Abstract
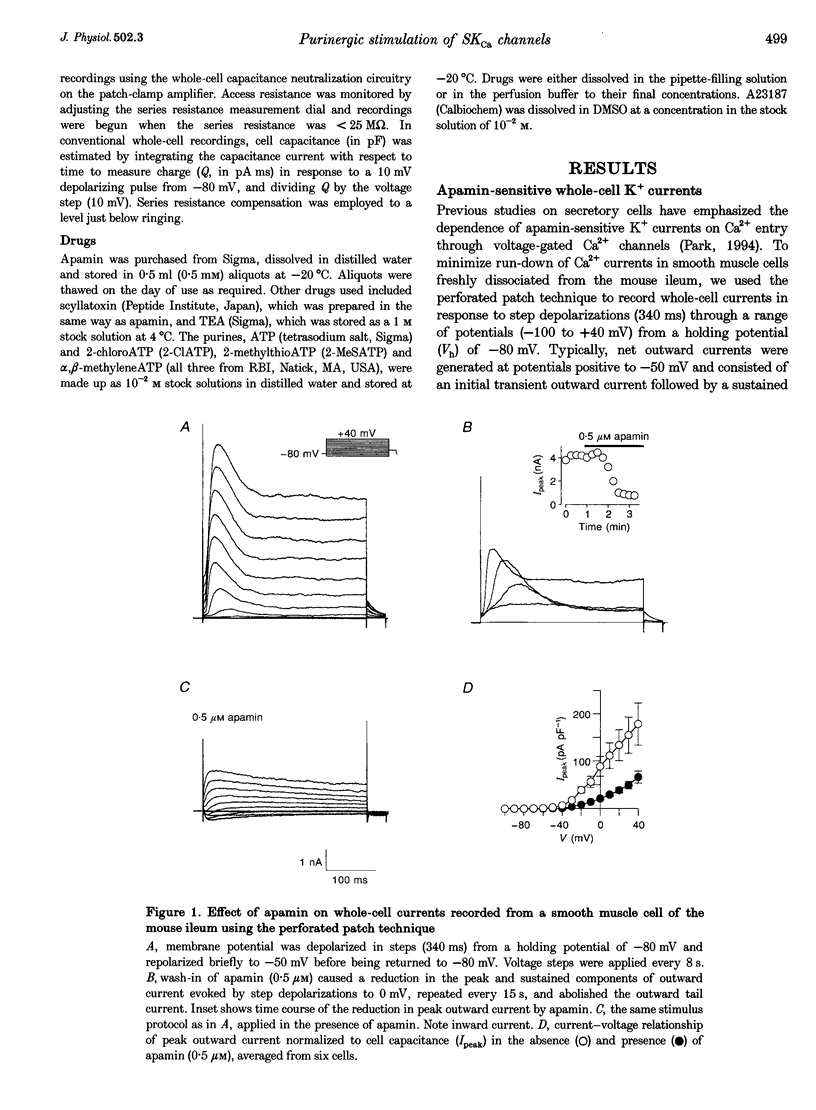
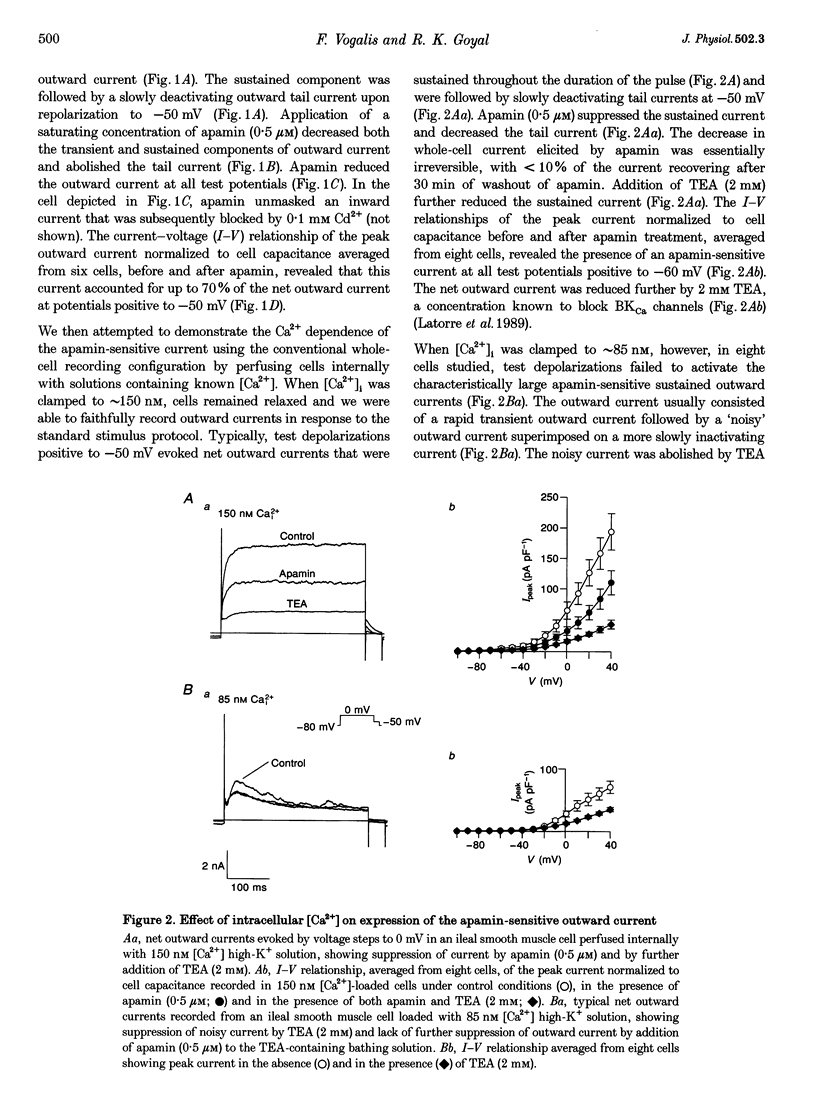
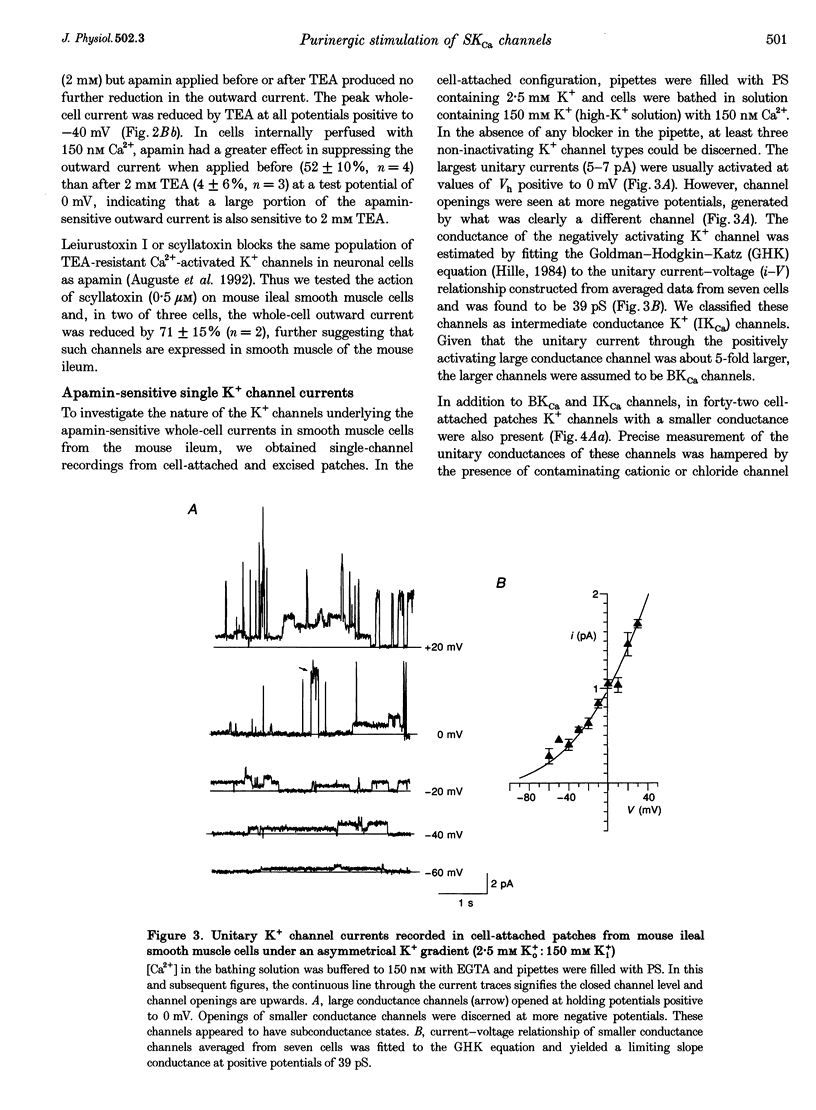
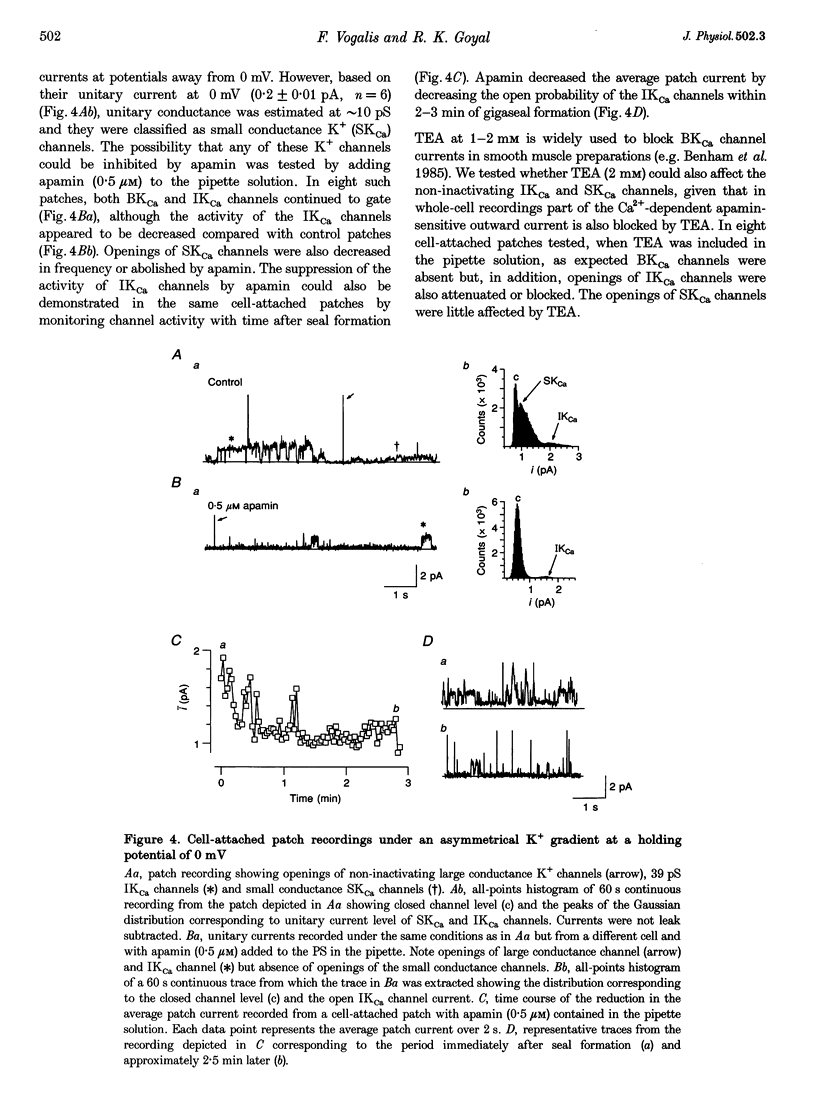
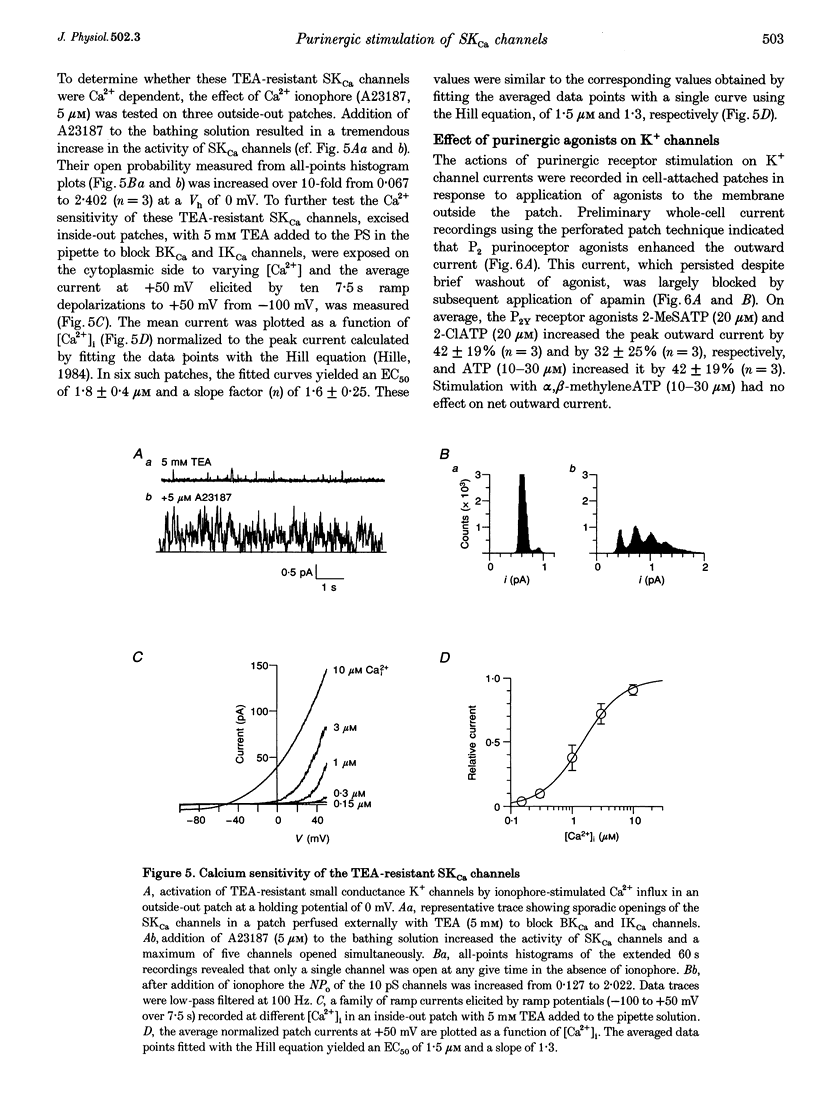
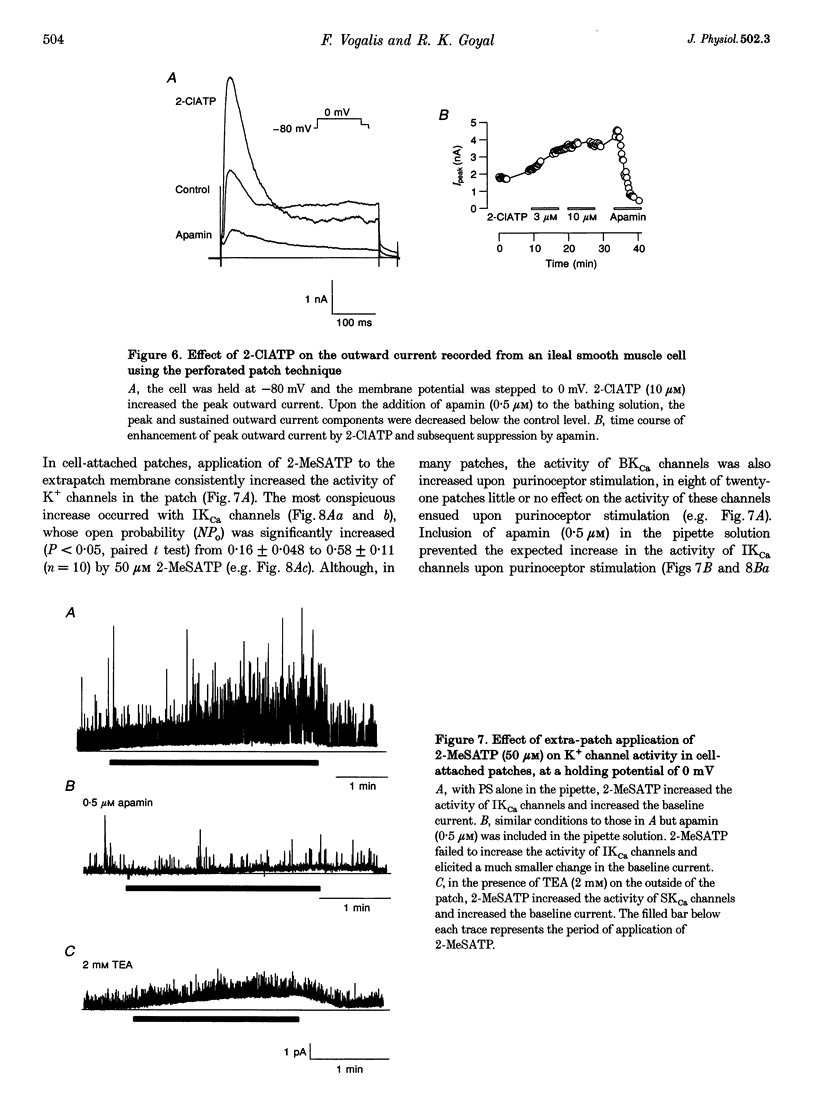
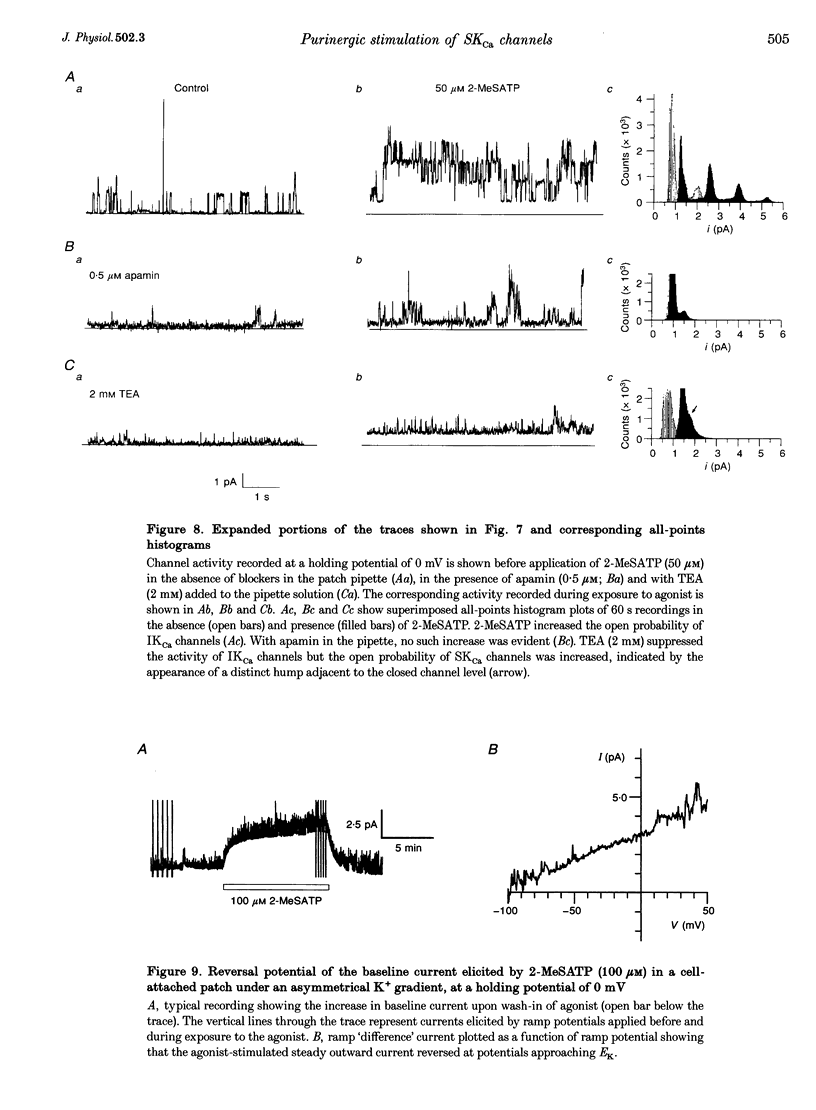
1. Whole-cell and single-channel K+ currents were recorded at room temperature (22-24 degrees C), from smooth muscle cells enzymatically dispersed from the mouse ileum, using variations of the patch-clamp technique. 2. Net outward K+ currents recorded through amphotericin-B-perforated patches in response to step depolarizations positive to -50 mV from a holding potential of -80 mV were decreased by up to 70% by external apamin (0.5 microM). Apamin-sensitive whole-cell currents were also recorded from cells perfused internally with 150 nM Ca2+ but not from cells perfused internally with 85 nM Ca2+. 3. Three types of non-inactivating Ca(2+)-sensitive K+ channels were identified in cell-attached and excised patches under an asymmetrical K+ gradient: (i) large conductance (BKCa; approximately 200 pS) channels blocked by 2 mM external TEA; (ii) intermediate conductance (IKCa; approximately 39 pS) channels blocked by 2 mM external TEA and inhibited by external apamin (0.5 microM); and (iii) small conductance (SKCa; approximately 10 pS) channels that were not blocked by 5 mM external TEA but were sensitive to extracellular apamin (0.5 microM). 4. The TEA-resistant SKCa channels were activated by an increase in [Ca2+]i with an EC50 of 1.5 microM and a Hill coefficient of 1.3. 5. P2 purinoceptor agonists 2-methylthioATP (2-MeSATP), 2-chloroATP and ATP (10-50 microM) increased an apamin-sensitive whole-cell outward K+ current. Extrapatch application of 2-MeSATP (20-100 microM) stimulated the apamin-sensitive IKCa and SKCa channels and activated an apamin-sensitive steady outward current at 0 mV. 6. Smooth muscle cells from the mouse ileum possess two apamin-sensitive K+ channels (IKCa and SKCa); of these, the IKCa channels are TEA sensitive while the SKCa channels are TEA resistant. These channels, along with an apamin-sensitive but TEA-resistant steady outward current, may mediate membrane hyperpolarization elicited by purinergic agonists.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auguste P., Hugues M., Borsotto M., Thibault J., Romey G., Coppola T., Lazdunski M. Characterization and partial purification from pheochromocytoma cells of an endogenous equivalent of scyllatoxin, a scorpion toxin which blocks small conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 25;599(2):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90396-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E., Brown C., Burgess G. M., Burnstock G., Claret M., Cocks T. M., Jenkinson D. H. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):415–417. doi: 10.1038/282415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer V., Kuriyama H. The nature of non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic transmission in longitudinal and circular muscles of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:375–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. The mechanism of action of Ba2+ and TEA on single Ca2+-activated K+ -channels in arterial and intestinal smooth muscle cell membranes. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Feb;403(2):120–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00584088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Burnstock G., Holman M. E. Transmission from perivascular inhibitory nerves to the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1966 Feb;182(3):527–540. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatz A. L., Magleby K. L. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):718–720. doi: 10.1038/323718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., Weisman G. A., Turner J. T., Wilkinson G. F. G protein-coupled P2 purinoceptors: from molecular biology to functional responses. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Apr;16(4):133–139. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. Non-cholinergic excitatory and inhibitory junction potentials in the circular smooth muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:153–164. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capiod T., Ogden D. C. The properties of calcium-activated potassium ion channels in guinea-pig isolated hepatocytes. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:285–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl A., Sanders K. M. Ca2+-activated K channels of canine colonic myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C470–C480. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. Both ATP and the peptide VIP are inhibitory neurotransmitters in guinea-pig ileum circular muscle. J Physiol. 1992 Feb;447:119–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebremedhin D., Kaldunski M., Jacobs E. R., Harder D. R., Roman R. J. Coexistence of two types of Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in rat renal arterioles. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jan;270(1 Pt 2):F69–F81. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1996.270.1.F69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X. D., Goyal R. K. Nitric oxide involvement in the peptide VIP-associated inhibitory junction potential in the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:485–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugues M., Duval D., Kitabgi P., Lazdunski M., Vincent J. P. Preparation of a pure monoiodo derivative of the bee venom neurotoxin apamin and its binding properties to rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2762–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jury J., Boev K. R., Daniel E. E. Nitric oxide mediates outward potassium currents in opossum esophageal circular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jun;270(6 Pt 1):G932–G938. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.270.6.G932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koumi S., Sato R., Hayakawa H. Modulation of the delayed rectifier K+ current by apamin in guinea-pig heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 11;261(1-2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koumi S., Sato R., Horikawa T., Aramaki T., Okumura H. Characterization of the calcium-sensitive voltage-gated delayed rectifier potassium channel in isolated guinea pig hepatocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1994 Jul;104(1):147–171. doi: 10.1085/jgp.104.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler M., Hirschberg B., Bond C. T., Kinzie J. M., Marrion N. V., Maylie J., Adelman J. P. Small-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from mammalian brain. Science. 1996 Sep 20;273(5282):1709–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5282.1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Oberhauser A., Labarca P., Alvarez O. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:385–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinders T., Vijverberg H. P. Ca2+ dependence of small Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in cultured N1E-115 mouse neuroblastoma cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Dec;422(3):223–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00376206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merot J., Bidet M., Le Maout S., Tauc M., Poujeol P. Two types of K+ channels in the apical membrane of rabbit proximal tubule in primary culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 16;978(1):134–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. B. Ion selectivity and gating of small conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in cultured rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 15;481(Pt 3):555–570. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuba M. F., Vladimirova I. A. Effect of apamin on the electrical responses of smooth muscle to adenosine 5'-triphosphate and to non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve stimulation. Neuroscience. 1980;5(5):853–859. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogalis F., Sanders K. M. Excitatory and inhibitory neural regulation of canine pyloric smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):G125–G133. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.1.G125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Ogawa H., Akaike N. ATP-induced rise in apamin-sensitive Ca(2+)-dependent K+ conductance in adult rat hepatocytes. Am J Physiol. 1996 Feb;270(2 Pt 1):G307–G313. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.270.2.G307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog A., Jager L. P. Ion fluxes during the inhibitory junction potential in the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;250(3):681–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


