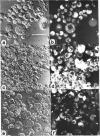
Abstract
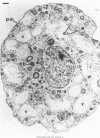
Plasma membranes have been isolated from protoplasts of suspension-cultured ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) endosperm cells. The protoplast membrane is coated before cell disruption with murine myeloma protein J539, a galactose-binding immunoglobulin A. The plasma membrane is labelled with 125I by using chemically or enzymically catalysed iodination techniques, or, more conveniently, by using 125I-labelled myeloma protein J539, which enables the membrane to be simultaneously coated and labelled. Protoplast lysis is effected by gentle mechanical means after swelling in hypo-osmotic medium. The plasma-membrane fraction is recovered at low centrifugal forces by fractionation of cell lysates on a discontinuous sucrose/sorbitol gradient. The plasma-membrane fraction is enriched 96-fold on a protein basis with respect to the specific radioactivity of 125I-labeled myeloma protein J539 in the homogenate. Electron microscopy showed long membrane profiles often associated with one another.
Full text
PDF


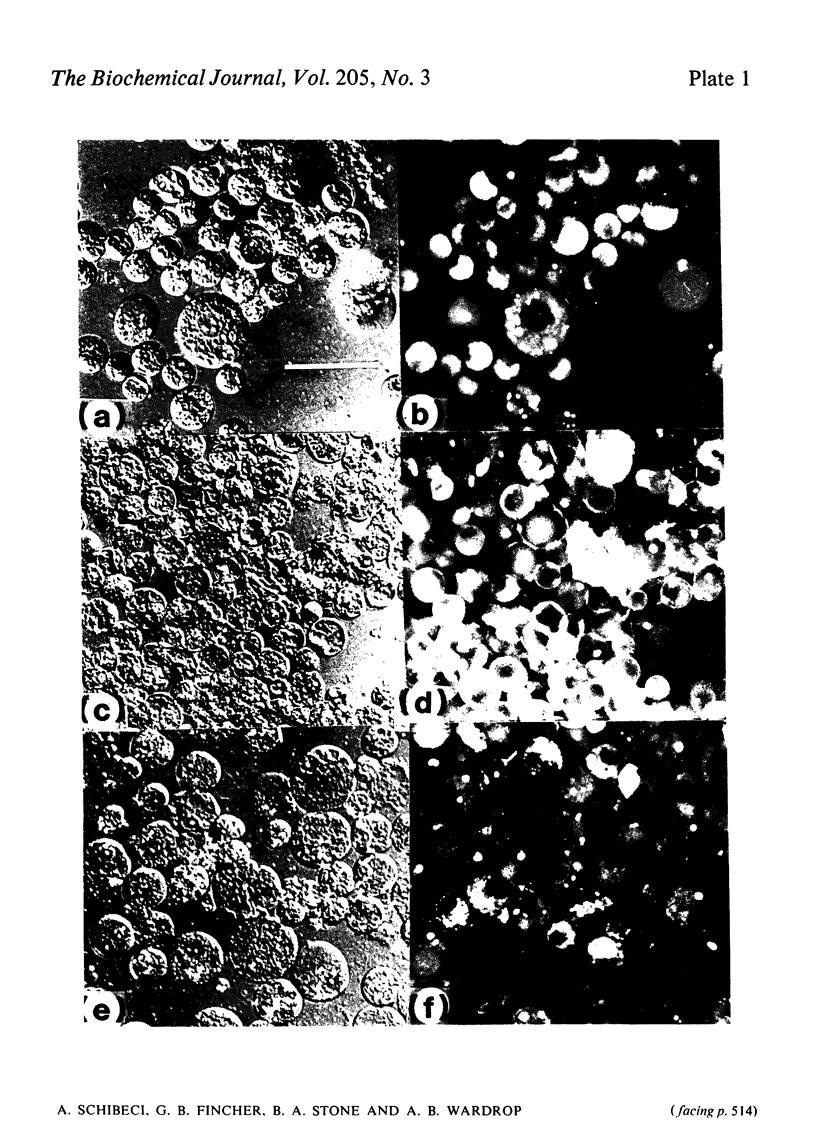



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boss W. F., Ruesink A. W. Isolation and Characterization of Concanavalin A-labeled Plasma Membranes of Carrot Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):1005–1011. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretting H., Kabat E. A. Purification and characterization of the agglutinins from the sponge Axinella polypoides and a study of their combining sites. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3228–3236. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
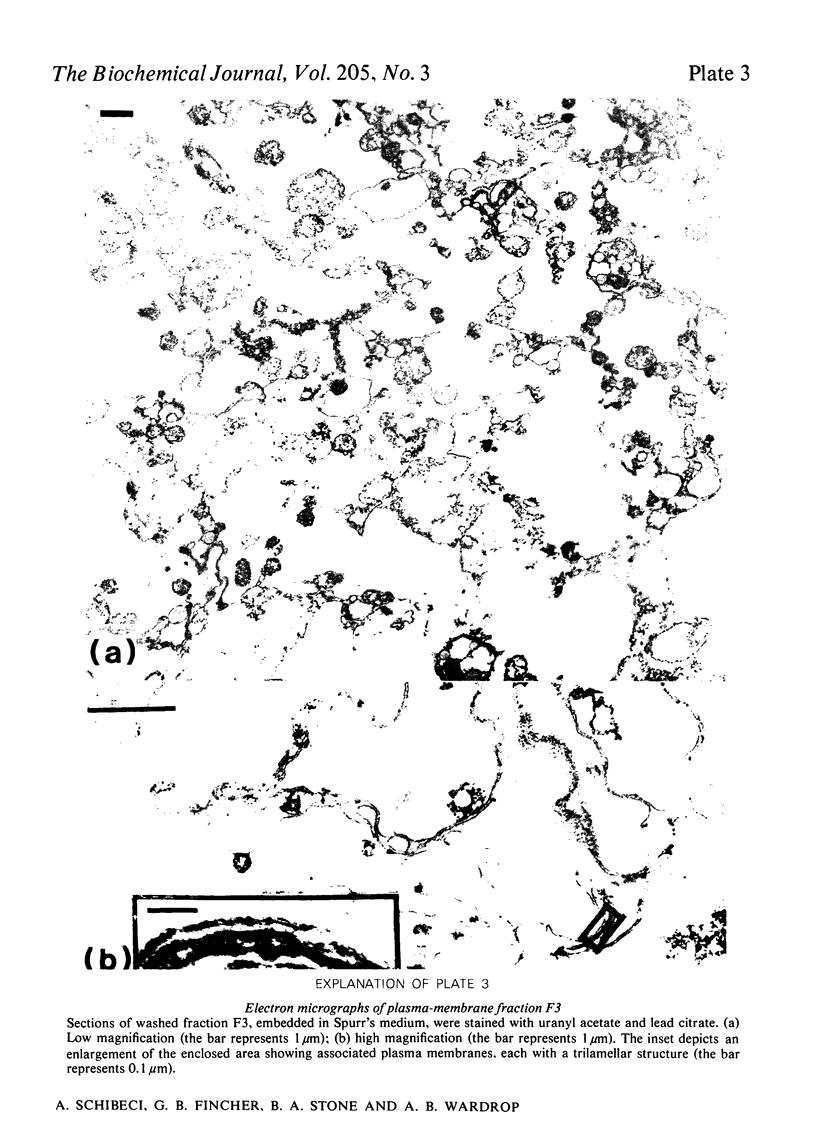
- Durán A., Bowers B., Cabib E. Chitin synthetase zymogen is attached to the yeast plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3952–3955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürr M., Boller T., Wiemken A. Polybase induced lysis of yeast spheroplasts. A new gentle method for preparation of vacuoles. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Nov 7;105(3):319–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00447152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. M., Kempson S. A., Carlson G. L., Dousa T. P. Diazontized (125I) diiodosulafanilic acid as a label for cell surface membranes. Studies on erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 3;553(1):54–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Uhlenbruck G., Baldo B. A. Similar combining specificities of invertebrate precipitins and mouse myeloma protein J 539 for beta-(1leads to6)-galactans. Immunochemistry. 1976 Jan;13(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith D. W., Northcote D. H. The isolation of plasma membrane from protoplasts of soybean suspension cultures. J Cell Sci. 1977 Apr;24:295–310. doi: 10.1242/jcs.24.1.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop-Harrison J., Heslop-Harrison Y. Evaluation of pollen viability by enzymatically induced fluorescence; intracellular hydrolysis of fluorescein diacetate. Stain Technol. 1970 May;45(3):115–120. doi: 10.3109/10520297009085351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolley M. E., Glaudemans C. P., Rudikoff S., Potter M. Structural requirements for the binding of derivatives of D-galactose to two homogeneous murine immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 16;13(15):3179–3184. doi: 10.1021/bi00712a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin P. J. Plant protoplast agglutination and membrane-bound beta-lectins. J Cell Sci. 1977 Aug;26:31–46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.26.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish R. W., Müller U. The isolation of plasma membranes from the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum using concanavalin A and Triton X-100. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):40–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80190-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlin D. S., Spanswick R. M. Labeling and isolation of plasma membranes from corn leaf protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1053–1057. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
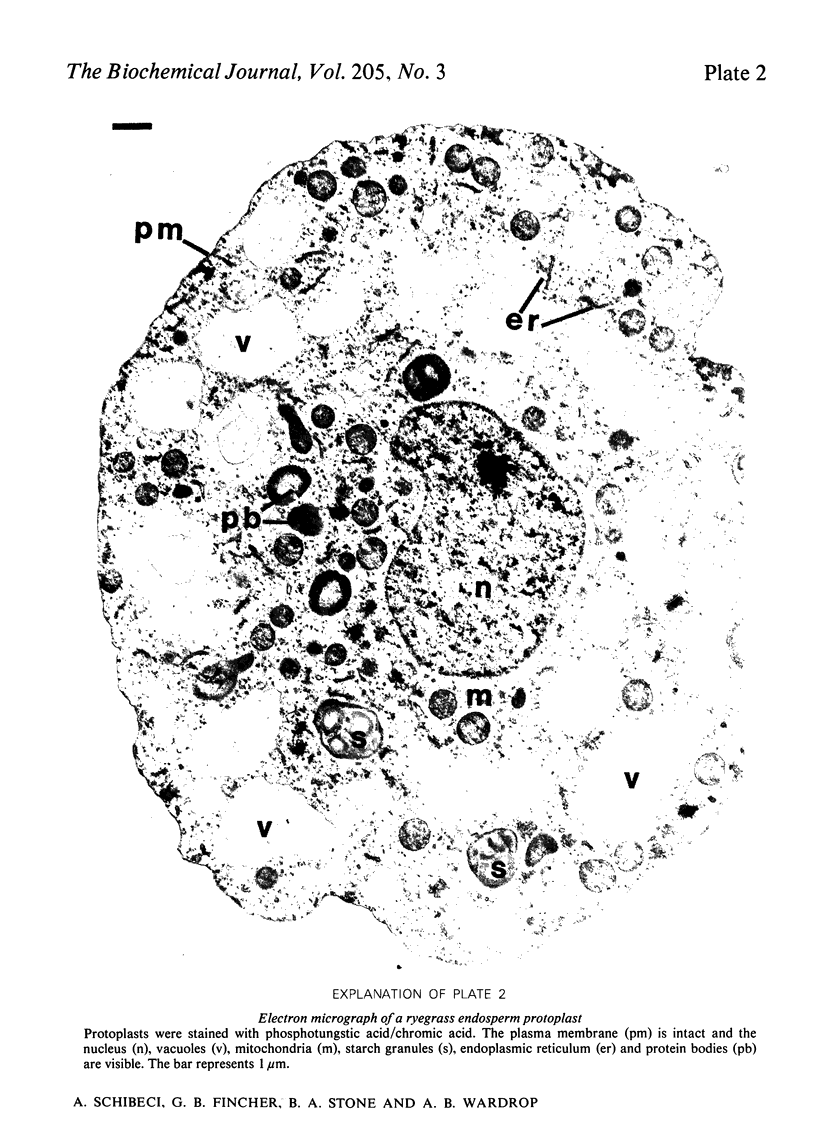
- Roland J. C., Lembi C. A., Morré D. J. Phosphotungstic acid-chromic acid as a selective electron-dense stain for plasma membranes of plant cells. Stain Technol. 1972 Jul;47(4):195–200. doi: 10.3109/10520297209116484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A. Isolation and characterization of Neurospora crassa plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1106–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]