Abstract
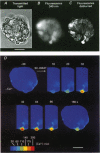
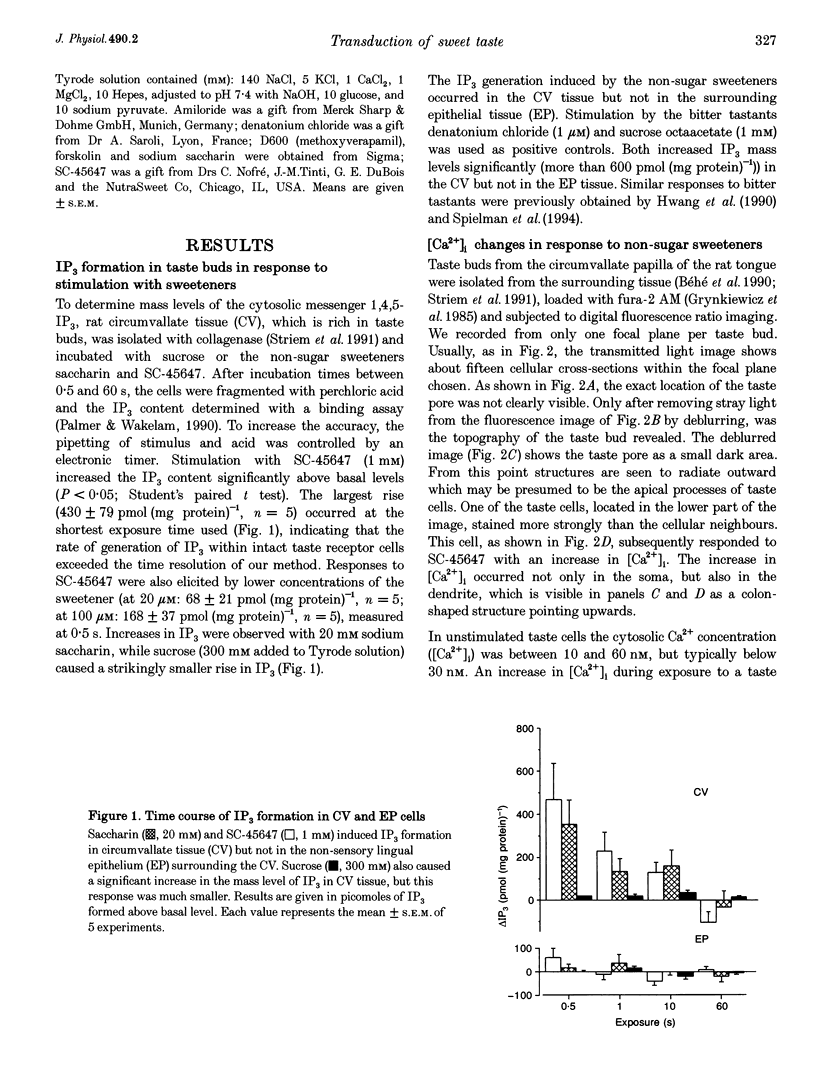
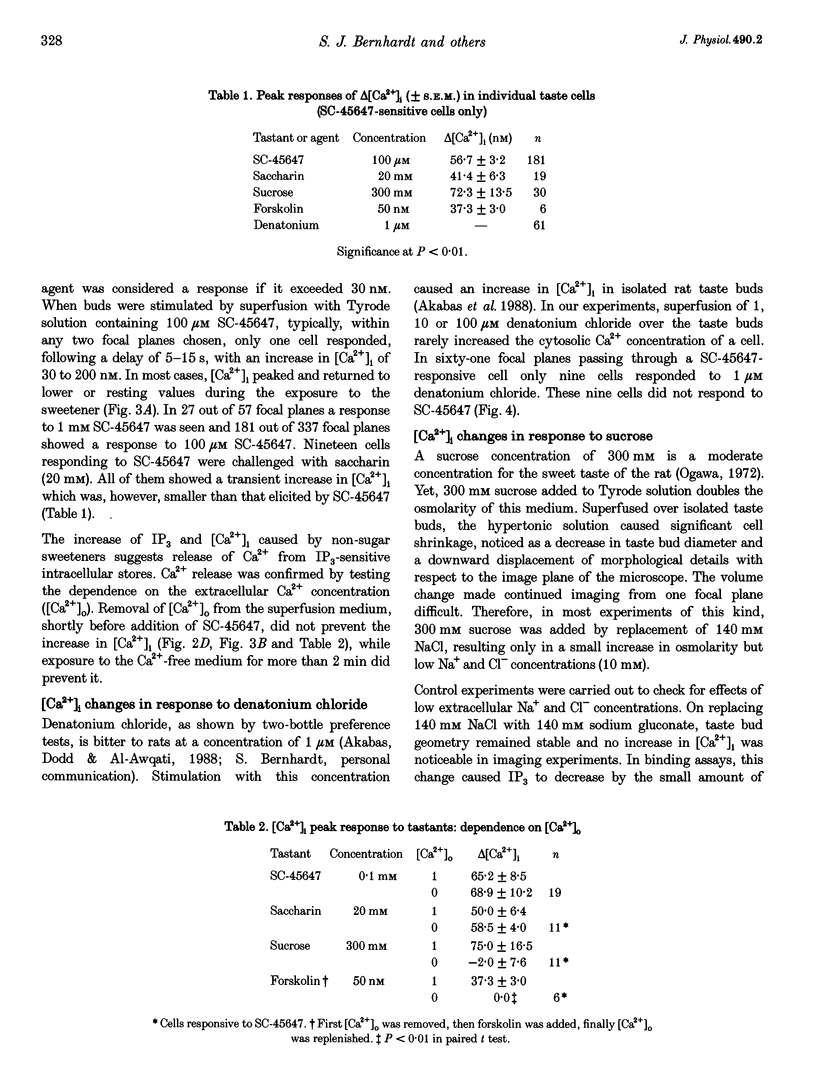
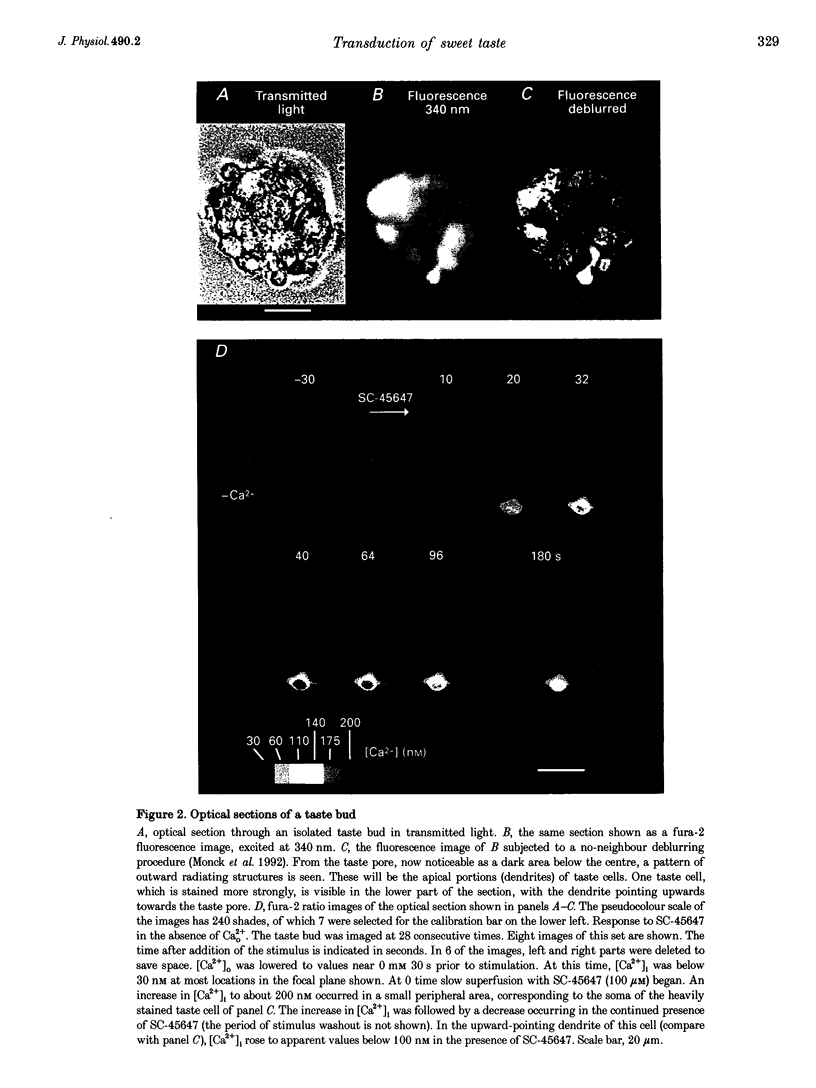
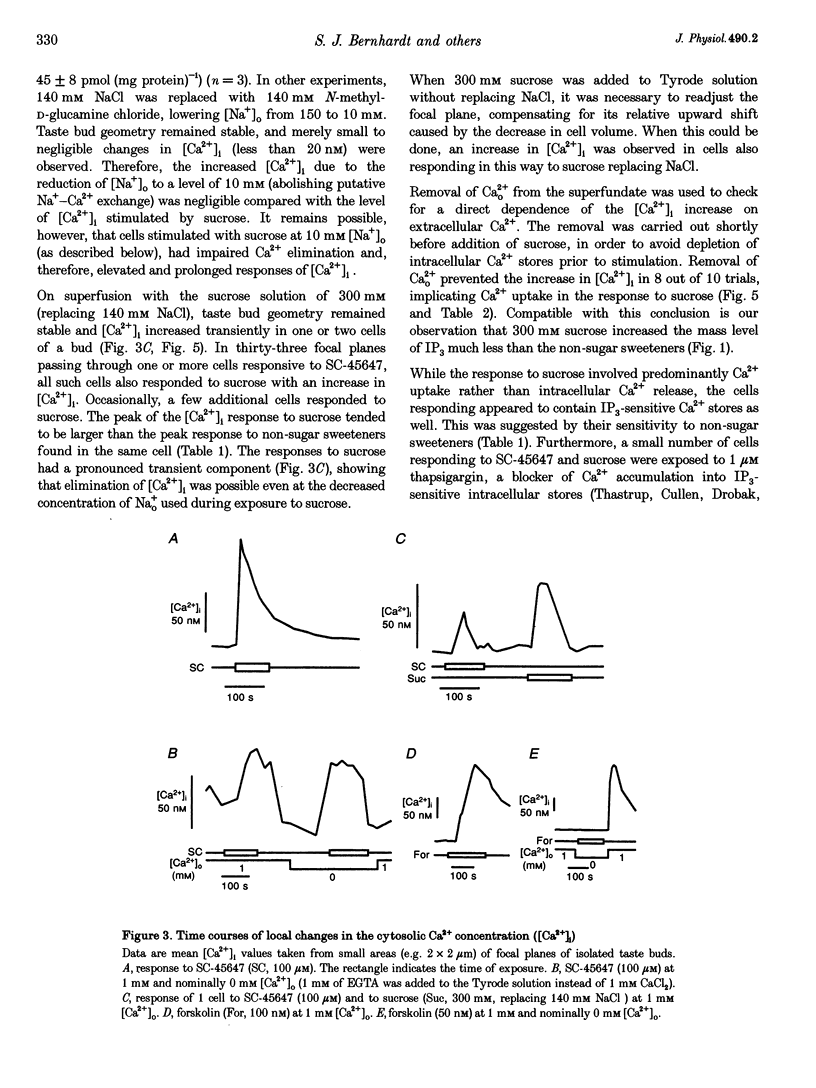
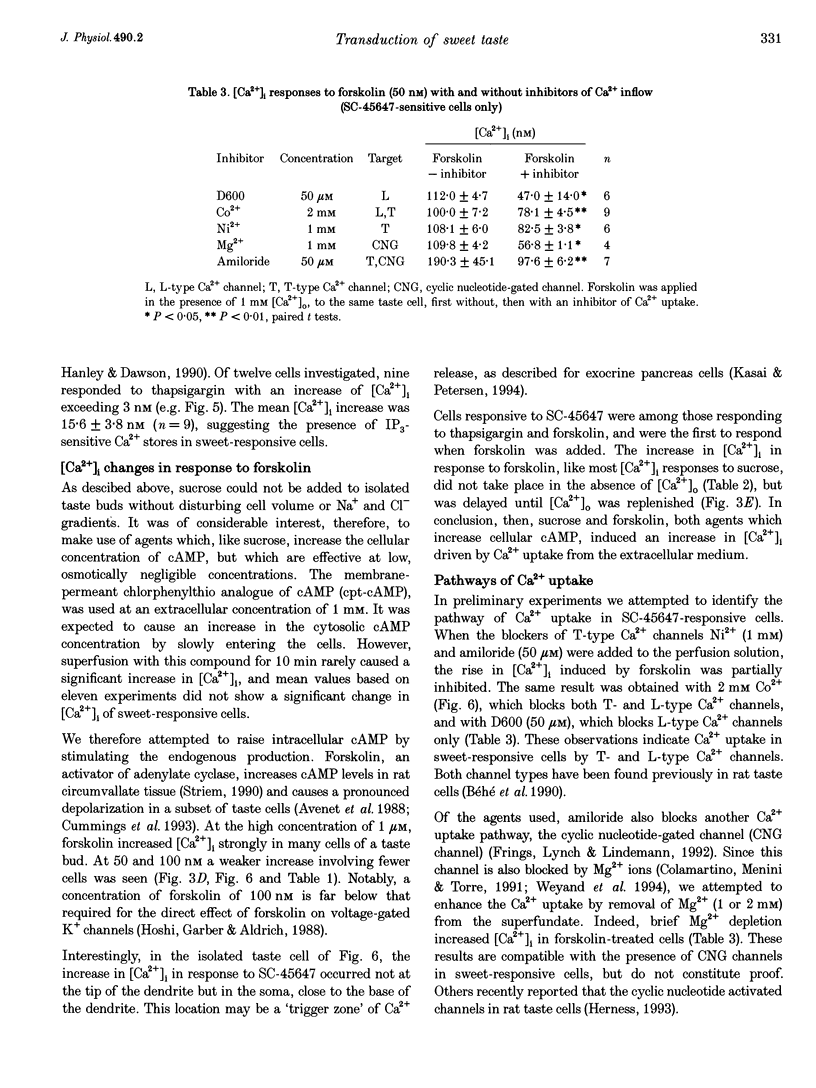
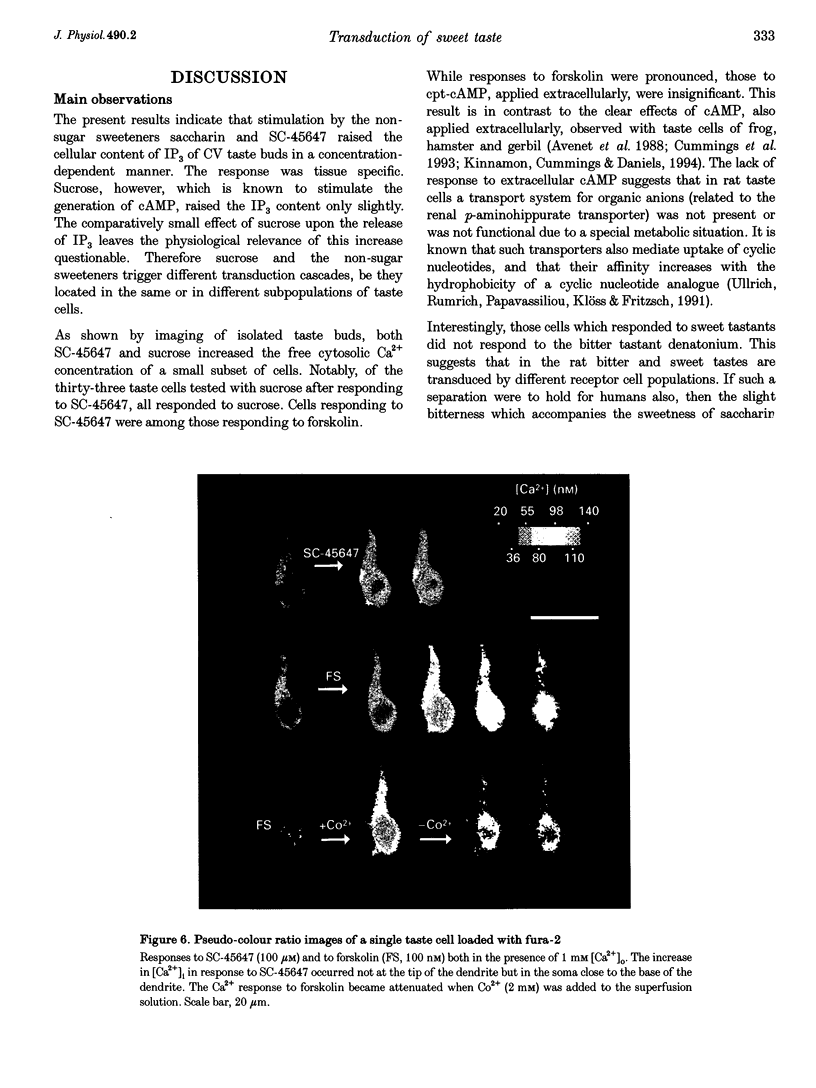
1. The transduction pathways of sweet-sensitive cells in rat circumvallate (CV) taste buds were investigated with assays for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and with Ca2+ imaging. Stimulation with the non-sugar sweeteners SC-45647 and saccharin rapidly increased the cellular content of IP3 by 400 pmol (mg protein)-1, while sucrose had a much smaller effect on IP3. As shown previously, sucrose, but not saccharin, increased the content of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) of this preparation. 2. Stimulation of isolated CV taste buds with SC-45647 increased the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) by 56.7 +/- 3.2 nM (n = 181). Due to the non-confocality of the measuring system, these concentrations are underestimates. The increase in [Ca2+]i did not require the presence of extracellular Ca2+, suggesting that the Ca2+ release was from intracellular stores. 3. Individual cells responding to the non-sugar sweeteners with Ca2+ release also responded to sucrose and to forskolin with an increase in [Ca2+]i. Such cells did not respond to the bitter tastant denatonium chloride. 4. Responses to sucrose were abolished by lowering the Ca2+ concentration of the stimulus solution, indicating Ca2+ uptake from the extracellular medium. 5. The responses of sweet-sensitive cells to forskolin were also abolished when Ca2+ ions were omitted from the stimulus solution. They were partially inhibited by the presence of Co2+, Ni2+, D600 (methoxyverapamil) and amiloride, indicating multiple pathways of Ca2+ uptake activated by cAMP. 6. In conclusion, a sweet-sensitive cell of the rat responds to sucrose with an increase in cAMP and Ca2+ uptake, but to non-sugar sweeteners with an increase in IP3 and Ca2+ release. The increase in [Ca2+]i, common to both pathways, is presumably required for synaptic exocytosis and for signal termination.
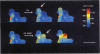
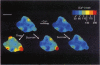
Full text
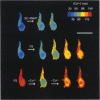
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S. Regulation of contractile proteins by phosphorylation. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):1863–1866. doi: 10.1172/JCI111148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akabas M. H., Dodd J., Al-Awqati Q. A bitter substance induces a rise in intracellular calcium in a subpopulation of rat taste cells. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1047–1050. doi: 10.1126/science.3194756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine G. J., Adler E. M., Charlton M. P. The calcium signal for transmitter secretion from presynaptic nerve terminals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:365–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avenet P., Hofmann F., Lindemann B. Transduction in taste receptor cells requires cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):351–354. doi: 10.1038/331351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avenet P., Kinnamon S. C. Cellular basis of taste reception. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1991 Aug;1(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(91)90078-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boekhoff I., Tareilus E., Strotmann J., Breer H. Rapid activation of alternative second messenger pathways in olfactory cilia from rats by different odorants. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2453–2458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béhé P., DeSimone J. A., Avenet P., Lindemann B. Membrane currents in taste cells of the rat fungiform papilla. Evidence for two types of Ca currents and inhibition of K currents by saccharin. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Nov;96(5):1061–1084. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.5.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamartino G., Menini A., Torre V. Blockage and permeation of divalent cations through the cyclic GMP-activated channel from tiger salamander retinal rods. J Physiol. 1991;440:189–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings T. A., Powell J., Kinnamon S. C. Sweet taste transduction in hamster taste cells: evidence for the role of cyclic nucleotides. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Dec;70(6):2326–2336. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.6.2326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S., Lynch J. W., Lindemann B. Properties of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels mediating olfactory transduction. Activation, selectivity, and blockage. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jul;100(1):45–67. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graminski G. F., Jayawickreme C. K., Potenza M. N., Lerner M. R. Pigment dispersion in frog melanophores can be induced by a phorbol ester or stimulation of a recombinant receptor that activates phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5957–5964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi T., Garber S. S., Aldrich R. W. Effect of forskolin on voltage-gated K+ channels is independent of adenylate cyclase activation. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.2454506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang P. M., Verma A., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Localization of phosphatidylinositol signaling components in rat taste cells: role in bitter taste transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7395–7399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakinovich W., Jr Stimulation of the gerbil's gustatory receptors by saccharin. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):49–56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00049.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Petersen O. H. Spatial dynamics of second messengers: IP3 and cAMP as long-range and associative messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Mar;17(3):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. Microdomains of high calcium concentration in a presynaptic terminal. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):677–679. doi: 10.1126/science.1350109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monck J. R., Oberhauser A. F., Keating T. J., Fernandez J. M. Thin-section ratiometric Ca2+ images obtained by optical sectioning of fura-2 loaded mast cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):745–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naim M., Ronen T., Striem B. J., Levinson M., Zehavi U. Adenylate cyclase responses to sucrose stimulation in membranes of pig circumvallate taste papillae. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1991;100(3):455–458. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(91)90203-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H. Taste response characteristics in the glossopharyngeal nerve of the rat. Kumamoto Med J. 1972 Dec 31;25(4):137–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striem B. J., Pace U., Zehavi U., Naim M., Lancet D. Sweet tastants stimulate adenylate cyclase coupled to GTP-binding protein in rat tongue membranes. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):121–126. doi: 10.1042/bj2600121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonosaki K., Funakoshi M. Cyclic nucleotides may mediate taste transduction. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):354–356. doi: 10.1038/331354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay E., Payet M. D., Gallo-Payet N. Effects of ACTH and angiotensin II on cytosolic calcium in cultured adrenal glomerulosa cells. Role of cAMP production in the ACTH effect. Cell Calcium. 1991 Nov;12(10):655–673. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90036-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Rumrich G., Papavassiliou F., Klöss S., Fritzsch G. Contraluminal p-aminohippurate transport in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. VII. Specificity: cyclic nucleotides, eicosanoids. Pflugers Arch. 1991 May;418(4):360–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00550874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand I., Godde M., Frings S., Weiner J., Müller F., Altenhofen W., Hatt H., Kaupp U. B. Cloning and functional expression of a cyclic-nucleotide-gated channel from mammalian sperm. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):859–863. doi: 10.1038/368859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Gilbert S., Birnbaumer M., Birnbaumer L. Dual signaling potential is common among Gs-coupled receptors and dependent on receptor density. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gersdorff H., Matthews G. Dynamics of synaptic vesicle fusion and membrane retrieval in synaptic terminals. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):735–739. doi: 10.1038/367735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]