Abstract
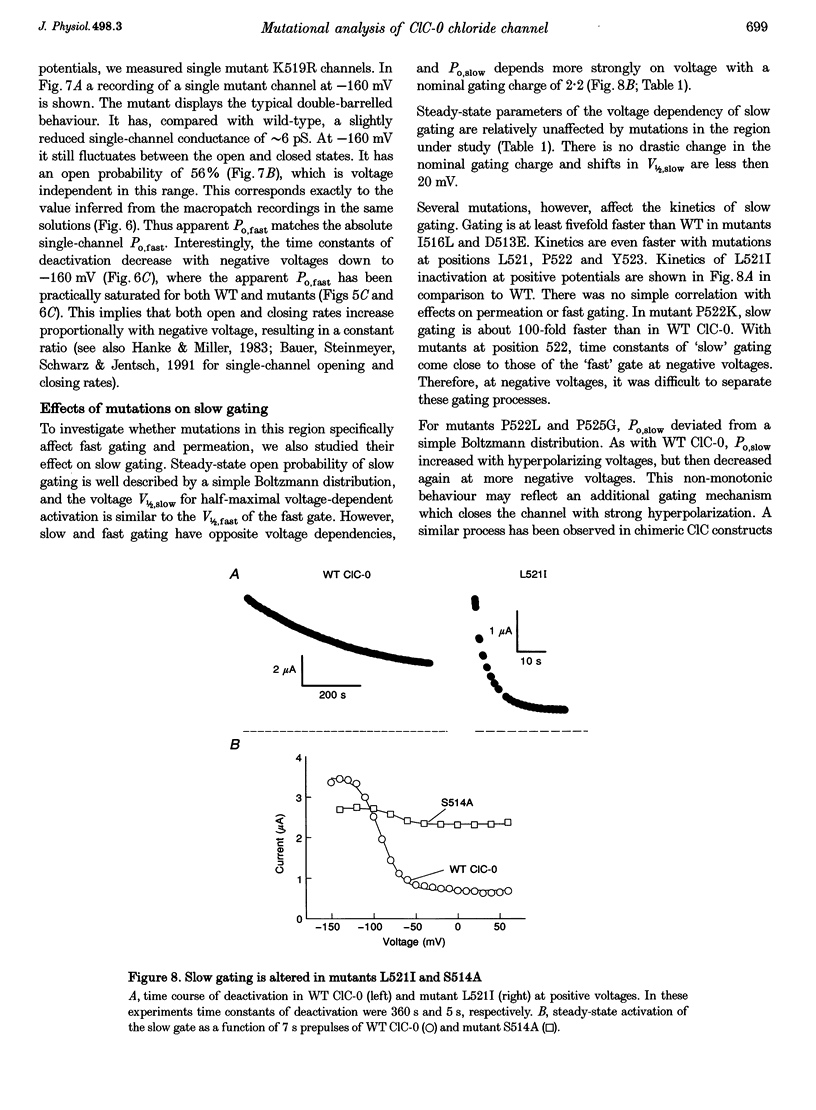
1. The chloride channel from the Torpedo electric organ, ClC-0, is controlled by two distinct ('fast' and 'slow') voltage-dependent gates. Here we investigate the effects of mutations in a region after putative transmembrane domain D12. A mutation in this region has previously been shown to change fast gating and permeation. 2. We used a combination of site-directed mutagenesis with two-electrode voltage-clamp and patch-clamp measurements. 3. Most conservative substitutions have minor effects, while more drastic mutations change kinetics and voltage dependence of fast gating, as well as ion selectivity and rectification. 4. While ClC-0 wild-type (WT) channels deactivate fully in two-electrode voltage clamp at negative voltages, channels do not close completely in patch-clamp experiments. Open probability is increased by intracellular chloride in a concentration- but not voltage-dependent manner. 5. In several mutants, including K519R, the minimal macroscopic open probability of fast gating is larger than in WT. Mutant channels fluctuate at negative potentials between open and closed conformations. Open probability is much more effectively increased by intracellular chloride than in WT. The observations support the idea that permeating ions inside the pore stabilize the open state. 6. Besides effects on permeation and gating of single protopores, some mutations affect 'slow' gating. In summary, the region after D12 participates in fast as well as in slow gating; mutations additionally influence permeation properties.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astill D. S., Rychkov G., Clarke J. D., Hughes B. P., Roberts M. L., Bretag A. H. Characteristics of skeletal muscle chloride channel C1C-1 and point mutant R304E expressed in Sf-9 insect cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Apr 26;1280(2):178–186. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. K., Steinmeyer K., Schwarz J. R., Jentsch T. J. Completely functional double-barreled chloride channel expressed from a single Torpedo cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11052–11056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Miller C. Nonequilibrium gating and voltage dependence of the ClC-0 Cl- channel. J Gen Physiol. 1996 Oct;108(4):237–250. doi: 10.1085/jgp.108.4.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahlke C., Rüdel R., Mitrovic N., Zhou M., George A. L., Jr An aspartic acid residue important for voltage-dependent gating of human muscle chloride channels. Neuron. 1995 Aug;15(2):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gründer S., Thiemann A., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. Regions involved in the opening of CIC-2 chloride channel by voltage and cell volume. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):759–762. doi: 10.1038/360759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Miller C. Single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Activation by protons. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jul;82(1):25–45. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Steinmeyer K., Schwarz G. Primary structure of Torpedo marmorata chloride channel isolated by expression cloning in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):510–514. doi: 10.1038/348510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieferle S., Fong P., Bens M., Vandewalle A., Jentsch T. J. Two highly homologous members of the ClC chloride channel family in both rat and human kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6943–6947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludewig U., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. Two physically distinct pores in the dimeric ClC-0 chloride channel. Nature. 1996 Sep 26;383(6598):340–343. doi: 10.1038/383340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Methfessel C., Witzemann V., Takahashi T., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Patch clamp measurements on Xenopus laevis oocytes: currents through endogenous channels and implanted acetylcholine receptor and sodium channels. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Dec;407(6):577–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00582635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton R. E., Pheasant D. J., Miller C. Homodimeric architecture of a ClC-type chloride ion channel. Nature. 1996 Sep 26;383(6598):337–340. doi: 10.1038/383337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton R. E., Pheasant D. J., Miller C. Purification, reconstitution, and subunit composition of a voltage-gated chloride channel from Torpedo electroplax. Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 15;33(45):13189–13198. doi: 10.1021/bi00249a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Open-state substructure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Dec 1;299(1097):401–411. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., White M. M. Dimeric structure of single chloride channels from Torpedo electroplax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2772–2775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Ludewig U., Rehfeldt A., Jentsch T. J. Gating of the voltage-dependent chloride channel CIC-0 by the permeant anion. Nature. 1995 Feb 9;373(6514):527–531. doi: 10.1038/373527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Steinmeyer K., Jentsch T. J. Low single channel conductance of the major skeletal muscle chloride channel, ClC-1. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80753-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Steinmeyer K., Koch M. C., Jentsch T. J. Mutations in dominant human myotonia congenita drastically alter the voltage dependence of the CIC-1 chloride channel. Neuron. 1995 Dec;15(6):1455–1463. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth F. J. Voltage gating of ion channels. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 Feb;27(1):1–40. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Lorenz C., Pusch M., Koch M. C., Jentsch T. J. Multimeric structure of ClC-1 chloride channel revealed by mutations in dominant myotonia congenita (Thomsen). EMBO J. 1994 Feb 15;13(4):737–743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Ortland C., Jentsch T. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a developmentally regulated skeletal muscle chloride channel. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):301–304. doi: 10.1038/354301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W. Electrophysiological recording from Xenopus oocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1992;207:319–339. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07021-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann A., Gründer S., Pusch M., Jentsch T. J. A chloride channel widely expressed in epithelial and non-epithelial cells. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):57–60. doi: 10.1038/356057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Sasaki S., Furukawa T., Hiraoka M., Imai T., Hirata Y., Marumo F. Molecular cloning of a chloride channel that is regulated by dehydration and expressed predominantly in kidney medulla. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3821–3824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. M., Miller C. A voltage-gated anion channel from the electric organ of Torpedo californica. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10161–10166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


