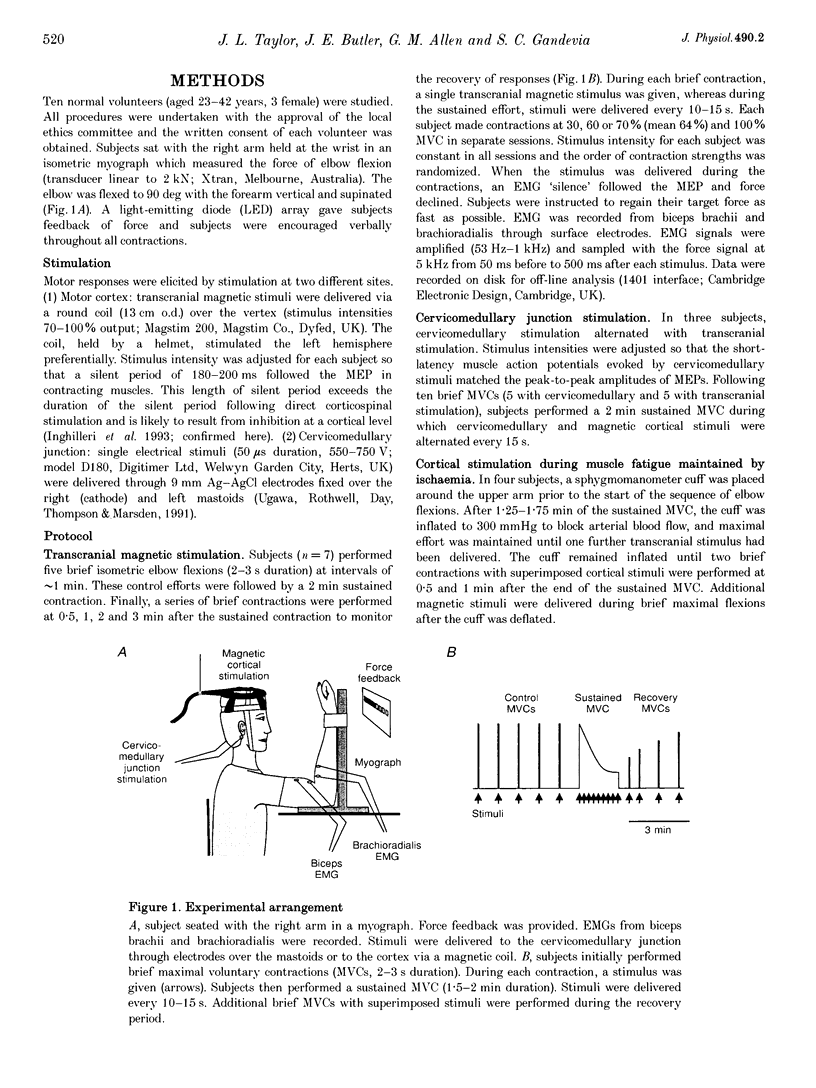
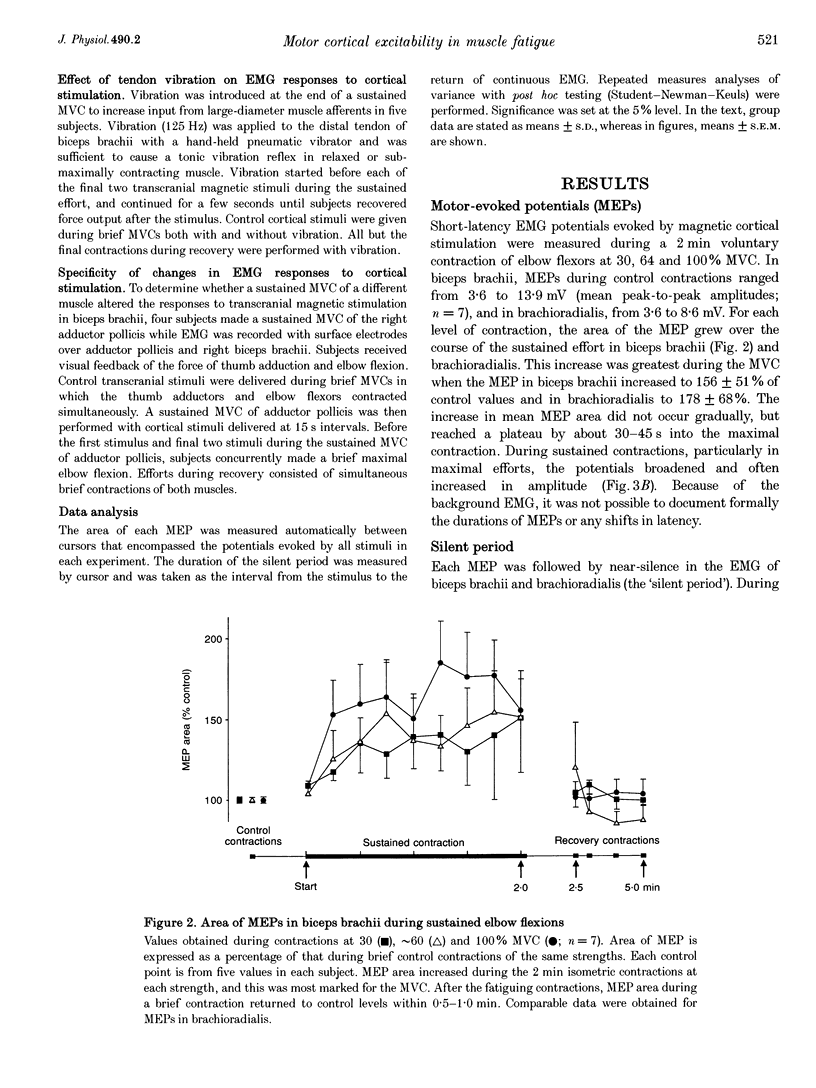
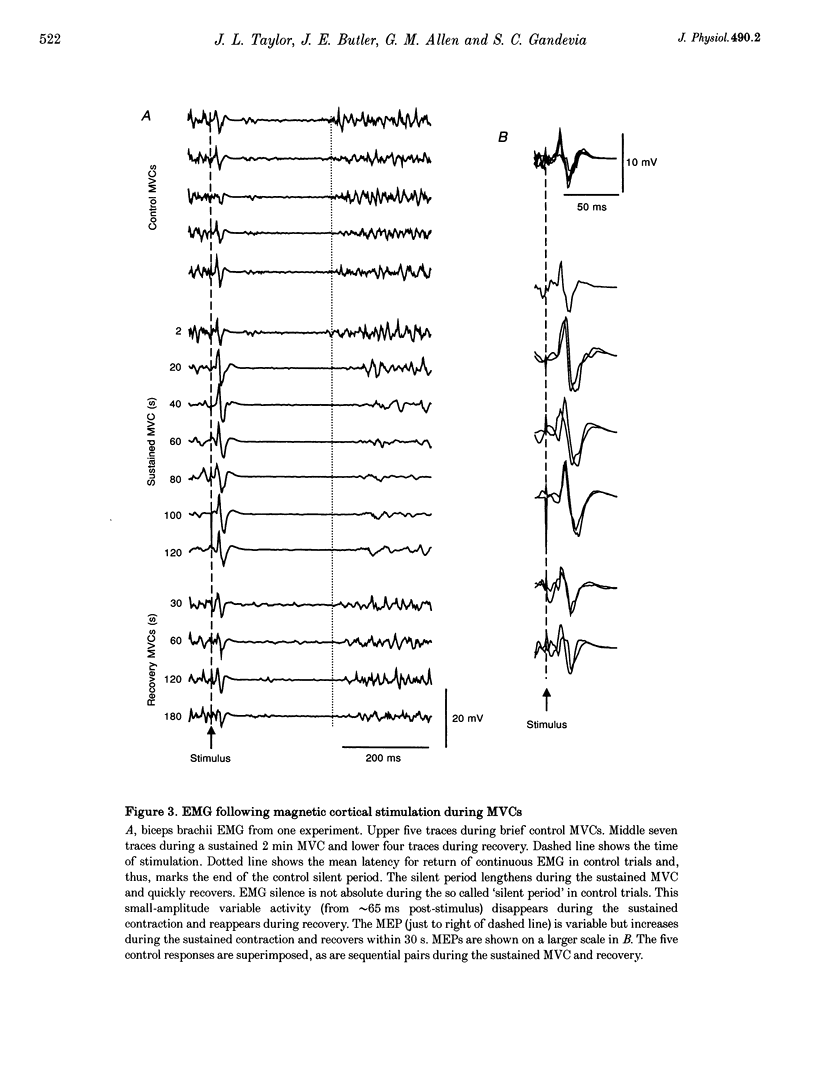
Abstract
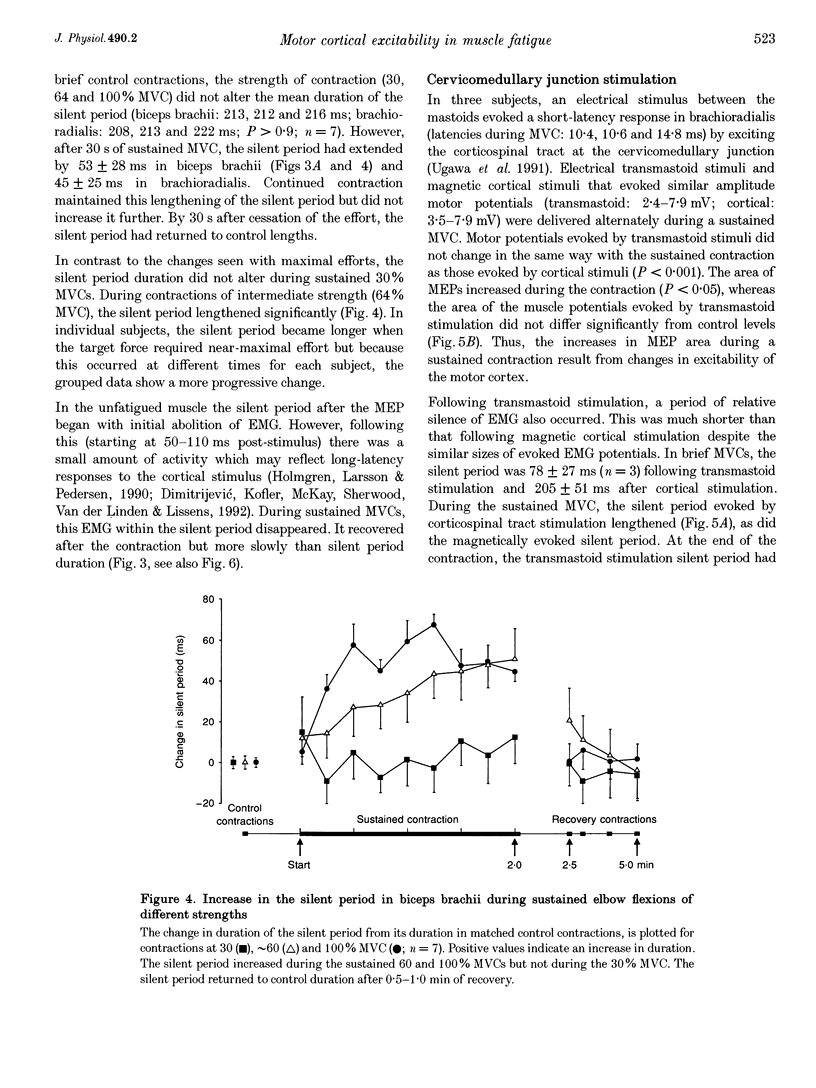
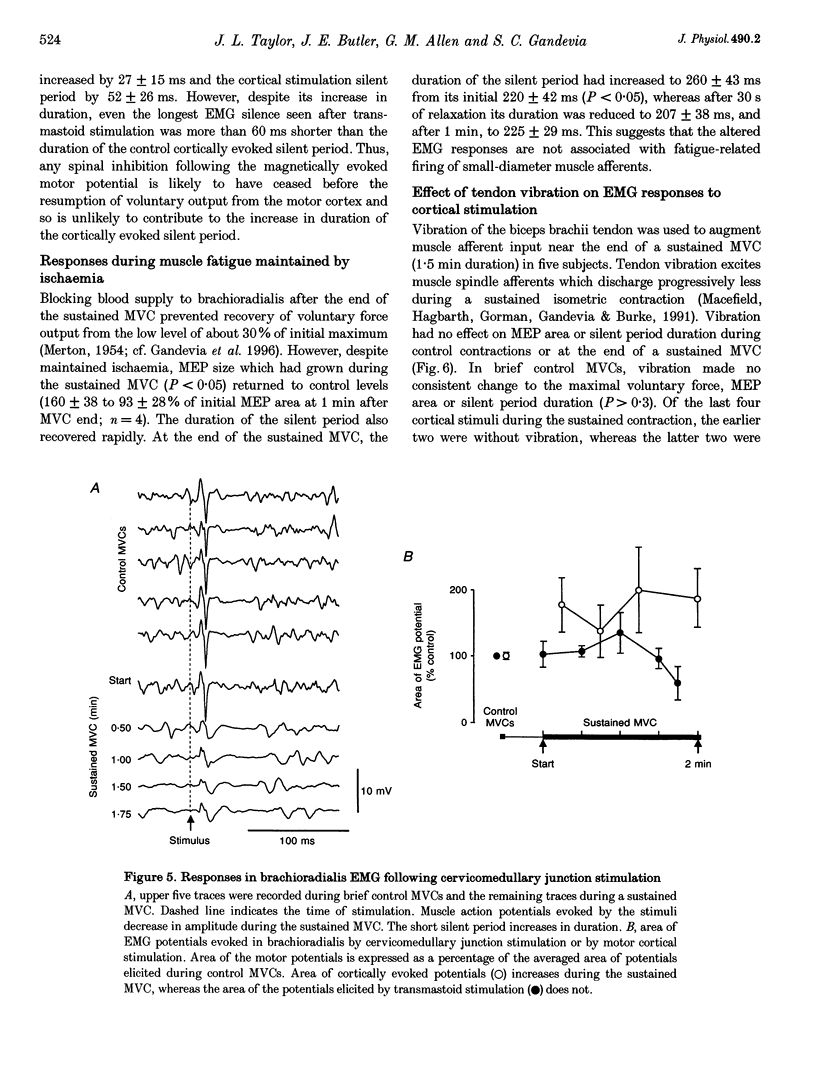
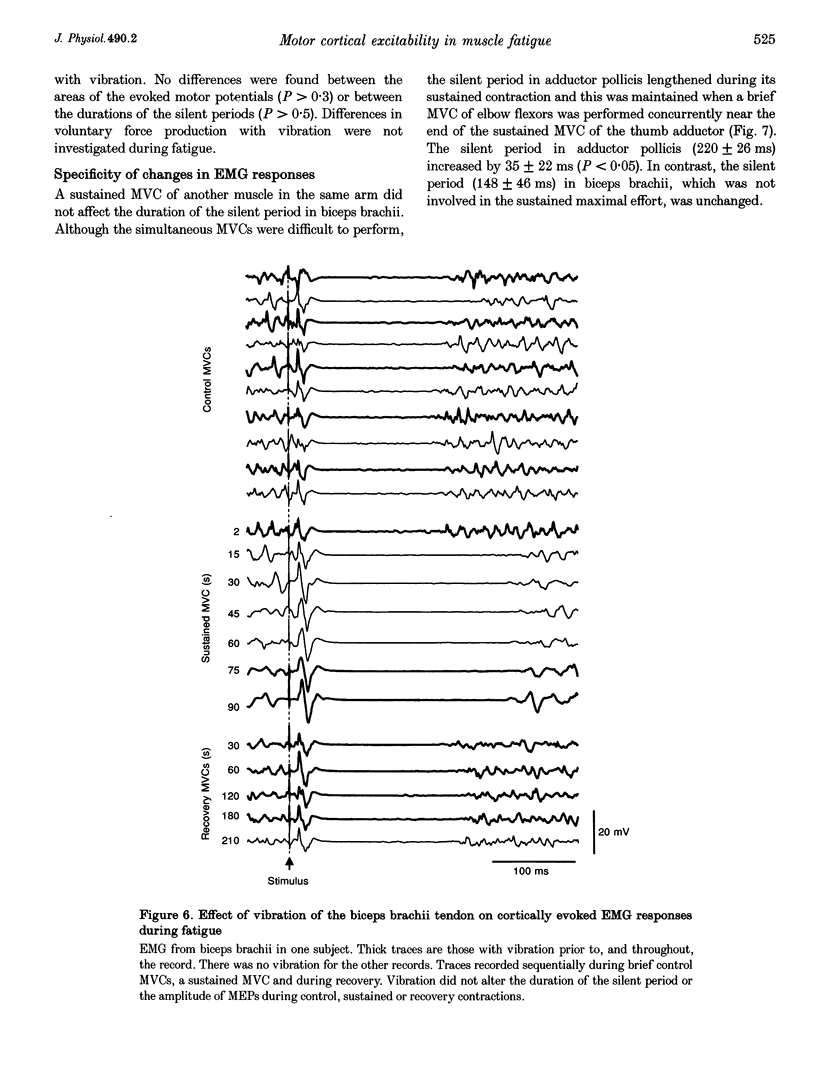
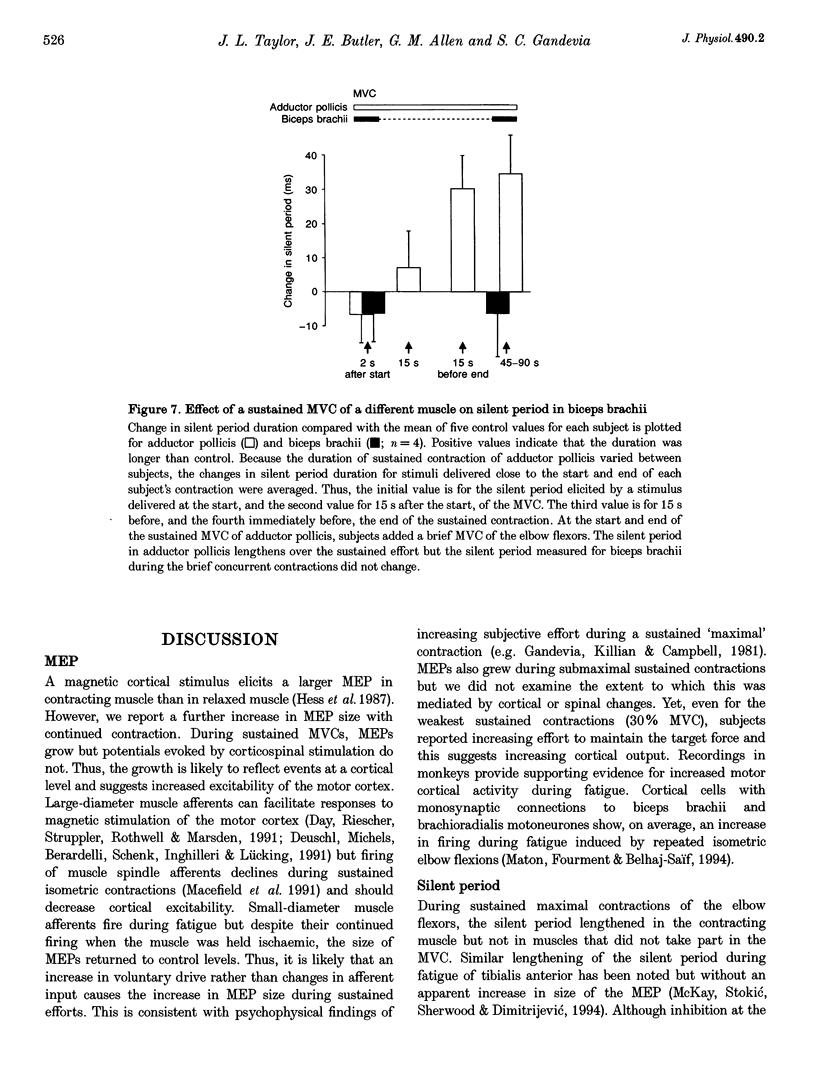
1. The excitability of the motor cortex was investigated during fatiguing con of the elbow flexors in human subjects. During sustained contractions at 30 and 1 voluntary force (MVC), the short-latency electromyographic responses (EMG) evoke brachii and brachioradialis by transcranial magnetic stimulation increased in si EMG in the elbow flexors following the evoked muscle potential (silent period), duration during a sustained MVC but not during 30% MVCs nor during a sustained M muscle (adductor pollicis). 2. When the blood supply to brachioradialis was blocked with sphygmomanometer cuff sustained MVC, the changes in EMG responses to transcranial stimulation rapidly control values, This suggests that changes in these responses during fatigue wer small-diameter muscle afferents. 3. Tendon vibration during sustained MVCs indicated that the changes in the resp cortial stimulation were not mediated by reduced muscle spindle inputs. 4. Muscle action potentials evoked in brachioradialis by electrical stimulation cervicomedullary junction did not increase in size during sustained MVCs. Thus, cortically evoked responses during sustained MVCs reflects a change in cortical Although the silent period following cervicomedullary stimulation lengthened, it substantially shorter than the cortically evoked silent period. 5. The altered EMG responses to transcranial stimulation during fatigue suggest exitation and increased inhibition in the motor cortex. As these changes were un manipulation of afferent input they presumably result from intrinsic cortical pr altered voluntary drive to the motor cortex.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amassian V. E., Stewart M., Quirk G. J., Rosenthal J. L. Physiological basis of motor effects of a transient stimulus to cerebral cortex. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jan;20(1):74–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasil-Neto J. P., Cohen L. G., Hallett M. Central fatigue as revealed by postexercise decrement of motor evoked potentials. Muscle Nerve. 1994 Jul;17(7):713–719. doi: 10.1002/mus.880170702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasil-Neto J. P., Pascual-Leone A., Valls-Solé J., Cammarota A., Cohen L. G., Hallett M. Postexercise depression of motor evoked potentials: a measure of central nervous system fatigue. Exp Brain Res. 1993;93(1):181–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00227794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey N. J., Romaiguère P., Maskill D. W., Ellaway P. H. Suppression of voluntary motor activity revealed using transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex in man. J Physiol. 1994 Jun 1;477(Pt 2):223–235. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Dressler D., Maertens de Noordhout A., Marsden C. D., Nakashima K., Rothwell J. C., Thompson P. D. Electric and magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex: surface EMG and single motor unit responses. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:449–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day B. L., Riescher H., Struppler A., Rothwell J. C., Marsden C. D. Changes in the response to magnetic and electrical stimulation of the motor cortex following muscle stretch in man. J Physiol. 1991 Feb;433:41–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschl G., Michels R., Berardelli A., Schenck E., Inghilleri M., Lücking C. H. Effects of electric and magnetic transcranial stimulation on long latency reflexes. Exp Brain Res. 1991;83(2):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00231165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrijević M. R., Kofler M., McKay W. B., Sherwood A. M., Van der Linden C., Lissens M. A. Early and late lower limb motor evoked potentials elicited by transcranial magnetic motor cortex stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 Dec;85(6):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(92)90049-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgley S. A., Eyre J. A., Lemon R. N., Miller S. Excitation of the corticospinal tract by electromagnetic and electrical stimulation of the scalp in the macaque monkey. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:301–320. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr P., Agostino R., Hallett M. Spinal motor neuron excitability during the silent period after cortical stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Aug;81(4):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(91)90011-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Allen G. M., Butler J. E., Taylor J. L. Supraspinal factors in human muscle fatigue: evidence for suboptimal output from the motor cortex. J Physiol. 1996 Jan 15;490(Pt 2):529–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandevia S. C., Killian K. J., Campbell E. J. The effect of respiratory muscle fatigue on respiratory sensations. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Apr;60(4):463–466. doi: 10.1042/cs0600463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess C. W., Mills K. R., Murray N. M. Responses in small hand muscles from magnetic stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:397–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren H., Larsson L. E., Pedersen S. Late muscular responses to transcranial cortical stimulation in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1990 Mar;75(3):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(90)90170-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghilleri M., Berardelli A., Cruccu G., Manfredi M. Silent period evoked by transcranial stimulation of the human cortex and cervicomedullary junction. J Physiol. 1993 Jul;466:521–534. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujirai T., Caramia M. D., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Thompson P. D., Ferbert A., Wroe S., Asselman P., Marsden C. D. Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:501–519. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macefield G., Hagbarth K. E., Gorman R., Gandevia S. C., Burke D. Decline in spindle support to alpha-motoneurones during sustained voluntary contractions. J Physiol. 1991;440:497–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzocchio R., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Thompson P. D. Effect of tonic voluntary activity on the excitability of human motor cortex. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 15;474(2):261–267. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priori A., Berardelli A., Inghilleri M., Polidori L., Manfredi M. Electromyographic silent period after transcranial brain stimulation in Huntington's disease. Mov Disord. 1994 Mar;9(2):178–182. doi: 10.1002/mds.870090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roick H., von Giesen H. J., Benecke R. On the origin of the postexcitatory inhibition seen after transcranial magnetic brain stimulation in awake human subjects. Exp Brain Res. 1993;94(3):489–498. doi: 10.1007/BF00230207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggs W. J., Cros D., Macdonell R. A., Chiappa K. H., Fang J., Day B. J. Cortical and spinal motor excitability during the transcranial magnetic stimulation silent period in humans. Brain Res. 1993 Nov 19;628(1-2):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90935-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugawa Y., Rothwell J. C., Day B. L., Thompson P. D., Marsden C. D. Percutaneous electrical stimulation of corticospinal pathways at the level of the pyramidal decussation in humans. Ann Neurol. 1991 Apr;29(4):418–427. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassermann E. M., Pascual-Leone A., Valls-Solé J., Toro C., Cohen L. G., Hallett M. Topography of the inhibitory and excitatory responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation in a hand muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1993 Dec;89(6):424–433. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(93)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]