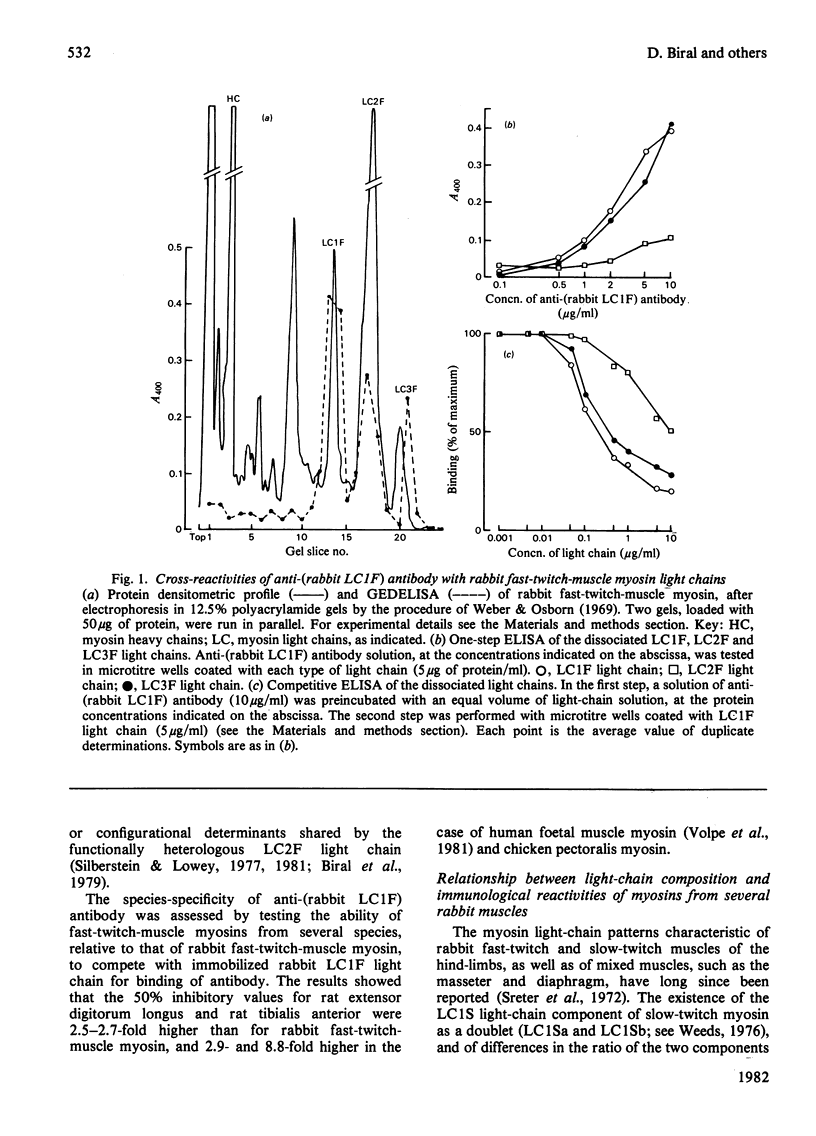
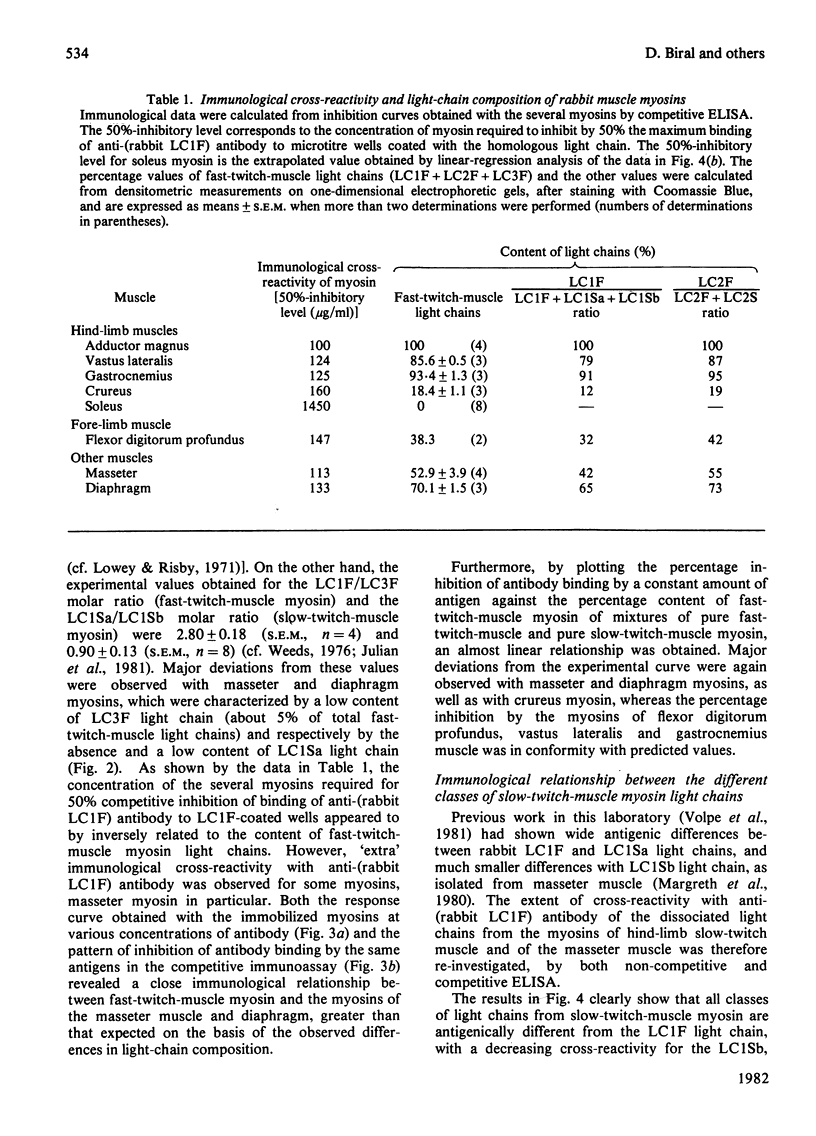
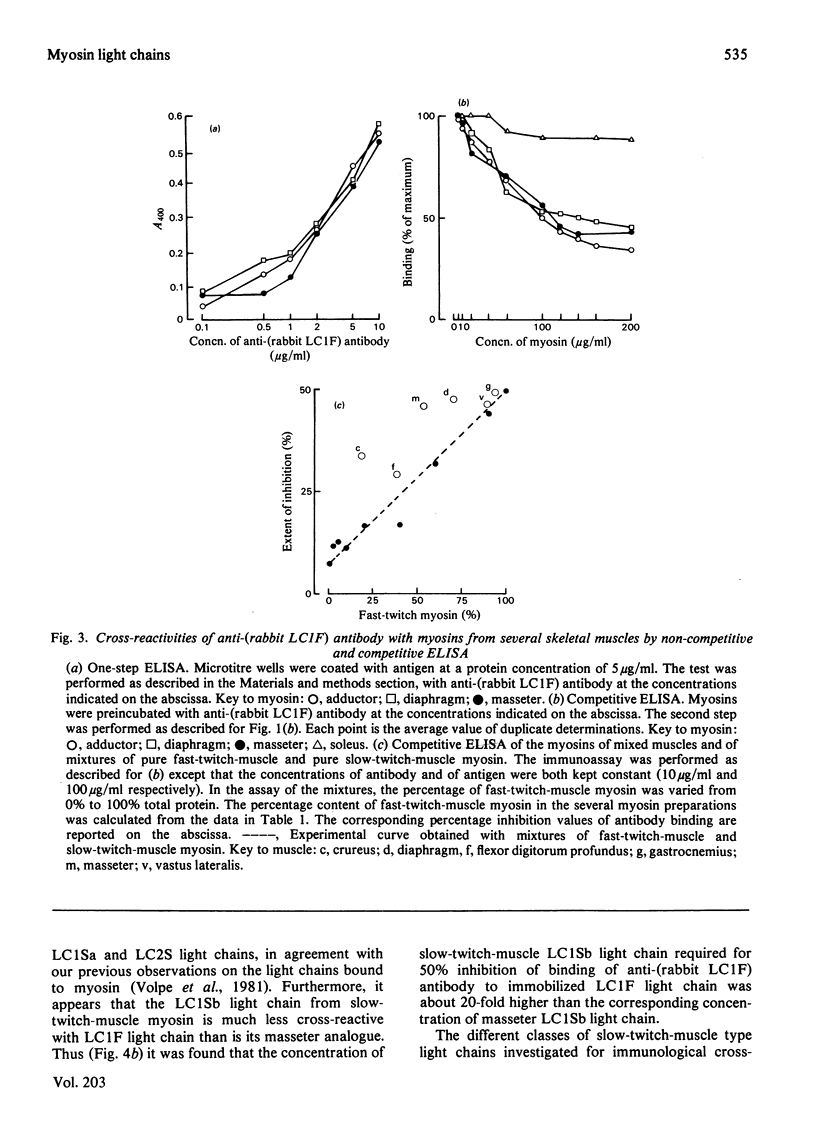
Abstract
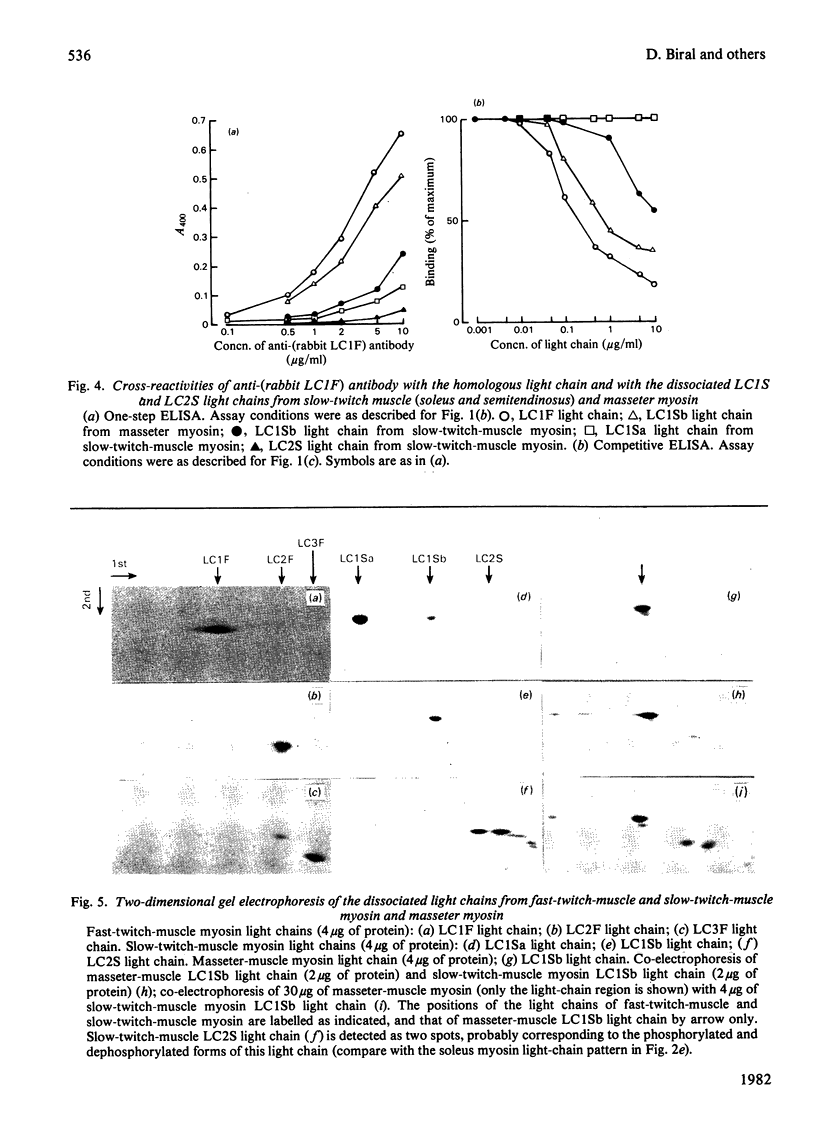
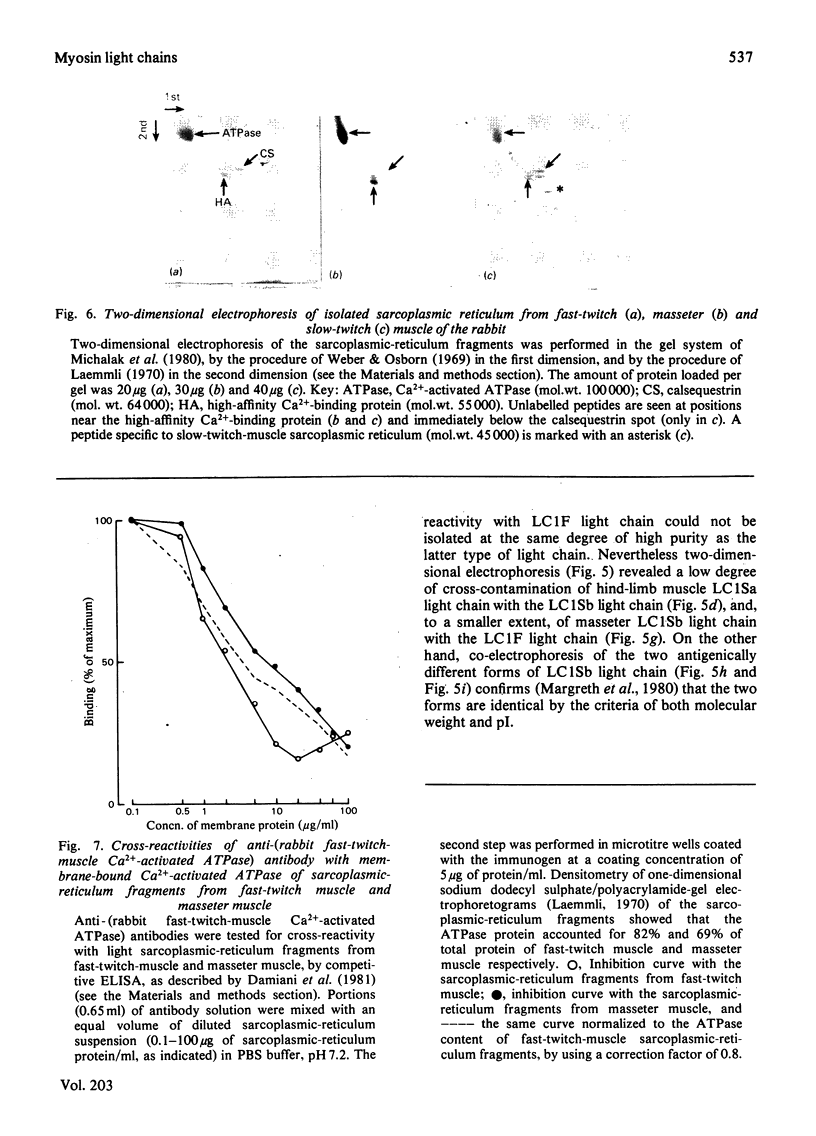
Antibodies specific for rabbit fast-twitch-muscle myosin LCIF light chain were purified by affinity chromatography and characterized by both non-competitive and competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and a gel-electrophoresis-derived assay (GEDELISA). The antibodies did not cross-react with myosin heavy chains, and were weakly cross-reactive with the LC2F [5,5'-dithio-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)-dissociated] light chain and with all classes of dissociated light chains (LC1Sa, LC1Sb and LC2S), as well as with the whole myosin, from hind-limb slow-twitch muscle. The immunoreactivity of myosins with a truly mixed light-chain pattern (e.g. vastus lateralis and gastrocnemius) correlated with percentage content of fast-twitch-muscle-type light chains. A more extensive immunoreactivity was observed with diaphragm and masseter myosins, which were also characterized, respectively, by a relative or absolute deficiency of LC1Sa light chain. Furthermore, it was found that the LC1Sb light chain of masseter myosin is antigenically different from its slow-twitch-muscle myosin analogue, and is immunologically related to the LC1F light chain. Rabbit masseter muscle from its metabolic and physiological properties and the content, activity and immunological properties of sarcoplasmic-reticulum adenosine triphosphatase, is classified as a red, predominantly fast-twitch, muscle. Therefore our results suggest that the two antigenically different iso-forms of LC1Sb light chain are associated with the myosins of fast-twitch red and slow-twitch red fibres respectively.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biral D., Dalla Libera L., Franceschi C., Margreth A. Microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in the study of the structural relationship between myosin light chains. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(1-2):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90289-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraro U., dalla Libera L., Catani C. Myosin light chains of avian and mammalian slow muscles: evidence of intraspecific polymorphism. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1981 Sep;2(3):335–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00713271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla Libera L., Sartore S., Pierobon-Bormioli S., Schiaffino S. Fast-white and fast-red isomyosins in guinea pig muscles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 31;96(4):1662–1670. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91365-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani E., Betto R., Salvatori S., Volpe P., Salviati G., Margreth A. Polymorphism of sarcoplasmic-reticulum adenosine triphosphatase of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):245–248. doi: 10.1042/bj1970245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiehn W., Peter J. B. Properties of the fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast twitch and slow twitch muscles. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):570–573. doi: 10.1172/JCI106526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G., Weeds A. G. The amino-acid sequence of the alkali light chains of rabbit skeletal-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):317–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S. Distribution of myosin isoenzymes among skeletal muscle fiber types. J Cell Biol. 1979 Apr;81(1):10–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. C., Lowey S. An immunological approach to the role of the low molecular weight subunits in myosin. I. Physical--chemical and immunological characterization of the light chains. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4600–4609. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. C., Lowey S. An immunological approach to the role of the low molecular weight subunits in myosin. II. Interaction of myosin and its subfragments with antibodies to the light chains. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4609–4620. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L., Waller G. S. Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new-born rabbits. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:201–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Risby D. Light chains from fast and slow muscle myosins. Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):81–85. doi: 10.1038/234081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H., Ermini M., Jenny E. The size of the fibre populations in rabbit skeletal muscles as revealed by indirect immunofluorescence with anti-myosin sera. Histochemistry. 1978 Sep 15;57(3):223–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00492082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz H., Weber H., Billeter R., Jenny E. Fast and slow myosin within single skeletal muscle fibres of adult rabbits. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):142–144. doi: 10.1038/281142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak M., Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Localization of the high affinity calcium binding protein and an intrinsic glycoprotein in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1317–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLANS E., ROSE M. E., MARRACK J. R. Fowl antibody. I. Some physical and immunochemical properties. Immunology. 1961 Jul;4:262–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrie W. T., Smillie L. B., Perry S. B. A phosphorylated light-chain component of myosin from skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):151–164. doi: 10.1042/bj1350151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter J. B., Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Gillespie C. A., Stempel K. E. Metabolic profiles of three fiber types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2627–2633. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierobon-Bormioli S., Sartore S., Libera L. D., Vitadello M., Schiaffino S. "Fast" isomyosins and fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Oct;29(10):1179–1188. doi: 10.1177/29.10.7028858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter K., Mabuchi K., Sreter F. A. Isoenzymes of rabbit slow myosin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):336–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80111-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Berg R., Martin G. R., Foidart J. M., Robey P. G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for connective tissue components. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salviati G., Betto R., Salvatori S., Margreth A. Evidence for the presence of the stearyl-CoA desaturase system in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit slow muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 30;574(2):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salviati G., Salvatori S., Betto R., Margreth A. Molecular and antigenic properties of cytochrome b5 from slow-muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):515–518. doi: 10.1042/bj1970515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachat F. H., Bronson D. D., McDonald O. B. Two kinds of slow skeletal muscle fibers which differ in their myosin light chain complements. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 15;122(1):80–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein L., Lowey S. Investigation of immunological relationships among myosin light chains and troponin C. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4403–4408. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein L., Lowey S. Isolated and distribution of myosin isoenzymes in chicken pectoralis muscle. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):153–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreter F. A., Sarkar S., Gergely J. Myosin light chains of slow twitch (red) muscle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):124–125. doi: 10.1038/newbio239124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Biral D., Damiani E., Margreth A. Characterization of human muscle myosins with respect to the light chains. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):251–258. doi: 10.1042/bj1950251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallimann T., Szent-Györgyi A. G. An immunological approach to myosin light-chain function in thick filament linked regulation. 1. Characterization, specificity, and cross-reactivity of anti-scallop myosin heavy- and light-chain antibodies by competitive, solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1176–1187. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G. B., Toon P. A., Birdsall N. J., Lee A. G., Metcalfe J. C. Reconstitution of a calcium pump using defined membrane components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G. Light chains from slow-twitch muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):157–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young O. A., Davey C. L. Electrophoretic analysis of proteins from single bovine muscle fibres. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):317–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1950317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]