Abstract
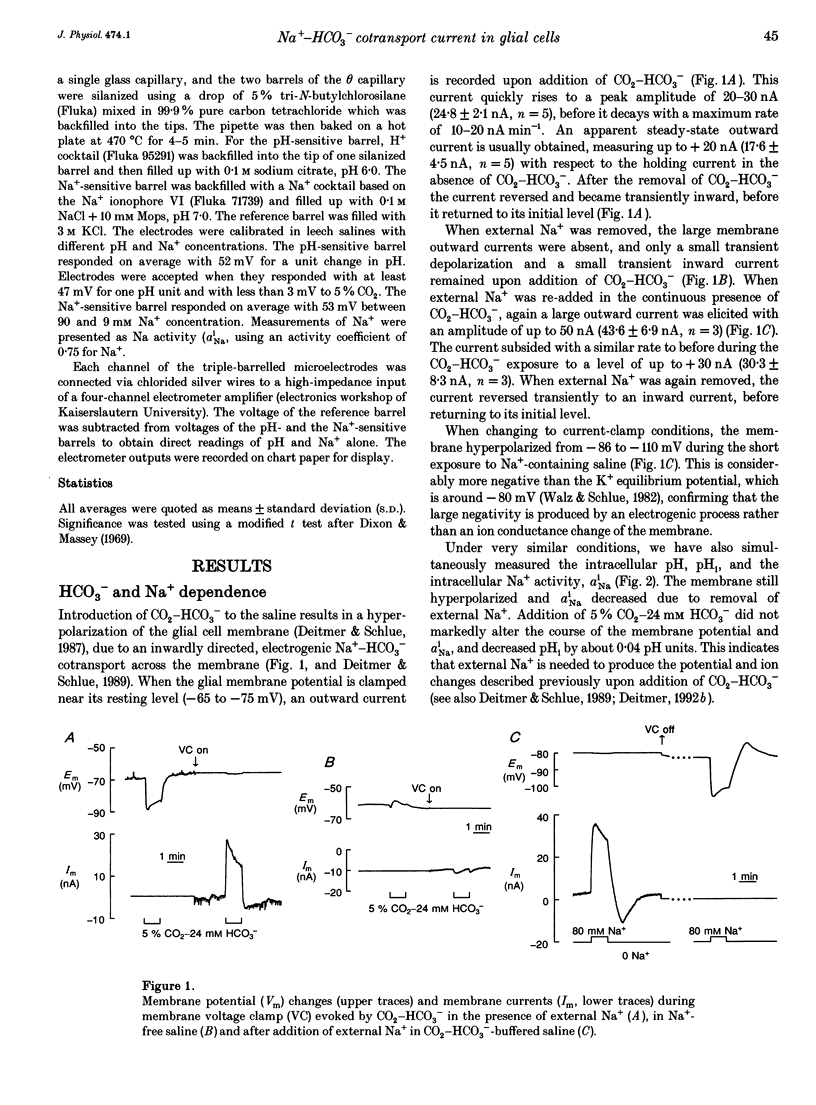
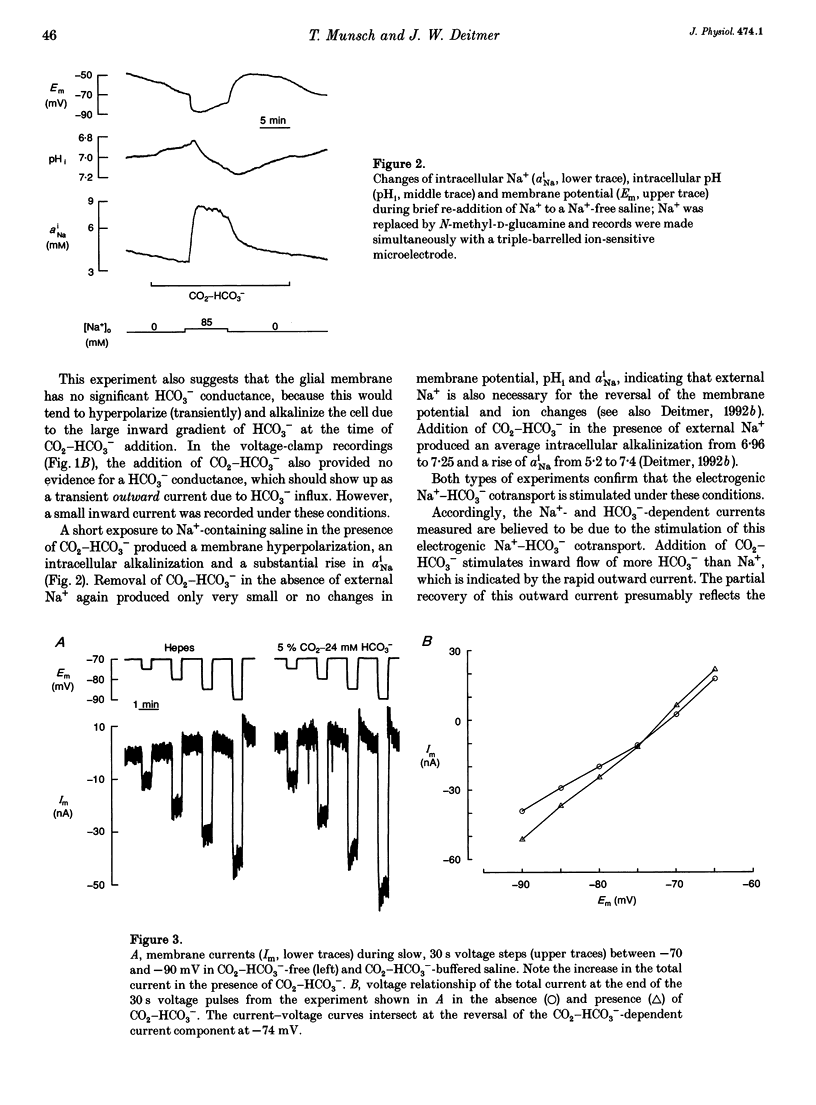
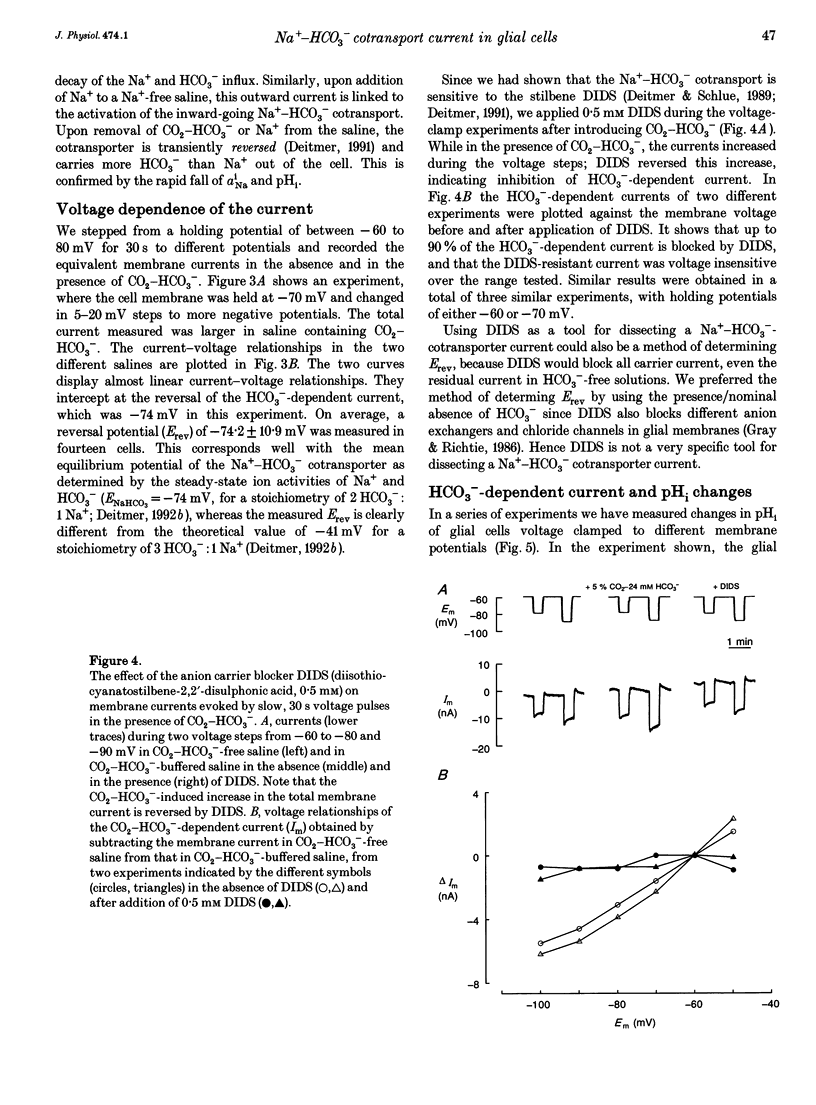
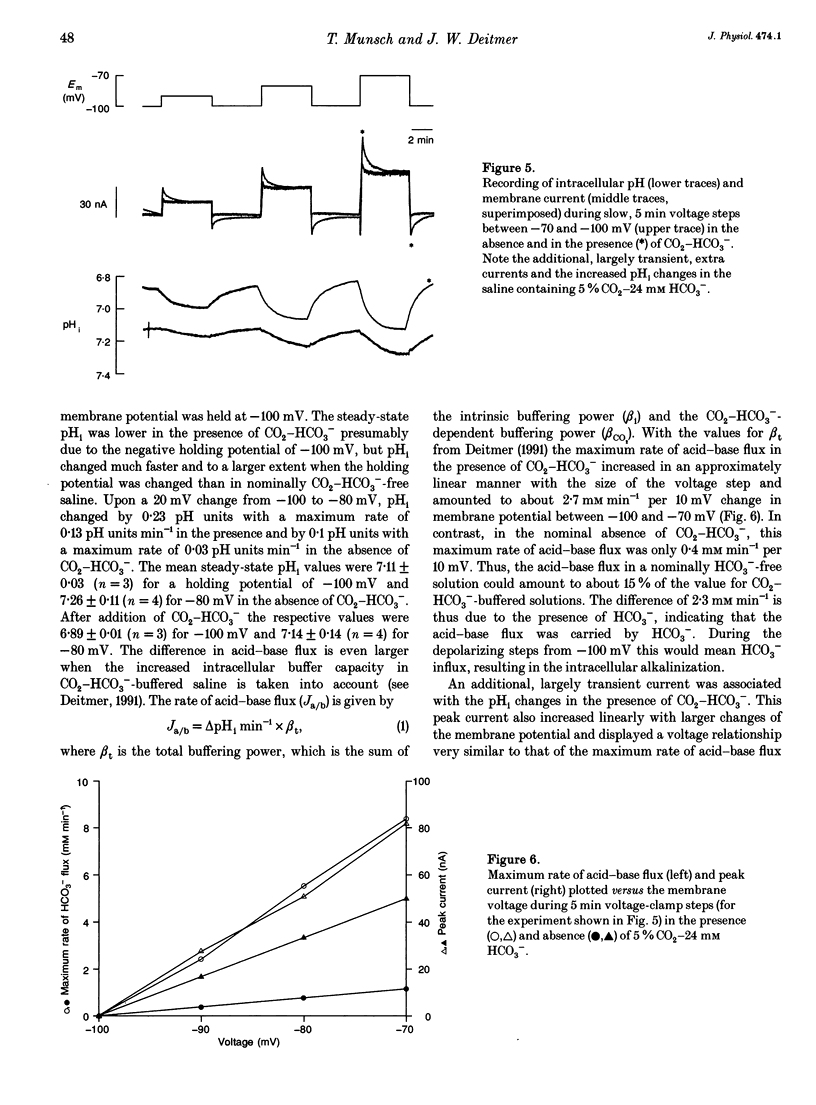
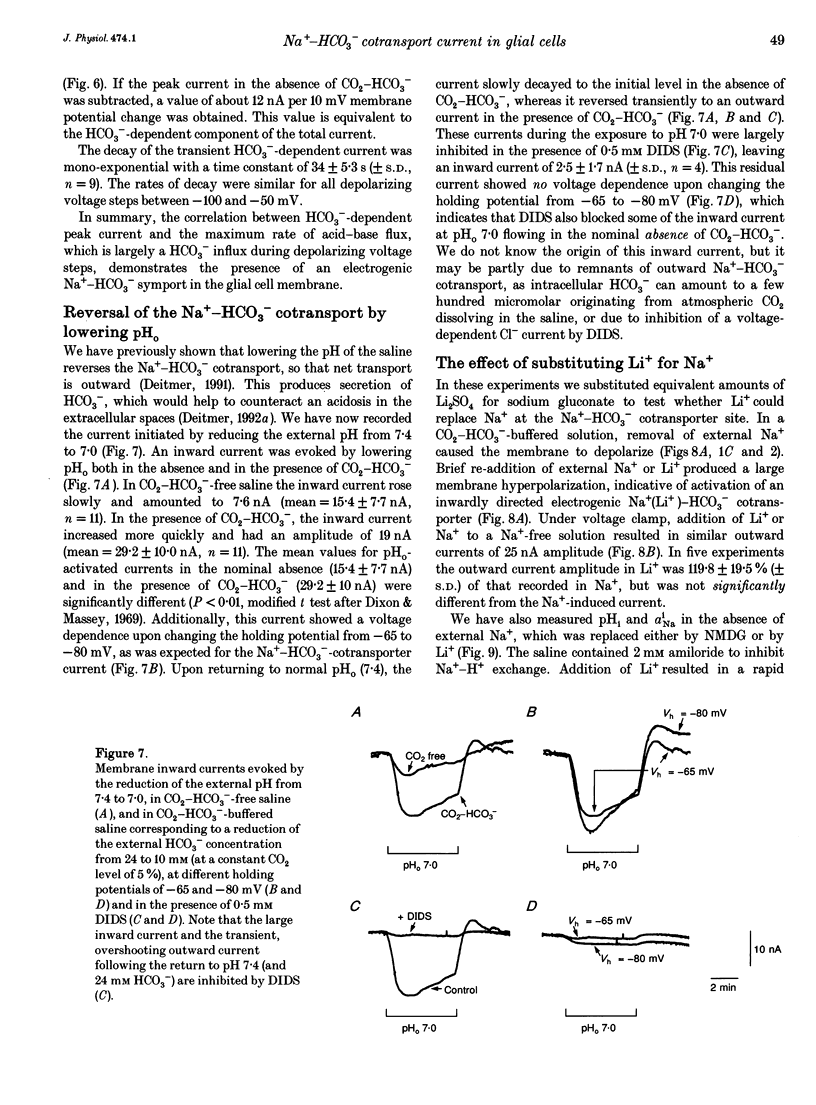
1. The membrane current associated with the cotransport of Na+ and HCO3- was investigated in neuropil glial cells in isolated ganglia of the leech Hirudo medicinalis L. using the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique. 2. The addition of 5% CO2-24 mM HCO3- evoked an outward current, which slowly decayed, and which was dependent upon the presence of external Na+. Removal of CO2-HCO3- elicited a transient inward current. Re-addition of Na+ to Na(+)-free saline in the presence of CO2-HCO3- also produced an outward current. Under these conditions an intracellular alkalinization and a rise in intracellular [Na+] were recorded using triple-barrelled, ion-sensitive microelectrodes. Addition or removal of HCO3-, in the absence of external Na+, caused little or no change in membrane voltage, membrane current and intracellular pH, indicating that the glial membrane has a very low HCO3- conductance. 3. Voltage steps revealed nearly linear current-voltage relationships both in the absence and presence of CO2-HCO3-, with an intersection at the assumed reversal potential of the HCO(3-)-dependent current. These results suggest a cotransport stoichiometry of 2HCO3-: 1 Na+. The HCO(3-)-dependent current could be inhibited by diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulphonic acid (DIDS). 4. Simultaneous recording of current and intracellular pH showed a correlation of the maximal acid-base flux with the transient HCO(3-)-dependent current during voltage steps in the presence of CO2-HCO3-. The maximum rate of acid-base flux and the HCO(3-)-dependent peak current showed a similar dependence on membrane voltage. Lowering the external pH from 7.4 to 7.0 produced an inward current, which increased twofold in the presence of CO2-HCO3-. This current was largely inhibited by DIDS, indicating outward-going electrogenic Na(+)-HCO3- cotransport during external acidification. 5. When external Na+ was replaced by Li+, a similar outward current and intracellular alkalinization were observed in the presence of CO2-HCO3-. The Li(+)-induced intracellular alkalinization was not inhibited by amiloride, a blocker of Na+(Li+)-H+ exchange, but was sensitive to DIDS. These results suggest that Li+ could, at least partly, substitute for Na+ at the cotransporter site. 6. Our results indicate that the Na(+)-HCO3- cotransport produces a current across the glial cell membrane in both directions with a reversal potential near the membrane resting potential, rendering pHi a function of the glial membrane potential.
Full text
PDF

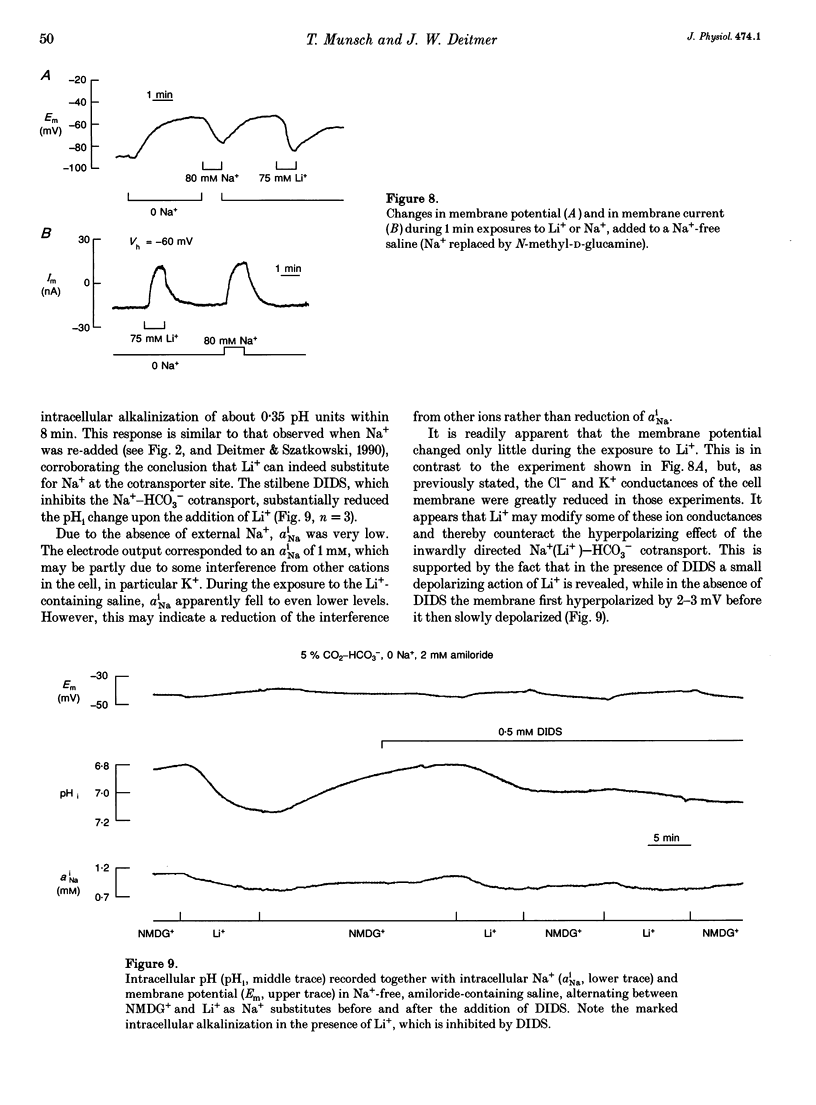



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astion M. L., Orkand R. K. Electrogenic Na+/HCO3- cotransport in neuroglia. Glia. 1988;1(5):355–357. doi: 10.1002/glia.440010508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballanyi K., Schlue W. R. Intracellular chloride activity in glial cells of the leech central nervous system. J Physiol. 1990 Jan;420:325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker B. F., Duhm J. Evidence for anionic cation transport of lithium, sodium and potassium across the human erythrocyte membrane induced by divalent anions. J Physiol. 1978 Sep;282:149–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander. Basolateral HCO3- transport. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Jan;81(1):53–94. doi: 10.1085/jgp.81.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F., Boulpaep E. L. The electrogenic Na/HCO3 cotransporter. Kidney Int. 1989 Sep;36(3):392–402. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. Y., Yen-Chow Y. C., White H. S., Woodbury D. M. pH regulation after acid load in primary cultures of mouse astrocytes. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 May 20;60(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(91)90156-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dart C., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Na(+)-HCO3- symport in the sheep cardiac Purkinje fibre. J Physiol. 1992;451:365–385. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W. Bicarbonate-dependent changes of intracellular sodium and pH in identified leech glial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Apr;420(5-6):584–589. doi: 10.1007/BF00374637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W. Electrogenic sodium-dependent bicarbonate secretion by glial cells of the leech central nervous system. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Sep;98(3):637–655. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W. Evidence for glial control of extracellular pH in the leech central nervous system. Glia. 1992;5(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/glia.440050107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Schlue W. R. An inwardly directed electrogenic sodium-bicarbonate co-transport in leech glial cells. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:179–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Schlue W. R. The regulation of intracellular pH by identified glial cells and neurones in the central nervous system of the leech. J Physiol. 1987 Jul;388:261–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitmer J. W., Szatkowski M. Membrane potential dependence of intracellular pH regulation by identified glial cells in the leech central nervous system. J Physiol. 1990 Feb;421:617–631. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz J. G., Lidofsky S. D., Xie M. H., Scharschmidt B. F. Transmembrane electrical potential difference regulates Na+/HCO3- cotransport and intracellular pH in hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4197–4201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. T., Ritchie J. M. A voltage-gated chloride conductance in rat cultured astrocytes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Aug 22;228(1252):267–288. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. A., Adorante J. S., Miller S. S., Lin H. Apical electrogenic NaHCO3 cotransport. A mechanism for HCO3 absorption across the retinal pigment epithelium. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jul;94(1):125–150. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch T. J., Keller S. K., Koch M., Wiederholt M. Evidence for coupled transport of bicarbonate and sodium in cultured bovine corneal endothelial cells. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):189–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01868713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettenmann H., Schlue W. R. Intracellular pH regulation in cultured mouse oligodendrocytes. J Physiol. 1988 Dec;406:147–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Cour M. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate co-transport across the retinal membrane of the frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:539–553. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagadic-Gossmann D., Buckler K. J., Vaughan-Jones R. D. Role of bicarbonate in pH recovery from intracellular acidosis in the guinea-pig ventricular myocyte. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:361–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munsch T., Deitmer J. W. Calcium transients in identified leech glial cells in situ evoked by high potassium concentrations and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Exp Biol. 1992 Jun;167:251–265. doi: 10.1242/jeb.167.1.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A., Astion M. L. Localization and stoichiometry of electrogenic sodium bicarbonate cotransport in retinal glial cells. Glia. 1991;4(4):424–428. doi: 10.1002/glia.440040411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman E. A. Sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in retinal Müller (glial) cells of the salamander. J Neurosci. 1991 Dec;11(12):3972–3983. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-12-03972.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani M., Lesoine G. A., Bergman J. A., Aronson P. S. Cation specificity and modes of the Na+:CO3(2-):HCO3- cotransporter in renal basolateral membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8706–8710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan-Jones R. D. Regulation of chloride in quiescent sheep-heart Purkinje fibres studied using intracellular chloride and pH-sensitive micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:111–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz W., Schlue W. R. External ions and membrane potential of leech neuropile glial cells. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):119–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90837-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuttke W. A. Mechanism of potassium uptake in neuropile glial cells in the central nervous system of the leech. J Neurophysiol. 1990 May;63(5):1089–1097. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.5.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour M. Kinetic properties and Na+ dependence of rheogenic Na(+)-HCO3- co-transport in frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:59–72. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


