Abstract
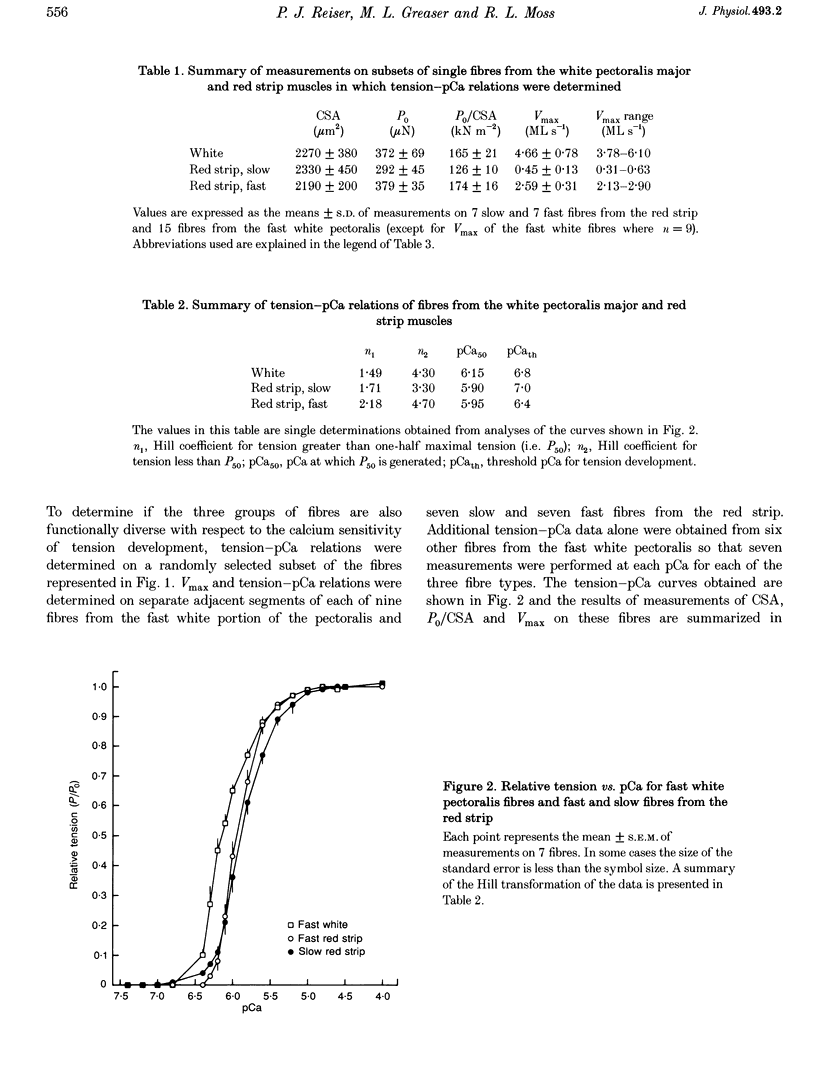
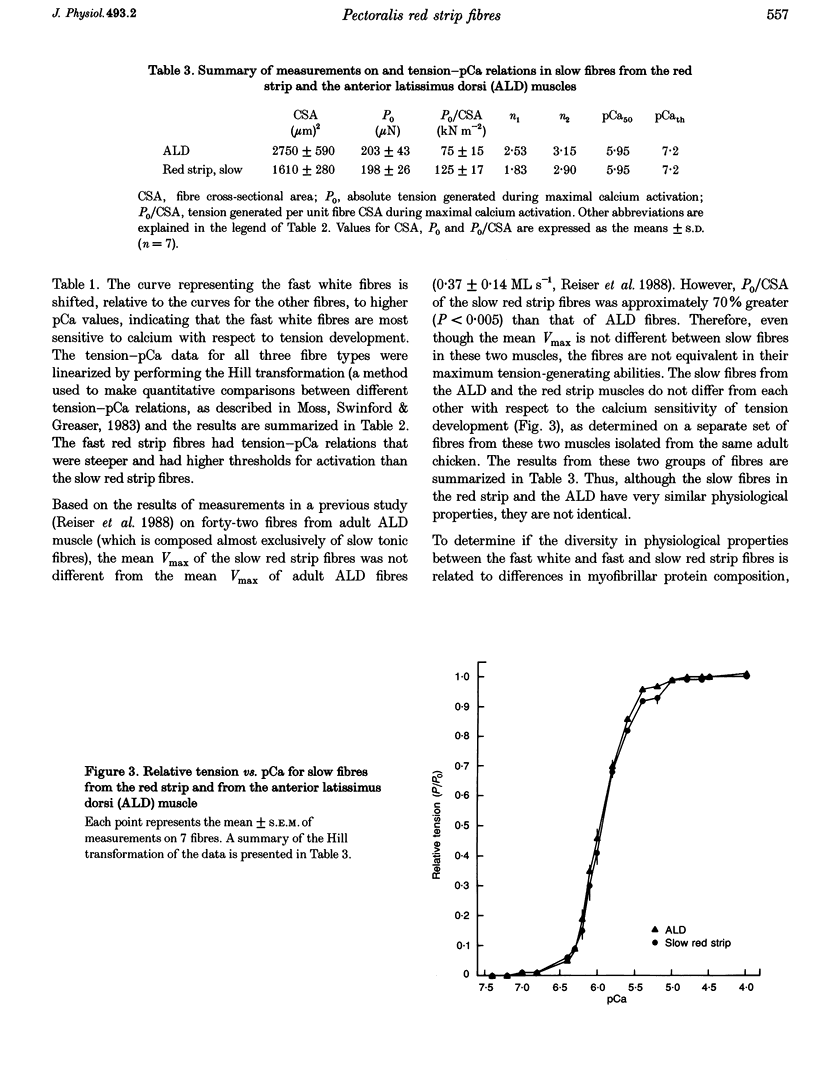
1. The contractile properties of single muscle fibres of the red strip region of adult chicken pectoralis major (PM) muscle, some of which are known to express an embryonic isoform of myosin heavy chain (MHC), were determined and compared with the properties of the fast white fibres of the PM and the slow tonic fibres of the anterior latissimus dorsi (ALD) muscle. 2. The red strip fibres could be classified into two groups, fast and slow. The mean velocity of unloaded shortening (Vmax) in fast red strip fibres was approximately half the Vmax of fast white fibres. Vmax of slow red strip fibres was less than 20% of the value for fast red strip fibres and was not different from Vmax of ALD fibres. 3. The tension-generating ability, i.e. the maximal isometric tension/fibre cross-sectional area (P0/CSA), was the same in fast red strip fibres and fast white fibres. P0/CSA was approximately 30% lower in slow red strip fibres compared with fast red strip fibres but was 70% greater in slow red strip fibres compared with ALD fibres. 4. The tension-pCa relation of fast red strip fibres was shifted to lower pCa values, indicating a lower calcium sensitivity compared with fast white fibres, and this difference was associated with a difference in troponin T isoform composition. The tension-pCa relation of slow red strip fibres was not different from that in ALD fibres. 5. The difference in Vmax between fast red strip fibres and fast white fibres was associated with different MHC compositions of these fibres. 6. The myofibrillar protein isoform composition of slow red strip fibres was identical to that of the slow tonic fibres of ALD muscle and these two groups of fibres had very similar contractile properties.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bormioli S. P., Sartore S., Vitadello M., Schiaffino S. "Slow" myosins in vertebrate skeletal muscle. An immunofluorescence study. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):672–681. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottinelli R., Betto R., Schiaffino S., Reggiani C. Unloaded shortening velocity and myosin heavy chain and alkali light chain isoform composition in rat skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 15;478(Pt 2):341–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottinelli R., Canepari M., Reggiani C., Stienen G. J. Myofibrillar ATPase activity during isometric contraction and isomyosin composition in rat single skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 15;481(Pt 3):663–675. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. T., Stockdale F. E. The developmental program of fast myosin heavy chain expression in avian skeletal muscles. Dev Biol. 1986 Dec;118(2):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhoot G. K. Identification and distribution of the fast class of troponin T in the adult and developing avian skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Oct;9(5):446–455. doi: 10.1007/BF01774070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddinger T. J., Moss R. L. Mechanical properties of skinned single fibers of identified types from rat diaphragm. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C210–C218. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman A. C., Lexell J., Sjöström M., Squire J. M. Structural diversity in muscle fibres of chicken breast. Cell Tissue Res. 1988 Feb;251(2):281–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00215835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman K. A. The velocity of unloaded shortening and its relation to sarcomere length and isometric force in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1979 Jun;291:143–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Lowey S. Polymorphism of myosin among skeletal muscle fiber types. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):760–779. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. Influence of osmotic compression on calcium activation and tension in skinned muscle fibers of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Oct;391(4):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00581519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Moss R. L., Reiser P. J. Variations in contractile properties of rabbit single muscle fibres in relation to troponin T isoforms and myosin light chains. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:85–98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove B. K., Cerny L., Perriard J. C., Eppenberger H. M., Thornell L. E. Fiber type-specific distribution of M-band proteins in chicken muscle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Apr;37(4):447–454. doi: 10.1177/37.4.2926123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hikida R. S. Quantitative ultrastructure of histochemically identified avian skeletal muscle fiber types. Anat Rec. 1987 Jun;218(2):128–135. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092180206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. S., Tu Z. H., Lemanski L. F. Anti-troponin-T monoclonal antibody crossreacts with all muscle types. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Oct;5(5):515–526. doi: 10.1007/BF00713258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Waller G. S., Trybus K. M. Function of skeletal muscle myosin heavy and light chain isoforms by an in vitro motility assay. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20414–20418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Waller G. S., Trybus K. M. Skeletal muscle myosin light chains are essential for physiological speeds of shortening. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):454–456. doi: 10.1038/365454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda R., Bandman E., Strohman R. C. Regional differences in the expression of myosin light chains and tropomyosin subunits during development of chicken breast muscle. Dev Biol. 1983 Feb;95(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Swinford A. E., Greaser M. L. Alterations in the Ca2+ sensitivity of tension development by single skeletal muscle fibers at stretched lengths. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84329-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser P. J., Greaser M. L., Moss R. L. Developmental changes in troponin T isoform expression and tension production in chicken single skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:573–588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser P. J., Greaser M. L., Moss R. L. Myosin heavy chain composition of single cells from avian slow skeletal muscle is strongly correlated with velocity of shortening during development. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser P. J., Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. Shortening velocity in single fibers from adult rabbit soleus muscles is correlated with myosin heavy chain composition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9077–9080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq S. A., Shimizu T., Fischman D. A. Heterogeneity of type 1 skeletal muscle fibers revealed by monoclonal antibody to slow myosin. Muscle Nerve. 1984 Jun;7(5):380–387. doi: 10.1002/mus.880070507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shear C. R., Bandman E., Rosser B. W. Myosin heavy chain expression during development and following denervation of fast fibers in the red strip of the chicken pectoralis. Dev Biol. 1988 Jun;127(2):326–337. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Kushmerick M. J., Mabuchi K., Sréter F. A., Gergely J. Myosin alkali light chain and heavy chain variations correlate with altered shortening velocity of isolated skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):9034–9039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K., Dhoot G. K. Heterogeneity and distribution of fast myosin heavy chains in some adult vertebrate skeletal muscles. Histochemistry. 1992 May;97(4):361–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00270039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]