Abstract
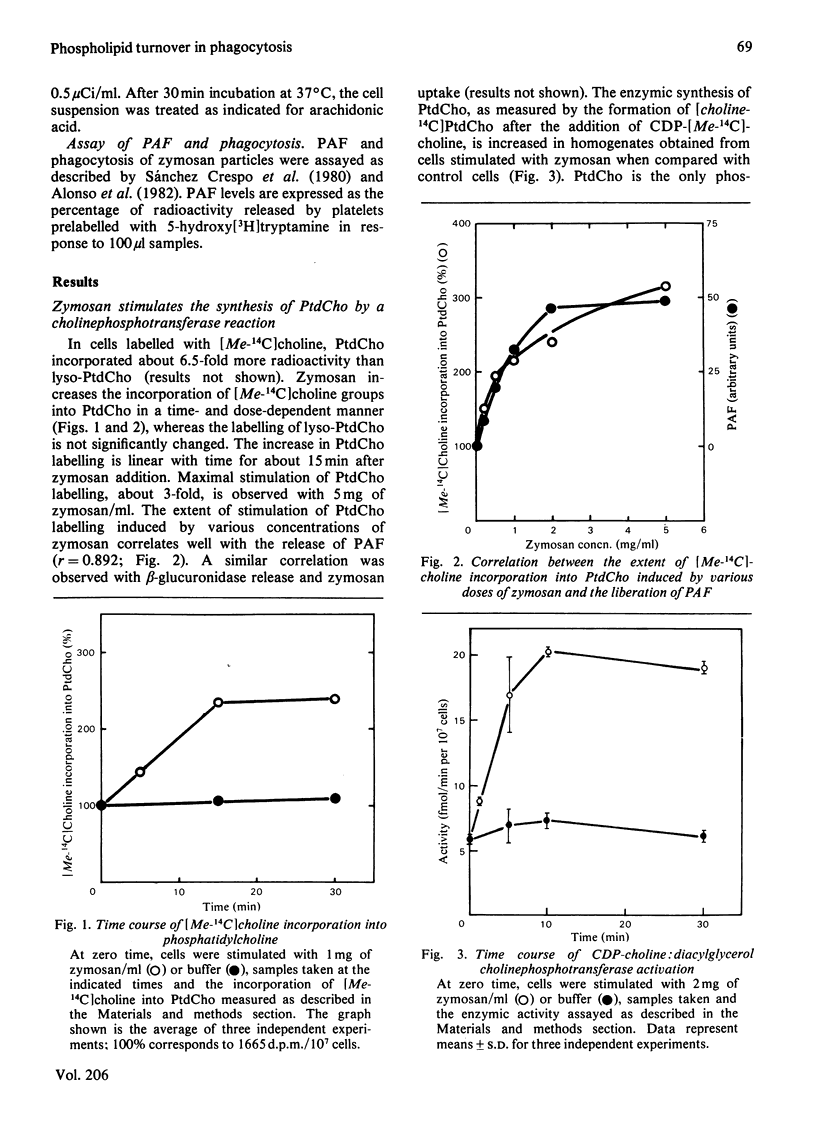
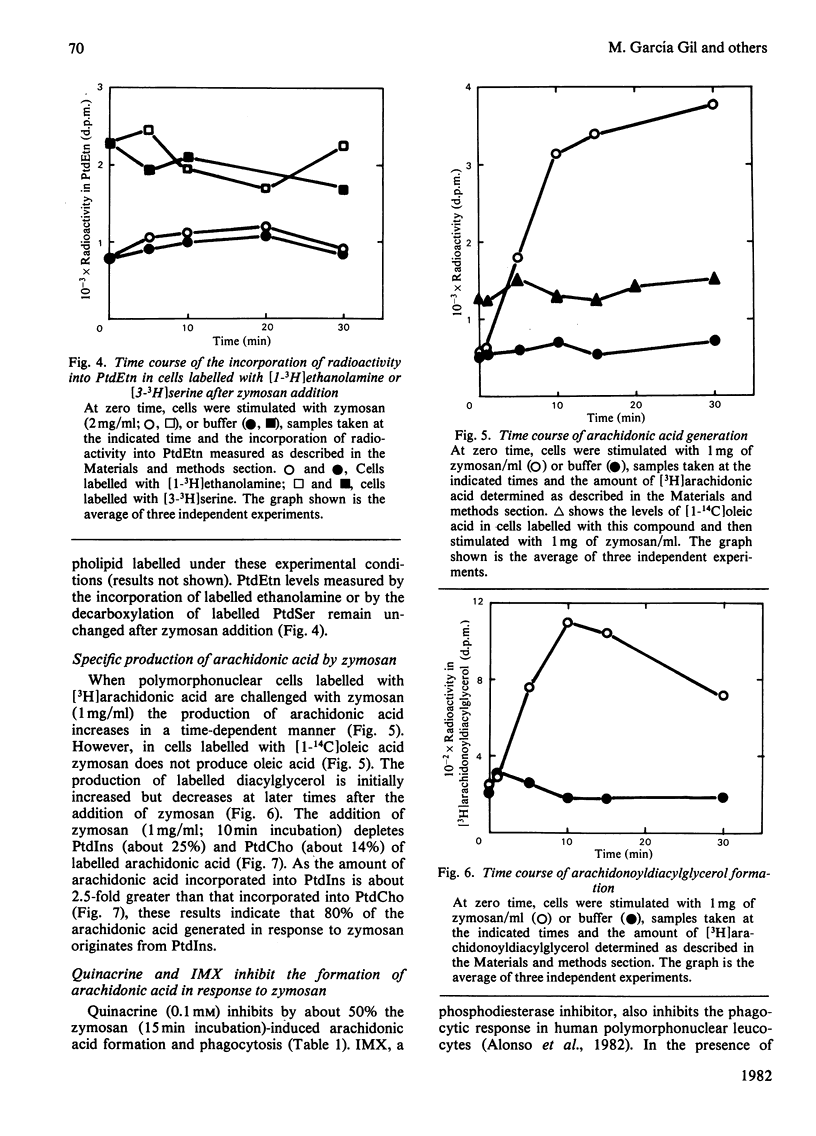
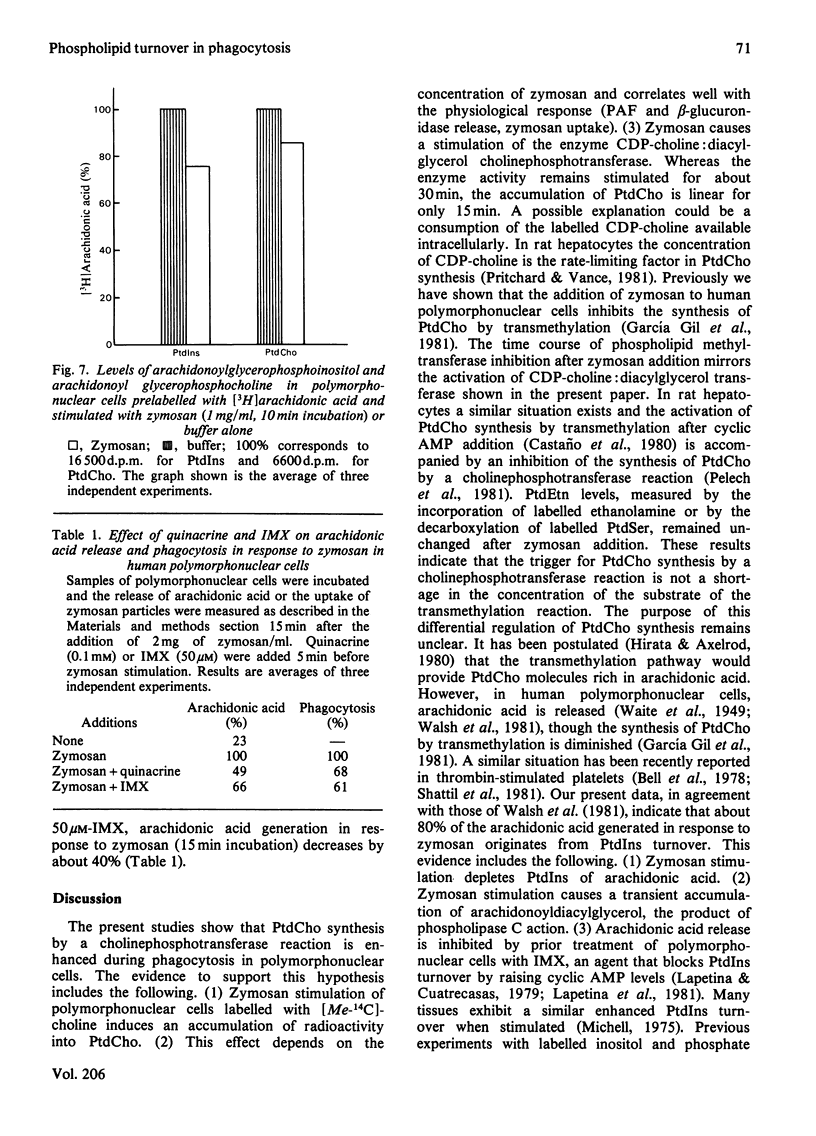
We have previously observed that the phagocytosis of zymosan particles coated with complement by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes is accompanied by a time- and dose-dependent inhibition of phosphatidylcholine synthesis by transmethylation [García Gil, Alonso, Sánchez Crespo & Mato (1981) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 101, 740–748]. The present studies show that phosphatidylcholine synthesis by a cholinephosphotransferase reaction is enhanced, up to 3-fold, during phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear cells. This effect was tested by both measuring the incorporation of radioactivity into phosphatidylcholine in cells labelled with [Me-14C]choline, and by assaying the activity of CDP-choline:diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase. The time course of CDP-choline:diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase activation by zymosan mirrors the inhibition of phospholipid methyltransferase activity previously reported. The extent of incorporation of radioactivity into phosphatidylcholine induced by various doses of zymosan correlates with the physiological response of the cells to this stimulus. This effect was specific for phosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidyl-ethanolamine turnover was not affected by zymosan. The purpose of this enhanced phosphatidylcholine synthesis is not to provide phospholipid molecules rich in arachidonic acid. The present studies show that about 80% of the arachidonic acid generated in response to zymosan derives from phosphatidylinositol. A transient accumulation of arachidonoyldiacylglycerol has also been observed, which indicates that a phospholipase C is responsible, at least in part, for the generation of arachidonic acid. Finally, isobutylmethylxanthine and quinacrine, inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol turnover, inhibit both arachidonic acid generation and phagocytosis, indicating a function for this pathway during this process.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso F., Sánchez-Crespo M., Mato J. M. Modulatory role of cyclic AMP in the release of platelet-activating factor from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Immunology. 1982 Mar;45(3):493–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C activities of platelets. Differential substrate specificity, Ca2+ requirement, pH dependence, and cellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10227–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broekman M. J., Ward J. W., Marcus A. J. Phospholipid metabolism in stimulated human platelets. Changes in phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidic acid, and lysophospholipids. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):275–283. doi: 10.1172/JCI109854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Alemany S., Nieto A., Mato J. M. Activation of phospholipid methyltransferase by glucagon in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9041–9043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil M. G., Alemany S., Cao D. M., Castano J. G., Mato J. M. Calmodulin modulates phospholipid methylation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1325–1330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil M. G., Alonso F., Sánchez-Crespo M., Mato J. M. Inhibition of phospholipid methyltransferase during zymosan induced secretion of platelet-activating factor in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):740–748. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91813-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Axelrod J. Phospholipid methylation and biological signal transmission. Science. 1980 Sep 5;209(4461):1082–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.6157192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. L., WALLACH D. F. The metabolic basis of phagocytosis. III. Incorporation of inorganic phosphate into various classes of phosphatides during phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jul;236:1895–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P., WEISS S. B. The function of cytidine coenzymes in the biosynthesis of phospholipides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Sep;222(1):193–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The phosphatidylinositol cycle and the regulation of arachidonic acid production. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):367–369. doi: 10.1038/292367a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid production in platelets precedes the formation of arachidonate and parallels the release of serotonin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa Y., Hostetler K. Y. Properties of phospholipase C isolated from rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):646–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Pritchard P. H., Vance D. E. cAMP analogues inhibit phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8283–8286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard P. H., Vance D. E. Choline metabolism and phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 15;196(1):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1960261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renooij W., Snyder F. Biosynthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor and a hypotensive lipid) by cholinephosphotransferase in various rat tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. S., Hokin L. E. Studies on the role of phospholipids in phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3354–3361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrey M. P., Rubin R. P. Characterization of a calcium-mediated activation of arachidonic acid turnover in adrenal phospholipids by corticotropin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11234–11241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., McDonough M., Burch J. W. Inhibition of platelet phospholipid methylation during platelet secretion. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):537–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Crespo M., Alonso F., Egido J. Platelet-activating factor in anaphylaxis and phagocytosis. I. Release from human peripheral polymorphonuclears and monocytes during the stimulation by ionophore A23187 and phagocytosis but not from degranulating basophils. Immunology. 1980 Aug;40(4):645–655. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tou J. S., Stjernholm R. L. Stimulation of the incorporation of 32Pi and myo-(2-3H)inositol into the phosphoinositides in polymorphonuclear leukocytes during phagocytosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90425-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., DeChatelet L. R., King L., Shirley P. S. Phagocytosis-induced release of arachidonic acid from human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):984–992. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91924-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. E., Waite B. M., Thomas M. J., DeChatelet L. R. Release and metabolism of arachidonic acid in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7228–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


