Abstract
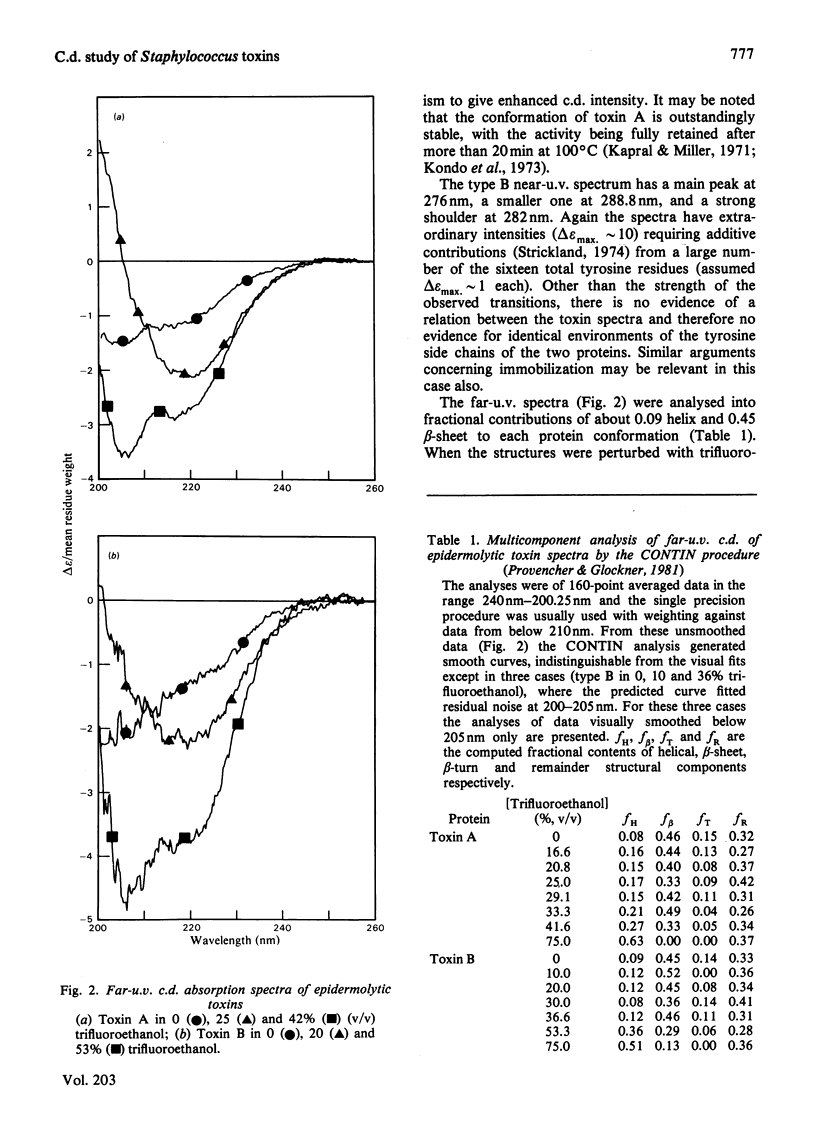
The far-u.v. circular-dichroism spectra of the two epidermolytic toxins was analysed into fractional contributions of 0.09 helix and 0.46 beta-sheet to each toxin structure. Trifluoroethanol perturbation caused an initial increase in dichroic absorption at 205 nm and then a change characterized as a beta-sheet-to-alpha-helix transition. The intense near-u.v. spectra suggested that the toxins have unusually rigid, though different, aromatic-side-chain arrangements.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B. Qualitative and quantitative methods for detecting staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):191–201. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey C. J., de Azavedo J., Arbuthnott J. P. A comparative study of two serotypes of epidermolytic toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 24;624(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D. H., Dimond R. L., Wuepper K. D. The epidermolytic toxin of Staphylococcus aureus: its failure to bind to cells and its detection in blister fluids of patients with bullous impetigo. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Oct;71(4):274–275. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Schlessinger J., Pecht I., Steinberg I. Z. Homogeneity and variability in the structure of azurin molecules studied by fluorescence decay and circular polarization. Biochemistry. 1975 May 6;14(9):1921–1929. doi: 10.1021/bi00680a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Strickland E. H., Billups C. Analysis of the vibrational structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of tyrosine derivatives and ribonuclease-A at 77 degrees K. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Apr 8;92(7):2119–2129. doi: 10.1021/ja00710a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Moore S. Determination of the tryptophan content of proteins by ion exchange chromatography of alkaline hydrolysates. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2828–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Metzger J. F., Spero L. Production, purification, and chemical characterization of Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1206–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1206-1210.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Spero L., Cades J. S., de Cicco B. T. Purification and characterization of different types of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):679–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.679-684.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.156-164.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka K., Katayama I., Sano S. Possible binding of epidermolytic toxin to a subcellular fraction of the epidermis. J Dermatol. 1981 Feb;8(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1981.tb02005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W., Glöckner J. Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):33–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Phage group II staphylococcal strains with chromosomal and extrachromosomal genes for exfoliative toxin production. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):44–52. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.44-52.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H. Aromatic contributions to circular dichroism spectra of proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):113–175. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland E. H., Horwitz J., Billups C. Fine structure in the near-ultraviolet circular dichroism and absorption spectra of tryptophan derivatives and chymotrypsinogen A at 77 degrees K. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3205–3213. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Rogolsky M. Molecular and serological differentiation of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin synthesized under chromosomal and plasmid control. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):487–494. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.487-494.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


