Abstract
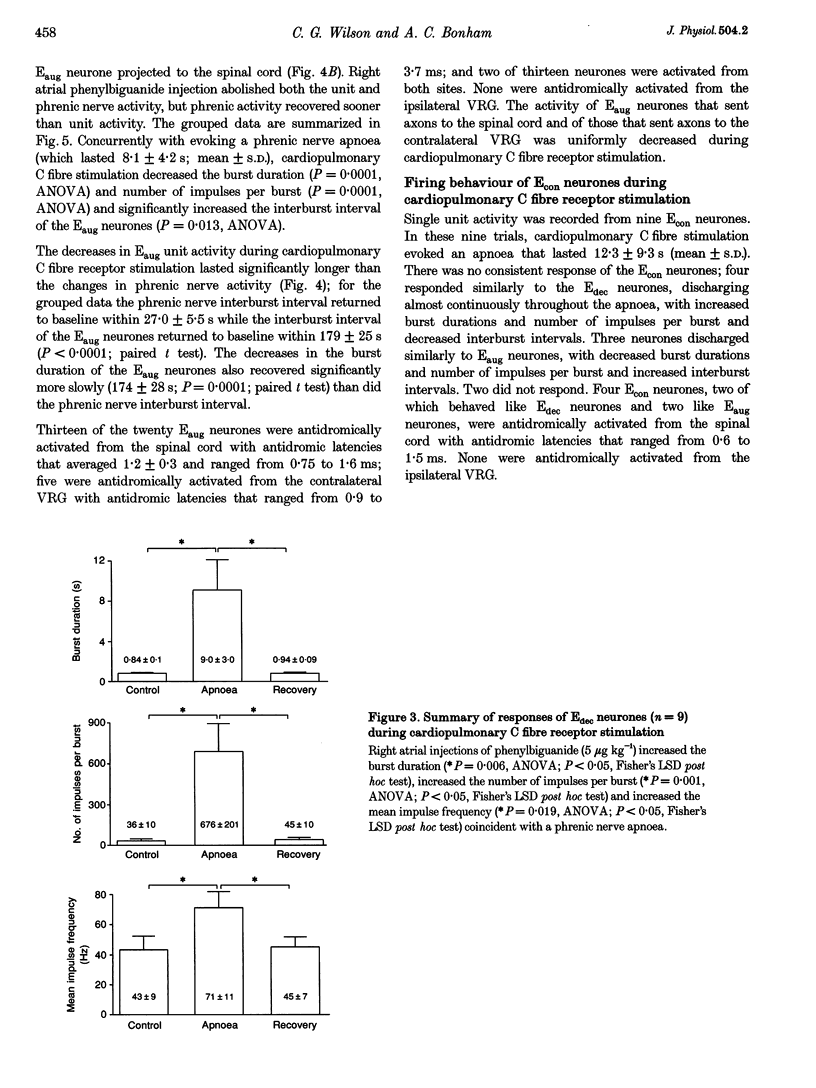
1. Cardiopulmonary C fibre receptor stimulation elicits apnoea and rapid shallow breathing, but the effects on the firing activity of central respiratory neurones are not well understood. This study examined the responses of ventral respiratory group neurones: decrementing expiratory (Edec), augmenting expiratory (Eaug), and inspiratory (I) neurones during cardiopulmonary C fibre receptor-evoked apnoea and rapid shallow breathing. 2. Extracellular neuronal activity, phrenic nerve activity and arterial pressure were recorded in urethane-anaesthetized rats. Cardiopulmonary C fibre receptors were stimulated by right atrial injections of phenylbiguanide. Neurones were tested for antidromic activation from the contra- and ipsilateral ventral respiratory group (VRG), spinal cord and cervical vagus nerve. 3. Edec neurones discharged tonically during cardiopulmonary C fibre-evoked apnoea and rapid shallow breathing, displaying increased burst durations, number of impulses per burst, and mean impulse frequencies. Edec neurones recovered either with the phrenic nerve activity (25 s) or much later (3 min). 4. By contrast, the firing activity of Eaug and most I neurones was decreased, featuring decreased burst durations and number of impulses per burst and increased interburst intervals. Eaug activity recovered in approximately 3 min and inspiratory activity in approximately 1 min. 5. The results indicate that cardiopulmonary C fibre receptor stimulation causes tonic firing of Edec neurones and decreases in Eaug and I neuronal activity coincident with apnoea or rapid shallow breathing.
Full text
PDF




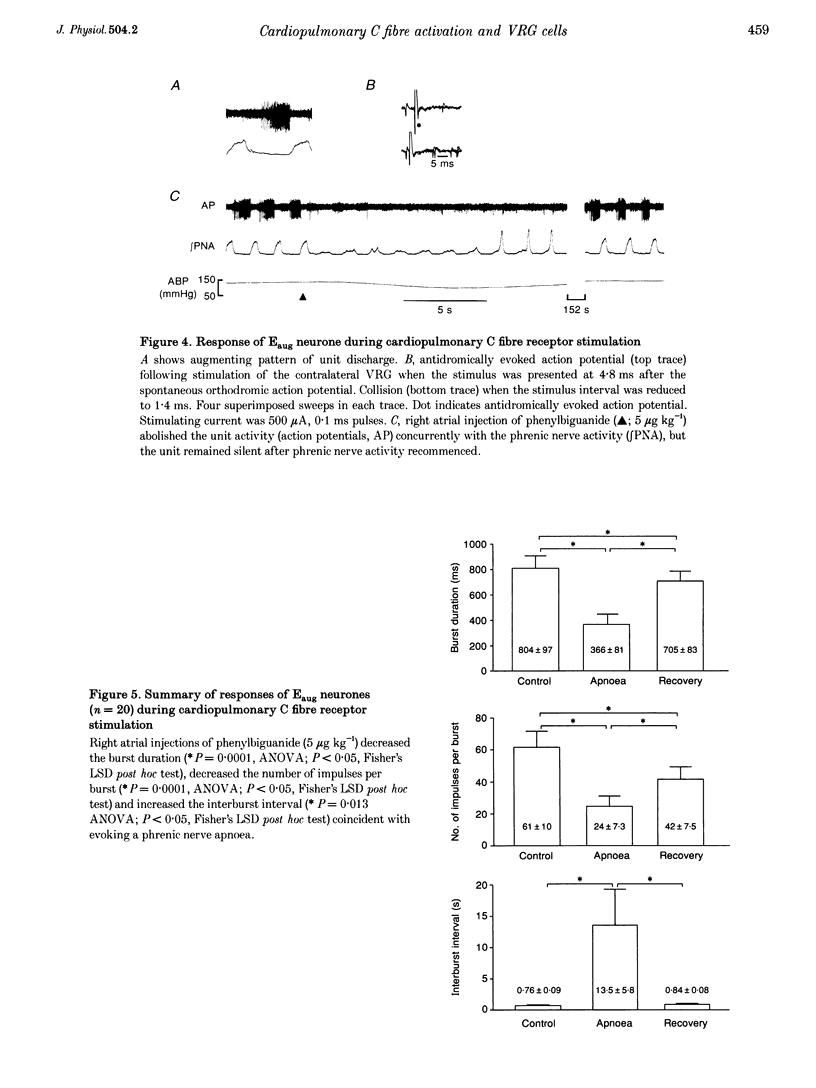
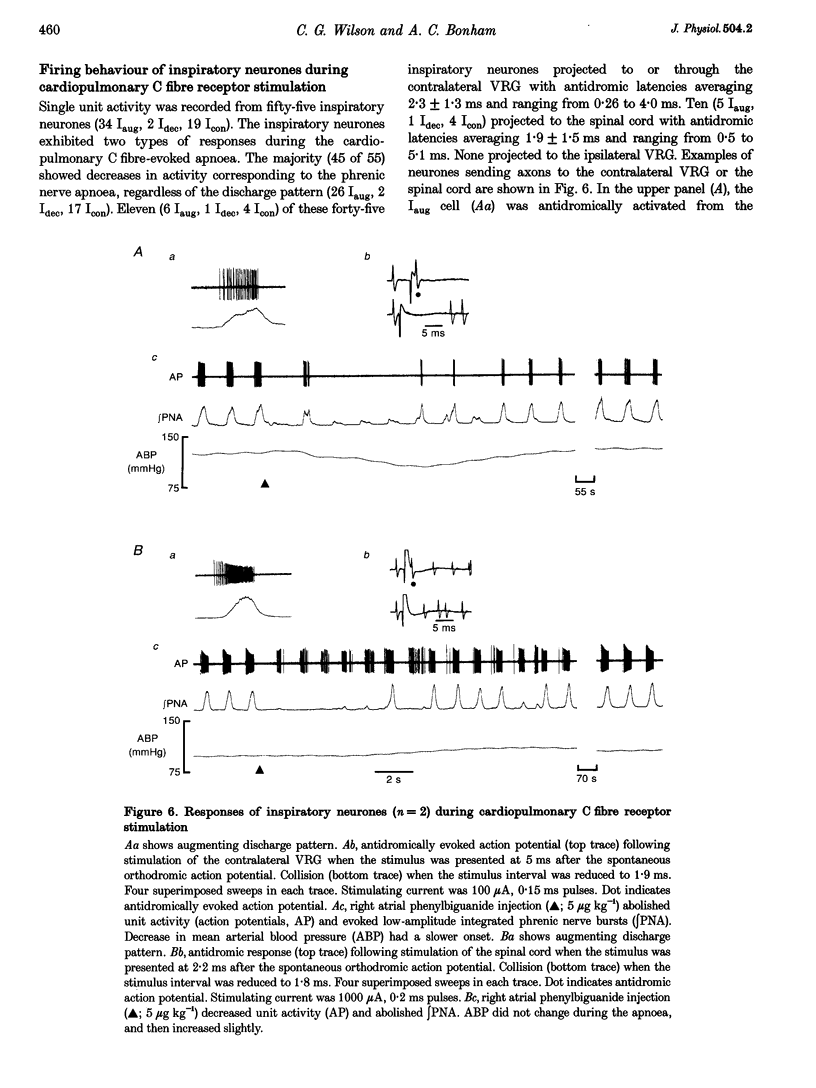
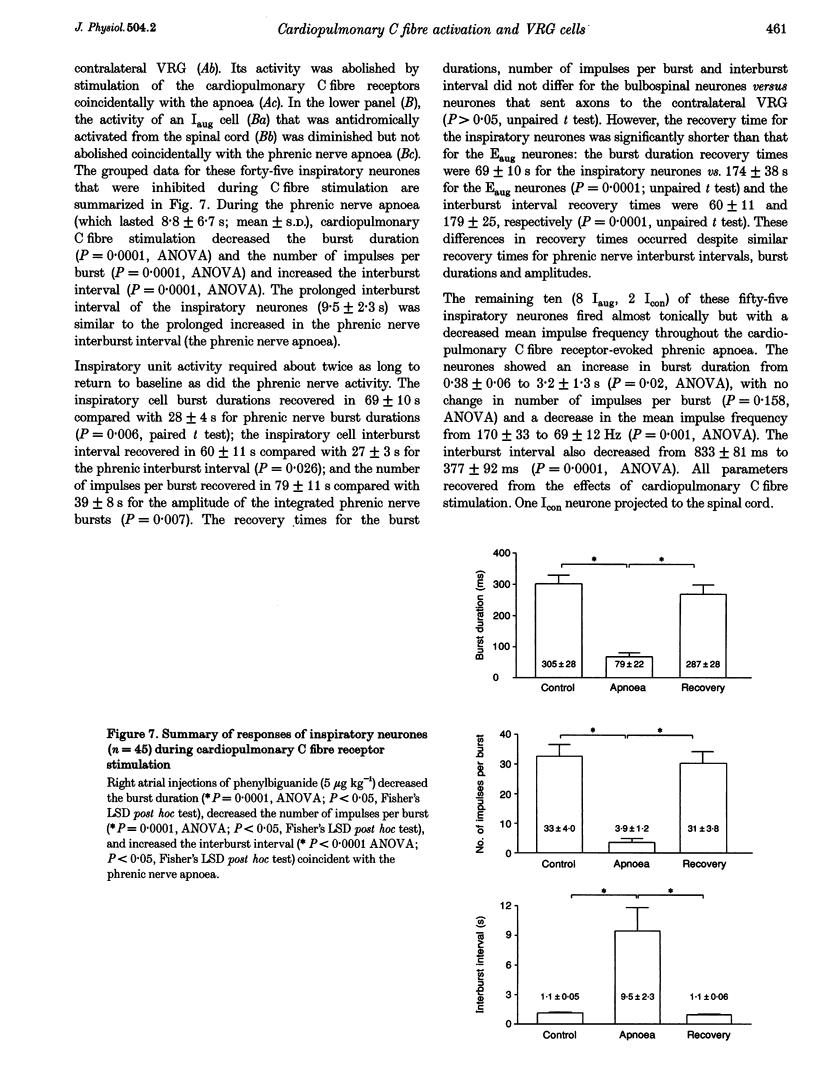




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balis U. J., Morris K. F., Koleski J., Lindsey B. G. Simulations of a ventrolateral medullary neural network for respiratory rhythmogenesis inferred from spike train cross-correlation. Biol Cybern. 1994;70(4):311–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00200329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonham A. C., Joad J. P. Neurones in commissural nucleus tractus solitarii required for full expression of the pulmonary C fibre reflex in rat. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:95–112. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleridge H. M., Coleridge J. C. Pulmonary reflexes: neural mechanisms of pulmonary defense. Annu Rev Physiol. 1994;56:69–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czyzyk-Krzeska M. F., Lawson E. E. Synaptic events in ventral respiratory neurones during apnoea induced by laryngeal nerve stimulation in neonatal pig. J Physiol. 1991 May;436:131–147. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezure K., Manabe M. Decrementing expiratory neurons of the Bötzinger complex. II. Direct inhibitory synaptic linkage with ventral respiratory group neurons. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(1):159–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00248511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezure K., Manabe M., Yamada H. Distribution of medullary respiratory neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 12;455(2):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezure K. Synaptic connections between medullary respiratory neurons and considerations on the genesis of respiratory rhythm. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35(6):429–450. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90030-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorko L., Duffin J., England S. Inhibition of inspiratory neurons of the nucleus retroambigualis by expiratory neurons of the Botzinger complex in the cat. Exp Neurol. 1989 Oct;106(1):74–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorko L., Merrill E. G. Axonal projections from the rostral expiratory neurones of the Bötzinger complex to medulla and spinal cord in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:487–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Schlag J. D. Determination of antidromic excitation by the collision test: problems of interpretation. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grélot L., Barillot J. C., Bianchi A. L. Pharyngeal motoneurones: respiratory-related activity and responses to laryngeal afferents in the decerebrate cat. Exp Brain Res. 1989;78(2):336–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00228905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxhiu M. A., van Lunteren E., Deal E. C., Cherniack N. S. Effect of stimulation of pulmonary C-fiber receptors on canine respiratory muscles. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Sep;65(3):1087–1092. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.3.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang C., Lipski J. Extensive monosynaptic inhibition of ventral respiratory group neurons by augmenting neurons in the Bötzinger complex in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1990;81(3):639–648. doi: 10.1007/BF02423514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jodkowski J. S., Berger A. J. Influences from laryngeal afferents on expiratory bulbospinal neurons and motoneurons. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Apr;64(4):1337–1345. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.4.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanjhan R., Lipski J., Kruszewska B., Rong W. A comparative study of pre-sympathetic and Bötzinger neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) of the rat. Brain Res. 1995 Nov 13;699(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)00814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood P. A., Sears T. A. Proceedings: Monosynaptic excitation of thoracic expiratory motoneurones from lateral respiratory neurones in the medulla of the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):87P–89P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson E. E., Richter D. W., Czyzyk-Krzeska M. F., Bischoff A., Rudesill R. C. Respiratory neuronal activity during apnea and other breathing patterns induced by laryngeal stimulation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991 Jun;70(6):2742–2749. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1991.70.6.2742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J. Antidromic activation of neurones as an analytic tool in the study of the central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods. 1981 Jun;4(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(81)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski J., Zhang X., Kruszewska B., Kanjhan R. Morphological study of long axonal projections of ventral medullary inspiratory neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1994 Mar 21;640(1-2):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91871-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manabe M., Ezure K. Decrementing expiratory neurons of the Bötzinger complex. I. Response to lung inflation and axonal projection. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(1):150–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00248510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Ezure K., Suzuki I. Control of abdominal muscles by brain stem respiratory neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Jul;54(1):155–167. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onai T., Saji M., Miura M. Projections of supraspinal structures to the phrenic motor nucleus in rats studied by a horseradish peroxidase microinjection method. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Dec;21(2-3):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onimaru H., Arata A., Homma I. Firing properties of respiratory rhythm generating neurons in the absence of synaptic transmission in rat medulla in vitro. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76(3):530–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00248909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkes M. J., Lara-Muñoz J. P., Izzo P. N., Spyer K. M. Responses of ventral respiratory neurones in the rat to vagus stimulation and the functional division of expiration. J Physiol. 1994 Apr 1;476(1):131–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Ballanyi K., Schwarzacher S. Mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Dec;2(6):788–793. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W. Generation and maintenance of the respiratory rhythm. J Exp Biol. 1982 Oct;100:93–107. doi: 10.1242/jeb.100.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saether K., Hilaire G., Monteau R. Dorsal and ventral respiratory groups of neurons in the medulla of the rat. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 1;419(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90571-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers L. S., Shannon R., Saporta S., Lindsey B. G. Functional associations among simultaneously monitored lateral medullary respiratory neurons in the cat. I. Evidence for excitatory and inhibitory actions of inspiratory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Apr;57(4):1078–1100. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.4.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Ellenberger H. H., Ballanyi K., Richter D. W., Feldman J. L. Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):726–729. doi: 10.1126/science.1683005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thames M. D., Schmid P. G. Cardiopulmonary receptors with vagal afferents tonically inhibit ADH release in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):H299–H304. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.237.3.H299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardhan A., Kachroo A., Sapru H. N. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarius mediate the responses to the stimulation of cardio-pulmonary vagal afferent C fiber endings. Brain Res. 1993 Jul 30;618(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90424-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. G., Zhang Z., Bonham A. C. Non-NMDA receptors transmit cardiopulmonary C fibre input in nucleus tractus solitarii in rats. J Physiol. 1996 Nov 1;496(Pt 3):773–785. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Barillot J. C., Bianchi A. L. Are the post-inspiratory neurons in the decerebrate rat cranial motoneurons or interneurons? Brain Res. 1991 Jun 14;551(1-2):256–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90940-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Barillot J. C., Bianchi A. L. Intracellular electrophysiological and morphological study of the medullary inspiratory neurons of the decerebrate rat. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 3;576(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90686-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Barillot J. C., Bianchi A. L. Medullary expiratory neurons in the decerebrate rat: an intracellular study. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 3;576(2):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90687-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


