Abstract
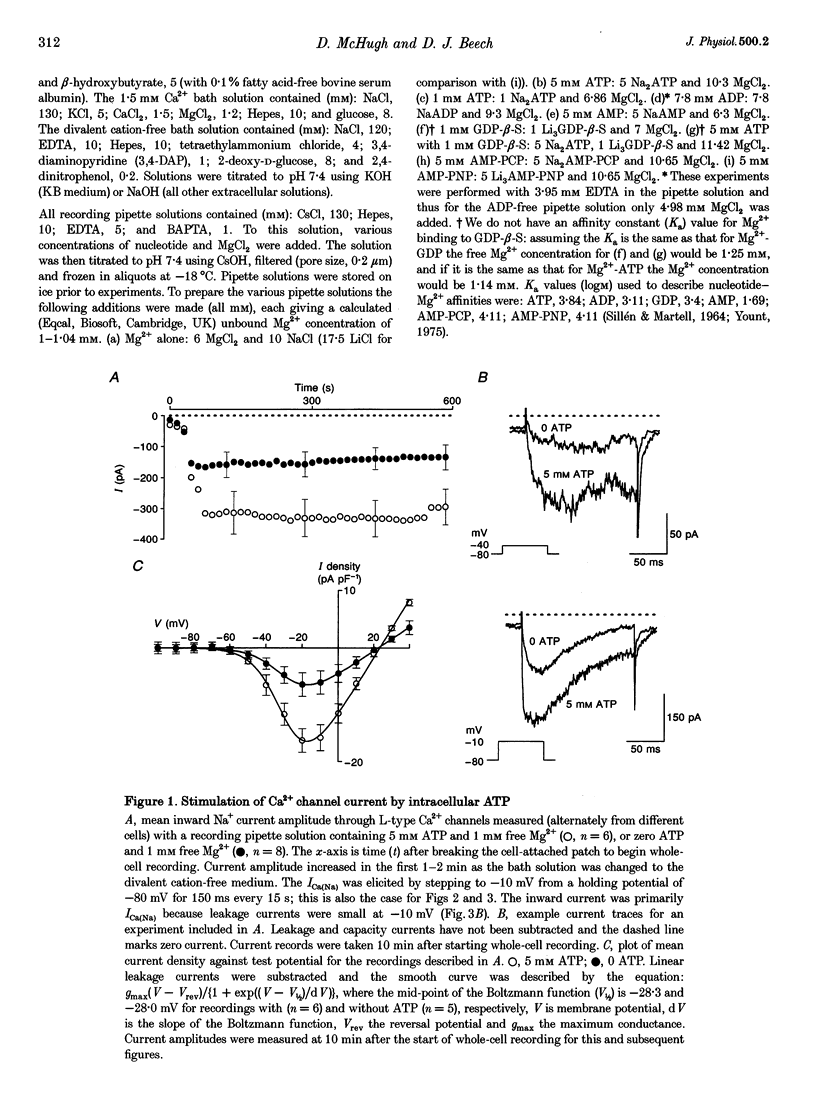
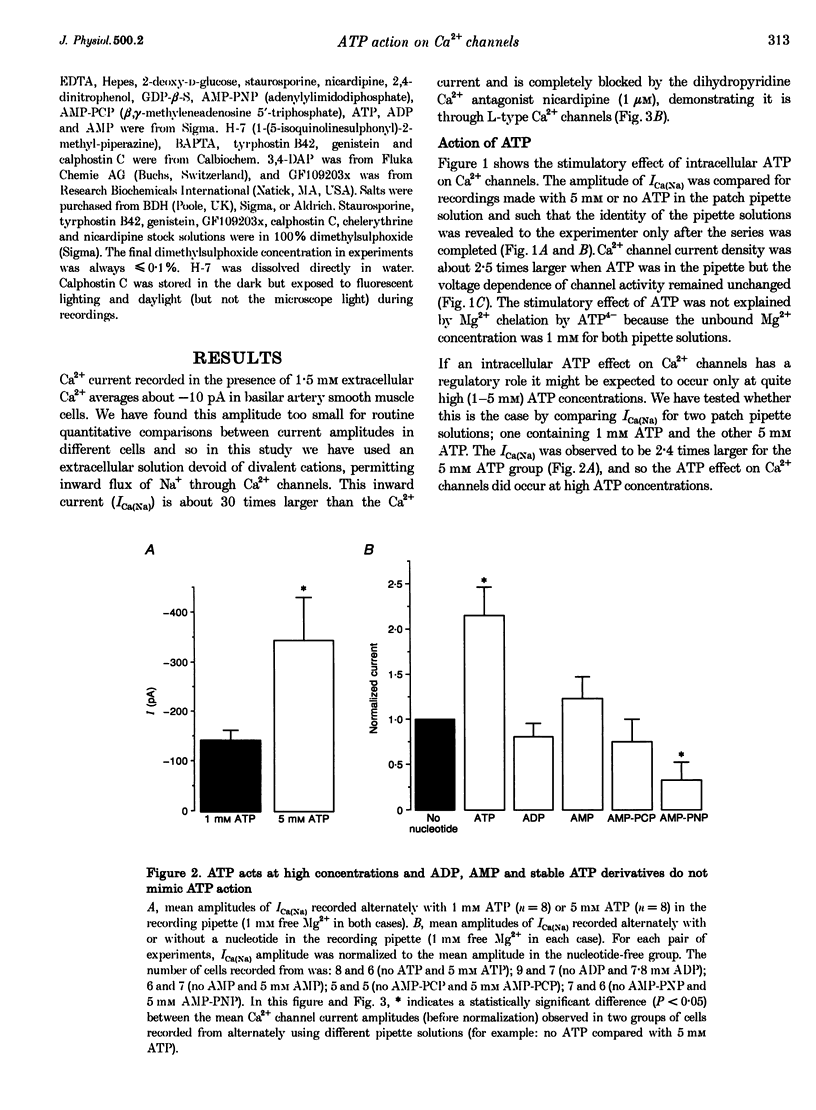
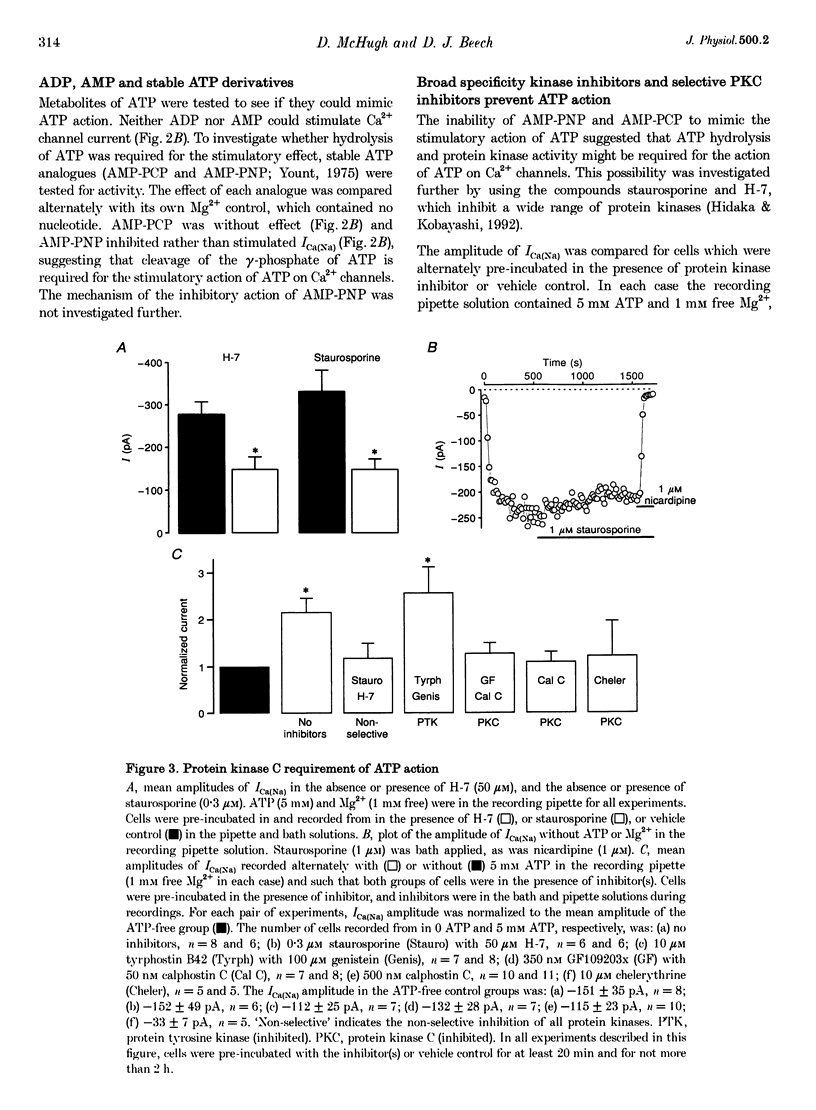
1. Smooth muscle cells were isolated from guinea-pig basilar artery and conventional whole-cell recordings of Ca2+ channel activity were made at room temperature within 7 h of the isolation procedure. The purpose of the study was to investigate the mechanism of the stimulatory action of intracellular ATP on Ca2+ channels. 2. High (millimolar) concentrations of ATP were needed to produce stimulation of Ca2+ channels, and neither ADP nor AMP mimicked the action of ATP. 3.The ATP effect was not mimicked by stable ATP derivatives (AMP-PNP or AMP-PCP) and was abolished by incubation of cells in non-specific protein kinase inhibitors (staurosporine or H-7) or specific protein kinase C inhibitors (GF109203x, calphostin C or chelerythrine) but not by tyrosine kinase inhibitors (tyrphostin B42 and genistein). 4. The data suggest that ATP-induced stimulation of L-type Ca2+ channels requires functional activity of a protein kinase C isozyme.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ogawara H. Use and specificity of genistein as inhibitor of protein-tyrosine kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:362–370. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01032-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Miller F. D., Merriman R. L., Howbert J. J., Heath W. F., Kobayashi E., Takahashi I., Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Inhibition of protein kinase C by calphostin C is light-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90922-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhamdani A., Bossu J. L., Feltz A. ADP exerts a protective effect against rundown of the Ca2+ current in bovine chromaffin cells. Pflugers Arch. 1995 Jul;430(3):401–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00373916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazit A., Osherov N., Posner I., Yaish P., Poradosu E., Gilon C., Levitzki A. Tyrphostins. 2. Heterocyclic and alpha-substituted benzylidenemalononitrile tyrphostins as potent inhibitors of EGF receptor and ErbB2/neu tyrosine kinases. J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1896–1907. doi: 10.1021/jm00110a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert J. M., Augereau J. M., Gleye J., Maffrand J. P. Chelerythrine is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):993–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Kobayashi R. Pharmacology of protein kinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:377–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.002113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakawa Y., Kuga T., Kobayashi S., Kanaide H., Takeshita A. Dual regulation of L-type Ca2+ channels by serotonin 2 receptor stimulation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 2):H544–H549. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1995.268.2.H544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvalby O., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Paulsen O., Czernik A. J., Nairn A. C., Godfraind J. M., Jensen V., Raastad M., Storm J. F., Andersen P. Specificity of protein kinase inhibitor peptides and induction of long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H., Jirousek M. R., Koya D., Takagi C., Xia P., Clermont A., Bursell S. E., Kern T. S., Ballas L. M., Heath W. F. Amelioration of vascular dysfunctions in diabetic rats by an oral PKC beta inhibitor. Science. 1996 May 3;272(5262):728–731. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5262.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Hume J. R., Keef K. D. Regulation of Ca2+ channels by cAMP and cGMP in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1993 Dec;73(6):1128–1137. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.6.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil R. A., Lajoie C., Resnick M. S., Morgan K. G. Ca(2+)-independent isoforms of protein kinase C differentially translocate in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):C714–C719. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.3.C714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Mikawa K., Hashimoto K., Yasuda I., Tanaka S., Tominaga M., Kuroda T., Nishizuka Y. Limited proteolysis of protein kinase C subspecies by calcium-dependent neutral protease (calpain). J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4088–4092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprêtre N., Mironneau J., Morel J. L. Both alpha 1A- and alpha 2A-adrenoreceptor subtypes stimulate voltage-operated L-type calcium channels in rat portal vein myocytes. Evidence for two distinct transduction pathways. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29546–29552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loirand G., Pacaud P., Mironneau C., Mironneau J. GTP-binding proteins mediate noradrenaline effects on calcium and chloride currents in rat portal vein myocytes. J Physiol. 1990 Sep;428:517–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., Pelzer S., Trautwein W., Pelzer D. J. Regulation and modulation of calcium channels in cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells. Physiol Rev. 1994 Apr;74(2):365–507. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1994.74.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh D., Beech D. J. Modulation of Ca2+ channel activity by ATP metabolism and internal Mg2+ in guinea-pig basilar artery smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1996 Apr 15;492(Pt 2):359–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke B., Backx P. H., Marban E. Phosphorylation-independent modulation of L-type calcium channels by magnesium-nucleotide complexes. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):245–248. doi: 10.1126/science.1321495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Modulation of ionic currents in smooth muscle balls of the rabbit intestine by intracellularly perfused ATP and cyclic AMP. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(5):465–473. doi: 10.1007/BF00585070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Sperelakis N. ATP regulation of the slow calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells of guinea pig mesenteric artery. Circ Res. 1989 Jan;64(1):145–154. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike M., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Histamine H3-receptor activation augments voltage-dependent Ca2+ current via GTP hydrolysis in rabbit saphenous artery. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:133–152. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okashiro T., Tokuno H., Fukumitsu T., Hayashi H., Tomita T. Effects of intracellular ATP on calcium current in freshly dispersed single cells of guinea-pig portal vein. Exp Physiol. 1992 Sep;77(5):719–731. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1992.sp003638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H. A., Dolphin A. C. Inhibition of omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca2+ channel currents by internal Mg2+ in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Dec;425(5-6):518–527. doi: 10.1007/BF00374880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuhmann K., Groschner K. Protein kinase-C mediates dual modulation of L-type Ca2+ channels in human vascular smooth muscle. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 21;341(2-3):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. K., Colbran R. J., Soderling T. R. Specificities of autoinhibitory domain peptides for four protein kinases. Implications for intact cell studies of protein kinase function. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1837–1840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toullec D., Pianetti P., Coste H., Bellevergue P., Grand-Perret T., Ajakane M., Baudet V., Boissin P., Boursier E., Loriolle F. The bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15771–15781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unno T., Komori S., Ohashi H. Inhibitory effect of muscarinic receptor activation on Ca2+ channel current in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1995 May 1;484(Pt 3):567–581. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivaudou M. B., Clapp L. H., Walsh J. V., Jr, Singer J. J. Regulation of one type of Ca2+ current in smooth muscle cells by diacylglycerol and acetylcholine. FASEB J. 1988 Jun;2(9):2497–2504. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.9.2453389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijetunge S., Hughes A. D. pp60c-src increases voltage-operated calcium channel currents in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Dec 26;217(3):1039–1044. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki T., Komuro I., Kudoh S., Zou Y., Shiojima I., Mizuno T., Takano H., Hiroi Y., Ueki K., Tobe K. Mechanical stress activates protein kinase cascade of phosphorylation in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jul;96(1):438–446. doi: 10.1172/JCI118054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount R. G. ATP analogs. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:1–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


