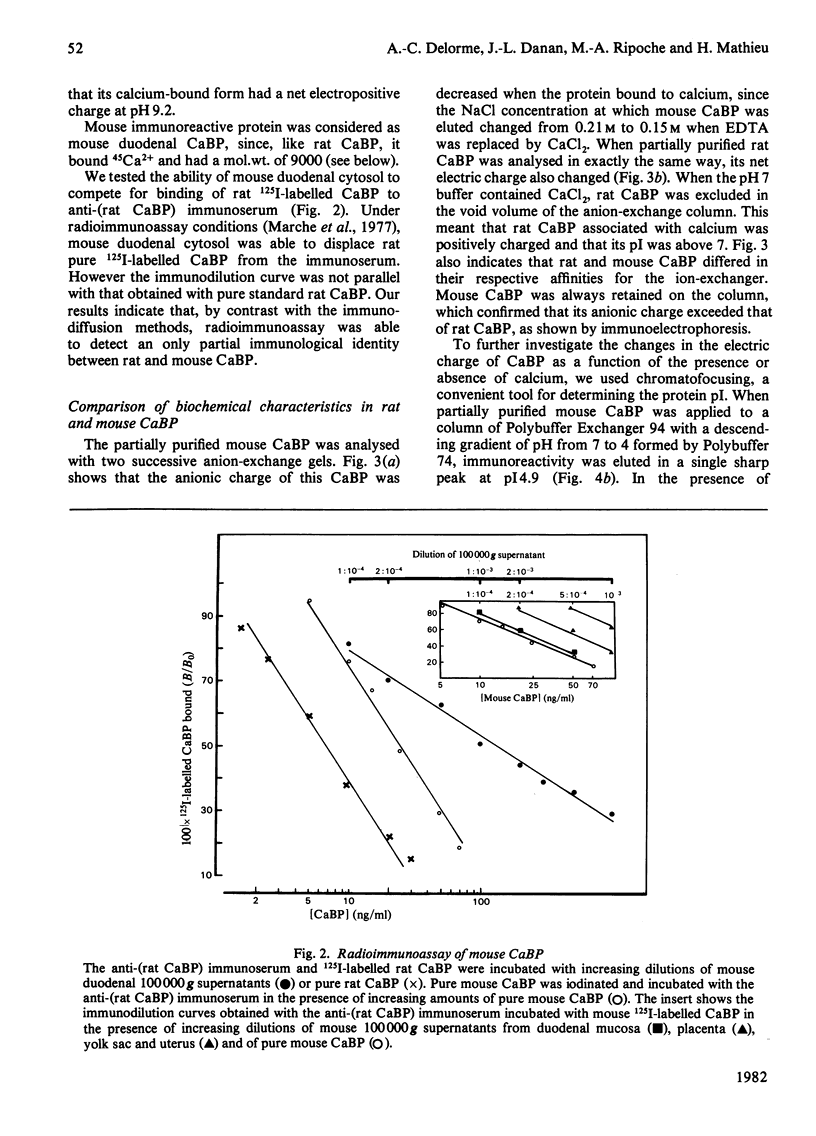
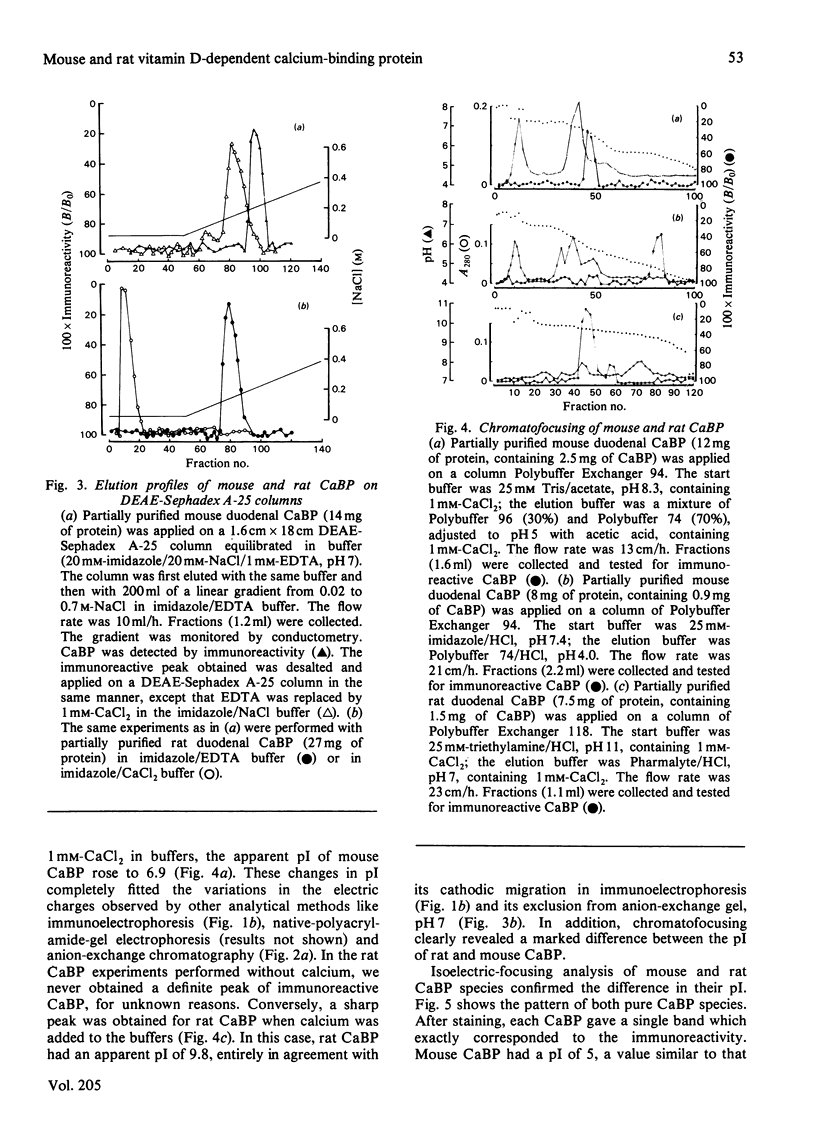
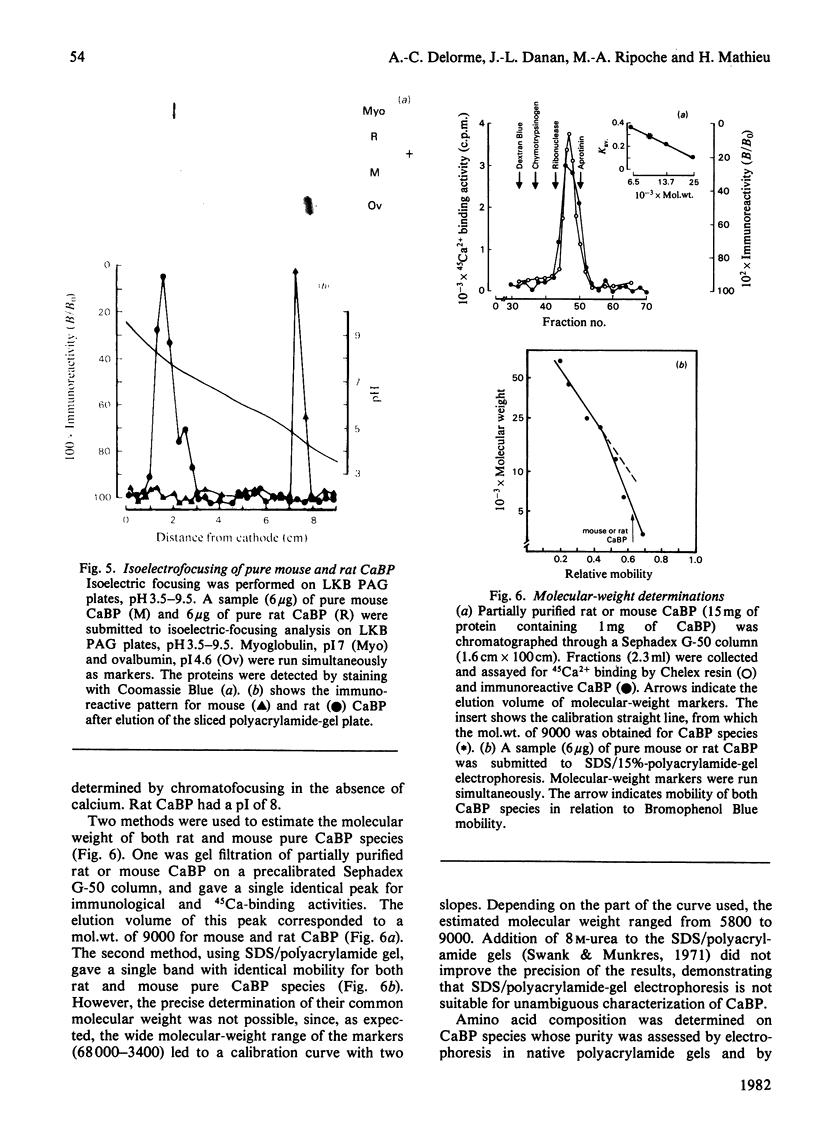
Abstract
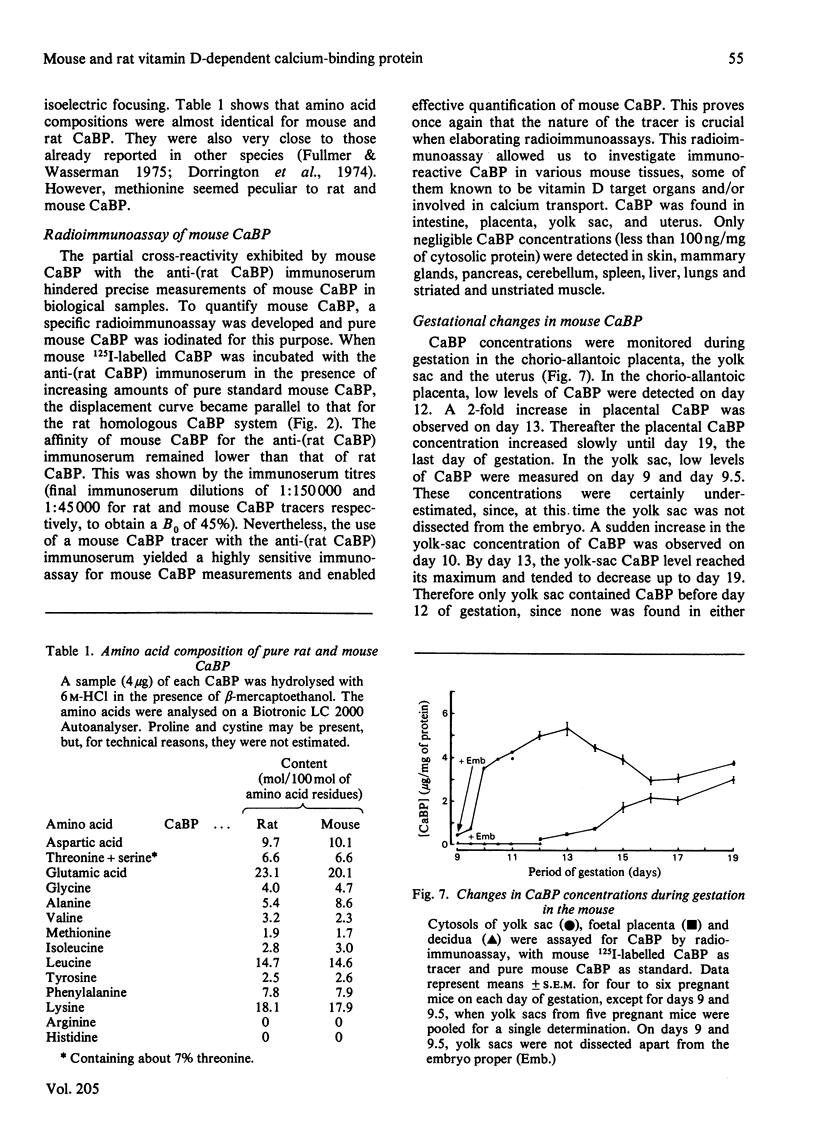
We compared immunochemical and biochemical properties of the vitamin D-dependent Ca2+-binding protein (CaBP) from rat and mouse intestine. The two intestinal CaBP species were extensively purified by gel filtration and successive anion-exchange chromatographies. Both had a similar mol.wt. of 9000. Their pI values differed markedly, being 8.0 and 4.9 in rat and mouse CaBP respectively. Accordingly, mouse CaBP displayed more anodal migration in electrophoresis under non-denaturing conditions. Both mouse and rat CaBP only exhibited partial immunochemical similarities, but their amino acid compositions were very similar. Chromatofocusing was also found to be a good method of detecting calcium-dependent changes in their pI. We developed a sensitive radioimmunoassay for mouse CaBP enabling us to detect substantial amounts of CaBP in uterus, yolk sac and chorio-allantoic placenta. During normal mouse gestation, CaBP appeared on day 12 in the chorio-allantoic placenta but was already present on day 9 in the yolk sac, where its level rose sharply between days 9.5 and 10. CaBP may therefore be considered as a new marker for mouse yolk-sac differentiation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armbrecht H. J., Zenser T. V., Bruns M. E., Davis B. B. Effect of age on intestinal calcium absorption and adaptation to dietary calcium. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):E769–E774. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.6.E769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Bruns D. E., Avioli L. V. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein of rat intestine: changes during postnatal development and sensitivity to 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Endocrinology. 1979 Oct;105(4):934–938. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-4-934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Fleisher E. B., Avioli L. V. Control of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein in rat intestine by growth and fasting. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4145–4150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M. E., Vollmer S., Wallshein V., Bruns D. E. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Immunochemical studies and synthesis by placental tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4649–4653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colston K., Hirt M., Feldman D. Organ distribution of the cytoplasmic 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptor in various mouse tissues. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1916–1922. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme A. C., Garel J. M., Mathieu H. Hormonal control of intestinal calcium-binding protein concentrations at weaning in rats. J Dev Physiol. 1980 Feb-Apr;2(1-2):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme A. C., Marche P., Garel J. M. Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. Changes during gestation, prenatal and postnatal development in rats. J Dev Physiol. 1979 Jun;1(3):181–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Hui A., Hofmann T., Hitchman A. J., Harrison J. E. Porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Molecular properties and the effect of binding calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drescher D., DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D stimulated calcium binding protein from rat intestinal mucosa. Purification and some properties. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2302–2307. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., McCain T. A., Hirst M. A., Chen T. L., Colston K. W. Characterization of a cytoplasmic receptor-like binder for 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in rat intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10378–10384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T., Bronner F. Regulation of intestinal calcium-binding protein calcium intake in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1975 Mar;228(3):861–869. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.3.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullmer C. S., Wasserman R. H. Isolation and partial characterization of intestinal calcium-binding proteins from the cow, pig, horse, guinea pig, and chick. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 30;393(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason W. A., Jr, Lankford G. L. Rat intestinal calcium-binding protein: rapid purification with AG MP-1 ion-exchange chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 15;116(2):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90353-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haar J. L., Ackerman G. A. Ultrastructural changes in mouse yolk sac associated with the initiation of vitelline circulation. Anat Rec. 1971 Aug;170(4):437–455. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091700406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallfelz F. A., Taylor A. N., Wasserman R. H. Vitamin D-induced calcium binding factor in rat intestinal mucosa. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 May;125(1):54–58. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawitt E. L., Schedl H. P. In vivo calcium transport by rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):232–236. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kream B. E., DeLuca H. F. A specific binding protein for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in rat intestinal cytosol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91561-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marche P., Cassier P., Mathieu H. Intestinal calcium-binding protein. A protein indicator of enterocyte maturation associated with the terminal web. Cell Tissue Res. 1980;212(1):63–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00234033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marche P., Le Guern C., Cassier P. Immunocytochemical localization of a calcium-binding protein in the rat duodenum. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Mar 9;197(1):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00233554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marche P., Pradelles P., Gros C., Thomasset M. Radioimmunoassay for a vitamin-D dependent calcium-binding protein in rat duodenal mucosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 20;76(4):1020–1026. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90958-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansu D., Bellaton C., Bronner F. Effect of Ca intake on saturable and nonsaturable components of duodenal Ca transport. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):G32–G37. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.240.1.G32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf W. E., Sar M., Reid F. A., Tanaka Y., DeLuca H. F. Target cells for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in intestinal tract, stomach, kidney, skin, pituitary, and parathyroid. Science. 1979 Dec 7;206(4423):1188–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.505004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasset M., Cuisinier-Gleizes P., Mathieu H. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol: dynamics of the stimulation of duodenal calcium-binding protein, calcium transport and bone calcium mobilization in vitamin D and calcium-deficient rats. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):91–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomasset M., Desplan C., Moukhtar M., Mathieu H. Primary Translation product of mRNA coding for rat duodenal vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):178–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80596-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueng T. H., Golub E. E., Bronner F. The effect of age and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment on the intestinal calcium-binding protein of suckling rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Sep;196(2):624–630. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wecksler W. R., Ross F. P., Norman A. W. Characterization of the 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor from rat intestinal cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9488–9491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]