Abstract
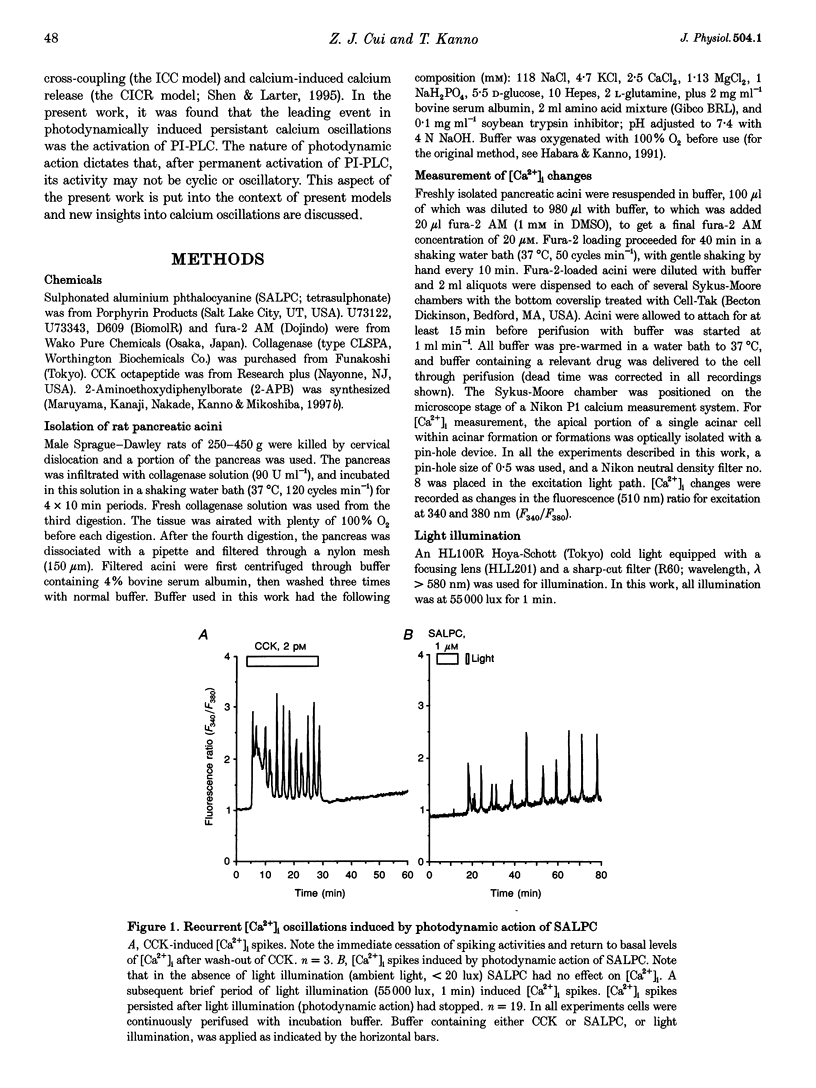
1. Photodynamic agents, due to their photon-dependent selective activation, can selectively activate a number of physiological processes and may directly modulate signal transduction in a number of cells including pancreatic acinar cells. 2. Activation of the photodynamic agent sulphonated aluminium phthalocyanine (SALPC) triggered recurrent cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+]i) spiking in pancreatic acinar cells. 3. The photodynamically triggered calcium spiking could be blocked by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) inhibitor U73122, but not by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C inhibitor D609. 4. Removal of extracellular Ca2+ abolished spiking, as did 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborate (2-APB), an inhibitory modulator of IP3-mediated Ca2+ release from intracellular stores. 5. These data suggest that SALPC photodynamic action may permanently fix PI-PLC in an active conformation, and this produced recurrent [Ca2+]i spiking.
Full text
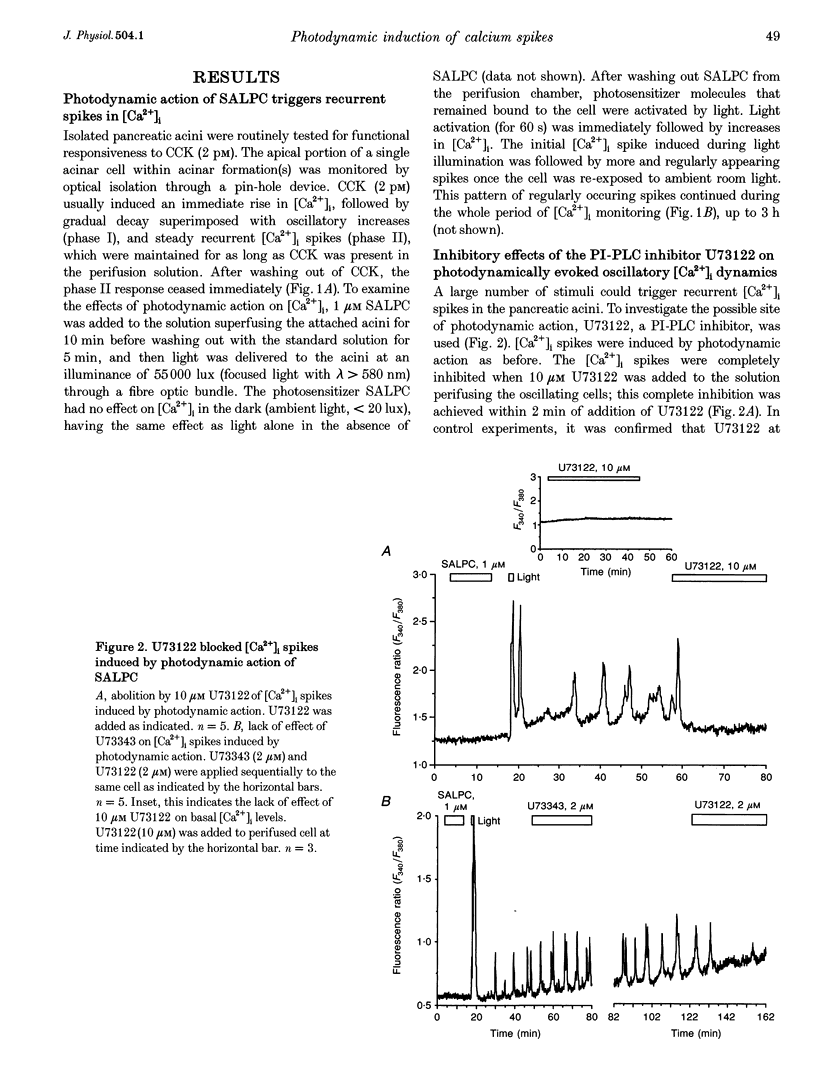
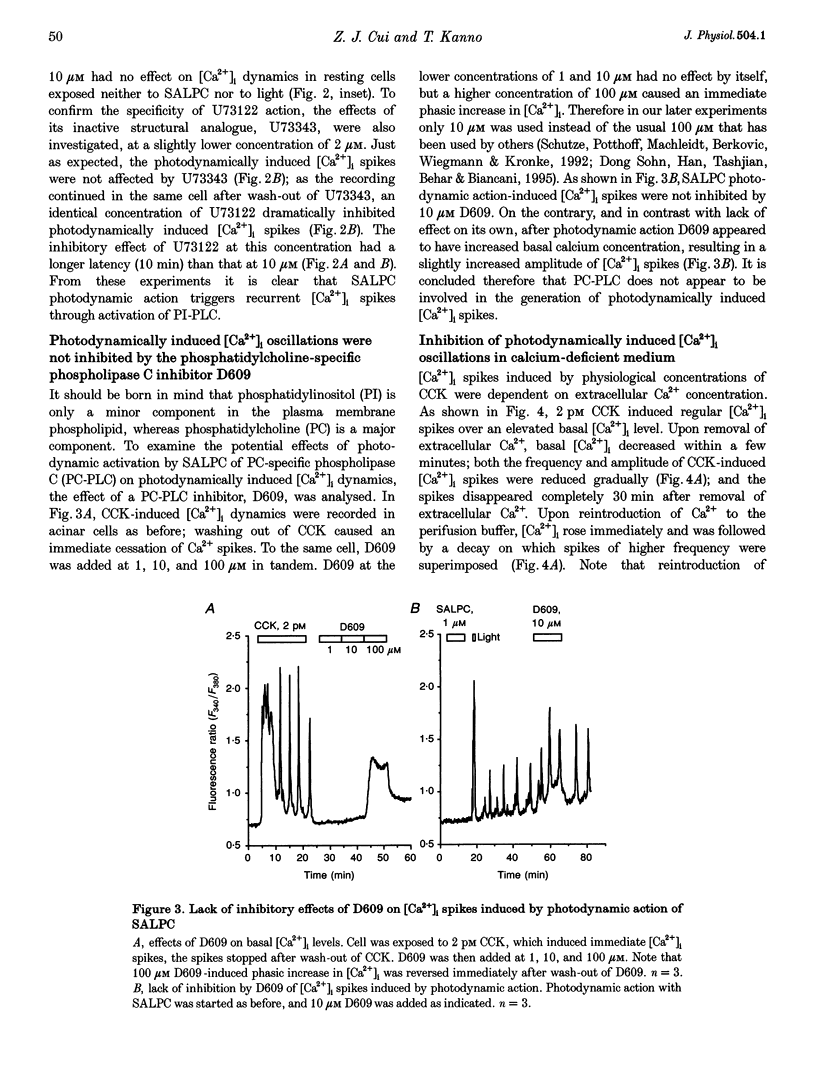
PDF
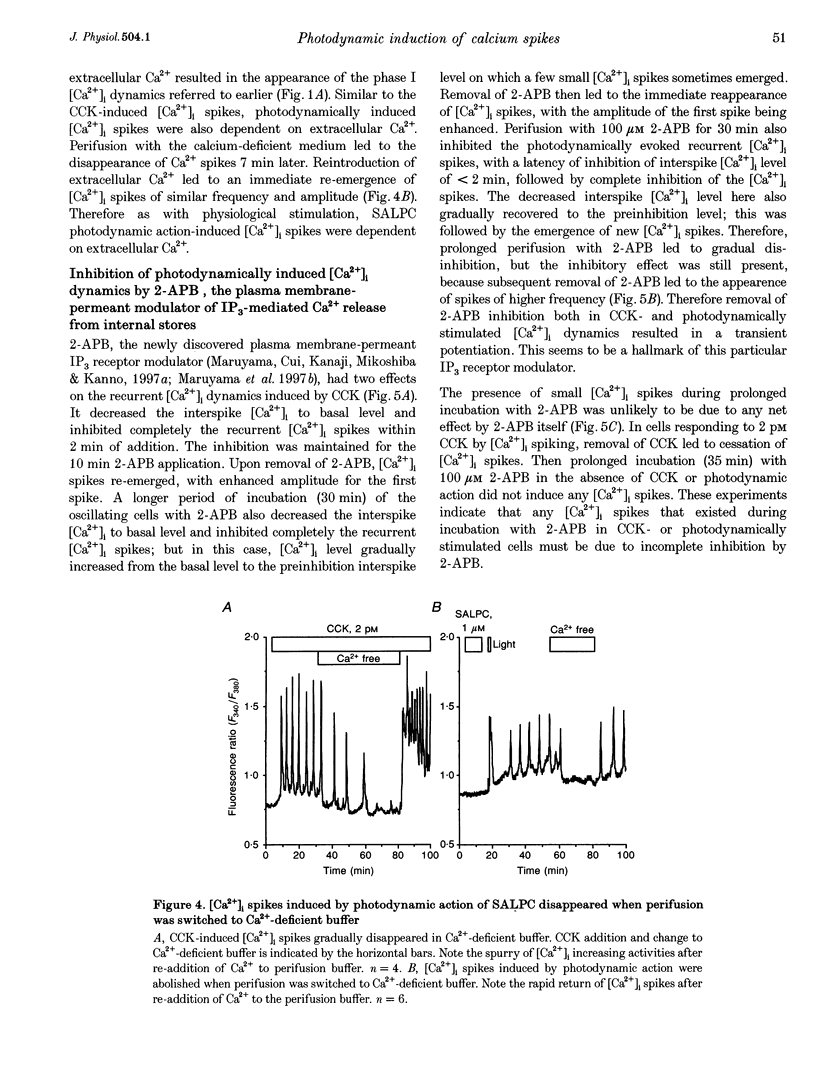




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Hur E., Dubbelman T. M., Van Steveninck J. Phthalocyanine-induced photodynamic changes of cytoplasmic free calcium in Chinese hamster cells. Photochem Photobiol. 1991 Aug;54(2):163–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1991.tb02002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berven L. A., Barritt G. J. Evidence obtained using single hepatocytes for inhibition by the phospholipase C inhibitor U73122 of store-operated Ca2+ inflow. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 May 17;49(10):1373–1379. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00050-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Watras J., Ehrlich B. E. Bell-shaped calcium-response curves of Ins(1,4,5)P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):751–754. doi: 10.1038/351751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combettes L., Cheek T. R., Taylor C. W. Regulation of inositol trisphosphate receptors by luminal Ca2+ contributes to quantal Ca2+ mobilization. EMBO J. 1996 May 1;15(9):2086–2093. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Z. J., Habara Y., Wang D. Y., Kanno T. A novel aspect of photodynamic action: induction of recurrent spikes in cytosolic calcium concentration. Photochem Photobiol. 1997 Feb;65(2):382–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1997.tb08574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Moel M. P., Van de Put F. H., Vermegen T. M., De Pont J. H., Willems P. H. Effect of the aminosteroid, U73122, on Ca2+ uptake and release properties of rat liver microsomes. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Dec 1;234(2):626–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.626_b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell C. Ca2+ oscillations in non-excitable cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:427–454. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.002235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D. TRP: its role in phototransduction and store-operated Ca2+ entry. Cell. 1996 May 31;85(5):617–619. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grierson J. P., Meldolesi J. Calcium homeostasis in mouse fibroblast cells: affected by U-73122, a putative phospholipase C beta blocker, via multiple mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):11–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habara Y., Kanno T. Dose-dependency in spatial dynamics of [Ca2+]c in pancreatic acinar cells. Cell Calcium. 1991 Sep;12(8):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90073-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubmer A., Hermann A., Uberriegler K., Krammer B. Role of calcium in photodynamically induced cell damage of human fibroblasts. Photochem Photobiol. 1996 Jul;64(1):211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1996.tb02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. C., Jhon D. Y., Bae Y. S., Kim J. H., Rhee S. G. Activation of phospholipase C-gamma by the concerted action of tau proteins and arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 2;271(31):18342–18349. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.31.18342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson O., Kindmark H., Brandstrom R., Fredholm B., Berggren P. O. Oscillations in KATP channel activity promote oscillations in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in the pancreatic beta cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):5161–5165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.5161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luna M. C., Wong S., Gomer C. J. Photodynamic therapy mediated induction of early response genes. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1374–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I. C., Taylor C. W. Biphasic effects of cytosolic Ca2+ on Ins(1,4,5)P3-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13214–13220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall I. C., Taylor C. W. Two calcium-binding sites mediate the interconversion of liver inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors between three conformational states. Biochem J. 1994 Jul 15;301(Pt 2):591–598. doi: 10.1042/bj3010591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Cui Z. J. Photodynamic action of rose bengal on isolated rat pancreatic acini: stimulation of amylase release. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 9;256(1-2):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81711-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Cui Z. J. Photodynamic action of sulphonated aluminium phthalocyanine (SALPC) on AR4-2J cells, a carcinoma cell line of rat exocrine pancreas. Br J Cancer. 1990 May;61(5):695–701. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Cui Z. J. Photodynamic action of sulphonated aluminium phthalocyanine (SALPC) on isolated rat pancreatic acini. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 May 1;39(9):1445–1457. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90426-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Mesler D. E. Photodynamic effects of erythrosine on the smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):555–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Taylor C. W. Luminal Ca2+ increases the sensitivity of Ca2+ stores to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;41(1):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oancea E., Meyer T. Reversible desensitization of inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release provides a mechanism for repetitive calcium spikes. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 19;271(29):17253–17260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.29.17253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldershaw K. A., Taylor C. W. Luminal Ca2+ increases the affinity of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate for its receptor. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):631–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2920631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penning L. C., VanSteveninck J., Dubbelman T. M. HPD-induced photodynamic changes in intracellular cyclic AMP levels in human bladder transitional carcinoma cells, clone T24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1084–1089. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Potthoff K., Machleidt T., Berkovic D., Wiegmann K., Krönke M. TNF activates NF-kappa B by phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C-induced "acidic" sphingomyelin breakdown. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):765–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90553-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Larter R. Chaos in intracellular Ca2+ oscillations in a new model for non-excitable cells. Cell Calcium. 1995 Mar;17(3):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(95)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohn U. D., Han B., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Behar J., Biancani P. Agonist-independent, muscle-type-specific signal transduction pathways in cat esophageal and lower esophageal sphincter circular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Apr;273(1):482–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoda Y. Receptor-operated Ca2+ signaling and crosstalk in stimulus secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 29;1154(2):105–156. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems P. H., Van de Put F. H., Engbersen R., Bosch R. R., Van Hoof H. J., de Pont J. J. Induction of Ca2+ oscillations by selective, U73122-mediated, depletion of inositol-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ stores in rabbit pancreatic acinar cells. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Jun;427(3-4):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00374529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonuschot G., Vaughn J. M., Novotny J. F. Intracellular calcium during photodynamic permeabilization of cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1992 Oct;24(10):1079–1088. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(92)93173-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng W., Xu X., Muallem S. Gbetagamma transduces [Ca2+]i oscillations and Galphaq a sustained response during stimulation of pancreatic acinar cells with [Ca2+]i-mobilizing agonists. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 2;271(31):18520–18526. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.31.18520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Laith M., Matthews E. K. Calcium-dependent photodynamic action of di- and tetrasulphonated aluminium phthalocyanine on normal and tumour-derived rat pancreatic exocrine cells. Br J Cancer. 1994 Nov;70(5):893–899. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1994.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Laith M., Matthews E. K., Cui Z. J. Photodynamic drug action on isolated rat pancreatic acini. Mobilization of arachidonic acid and prostaglandin production. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 17;46(4):567–573. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90539-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


