Abstract
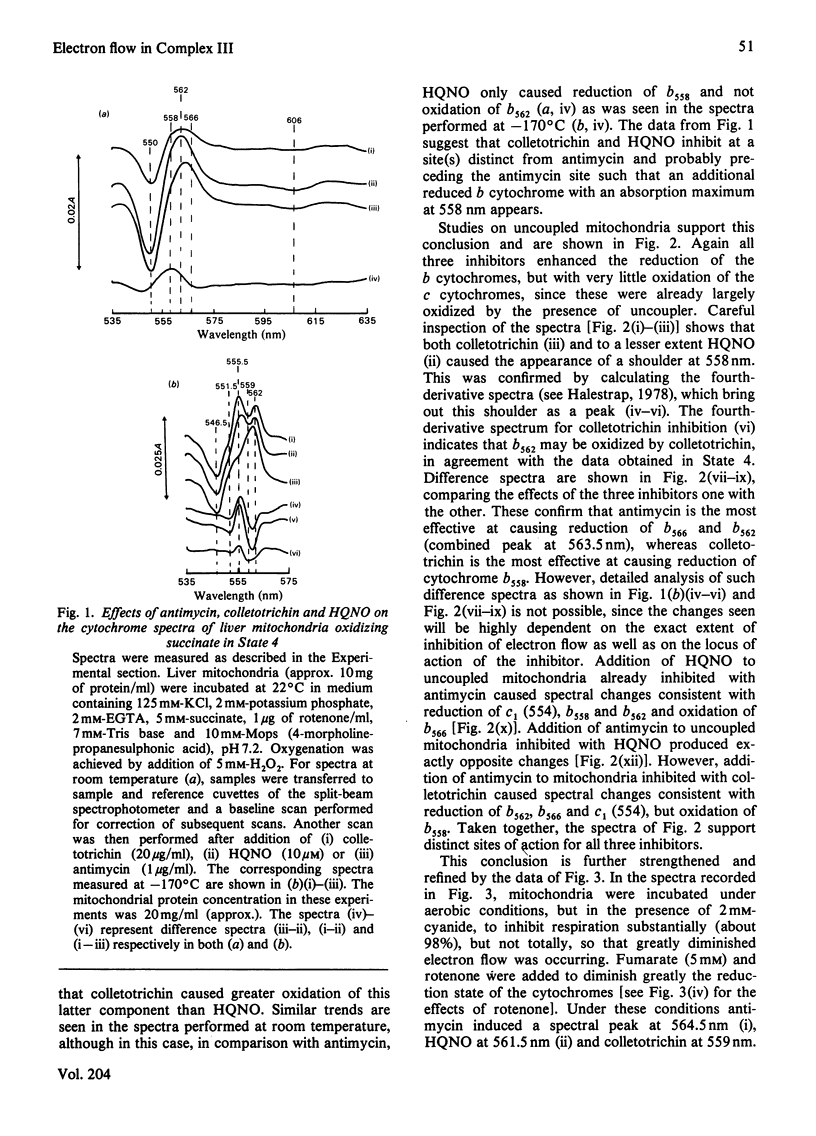
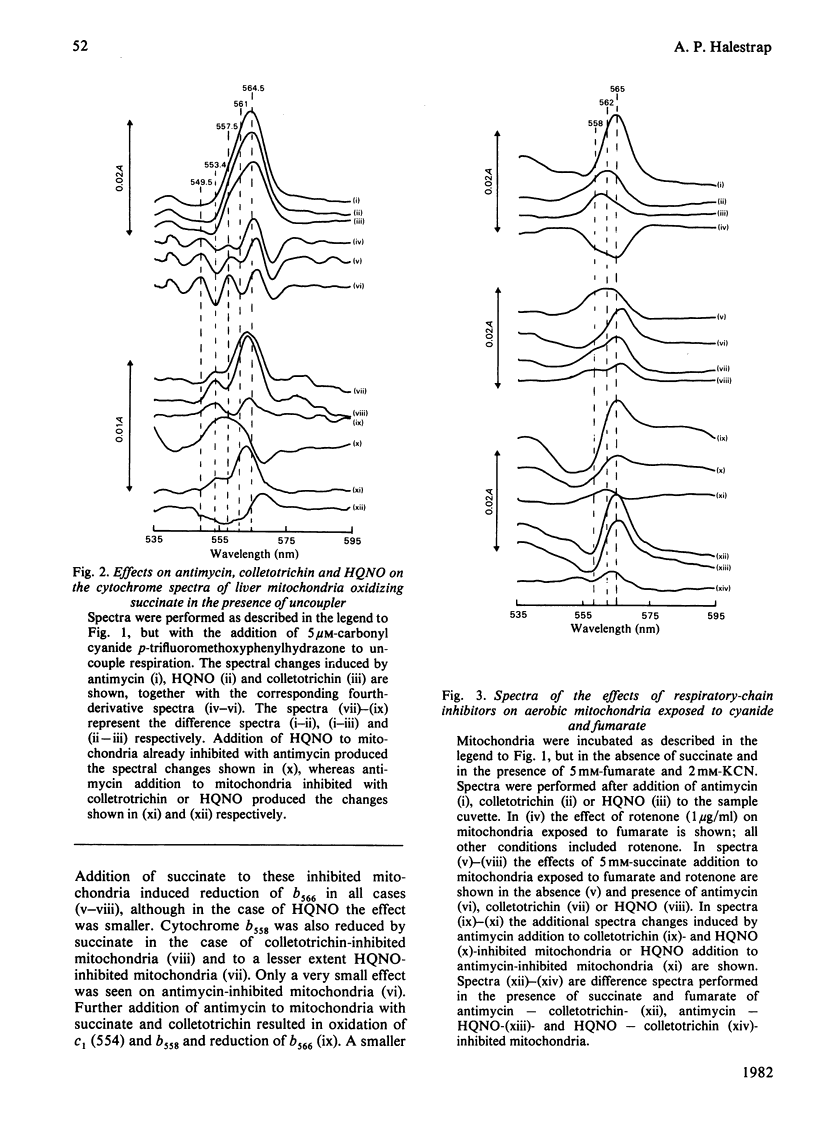
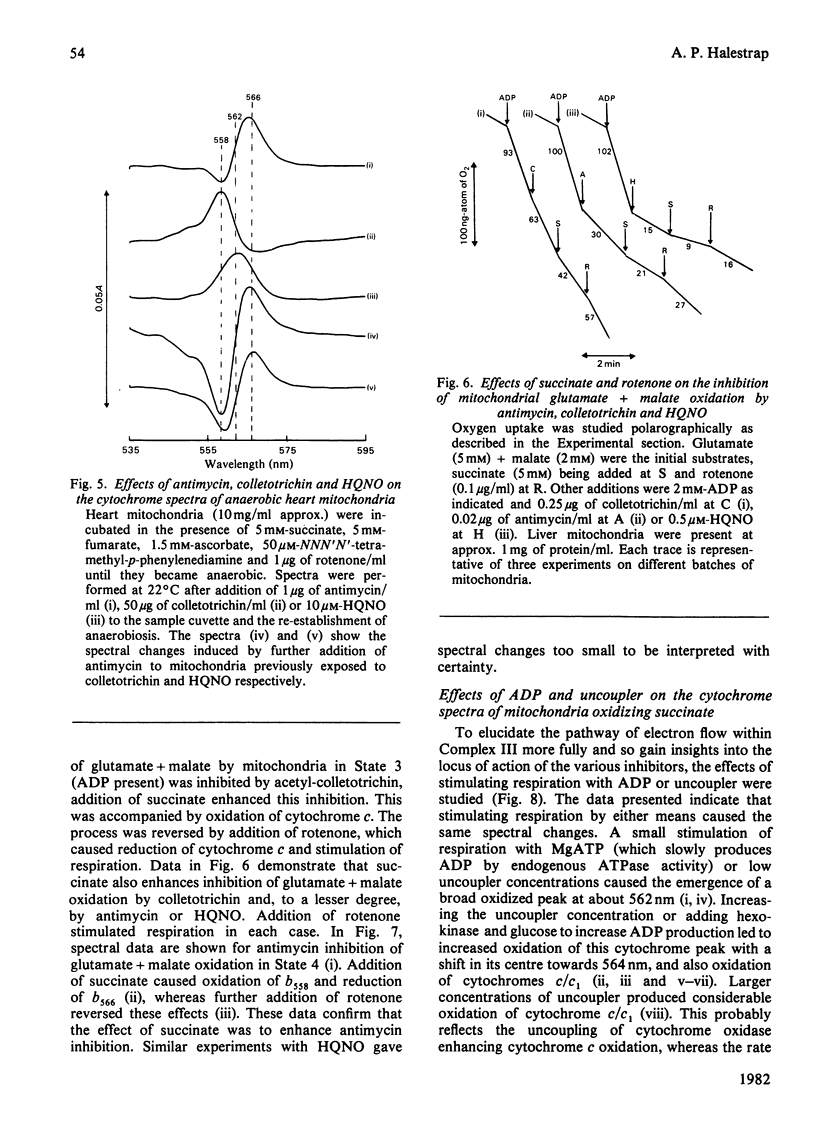
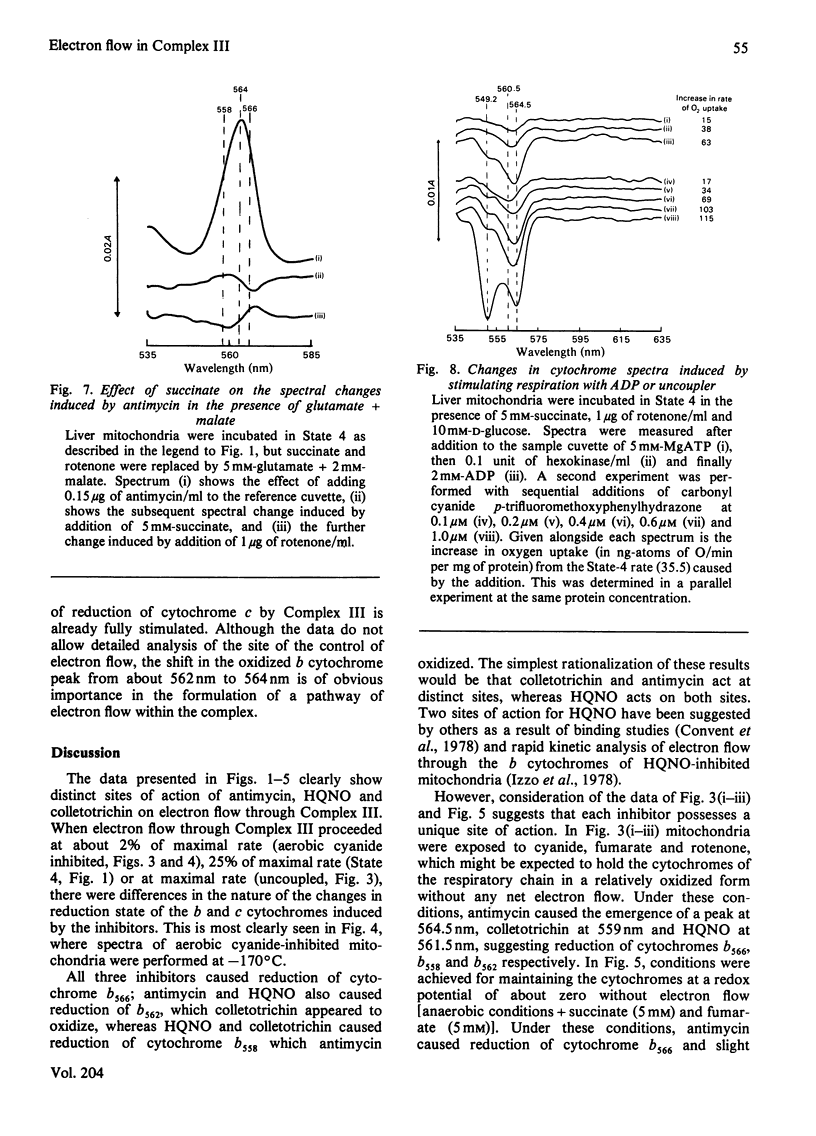
1. Cytochrome spectra of the liver and heart mitochondria incubated under various conditions are presented to compare the effects of antimycin, colletotrichin and 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline N-oxide (HQNO) additions. 2. Under aerobic conditions, in State 4, in the presence of uncoupler or in the presence of cyanide, all three inhibitors caused oxidation of cytochromes c and c1, but different changes in the spectra of the b cytochromes. Antimycin caused oxidation of a peak at 558 nm and reduction of peaks at 562 nm and 566 nm, whereas colletotrichin caused reduction of peaks at 558 nm and 566 nm and oxidation at 562 nm. HQNO had an effect on the spectra intermediate between those of the two other inhibitors. 3. Under aerobic conditions in the presence of 5 mM-succinate and 5 mM-fumarate, antimycin caused reduction of a peak at 566 nm and oxidation of a peak at 558 nm, whereas colletotrichin had the reverse effect and HQNO caused reduction of a peak at 562 nm. 4. Colletotrichin inhibition of the ADP-stimulated oxidation of glutamate + malate was enhanced by succinate addition and declined again with rotenone addition. Similar but smaller effects were seen with inhibition by antimycin and HQNO. 5. Cytochrome spectra are shown of the effects of ADP and uncoupler addition to stimulate respiration progressively. 6. The results are interpreted in terms of a modified 'Q cycle' [Mitchell (1976) J. Theor. Biol. 62, 327-367] in which the three inhibitors are postulated to displace ubiquinone and ubisemiquinone specifically bound to cytochromes b on both sides of the membrane. 7. It is suggested that cytochromes b558 and b566 are the same b cytochrome located on the outer surface of the membrane, but binding ubisemiquinone or colletotrichin and ubiquinone or antimycin respectively. Cytochrome b562 is postulated to be on the inner surface of the mitochondrial membrane and to bind either ubiquinone or ubisemiquinone, HQNO would bind to the reduced form of the cytochrome and colletotrichin to the oxidized form. 8. Sites for the locus of action of glucagon and the protonmotive force on electron flow are suggested.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arutjunjan A. M., Kamensky Y. A., Milgröm E., Surkov S., Konstantinov A. A., Sharonov Y. A. Is mitochondrial cytochrome b-566/558 a single hemoprotein or two individual components? A magnetic circular dichroism study. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 1;95(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzi A., Santato M. ATP and pH induced spectral changes of cytochrome b in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov;45(4):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer J. R., Dutton P. L., Prince R. C., Crofts A. R. The role of the Rieske iron-sulfur center as the electron donor to ferricytochrome c2 in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 3;592(3):445–460. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer J. R., Trumpower B. L. Inhibition of the oxidant--induced reduction of cytochrome b by a synthetic analogue of ubiquinone. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer J. R., Trumpower B. L. Rapid reduction of cytochrome c1 in the presence of antimycin and its implication for the mechanism of electron transfer in the cytochrome b-c1 segment of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2245–2251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B. The nature of electron transfer and energy coupling reactions. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):3–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Wilson D. F., Dutton P. L., Erecińska M. Energy-coupling mechanisms in mitochondria: kinetic, spectroscopic, and thermodynamic properties of an energy-transducing form of cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1175–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convent B., Briquet M., Goffeau A. Kinetic evidence for two sites in the inhibition by diuron of the electron transport in the bc1 segment of the respiratory chain in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):137–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convent B., Briquet M. Properties of 3-(3, 4-dichlorophenyl)-1, 1-dimethylurea and other inhibitors of the cytochrome bc1 segment of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 16;82(2):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erecińska M., Wilson D. F., Miyata Y. Mitochondrial cytochrome b-c complex: its oxidation-reduction components and their stoichiometry. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Nov;177(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90423-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foucher B., Chappell J. B., McGivan J. D. The effects of acetylcolletotrichin on the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;138(3):415–423. doi: 10.1042/bj1380415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrieri F., Izzo G., Maida I., Papa S. Redox Bohr-effects in isolated cytochrome bc1 complex and cytochrome c oxidase from beef-heart mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80734-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P. Stimulation of the respiratory chain of rat liver mitochondria between cytochrome c1 and cytochrome c by glucagon treatment of rats. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 15;172(3):399–405. doi: 10.1042/bj1720399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P. The mitochondrial pyruvate carrier. Kinetics and specificity for substrates and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;148(1):85–96. doi: 10.1042/bj1480085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P. The nature of the stimulation of the respiratory chain of rat liver mitochondria by glucagon pretreatment of animals. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 15;204(1):37–47. doi: 10.1042/bj2040037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuti T., Mizuno S., Muraoka S. Stepwise reduction of cytochromes b-562, b-566 and b-558 in rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 8;396(1):36–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo G., Guerrieri F., Papa S. On the mechanism of inhibition of the respiratory chain by 2-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide. FEBS Lett. 1978 Sep 15;93(2):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)81130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. Y., Slater E. C. Reducibility of cytochromes b in aerobic beef-heart mitochondria treated with antimycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 14;283(3):395–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura K., Packham N. K., Mueller P., Dutton P. L. The recognition and redox properties of a component, possibly a quinone, which determines electron transfer rate in ubiquinone-cytochrome c oxidoreductase of mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 17;131(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80877-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Possible molecular mechanisms of the protonmotive function of cytochrome systems. J Theor Biol. 1976 Oct 21;62(2):327–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(76)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Lorusso M., Izzo G., Capuano F. Control of electron transfer in the cytochrome system of mitochondria by pH, transmembrane pH gradient and electrical potential. The cytochromes b-c segment. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 15;194(2):395–406. doi: 10.1042/bj1940395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S. Proton translocation reactions in the respiratory chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;456(1):39–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(76)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich P. R. A generalised model for the equilibration of quinone pools with their biological donors and acceptors in membrane-bound electron transfer chains. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieske J. S. Composition, structure, and function of complex III of the respiratory chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;456(2):195–247. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(76)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts H., Choo W. M., Smith S. C., Marzuki S., Linnane A. W., Porter T. H., Folkers K. The site of inhibition of mitochondrial electron transfer by coenzyme Q analogues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Nov;191(1):306–315. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts H., Smith S. C., Marzuki S., Linnane A. W. Evidence that cytochrome b is the antimycin-binding component of the yeast mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpower B. L. Evidence for a protonmotive Q cycle mechanism of electron transfer through the cytochrome b-c1 complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trumpower B. L., Haggerty J. G. Inhibition of electron transfer in the cytochrome b-c, segment of the mitochondrial respiratory chain by a synthetic analogue of ubiquinone. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1980 Aug;12(3-4):151–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00744680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban P. F., Klingenberg M. On the redox potentials of ubiquinone and cytochrome b in the respiratory chain. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jul;9(4):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Jagow G., Klingenberg M. Close correlation between antimycin titer and cytochrome b(T) content in mitochondria of chloramphenicol treated Neurospora crassa. FEBS Lett. 1972 Aug 15;24(3):278–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Y., Scholes C. P., King T. E. Ubisemiquinone radicals from the cytochrome b-c1 complex of the mitochondrial electron transport chain--demonstration of QP-S radical formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1411–1419. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F., Erecińska M., Leigh J. S., Jr, Koppelman M. The properties of the mitochondrial succinate-cytochrome c reductase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):112–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Nagaoka S., Yu L., King T. E. Evidence for the existence of a ubiquinone protein and its radical in the cytochromes b and c1 region in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jun 29;82(4):1070–1078. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Nagoaka S., Yu L., King T. E. Evidence of ubisemiquinone radicals in electron transfer at the cytochromes b and c1 region of the cardiac respiratory chain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Oct 1;204(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Yu L. Identification of ubiquinone binding proteins in ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase by arylazido ubiquinone derivative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Yu L., King T. E. The existence of an ubiquinone binding protein in the reconstitutively active cytochrome b-c1 complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91248-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Yu L. Study of ubiquinone binding in ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase by spin labeled ubiquinone derivative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 27;98(4):1063–1069. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu L., Yu C. A., King T. E. The indispensability of phospholipid and ubiquinone in mitochondrial electron transfer from succinate to cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2657–2663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Jagow G., Engel W. D. A model for the cytochrome b dimer of the ubiquinol: cytochrome c oxidoreductase as a proton translocator. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


