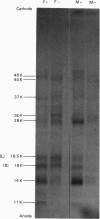
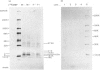
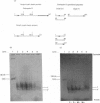
Abstract
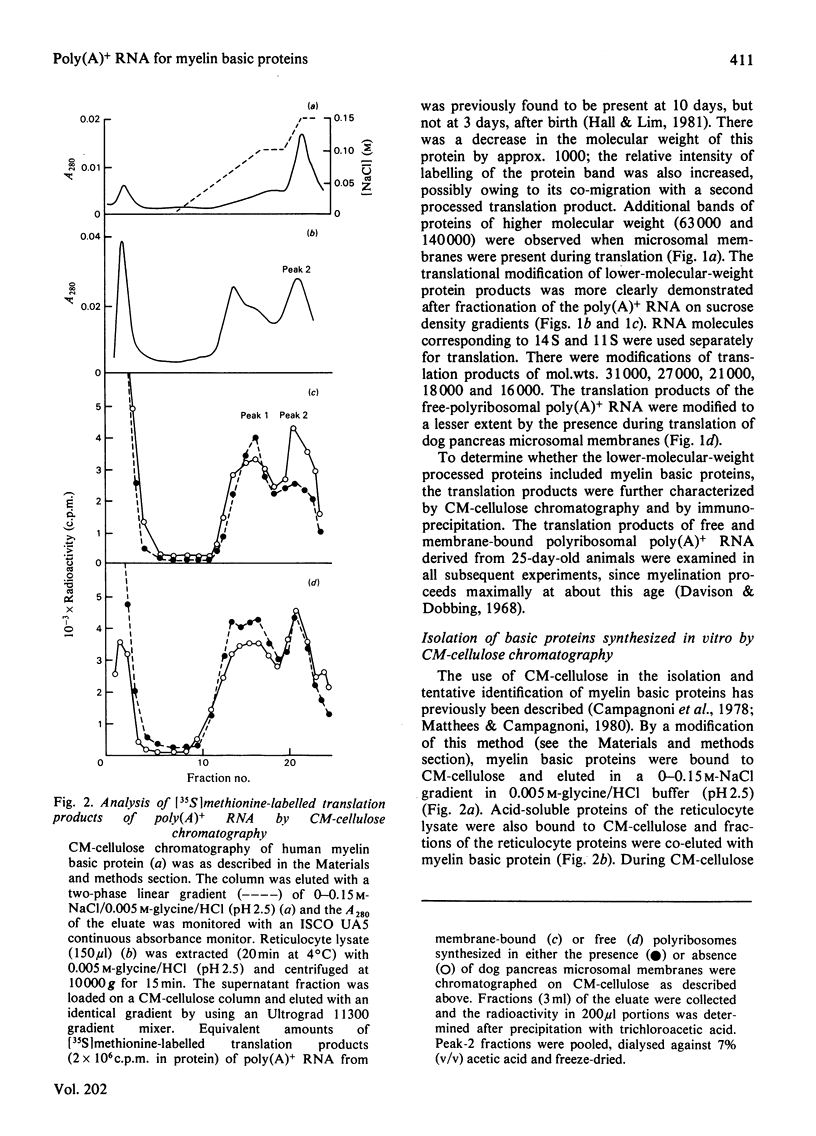
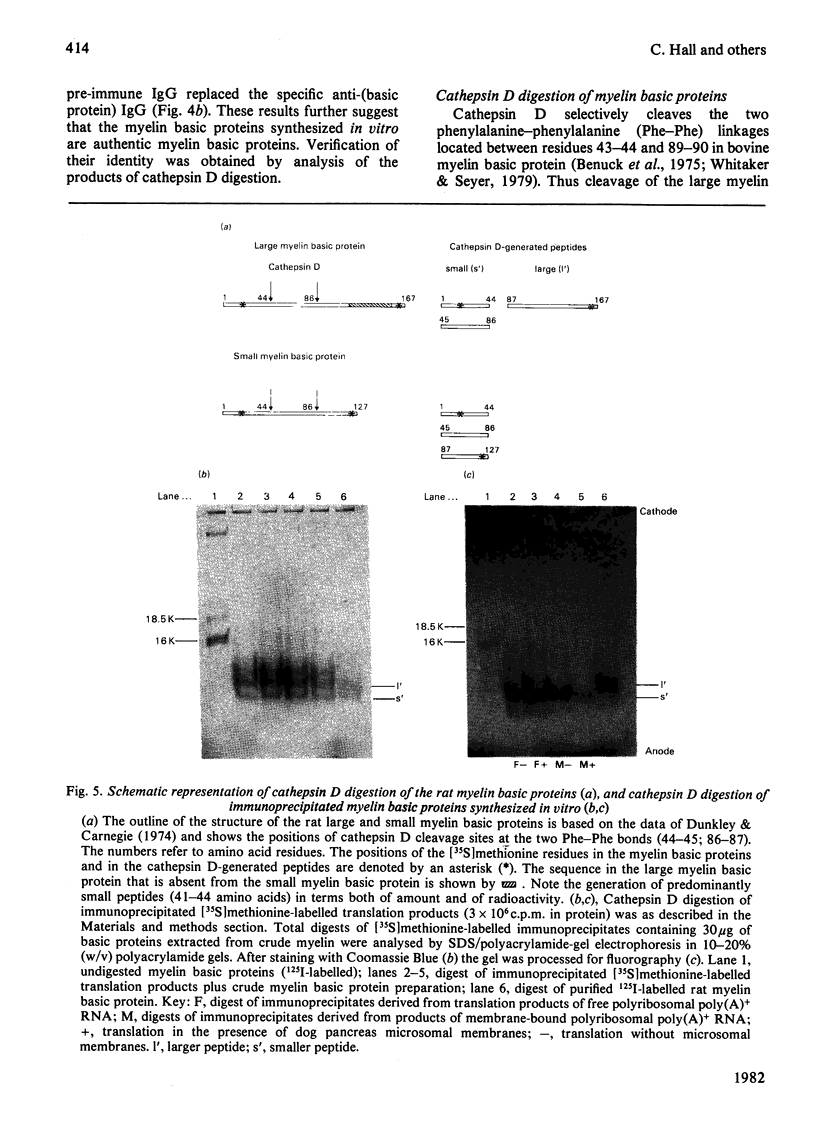
Free and membrane-bound polyribosomes were isolated from the forebrain of actively myelinating 24-day-old rats. The poly(A)+ RNA (polyadenylated RNA) extracted from both fractions was translated in vitro in reticulocyte lysates [Hall & Lim (1981) Biochem. J. 196. 327-336] in the presence or absence of a heterologous microsomal membrane fraction from dog pancreas. The rat myelin basic proteins synthesized in vitro were isolated by CM-cellulose chromatography and by immunoprecipitation with purified anti-(myelin basic protein) antibody. The large (mol.wt. 18 500) and small (mol.wt. 16 000) myelin basic proteins were translational products of poly(A)+ RNA from both free and membrane-bound polyribosomes. The identity of the myelin basic proteins was verified by analysis of peptides generated by the cathepsin D digestion of the immunoprecipitated proteins synthesized in vitro, in comparison with authentic rat myelin basic proteins. Although several other translational products of membrane-bound polyribosomal poly(A)+ RNA were modified when microsomal membranes were present during translation, molecular weights of the myelin basic proteins themselves were unchanged. The myelin basic proteins synthesized in vitro also did not differ significantly in size from the authentic myelin basic proteins, indicating that these membrane proteins are unlikely to be synthesized as substantially larger precursor molecules. The presence of the specific mRNA species on both free and membrane-bound polyribosomes is compatible with the extrinsic location of the myelin basic proteins on the cytoplasmic surface of the myelin membrane.
Full text
PDF


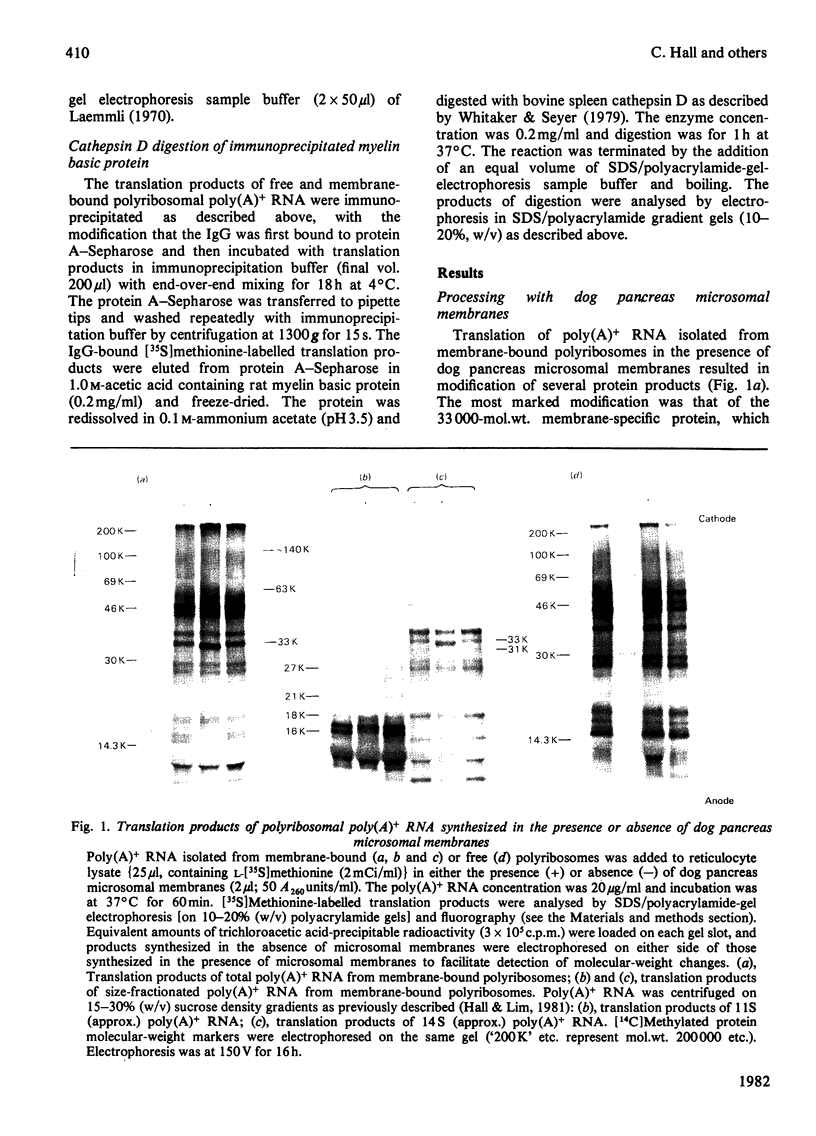





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banik N. L., Davison A. N. Isolation of purified basic protein from human brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Sep;21(3):489–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb05994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbarese E., Braun P. E., Carson J. H. Identification of prelarge and presmall basic proteins in mouse myelin and their structural relationship to large and small basic proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbarese E., Carson J. H., Braun P. E. Accumulation of the four myelin basic proteins in mouse brain during development. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):779–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benuck M., Marks N., Hashim G. A. Metabolic instability of myelin proteins. Breakdown of basic protein induced by brain cathepsin D. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Apr 1;52(3):615–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnoni A. T., Carey G. D., Yu Y. T. In vitro synthesis of the myelin basic proteins: subcellular site of synthesis. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):677–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnoni A. T., Magno C. S. Molecular weight estimation of mouse and guinea-pig myelin basic proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate: influence of ionic strength. J Neurochem. 1974 Oct;23(4):887–890. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campagnoni C. W., Carey G. D., Campagnoni A. T. Synthesis of myelin basic proteins in the developing mouse brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):118–125. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. Amino acid sequence of the encephalitogenic basic protein from human myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):57–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1230057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chyn T. L., Martonosi A. N., Morimoto T., Sabatini D. D. In vitro synthesis of the Ca2+ transport ATPase by ribosomes bound to sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1241–1245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Carnegie P. R. Amino acid sequence of the smaller basic protein from rat brain myelin. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):243–255. doi: 10.1042/bj1410243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Brostoff S., Hashim G., Caccam J., Burnett P. Basic A1 protein of the myelin membrane. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5770–5784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golds E. E., Braun P. E. Cross-linking studies on the conformation and dimerization of myelin basic protein in solution. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8171–8177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C., Lim L. Developmental changes in the composition of polyadenylated RNA isolated from free and membrane-bound polyribosomes of the rat forebrain, analysed by translation in vitro. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 15;196(1):327–336. doi: 10.1042/bj1960327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kies M. W., Martenson R. E., Deibler G. E. Myelin basic proteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;32(0):201–214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6979-0_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz D. T., Chan K. M., Feigelson P. Translational control of hepatic alpha2u globulin synthesis by growth hormone. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):743–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D. The fate of foreign proteins introduced in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):281–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., White J. O., Hall C., Berthold W., Davison A. N. Isolation of microsomal poly(A)-RNA from rat brain directing the synthesis of the myelin encephalitogenic protein in Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 29;361(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthees J., Campagnoni A. T. Cell-free synthesis of the myelin basic proteins in a wheat germ system programmed with brain messenger RNA. J Neurochem. 1980 Oct;35(4):867–872. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07084.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman J. W., Thomas D. G., Ratcliffe J. G. Radioimmunoassay of human myelin basic protein in tissue extract, cerebrospinal fluid and serum and its clinical application to patients with head injury. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jan 16;82(3):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poduslo J. F., Braun P. E. Topographical arrangement of membrane proteins in the intact myelin sheath. Lactoperoxidase incorproation of iodine into myelin surface proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1099–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachubinski R. A., Verma D. P., Bergeron J. J. Synthesis of rat liver microsomal cytochrome b5 by free ribosomes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):705–716. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey J. C., Steele W. J. A procedure for the quantitative recovery of homogeneous populations of undegraded free and bound polysomes from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1704–1712. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey J. C., Steele W. J. Quantitative isolation and properties of nearly homogeneous populations of undegraded free and bound polysomes from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1977 Mar;28(3):517–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph D. H., Kibler R. F., Fritz R. B. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of antibodies to myelin basic protein. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(3-4):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90175-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollery J. G., Boggs J. M., Moscarello M. A. Variable interaction of spin-labeled human myelin basic protein with different acidic lipids. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1219–1226. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulakhe P. V., Petrali E. H., Davis E. R., Thiessen B. J. Calcium ion stimulated endogenous protein kinase catalyzed phosphorylation of basic proteins in myelin subfractions and myelin-like membrane fraction from rat brain. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5363–5371. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan N., Steele W. J. Free and membrane-bound polysomes of rat liver: separation in nearly quantitative yield and analysis of structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 22;287(3):526–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waehneldt T. V. Protein heterogeneity in rat CNS myelin subfractions. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;100:117–133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2514-7_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Jen Chou C. H., Chou F. C., Kibler R. F. Antigenic determinants of bovine myelin encephalitogenic protein recognized by rabbit antibody to myelin encephalitogenic protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9106–9111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Seyer J. M. The sequential limited degradation of bovine myelin basic protein by bovine brain cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6956–6963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. The assembly of proteins into biological membranes: The membrane trigger hypothesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:23–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. D., Epand R. M., Moscarello M. A. Localization of the basic protein and lipophilin in the myelin membrane with a non-penetrating reagent. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 2;467(2):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. H., Strair R. K., Shafritz D. A. Distribution of rat liver albumin mRNA membrane-bound and free in polyribosomes as determined by molecular hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5397–5401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap S. H., Strair R. K., Shafritz D. A. Effect of a short term fast on the distribution of cytoplasmic albumin messenger ribonucleic acid in rat liver. Evidence for formation of free albumin messenger ribonucleoprotein particles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4944–4950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomzely C. E., Roberts S., Peache S. Isolation of RNA with properties of messenger RNA from cerebral polyribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):644–651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]