine-induced inhibition of Ca current in bullfrog atrial myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Oct;96(4):865–885. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Modulation of ionic currents in smooth muscle balls of the rabbit intestine by intracellularly perfused ATP and cyclic AMP. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):465–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00585070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ousterhout J. M., Sperelakis N. Cyclic nucleotides depress action potentials in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 24;144(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit-Jacques J., Bois P., Bescond J., Lenfant J. Mechanism of muscarinic control of the high-threshold calcium current in rabbit sino-atrial node myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Apr;423(1-2):21–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00374956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Somlyo A. P. Modulation of voltage-dependent Ca channel current by arachidonic acid and other long-chain fatty acids in rabbit intestinal smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jul;100(1):27–44. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usuki T., Obara K., Someya T., Ozaki H., Karaki H., Fusetani N., Yabu H. Calyculin A increases voltage-dependent inward current in smooth muscle cells isolated from guinea pig taenia coli. Experientia. 1991 Sep 15;47(9):939–941. doi: 10.1007/BF01929886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivaudou M. B., Clapp L. H., Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Regulation of one type of Ca2+ current in smooth muscle cells by diacylglycerol and acetylcholine. FASEB J. 1988 Jun;2(9):2497–2504. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.9.2453389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabu H., Obara K., Usuki T. Calcium and potassium channel regulation by protein phosphorylation in smooth muscle cells of guinea pig taenia coli. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;311:41–52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3362-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


