Abstract
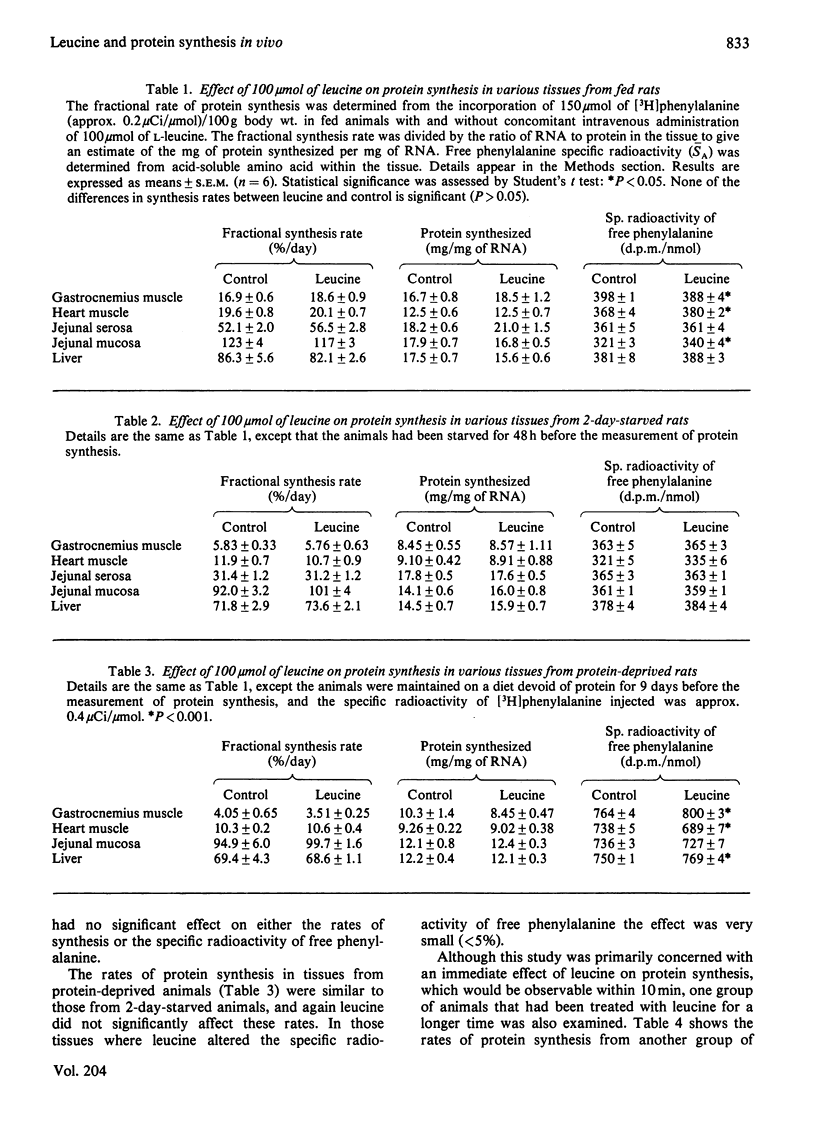
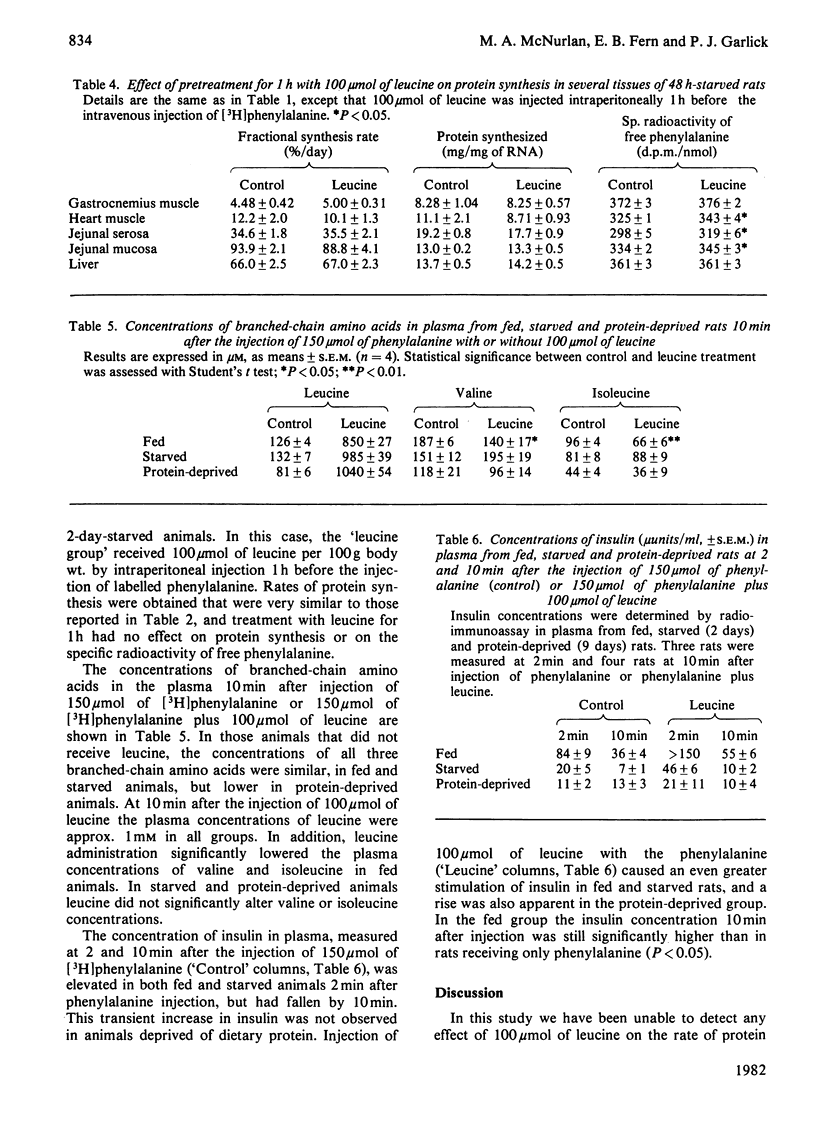
The effect of 100 mumol of leucine on protein synthesis in several tissues was assessed in the intact rat. Leucine had no immediate effect on protein synthesis in gastrocnemius muscle, heart, jejunal serosa, jejunal mucosa or liver in rats which were fed, starved for 2 days or deprived of dietary protein for 9 days. Leucine treatment for 1 h also failed to stimulate protein synthesis in tissues of 2-day-starved animals.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin S. A., Clemens M. J. The regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells by amino acid supply. Biosci Rep. 1981 Jan;1(1):35–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01115147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn G. L., Moldawer L. L., Usui S., Bothe A., Jr, O'Keefe S. J., Bistrian B. R. Branched chain amino acid administration and metabolism during starvation, injury, and infection. Surgery. 1979 Aug;86(2):307–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse M. G., Atwell R., Mancusi V. In vitro effect of branched chain amino acids on the ribosomal cycle in muscles of fasted rats. Horm Metab Res. 1979 Apr;11(4):289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse M. G., Reid S. S. Leucine. A possible regulator of protein turnover in muscle. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1250–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI108201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Some special kinetic problems of transport. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:1–20. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua B., Siehl D. L., Morgan H. E. Effect of leucine and metabolites of branched chain amino acids on protein turnover in heart. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8358–8362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H. R., James J. H., Fischer J. E. Nitrogen-sparing mechanisms of singly administered branched-chain amino acids in the injured rat. Surgery. 1981 Aug;90(2):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H., Hoover H. C., Jr, Atamian S., Fischer J. E. Infusion of the branched chain amino acids in postoperative patients. Anticatabolic properties. Ann Surg. 1979 Jul;190(1):18–23. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197907000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund H., Yoshimura N., Fischer J. E. The role of alanine in the nitrogen conserving quality of the branched-chain amino acids in the postinjury state. J Surg Res. 1980 Jul;29(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricke U. Tritosol: a new scintillation cocktail based on Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):555–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulks R. M., Li J. B., Goldberg A. L. Effects of insulin, glucose, and amino acids on protein turnover in rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., McNurlan M. A., Preedy V. R. A rapid and convenient technique for measuring the rate of protein synthesis in tissues by injection of [3H]phenylalanine. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):719–723. doi: 10.1042/bj1920719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Millward D. J., James W. P. The diurnal response of muscle and liver protein synthesis in vivo in meal-fed rats. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):935–945. doi: 10.1042/bj1360935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Millward D. J., James W. P., Waterlow J. C. The effect of protein deprivation and starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 18;414(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw E. C., Hirsch C. A., Morton B. E., Hiatt H. H. Control of protein synthesis in mammalian tissues through changes in ribosome activity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):436–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. B., Jefferson L. S. Influence of amino acid availability on protein turnover in perfused skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 1;544(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Garlick P. J. Protein synthesis in liver and small intestine in protein deprivation and diabetes. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):E238–E245. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.241.3.E238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Pain V. M., Garlick P. J. Conditions that alter rates of tissue protein synthesis in vivo. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):283–285. doi: 10.1042/bst0080283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Tomkins A. M., Garlick P. J. The effect of starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in rat liver and small intestine. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1780373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Bates P. C., Grimble G. K., Brown J. G., Nathan M., Rennie M. J. Quantitative importance of non-skeletal-muscle sources of N tau-methylhistidine in urine. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):225–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1900225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Garlick P. J., Nnanyelugo D. O., Waterlow J. C. The relative importance of muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in the regulation of muscle mass. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):185–188. doi: 10.1042/bj1560185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitch W. E., Walser M., Sapir D. G. Nitrogen sparing induced by leucine compared with that induced by its keto analogue, alpha-ketoisocaproate, in fasting obese man. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):553–562. doi: 10.1172/JCI110066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penney C. L. A simple micro-assay for inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels D. E., Hjalmarson A. C., Morgan H. E. Effects of noncarbohydrate substrates on protein synthesis in muscle. Am J Physiol. 1974 Mar;226(3):528–539. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.3.528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapir D. G., Walser M. Nitrogen sparing induced early in starvation by infusion of branched-chain ketoacids. Metabolism. 1977 Mar;26(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S. Effect of starvation on the turnover and metabolic response to leucine. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1471–1481. doi: 10.1172/JCI109067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodside K. H., Mortimore G. E. Suppression of protein turnover by amino acids in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6474–6481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


