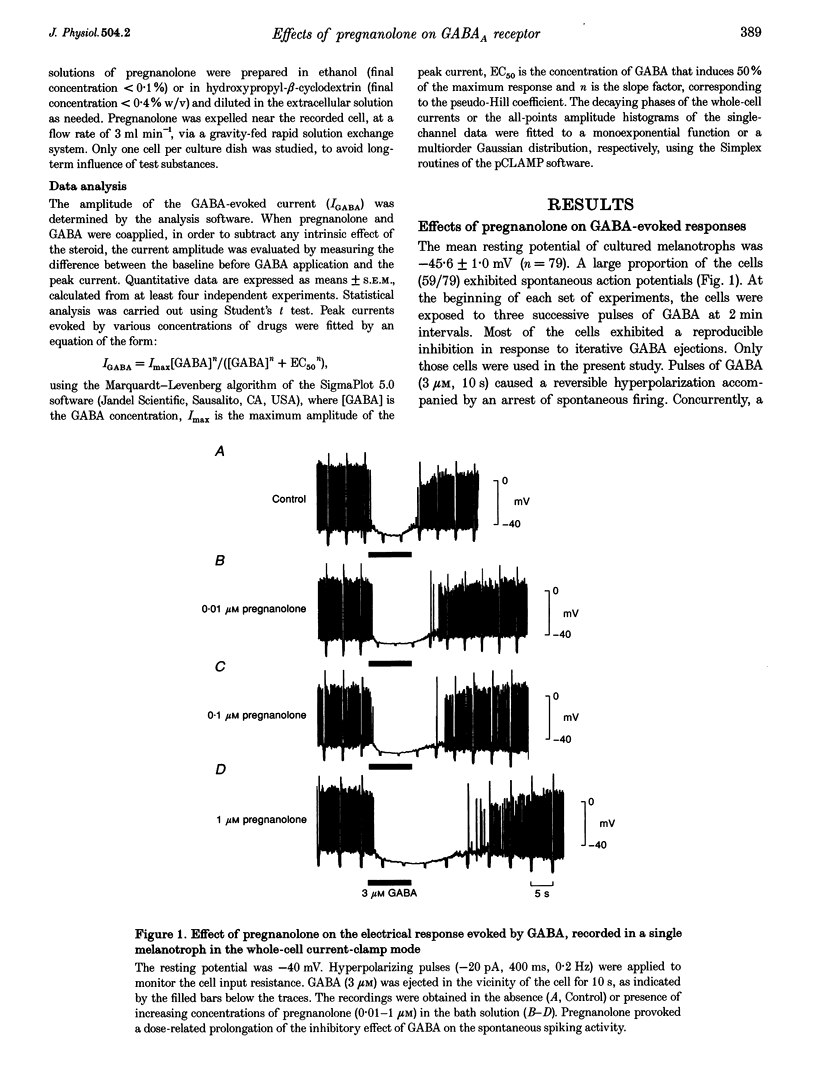
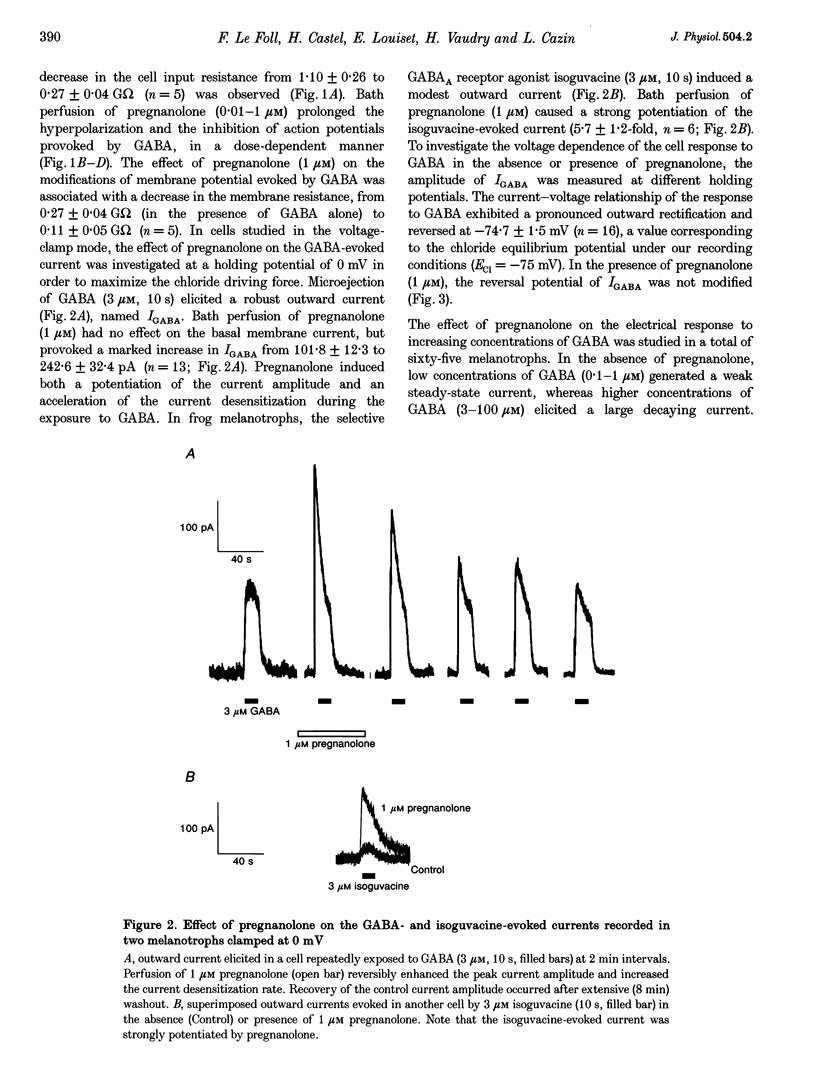
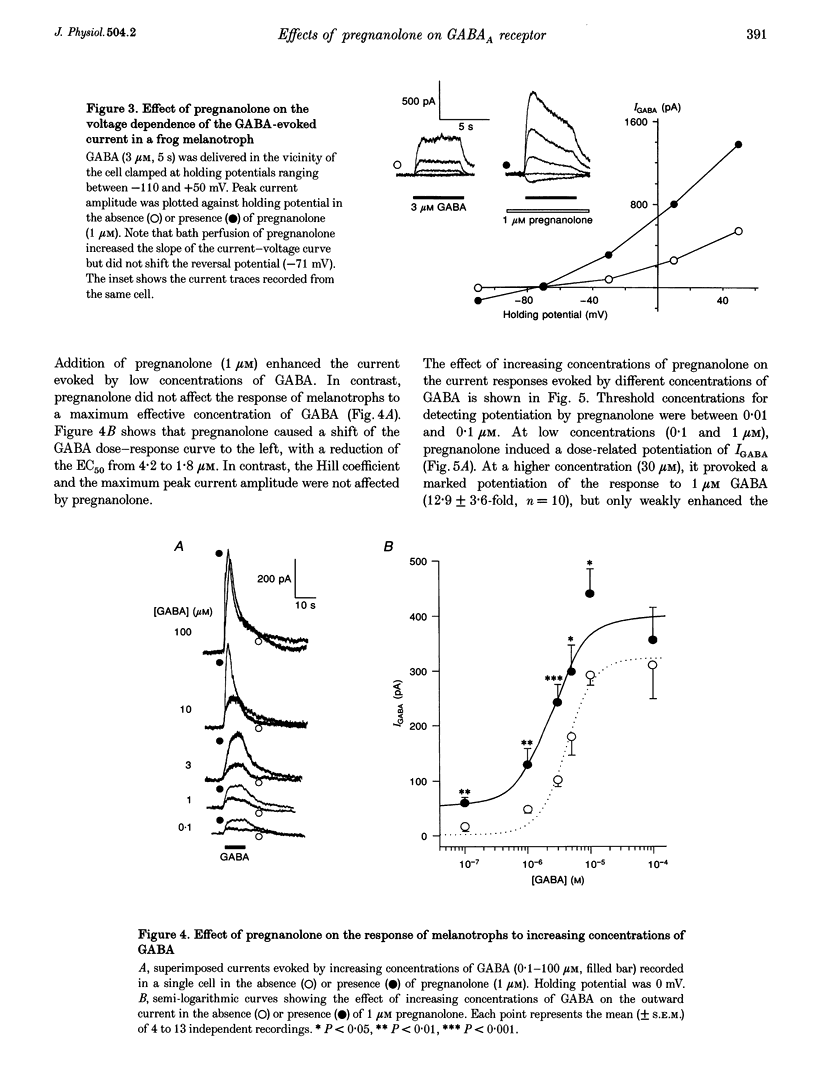
Abstract
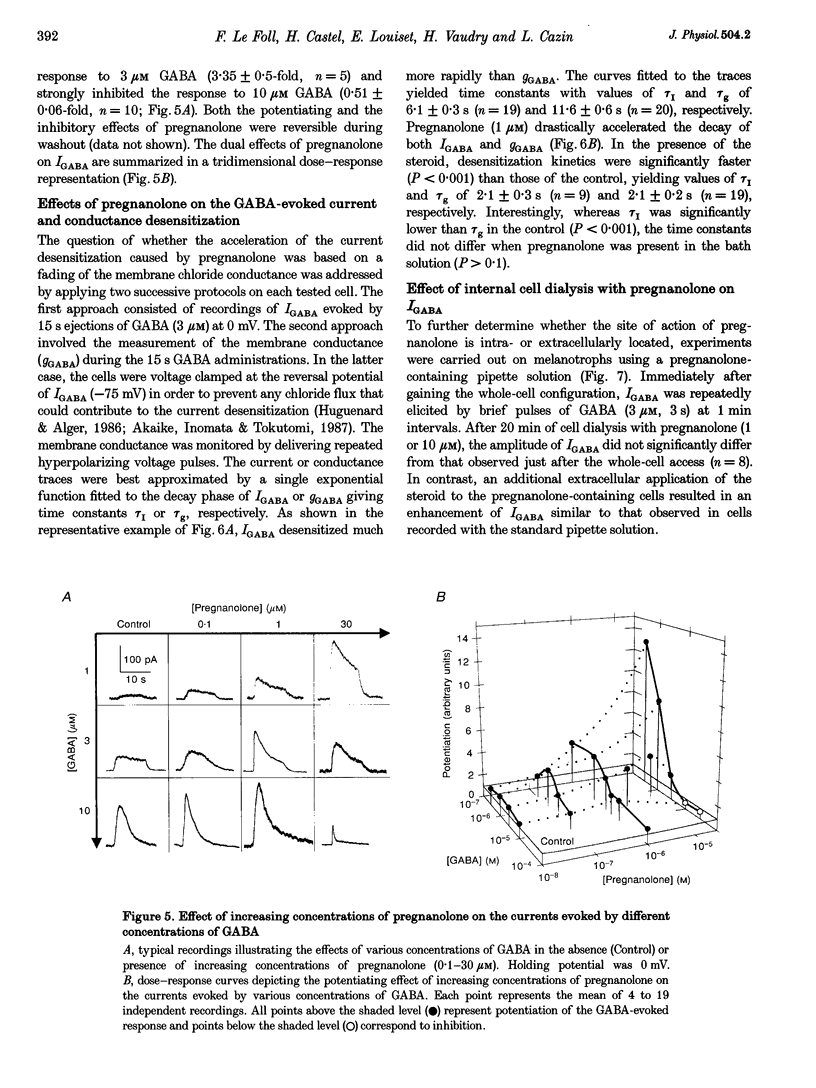
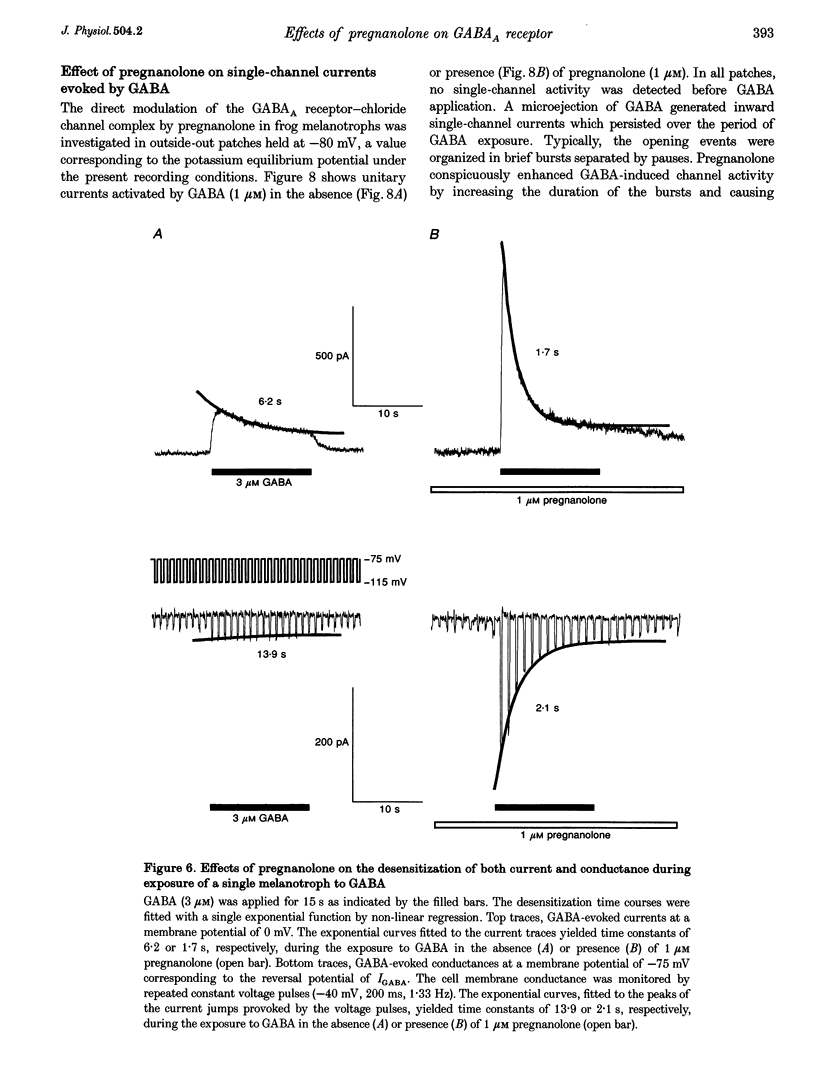
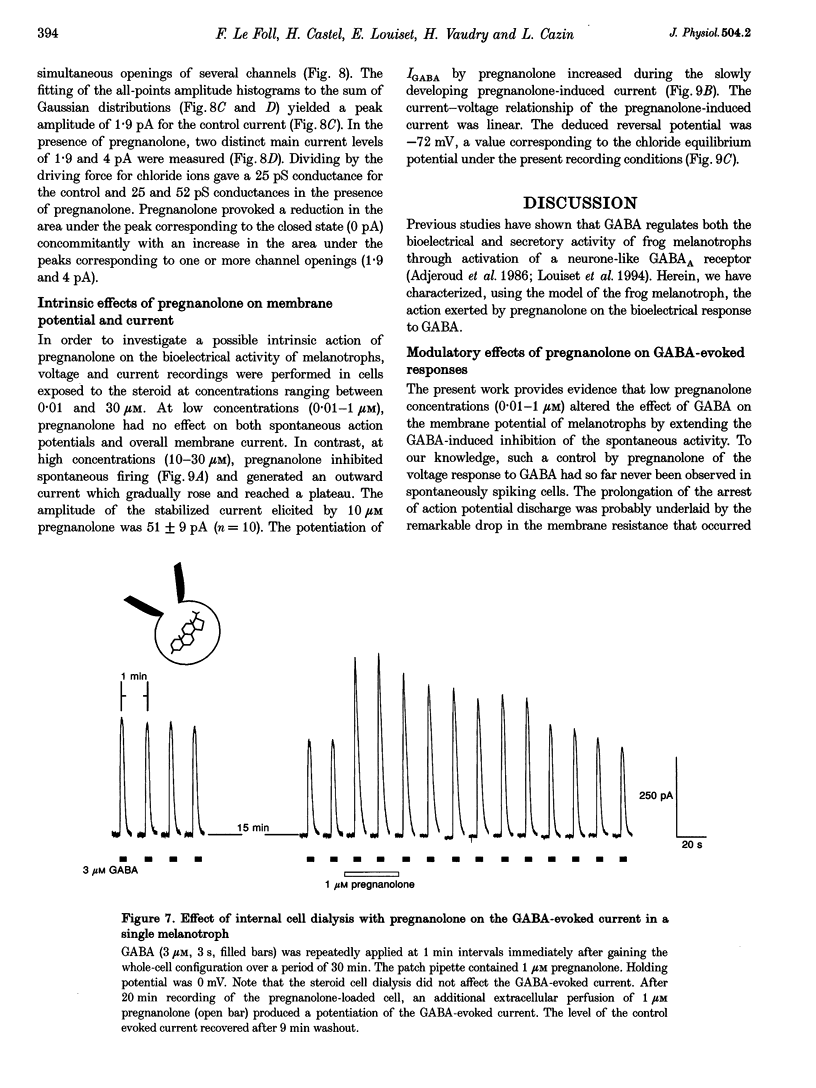
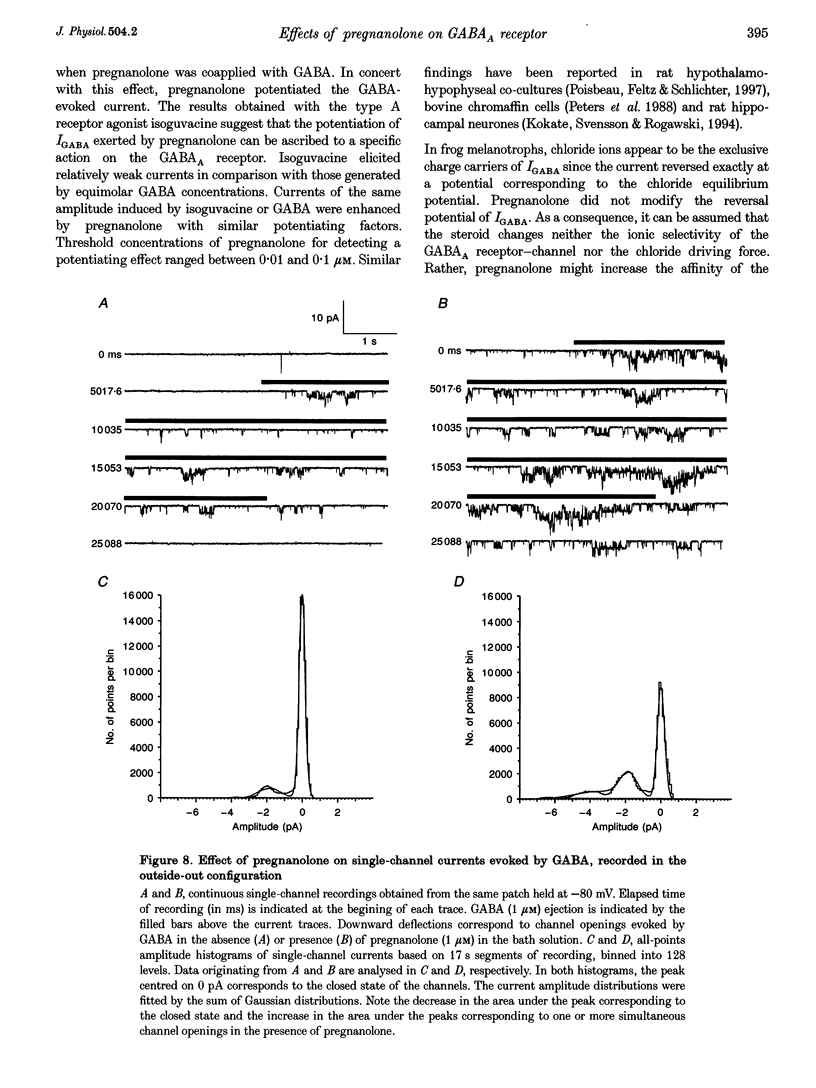
1. The effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone (5 beta-pregnan-3 alpha-ol-20-one) on the electrical response to GABA were investigated in cultured frog pituitary melanotrophs using the patch-clamp technique. 2. Low concentrations of pregnanolone (0.01-1 microM) in the extracellular solution enhanced the current evoked by submaximal concentrations of GABAA receptor agonists and prolonged the GABA-induced inhibition of the spontaneous action potentials in a dose-dependent manner. 3. Pregnanolone augmented the opening probability of the single GABA-activated channels but did not modify the conductance levels. 4. Pregnanolone (1 microM) shifted the GABA dose-response curve towards the low GABA concentrations, reducing the EC50 from 4.2 to 1.8 microM. 5. Internal cell dialysis with pregnanolone (1 or 10 microM) did not alter the GABA-evoked current. 6. Pregnanolone accelerated the desensitization of both the current and conductance increases caused by GABA. 7. High concentrations of pregnanolone (30 microM) markedly and reversibly diminished the current evoked by 10 microM GABA. 8. At high concentrations (10-30 microM), pregnanolone induced an outward current which reversed at the chloride equilibrium potential. 9. It is concluded that, in frog pituitary melanotrophs, pregnanolone exerts a dual inverse modulation and a direct activation of the GABAA receptor-channel depending on the concentrations of both GABA and steroid. Pregnanolone acts on an extracellular site on the GABAA receptor inducing conformational changes of the receptor-channel complex, resulting in a desensitized less-conducting state.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adjeroud S., Tonon M. C., Lamacz M., Leneveu E., Stoeckel M. E., Tappaz M. L., Cazin L., Danger J. M., Bernard C., Vaudry H. GABA-ergic control of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) release by frog neurointermediate lobe in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 1986 Nov;17(5):717–723. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(86)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adjeroud S., Tonon M. C., Leneveu E., Lamacz M., Danger J. M., Gouteux L., Cazin L., Vaudry H. The benzodiazepine agonist clonazepam potentiates the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on alpha-MSH release from neurointermediate lobes in vitro. Life Sci. 1987 May 11;40(19):1881–1887. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Inomata N., Tokutomi N. Contribution of chloride shifts to the fade of gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated currents in frog dorsal root ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:219–234. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyamina M., Delbende C., Jégou S., Leroux P., Leboulenger F., Tonon M. C., Guy J., Pelletier G., Vaudry H. Localization and identification of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (alpha-MSH) in the frog brain. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 26;366(1-2):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91300-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D. Transmitter timecourse in the synaptic cleft: its role in central synaptic function. Trends Neurosci. 1996 May;19(5):163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(96)10024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. A., Hanna M. C., Hales T. G., Kirkness E. F. Insensitivity to anaesthetic agents conferred by a class of GABA(A) receptor subunit. Nature. 1997 Feb 27;385(6619):820–823. doi: 10.1038/385820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrues L., Vaudry H., Lamacz M., Tonon M. C. Mechanism of action of gamma-aminobutyric acid on frog melanotrophs. J Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Feb;14(1):1–12. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0140001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnough D. B., Hawkinson J. E. Neuroactive steroid modulation of [3H]muscimol binding to the GABAA receptor complex in rat cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan 16;288(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Majewska M. D., Harrington J. W., Barker J. L. Structure-activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Apr;241(1):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Modulation of the GABA receptor complex by a steroid anaesthetic. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 10;323(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser C. A., Chesnoy-Marchais D., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Modulation of recombinant alpha 6 beta 2 gamma 2 GABAA receptors by neuroactive steroids. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr 28;289(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkinson J. E., Kimbrough C. L., McCauley L. D., Bolger M. B., Lan N. C., Gee K. W. The neuroactive steroid 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 beta-pregnan-20-one is a two-component modulator of ligand binding to the GABAA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 14;269(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzbauer M., Birmingham M. K., De Nicola A. F., Oliver J. T. In vivo secretion of 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one, a potent anaesthetic steroid, by the adrenal gland of the rat. J Steroid Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(85)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenard J. R., Alger B. E. Whole-cell voltage-clamp study of the fading of GABA-activated currents in acutely dissociated hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1986 Jul;56(1):1–18. doi: 10.1152/jn.1986.56.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokate T. G., Svensson B. E., Rogawski M. A. Anticonvulsant activity of neurosteroids: correlation with gamma-aminobutyric acid-evoked chloride current potentiation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Sep;270(3):1223–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louiset E., Mei Y. A., Valentijn J. A., Vaudry H., Cazin L. Characterization of the GABA-induced current in frog pituitary melanotrophs. J Neuroendocrinol. 1994 Feb;6(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1994.tb00553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louiset E., Valentijn J. A., Vaudry H., Cazin L. Central-type benzodiazepines modulate GABAA receptor chloride channels in cultured pituitary melanotrophs. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Jan;12(1-3):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90062-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Harrison N. L., Schwartz R. D., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.2422758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensah-Nyagan A. G., Feuilloley M., Dupont E., Do-Rego J. L., Leboulenger F., Pelletier G., Vaudry H. Immunocytochemical localization and biological activity of 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the central nervous system of the frog. J Neurosci. 1994 Dec;14(12):7306–7318. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-12-07306.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mody I., De Koninck Y., Otis T. S., Soltesz I. Bridging the cleft at GABA synapses in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem N., Green T. P., Martin I. L., Barnard E. A. Quaternary structure of the native GABAA receptor determined by electron microscopic image analysis. J Neurochem. 1994 Feb;62(2):815–818. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62020815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Purdy R. H. Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2311–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. A., Kirkness E. F., Callachan H., Lambert J. J., Turner A. J. Modulation of the GABAA receptor by depressant barbiturates and pregnane steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1257–1269. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poisbeau P., Feltz P., Schlichter R. Modulation of GABAA receptor-mediated IPSCs by neuroactive steroids in a rat hypothalamo-hypophyseal coculture model. J Physiol. 1997 Apr 15;500(Pt 2):475–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1997.sp022034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Santi M. R., Vicini S., Pritchett D. B., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90202-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabow L. E., Russek S. J., Farb D. H. From ion currents to genomic analysis: recent advances in GABAA receptor research. Synapse. 1995 Nov;21(3):189–274. doi: 10.1002/syn.890210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers-Neame N. T., Covey D. F., Hu Y., Isenberg K. E., Zorumski C. F. Effects of a benz[e]indene on gamma-aminobutyric acid-gated chloride currents in cultured postnatal rat hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):952–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlinger B. A., Fivizzani A. J., Callard G. V. Aromatase, 5 alpha- and 5 beta-reductase in brain, pituitary and skin of the sex-role reversed Wilson's phalarope. J Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;122(2):573–581. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R. Allosteric modulation by benzodiazepine receptor ligands of the GABAA receptor channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):289–295. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00289.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. A., Whiting P. J., Wafford K. A. Barbiturate interactions at the human GABAA receptor: dependence on receptor subunit combination. Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Feb;117(3):521–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonon M. C., Bosler O., Stoeckel M. E., Pelletier G., Tappaz M., Vaudry H. Co-localization of tyrosine hydroxylase, GABA and neuropeptide Y within axon terminals innervating the intermediate lobe of the frog Rana ridibunda. J Comp Neurol. 1992 May 22;319(4):599–605. doi: 10.1002/cne.903190409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Macdonald R. L. Neurosteroid regulation of GABAA receptor single-channel kinetic properties of mouse spinal cord neurons in culture. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:215–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Draguhn A., Ymer S., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional properties of recombinant rat GABAA receptors depend upon subunit composition. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincens M., Shu C., Moguilewsky M., Philibert D. A progesterone metabolite enhances the activity of the GABAA receptor complex at the pituitary level. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 1;168(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90627-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Burnett D. M., Leidenheimer N. J., Burt D. R., Wang J. B., Kofuji P., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Sikela J. M. Ethanol sensitivity of the GABAA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes requires 8 amino acids contained in the gamma 2L subunit. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong Y., Simmonds M. A. Pharmacological characterisation of multiple components in the enhancement by pregnanolone and propofol of [3H]flunitrazepam binding to GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1996;35(9-10):1193–1198. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(96)00056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W. J., Wang J. F., Krueger K. E., Vicini S. Delta subunit inhibits neurosteroid modulation of GABAA receptors. J Neurosci. 1996 Nov 1;16(21):6648–6656. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-21-06648.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]