Abstract
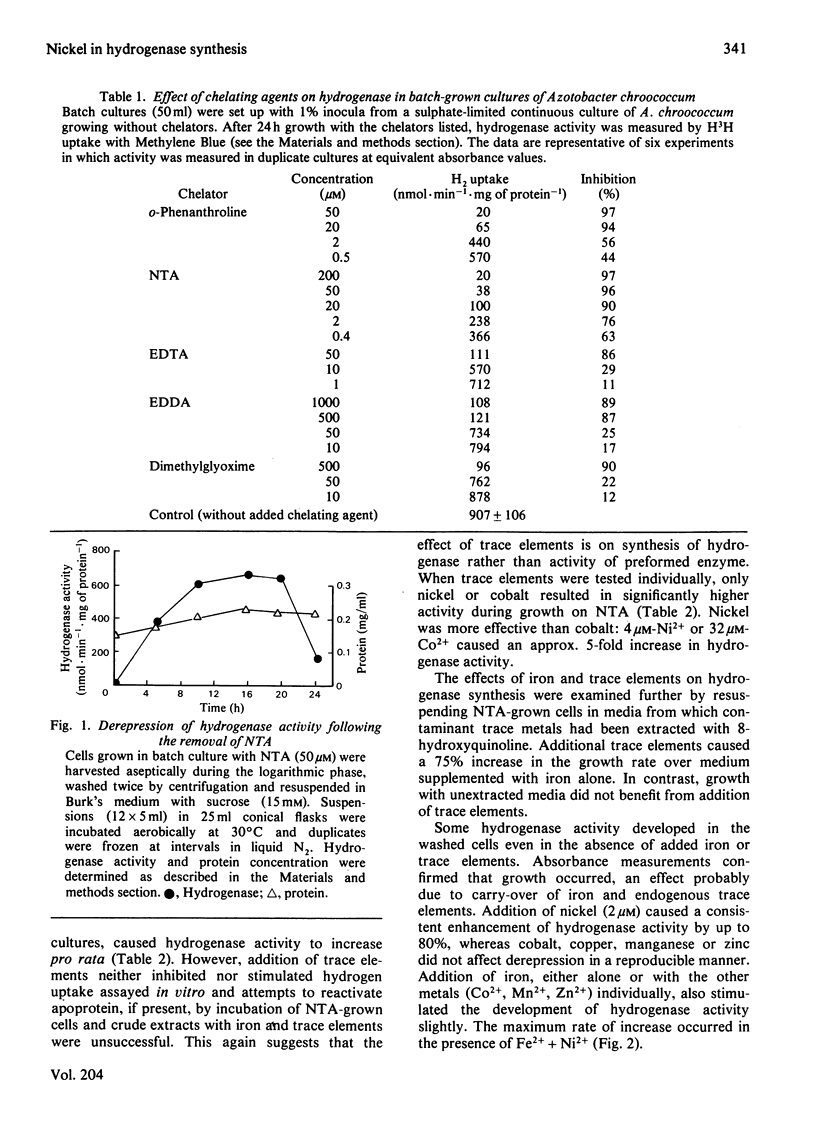
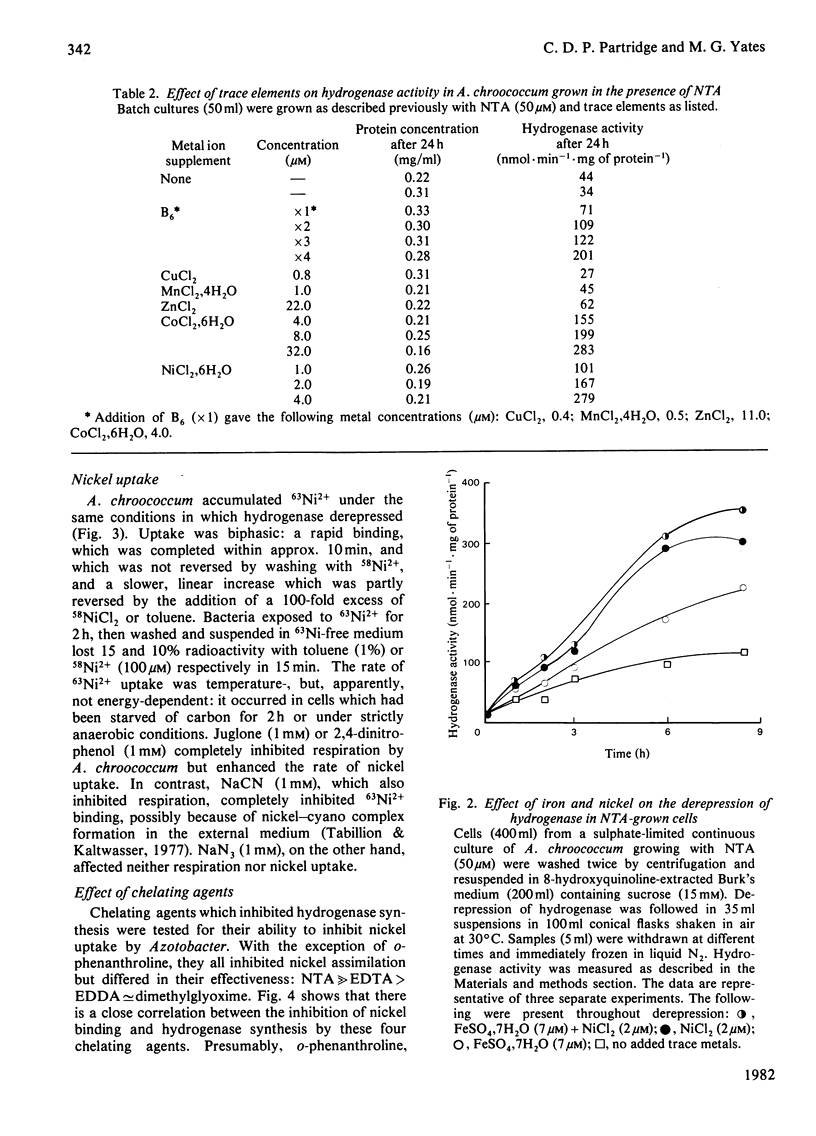
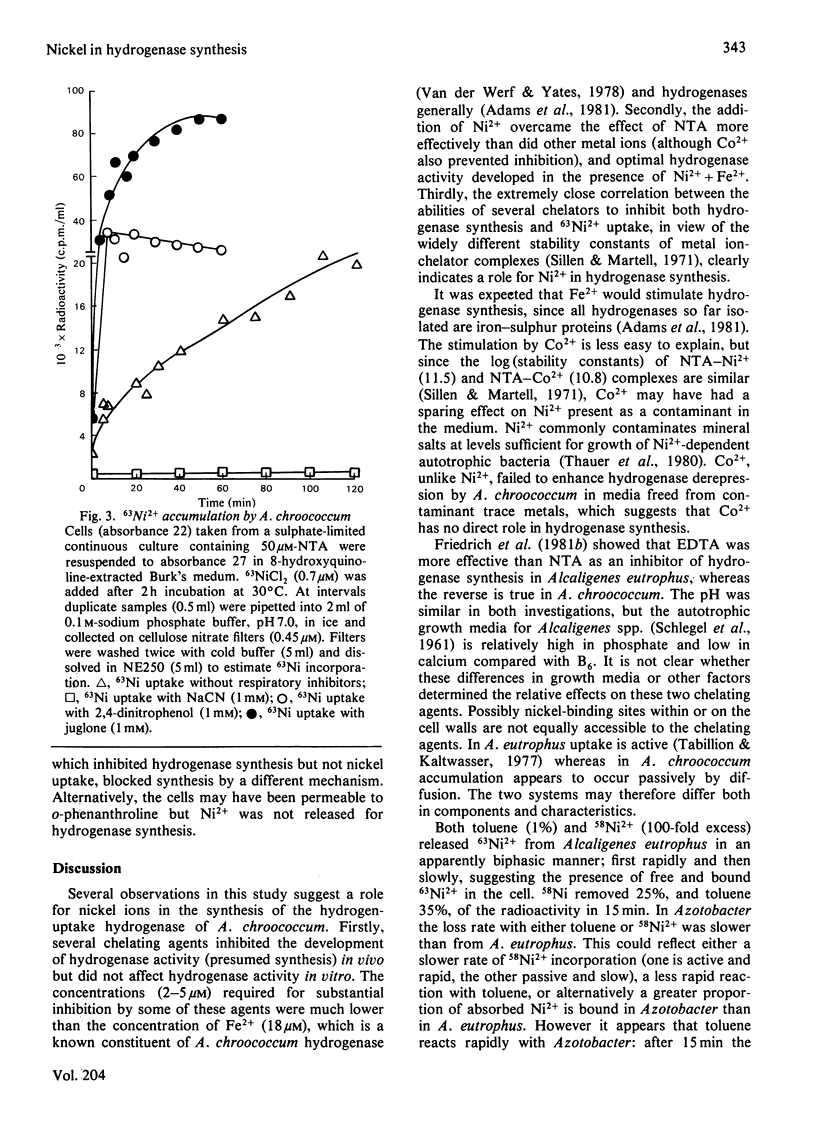
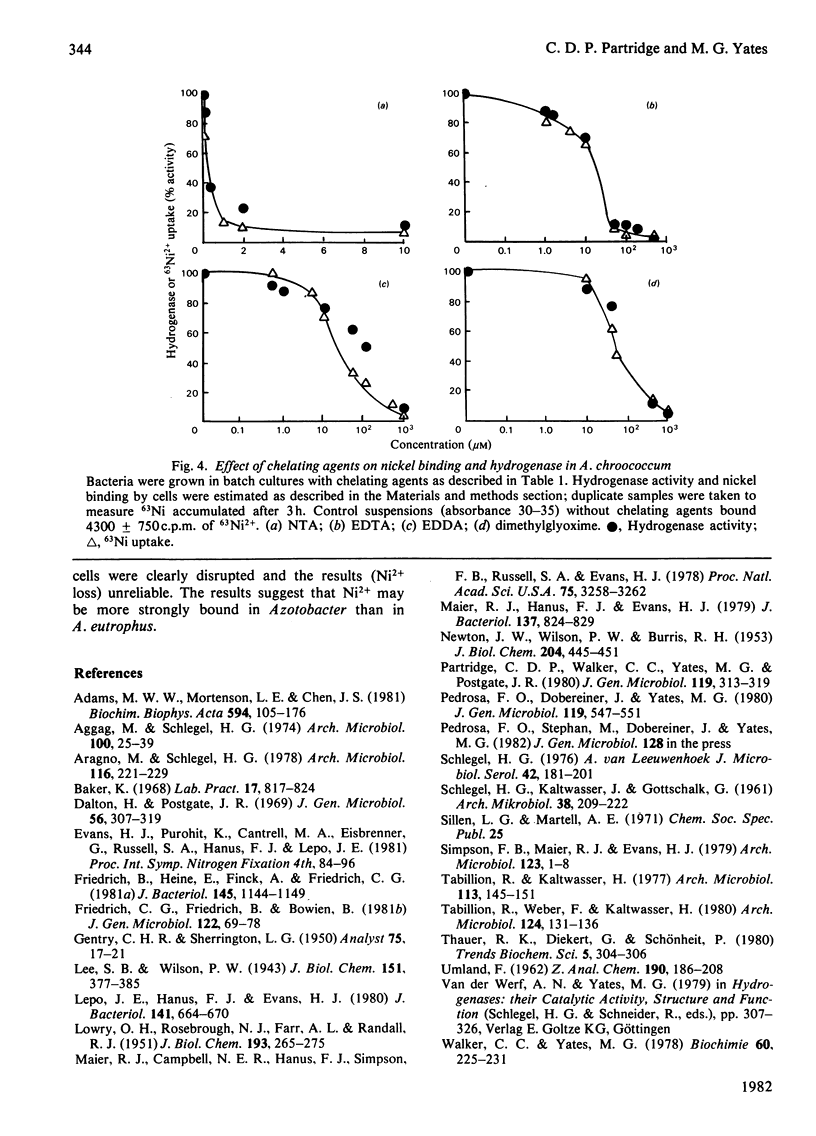
The chelating agents EDTA, o-phenanthroline, nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA), ethylenediamine-bis(o-hydroxyphenylacetic acid) (EDDA) or dimethylglyoxime prevented the expression of hydrogenase activity in batch cultures of nitrogen-fixing Azotobacter chroococcum, but did not inhibit preformed enzyme. The inhibition was reversed either by adding a mixture of trace elements (Cu2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Co2+) or Ni2+ or, to a lesser degree, Co2+ alone. Ni2+ or Ni2+ + Fe2+ also enhanced the rate of hydrogenase derepression in A. chroococcum in the absence of any added chelator, if the medium was first extracted with 8-hydroxyquinoline. A. chroococcum accumulated 63Ni2+ by an energy-independent mechanism. Both, Ni2+ uptake and hydrogenase synthesis were equally inhibited by either NTA, EDTA, EDDA or dimethylglyoxime. The evidence suggests a role for Ni2+ in hydrogenase synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. W., Mortenson L. E., Chen J. S. Hydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec;594(2-3):105–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(80)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggag M., Schlegel H. G. Studies on a gram-positive hydrogen bacterium, Nocardia opaca 1 b. III. Purification, stability and some properties of the soluble hydrogen dehydrogenase. Arch Microbiol. 1974;100(1):25–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00446303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepo J. E., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Chemoautotrophic growth of hydrogen-uptake-positive strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):664–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.664-670.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Campbell N. E., Hanus F. J., Simpson F. B., Russell S. A., Evans H. J. Expression of hydrogenase activity in free-living Rhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3258–3262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Hanus F. J., Evans H. J. Regulation of hydrogenase in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):825–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.825-829.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON J. W., WILSON P. W., BURRIS R. H. Direct demonstration of ammonia as an intermediate in nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., KALTWASSER H., GOTTSCHALK G. [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies]. Arch Mikrobiol. 1961;38:209–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel H. G. The fifth A.J. Kluyver Memorial Lecture delivered before the Netherlands Society for Microbiology on October 9th, 1975, at the Delft University of Technology, Delft. The physiology of hydrogen bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1976;42(3):181–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00394115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabillion R., Kaltwasser H. Energieabhängige 63Ni-Aufnahme bei Alcaligenes eutrophus Stamm H1 und H16. Arch Microbiol. 1977 May 13;113(1-2):145–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00428595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. C., Yates M. G. The hydrogen cycle in nitrogen-fixing Azotobacter chroococcum. Biochimie. 1978;60(3):225–231. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80818-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


