Abstract
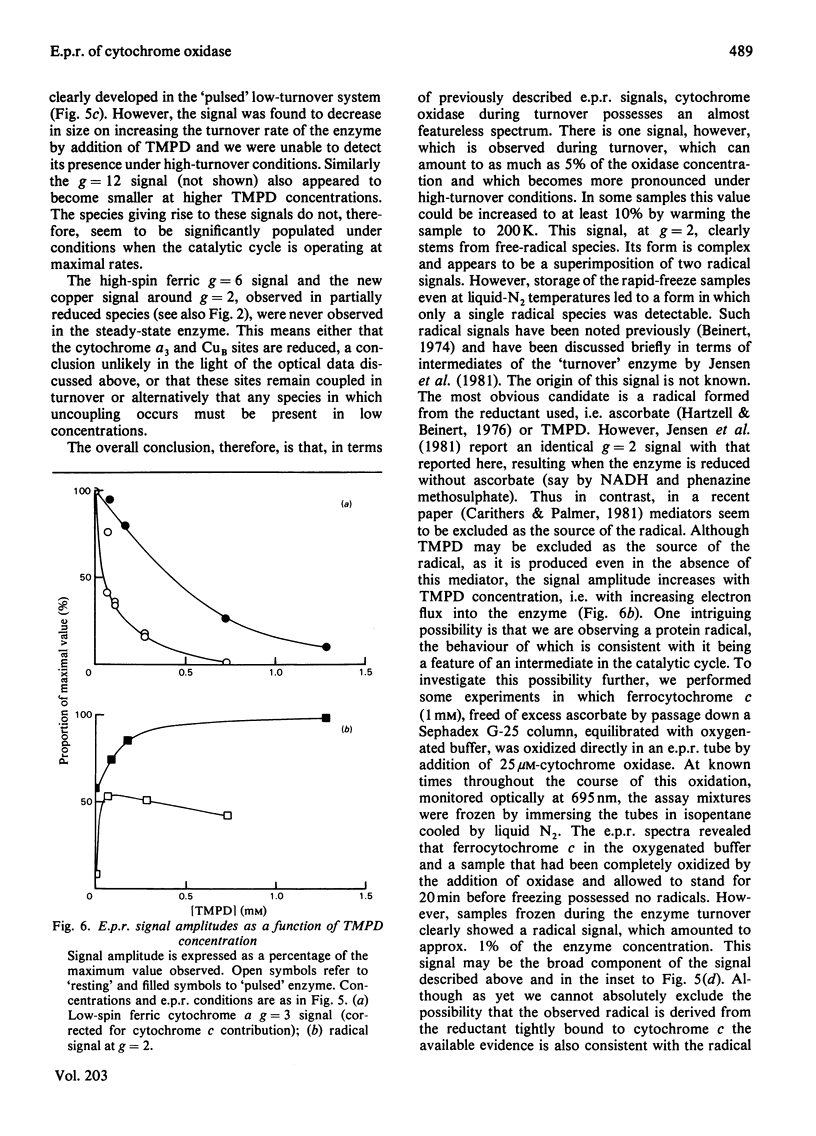
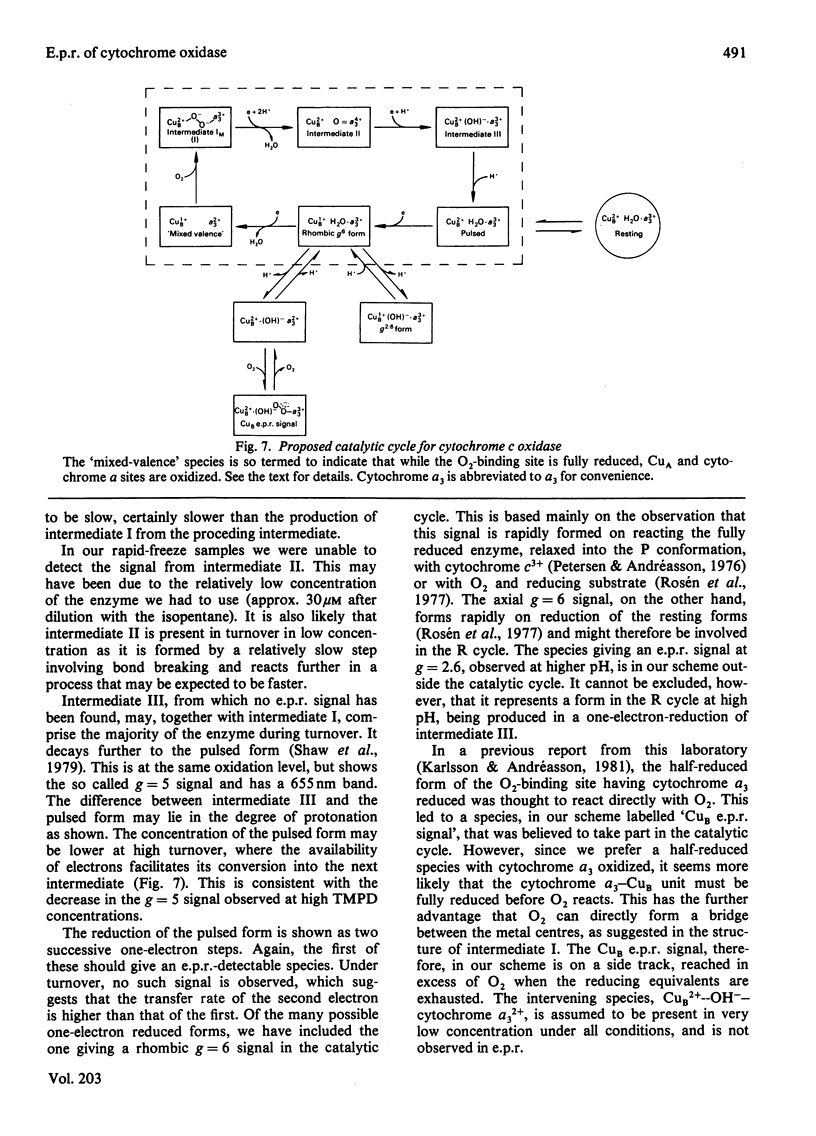
Cytochrome oxidase (EC 1.9.3.1; ferrocytochrome c:oxygen oxidoreductase) was studied during steady-state by optical and e.p.r. methods. Starting with either the 'resting' or the 'pulsed' enzyme, oxidase, cytochrome c, ascorbate and O2 were mixed and the reaction monitored optically. Tetramethylphenylenediamine was used as mediator to poise the steady-state to the desired reduction level. After mixing, the reaction was quenched by the used of rapid-freeze techniques. The e.p.r. spectra of samples captured at increasing tetramethylphenylenediamine concentrations (i.e. higher electron flux) show decreasing g = 2 (Cu A) and g = 3 (cytochrome a) signals. No Cu B or g = 6 signals (high-spin cytochrome a3) could be found during the reaction. Also, the signal with peaks at g = 1.69, 1.78 and 5 as well as the g = 12 signal was hardly detectable at higher turnover rates. The only new signal appearing during turnover is a radical signal, which is discussed in terms of a protein radical. Finally, a scheme is presented, proposing a catalytic cycle for cytochrome oxidase with respect to the O2 binding Cu B-cytochrome a3 unit.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasa R., Albracht P. J., Falk K. E., Lanne B., Vänngard T. EPR signals from cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 13;422(2):260–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andréasson L. E. Characterization of the reaction between ferrocytochrome c and cytochrome c oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May 6;53(2):591–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini E., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Greenwood C., Wilson M. T. Oxygen "pulsed" cytochrome c oxidase: functional properties and catalytic relevance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3128–3132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudvig G. W., Stevens T. H., Chan S. I. Reactions of nitric oxide with cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5275–5285. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brudvig G. W., Stevens T. H., Morse R. H., Chan S. I. Conformations of oxidized cytochrome c oxidase. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3912–3921. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunori M., Colosimo A., Rainoni G., Wilson M. T., Antonini E. Functional intermediates of cytochrome oxidase. Role of "pulsed" oxidase in the pre-steady state and steady state reactions of the beef enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10769–10775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Palmer G. Characterization of the potentiometric behavior of soluble cytochrome oxidase by magnetic circular dichroism. Evidence in support of heme-heme interaction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7967–7976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Saronio C., Leigh J. S., Jr Functional intermediates in the reaction of membrane-bound cytochrome oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9226–9237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Andréasson L. E., Karlsson B., Aasa R., Malmström B. G. Characterization of the intermediates in the reaction of mixed-valence state soluble cytochrome oxidase with oxygen at low temperatures by optical and electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):155–167. doi: 10.1042/bj1850155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Andréasson L. E., Karlsson B., Aasa R., Malmström B. G. Characterization of the low-temperature intermediates of the reaction of fully reduced soluble cytochrome oxidase with oxygen by electron-paramagnetic-resonance and optical spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):139–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1850139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Gibson Q. H. The reaction of reduced cytochrome C oxidase with oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1782–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Wilson M. T., Brunori M. Studies on partially reduced mammalian cytochrome oxidase. Reactions with carbon monoxide and oxygen. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):205–215. doi: 10.1042/bj1370205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell C. R., Beinert H. Components of cytochrome c oxidase detectable by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 19;368(3):318–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell C. R., Beinert H. Oxido-reductive titrations of cytochrome c oxidase followed by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 16;423(2):323–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P., Aasa R., Malmström B. G. Electron redistribution in cytochrome c oxidase during freezing under turnover conditions. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80709-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson B., Andréasson L. E. The identity of a new copper(II) electron paramagnetic resonance signal in cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 12;635(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanne B., Malmström B. G., Vänngård T. The influence of pH on the EPR and redox properties of cytochrome c oxidase in detergent solution and in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 8;545(2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen L. C., Andréasson L. E. The reaction between oxidized cytochrome c and reduced cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80583-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen L. C., Cox R. P. Reduction of oxygen-pulsed cytochrome c oxidase by cytochrome c and other electron donors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 7;590(1):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Kraut J. A hypothetical model of the cytochrome c peroxidase . cytochrome c electron transfer complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10322–10330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhammar B., Malkin R., Jensen P., Karlsson B., Andréasson L. E., Aasa R., Vänngård T., Malmström B. G. A new copper(II) electron paramagnetic resonance signal in two laccases and in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5000–5003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. W., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. The oxygen reactions of reduced cytochrome c oxidase. Position of a form with an unusual EPR signal in the sequence of early intermediates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 8;548(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. T., Peterson J., Antonini E., Brunori M., Colosimo A., Wyman J. A plausible two-state model for cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7115–7118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONETANI T. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. I. Absolute and difference absorption spectra. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Yu L., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1383–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


