Abstract
At 37 degrees C, human plasma kallikrein I follows Michaelis-Menten behaviour and exhibits a normal linear relationship between the initial velocity of hydrolysis of Ac-Pro-Phe-Arg-OMe,HCl and enzyme concentration in the range 0--150 pM. At temperatures of 30 degrees C and below substantial deviations from linearity are observed over the same enzyme concentration range. The temperature-dependent autoinhibition of kallikrein I activity is reversible and is not due to low-molecular-weight endogenous inhibitors or cofactors. The kinetic effect is apparently due to aggregation and can be abolished by the addition of sodium deoxycholate.
Full text
PDF
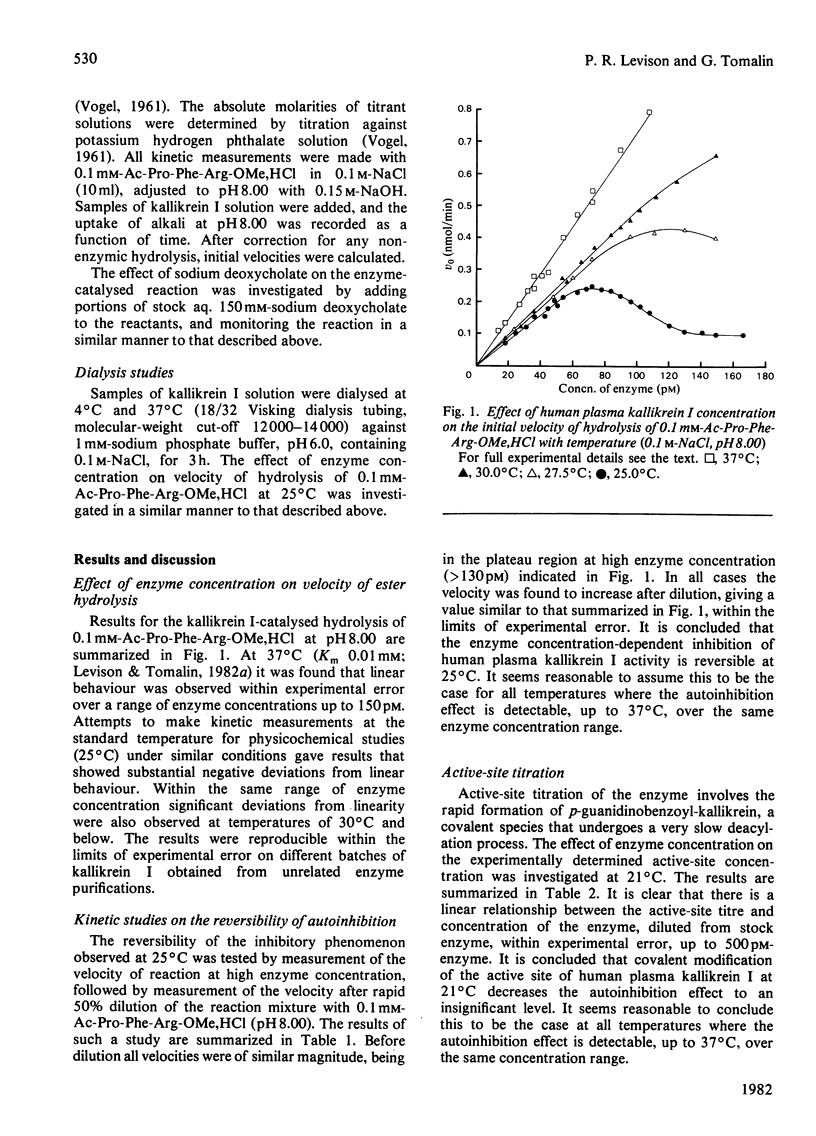
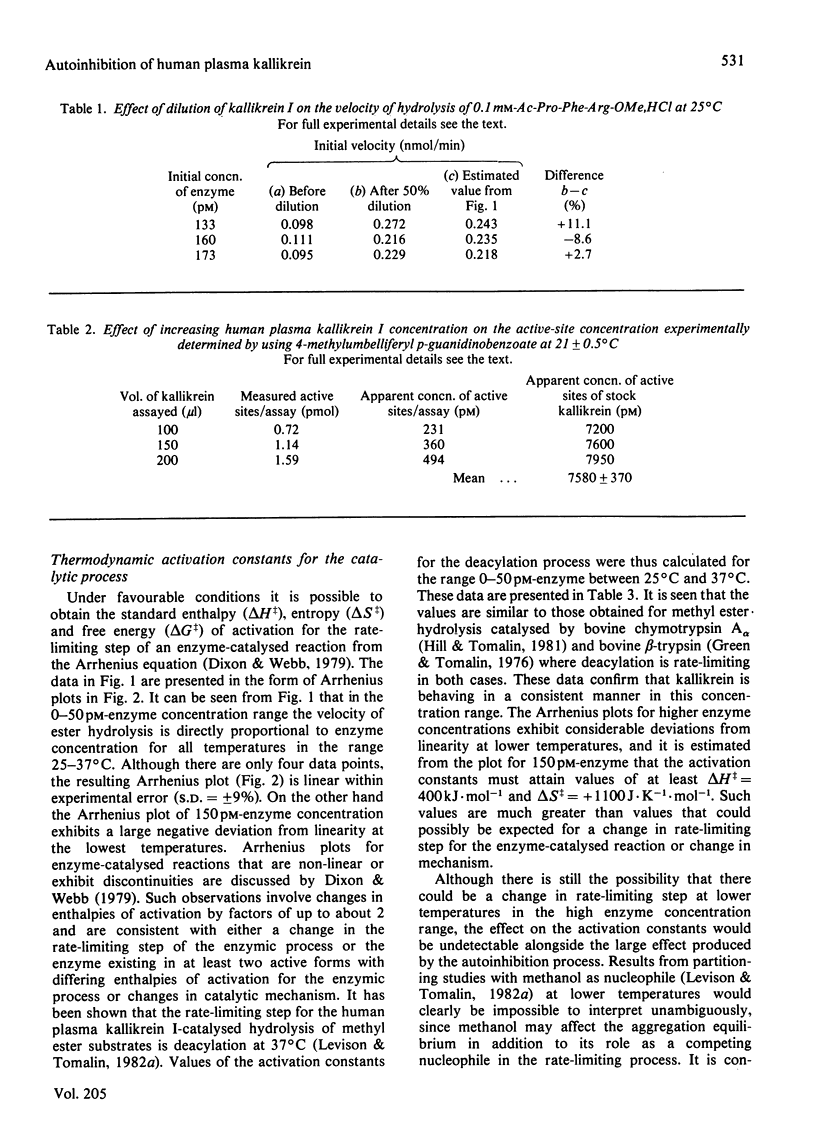
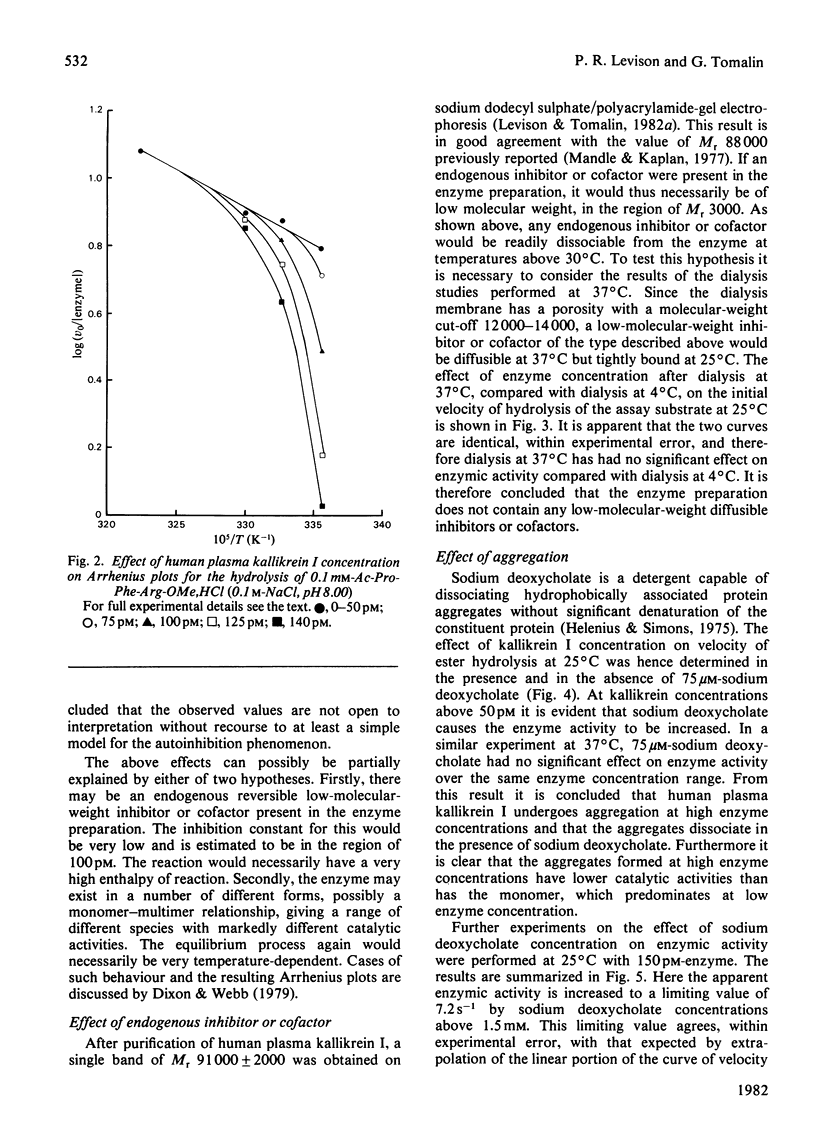
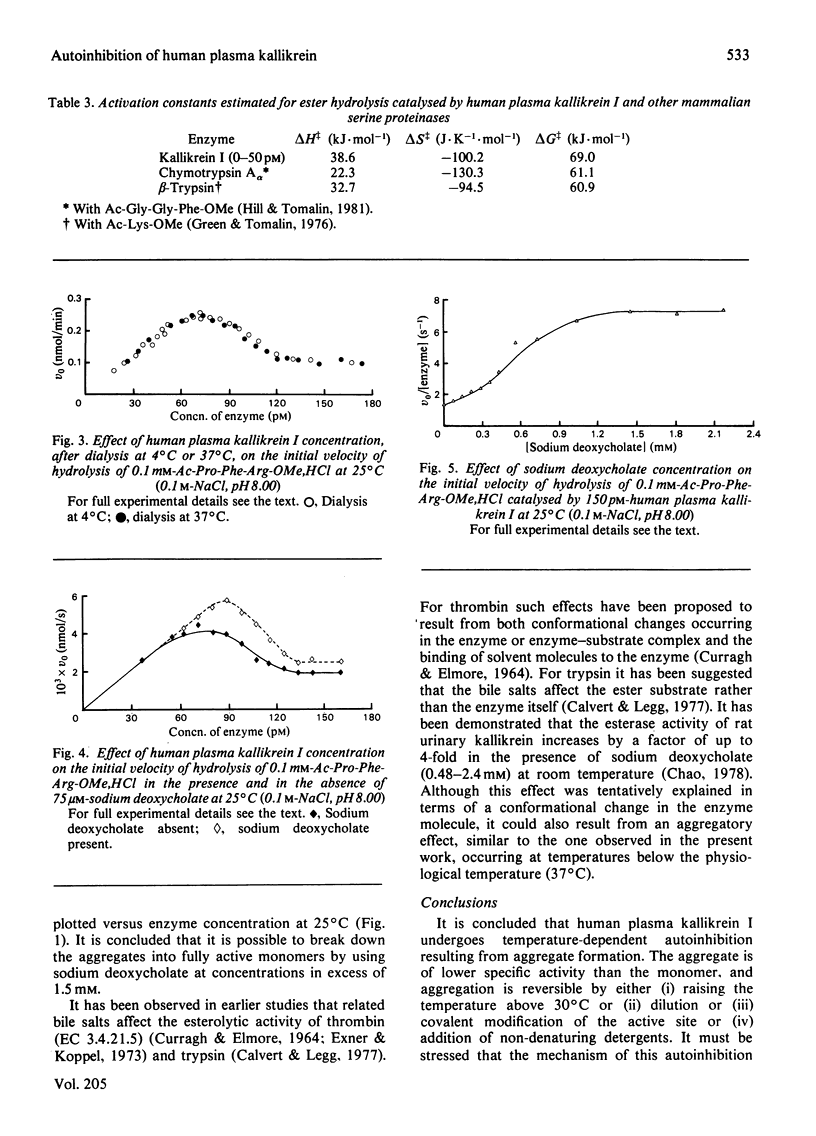

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calvert G. D., Legg E. F. The effect of bile salts on the esterolytic assay of trypsin. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Nov 1;80(3):535–541. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J. Activity and structural changes of purified kallikrein with detergent treatment. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 30;185(2):549–556. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Mattler L., Sherry S. Studies on the prekallikrein (kallikreinogen)--kallikrein enzyme system of human plasma. I. Isolation and purification of plasma kallikreins. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):11–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI105959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curragh E. F., Elmore D. T. Kinetics and mechanism of catalysis by proteolytic enzymes. 2. Kinetic studies of thrombin-catalysed reactions and their modification by bile salts and other detergents. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):163–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0930163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exner T., Koppel J. L. Cholate enhancement of interaction between thrombin and tosyl lysine chloromethyl ketone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 5;329(2):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F., Leysath G. Substrate specificity of porcine pancreatic kallikrein. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;120A:261–271. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0926-1_26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. D., Tomalin G. The kinetics of hydrolysis of some extended N-aminoacyl-l-lysine methyl esters. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10771.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber H., Geiger R., Heimburger N. Human plasma kallikrein: purification, enzyme characterization and quantitative determination in plasma. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Jun;359(6):659–669. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimark R. L., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine plasma prekallikrein (Fletcher factor). Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 11;18(25):5743–5750. doi: 10.1021/bi00592a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. R., Tomalin G. The kinetics of hydrolysis of some extended N-aminoacyl-L-phenylalanine methyl esters by bovine chymotrypsin A-alpha. Evidence for enzyme subsite S5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson G. W., Roberts D. V., Adams R. W., Kyle W. S., Elmore D. T. Determination of the operational molarity of solutions of bovine alpha-chymotrypsin, trypsin, thrombin and factor Xa by spectrofluorimetric titration. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):107–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1310107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison P. R., Tomalin G. The kinetics of hydrolysis of some extended N-aminoacyl-L-arginine methyl esters by human plasma kallikrein. Evidence for subsites S2 and S3. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):149–153. doi: 10.1042/bj2030149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandle R., Jr, Kaplan A. P. Hageman factor substrates. Human plasma prekallikrein: mechanism of activation by Hageman factor and participation in hageman factor-dependent fibrinolysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6097–6104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRae B. J., Kurachi K., Heimark R. L., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W., Powers J. C. Mapping the active sites of bovine thrombin, factor IXa, factor Xa, factor XIa, factor XIIa, plasma kallikrein, and trypsin with amino acid and peptide thioesters: development of new sensitive substrates. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7196–7206. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


