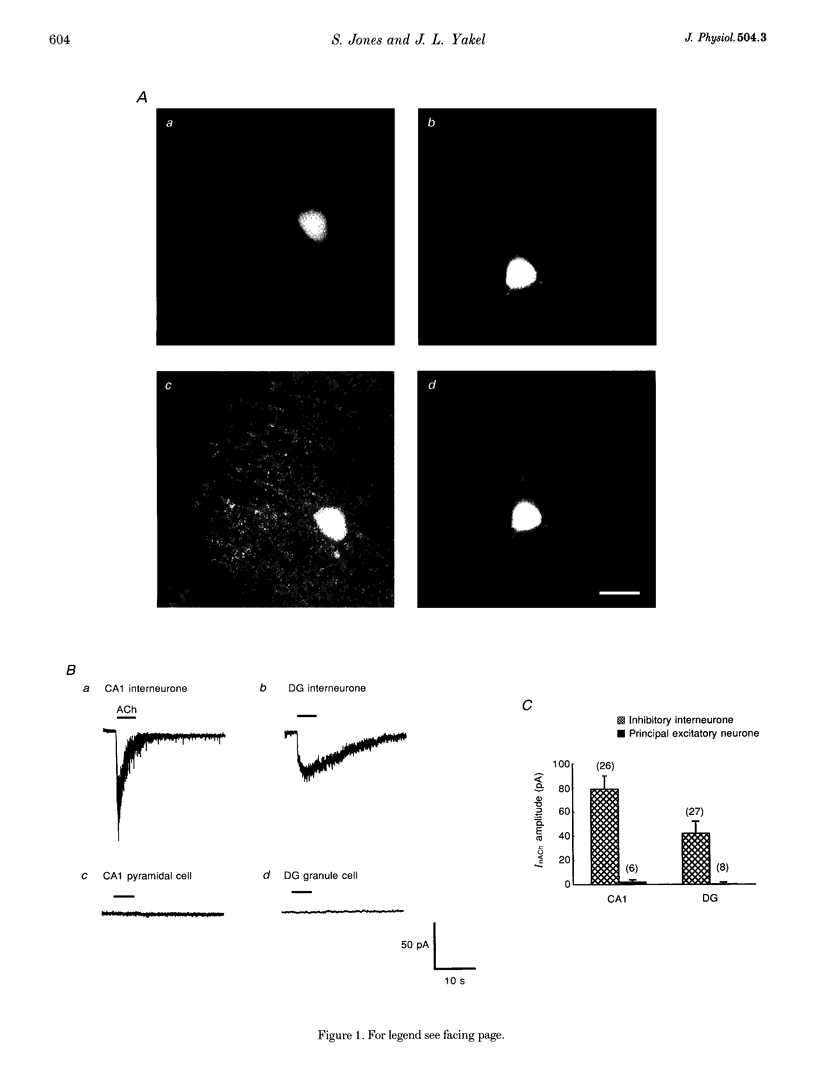
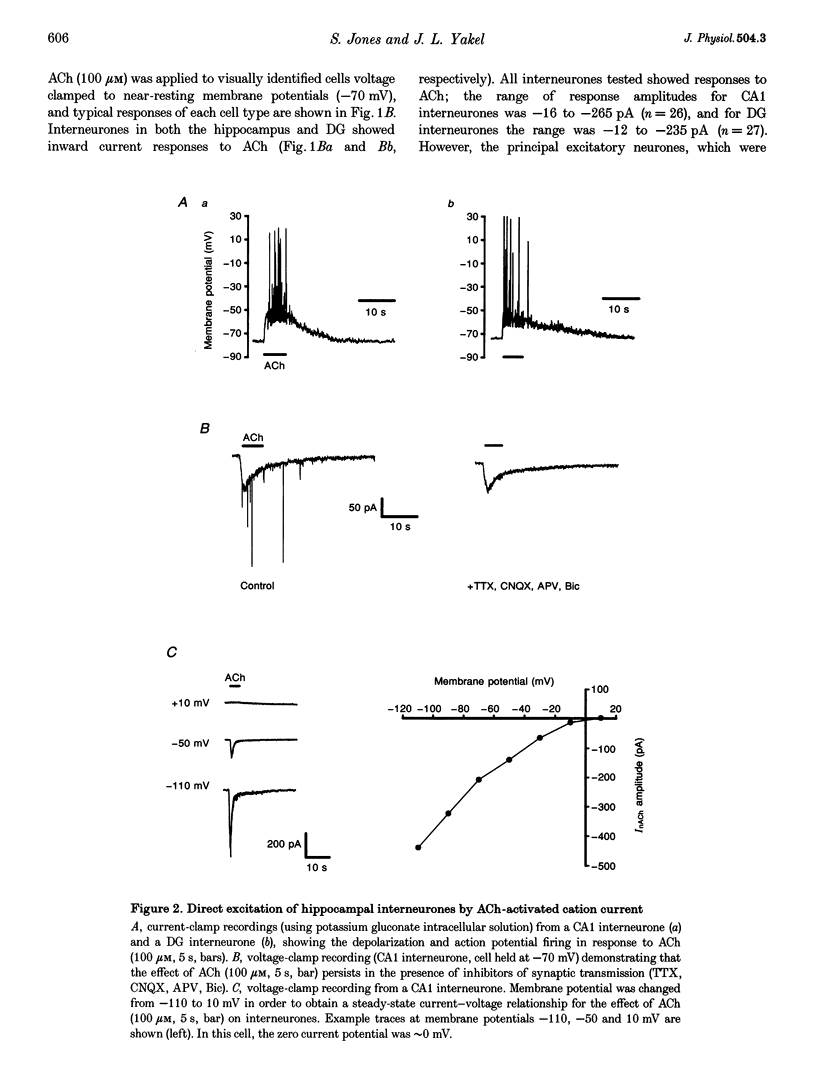
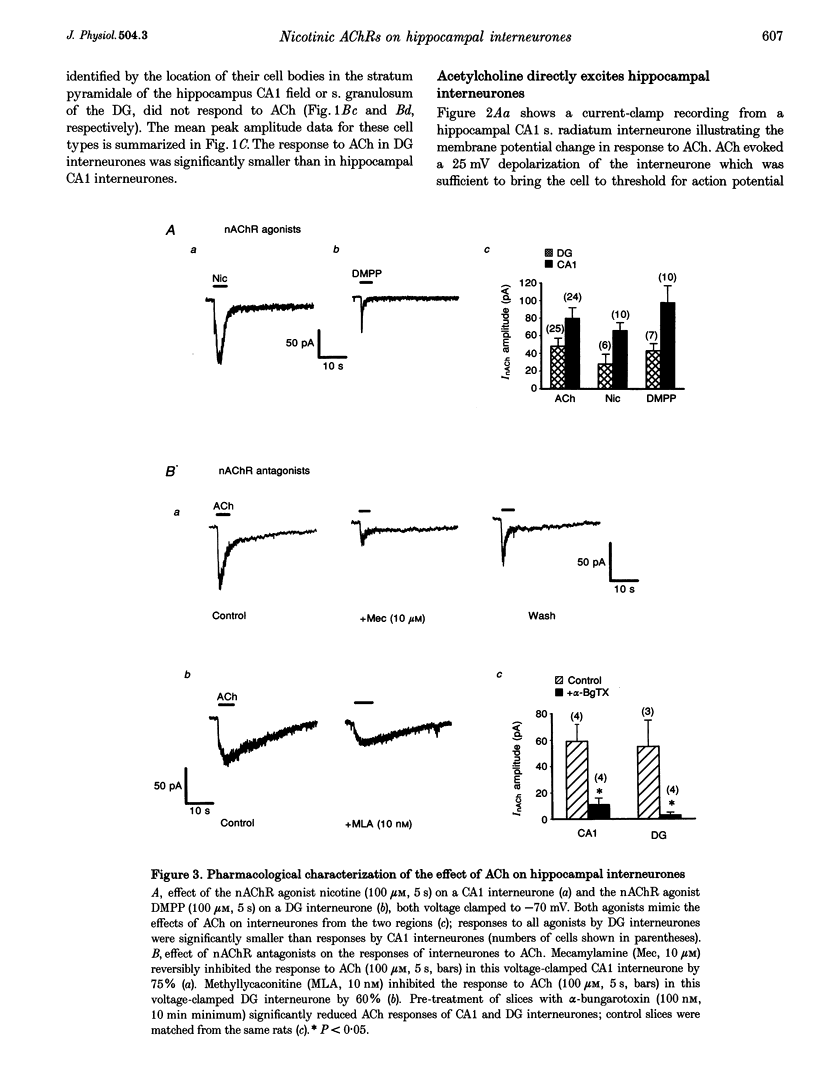
Abstract
1. Neuronal nicotinic ACh receptors (nAChRs) were studied in the rat hippocampal slice preparation using whole-cell patch-clamp recording techniques. 2. Responses to ACh (100 microM) were detected on inhibitory interneurones in the Ca1 field of the hippocampus proper and in the dentate gyrus, but not on principal excitatory neurones in either region. The different neuronal types were identified based on their morphology and location. 3. ACh excited interneurones in the hippocampus and dentate gyrus in current-clamp recordings. In voltage-clamp recordings, ACh-activated inward currents were recorded from interneurones in the presence of blockers of synaptic transmission and the muscarinic ACh receptor antagonist atropine. The zero current potential for this response to ACh was near 0 mV. 4. The effect of ACh was mimicked by the nAChR-selective agonists nicotine (100 microM) and 1,1-dimethyl-4-phenyl-piperazinium iodide (DMPP, 100 microM). The response to ACh was reversibly antagonized by the neuronal nAChR antagonist mecamylamine (10 microM). The nAChR alpha 7 subunit-selective antagonists alpha-bungarotoxin (100 nM) and methyllycaconitine (10 nM) also inhibited the response to ACh. 5. These observations demonstrate the presence of functional nAChRs on inhibitory interneurones in the rat hippocampus. Thus, a novel mechanism by which ACh can regulate neuronal activity in the hippocampus is revealed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkondon M., Albuquerque E. X. Initial characterization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. J Recept Res. 1991;11(6):1001–1021. doi: 10.3109/10799899109064693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkondon M., Pereira E. F., Wonnacott S., Albuquerque E. X. Blockade of nicotinic currents in hippocampal neurons defines methyllycaconitine as a potent and specific receptor antagonist. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):802–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benardo L. S., Prince D. A. Cholinergic excitation of mammalian hippocampal pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):315–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki G., Chrobak J. J. Temporal structure in spatially organized neuronal ensembles: a role for interneuronal networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Aug;5(4):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb S. R., Buhl E. H., Halasy K., Paulsen O., Somogyi P. Synchronization of neuronal activity in hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature. 1995 Nov 2;378(6552):75–78. doi: 10.1038/378075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R., Wetmore C., Strömberg I., Leonard S., Olson L. Alpha-bungarotoxin binding to hippocampal interneurons: immunocytochemical characterization and effects on growth factor expression. J Neurosci. 1993 May;13(5):1965–1975. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-05-01965.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R. K., Jungschaffer D. A., Collins A. C., Wehner J. M. Evidence for modulation of GABAergic neurotransmission by nicotine. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 21;453(1-2):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frotscher M., Léránth C. Cholinergic innervation of the rat hippocampus as revealed by choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry: a combined light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Sep 8;239(2):237–246. doi: 10.1002/cne.902390210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R., Rajan A. S., Radcliffe K. A., Yakehiro M., Dani J. A. Hippocampal synaptic transmission enhanced by low concentrations of nicotine. Nature. 1996 Oct 24;383(6602):713–716. doi: 10.1038/383713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Ion Channels. 1996;4:377–450. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1775-1_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGehee D. S., Role L. W. Physiological diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by vertebrate neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:521–546. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. The coupling of neurotransmitter receptors to ion channels in the brain. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):545–551. doi: 10.1126/science.2456612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordberg A. Human nicotinic receptors--their role in aging and dementia. Neurochem Int. 1994 Jul;25(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropert N., Krnjević K. Pharmacological characteristics of facilitation of hippocampal population spikes by cholinomimetics. Neuroscience. 1982;7(8):1963–1977. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovira C., Ben-Ari Y., Cherubini E., Krnjevic K., Ropert N. Pharmacology of the dendritic action of acetylcholine and further observations on the somatic disinhibition in the rat hippocampus in situ. Neuroscience. 1983 Jan;8(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sik A., Penttonen M., Ylinen A., Buzsáki G. Hippocampal CA1 interneurons: an in vivo intracellular labeling study. J Neurosci. 1995 Oct;15(10):6651–6665. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-10-06651.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloviter R. S., Nilaver G. Immunocytochemical localization of GABA-, cholecystokinin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the area dentata and hippocampus of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Feb 1;256(1):42–60. doi: 10.1002/cne.902560105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M., Fox S. E. Do septal neurons pace the hippocampal theta rhythm? Trends Neurosci. 1990 May;13(5):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90040-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguéla P., Wadiche J., Dineley-Miller K., Dani J. A., Patrick J. W. Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: a nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):596–604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00596.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada E., Wada K., Boulter J., Deneris E., Heinemann S., Patrick J., Swanson L. W. Distribution of alpha 2, alpha 3, alpha 4, and beta 2 neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit mRNAs in the central nervous system: a hybridization histochemical study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jun 8;284(2):314–335. doi: 10.1002/cne.902840212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. W., Coggan J. S., Berg D. K. Synaptic currents generated by neuronal acetylcholine receptors sensitive to alpha-bungarotoxin. Neuron. 1996 Dec;17(6):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80253-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]