Abstract
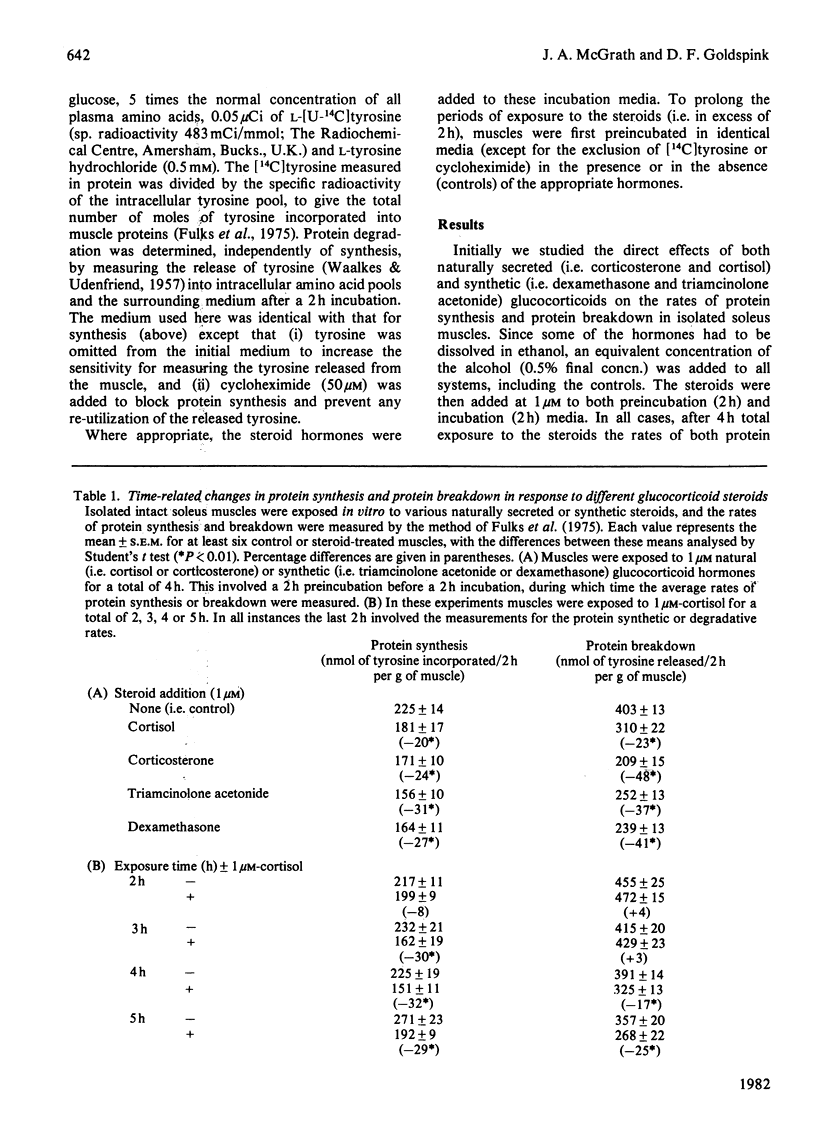
The direct actions of glucocorticoid hormones on protein turnover were studied in isolated soleus muscles. These steroids were found to decrease the rates of both protein synthesis and protein breakdown within 3 h and 4 h respectively. Synthetic steroids (e.g. dexamethasone) were found to be more potent than naturally secreted hormones (e.g. cortisol) in inducing these changes, but only at concentrations in vitro less than 10nm.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLODGETT F. M., BURGIN L., IEZZONI D., GRIBETZ D., TALBOT N. B. Effects of prolonged cortisone therapy on the statural growth, skeletal maturation and metabolic status of children. N Engl J Med. 1956 Apr 5;254(14):636–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195604052541402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Bird J. W. Properties of muscle and liver lysosomes in adrenalectomized rats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Jul;79(3):335–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. G., Bates P. C., Holliday M. A., Millward D. J. Thyroid hormones and muscle protein turnover. The effect of thyroid-hormone deficiency and replacement in thryoidectomized and hypophysectomized rats. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 15;194(3):771–782. doi: 10.1042/bj1940771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock G. R., Carter E. E., Elliott P., Peters R. F., Simpson P., White A. M. Relative changes in the function of muscle ribosomes and mitochondria during the early phase of steroid-induced catabolism. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(5):881–892. doi: 10.1042/bj1270881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulks R. M., Li J. B., Goldberg A. L. Effects of insulin, glucose, and amino acids on protein turnover in rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):290–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Goldspink D. F. Influence of food deprivation and adrenal steroids on DNA synthesis in various mammalian tissues. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jan;228(1):310–317. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.1.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L. Protein turnover in skeletal muscle. II. Effects of denervation and cortisone on protein catabolism in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3223–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyo J. L., Redmond A. F. Role of protein synthesis in the inhibitory action of adrenal steroid hormones on amino acid transport by muscle. Endocrinology. 1966 Sep;79(3):531–540. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. N. Corticosteroids and growth. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 2;295(10):547–552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609022951007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M., Kaiser N., Milholland R. J., Rosen F. The binding of dexamethasone and triamcinolone acetonide to glucocorticoid receptors in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5236–5240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. A., Goldspink D. F. The effects of cortisone treatment on the protein turnover of the soleus muscle after immobilization. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):1017–1019. doi: 10.1042/bst0061017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M., Kipnis D. M. Effect of glucocorticoids on plasma insulin. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 2;274(22):1237–1241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606022742205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. F., Richardson M. C., Small M., White A. M. Some biochemical effects of triamcinolone acetonide on rat liver and muscle. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):349–355. doi: 10.1042/bj1160349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels S. R., Jefferson L. S. Effects of glucocorticoids on muscle protein turnover in perfused rat hemicorpus. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):E564–E572. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.6.E564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santidrian S., Moreyra M., Munro H. N., Young V. R. Effect of corticosterone and its route of administration on muscle protein breakdown, measured in vivo by urinary excretion of N tau-methylhistidine in rats: response to different levels of dietary protein and energy. Metabolism. 1981 Aug;30(8):798–804. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Pennington R. J. Binding of dexamethasone and cortisol to cytosol receptors in rat extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles. Exp Neurol. 1977 Nov;57(2):342–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Pennington R. J. The effect of cortisone on protein breakdown and synthesis in rat skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1977 Jan;6(3):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(77)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Lippman M. E. Mechanism of action of glucocorticoids. Metabolism. 1974 Feb;23(2):159–202. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomas F. M., Munro H. N., Young V. R. Effect of glucocorticoid administration on the rate of muscle protein breakdown in vivo in rats, as measured by urinary excretion of N tau-methylhistidine. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):139–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1780139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAALKES T. P., UDENFRIEND S. A fluorometric method for the estimation of tyrosine in plasma and tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOL I. G., WEINSHELBAUM E. I. Incorporation of C14-amino acids into protein of isolated diaphragms: role of the adrenal steroids. Am J Physiol. 1959 Nov;197:1089–1092. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.5.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. R., Chen S. C., Macdonald J. The sedimentation of rat skeletal-muscle ribosomes. Effect of hydrocortisone, insulin and diet. Biochem J. 1968 Feb;106(4):913–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1060913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


