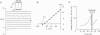Abstract
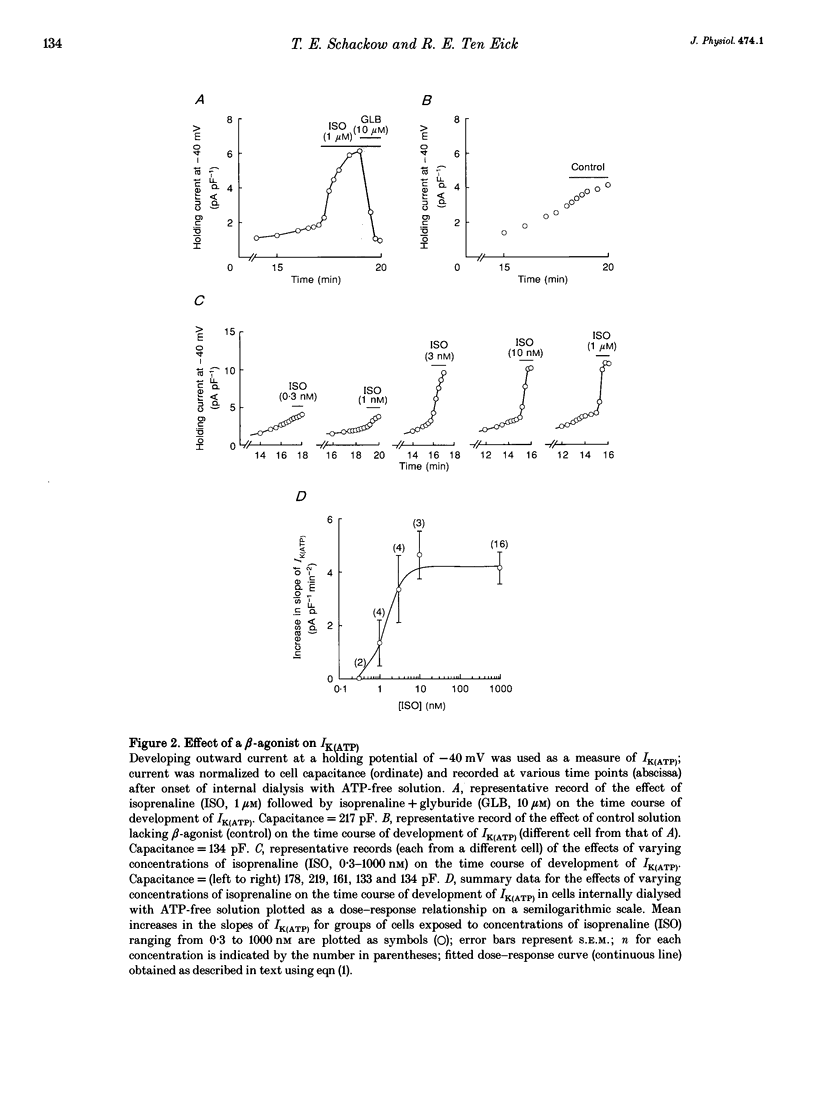
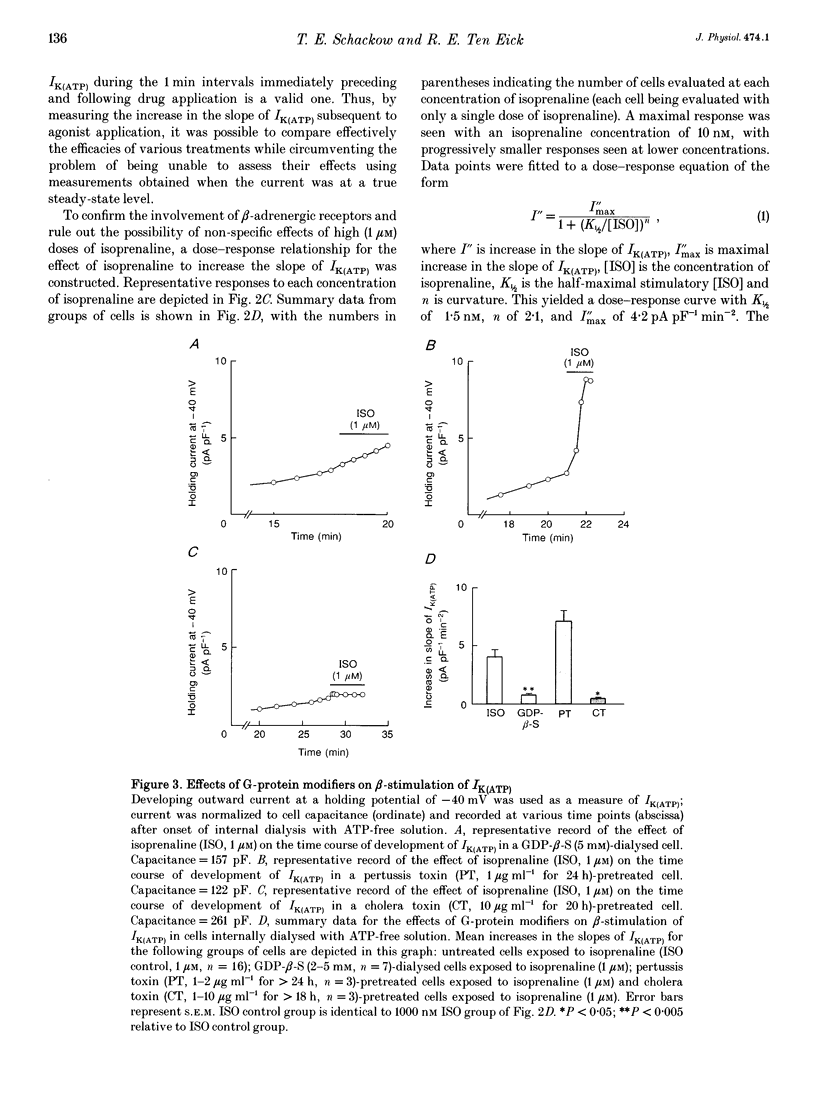
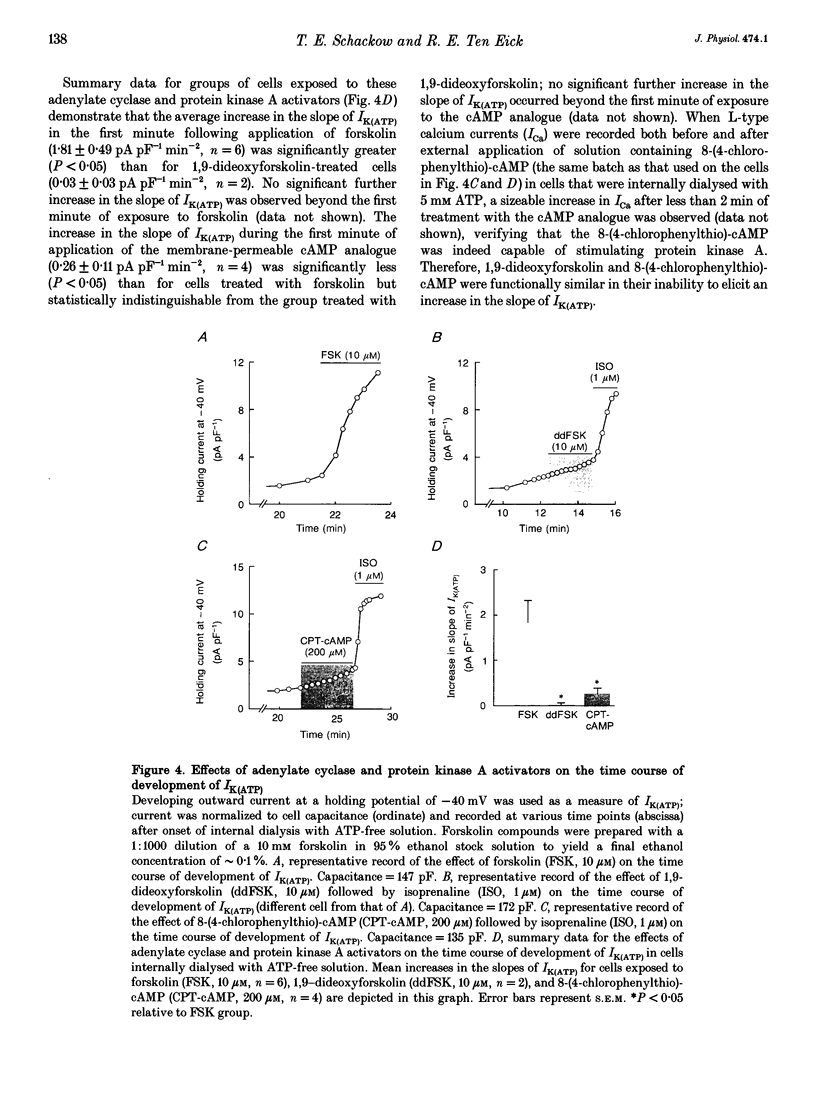
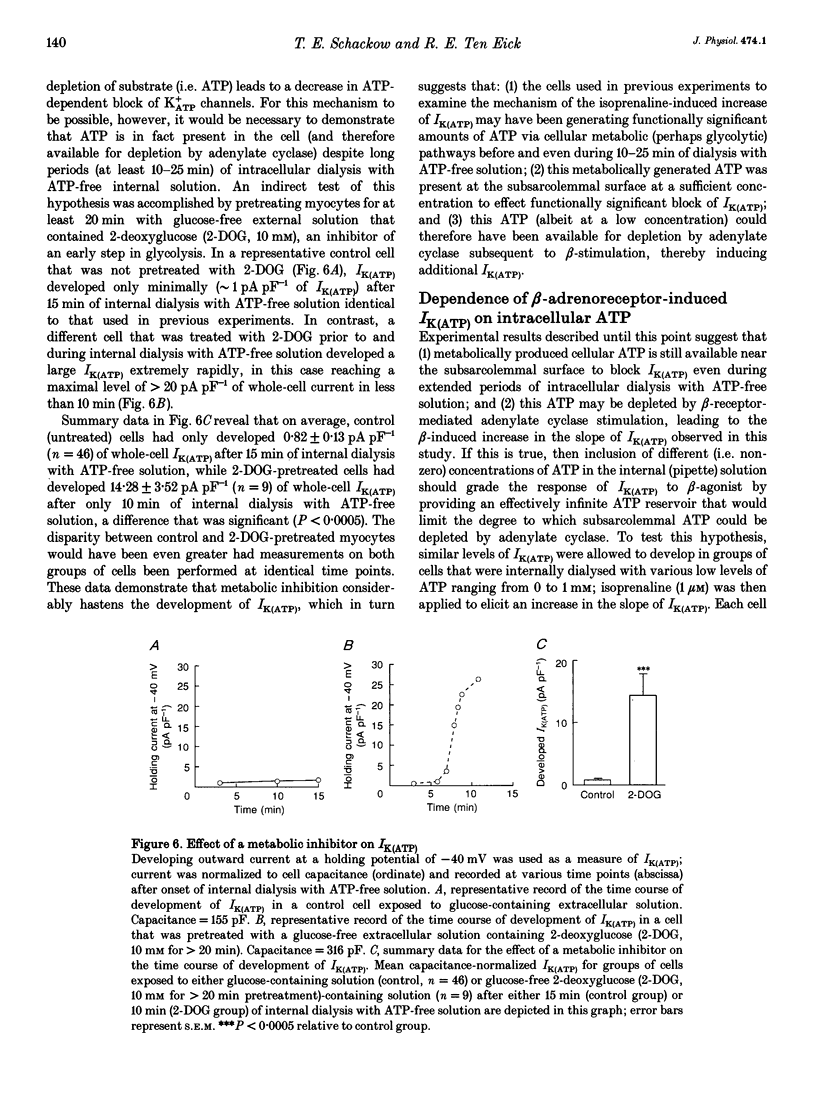
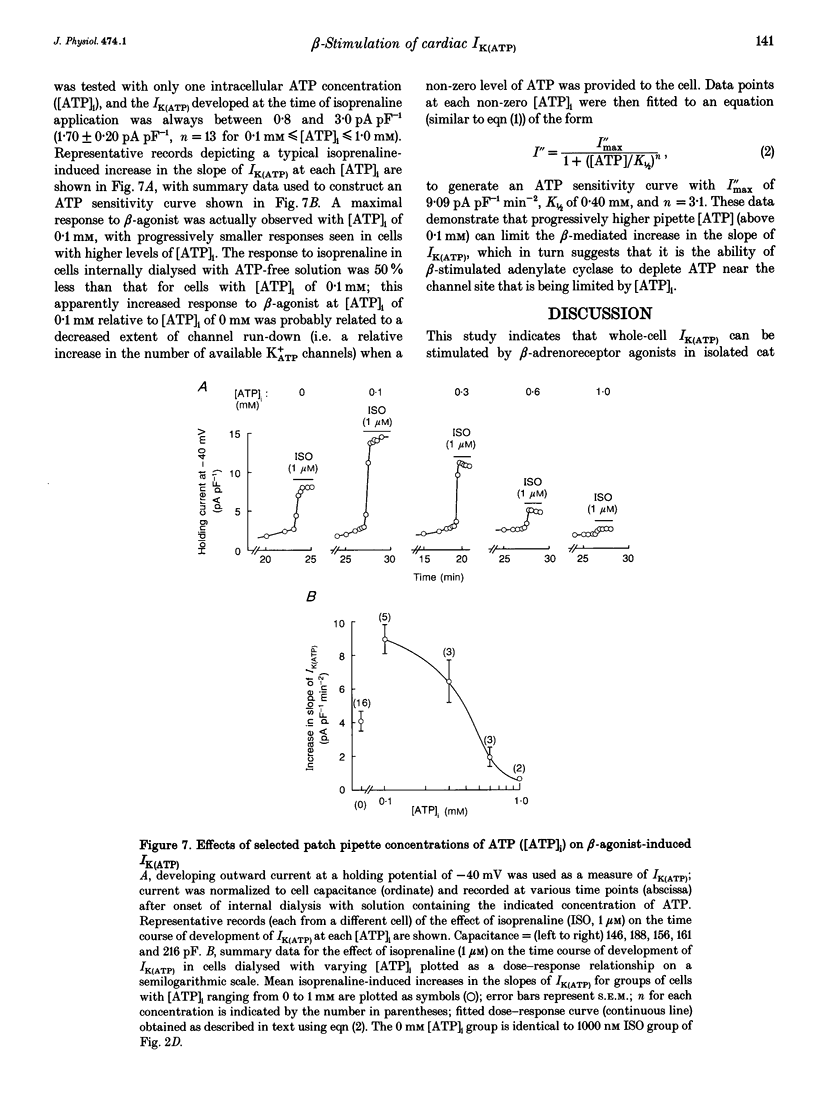
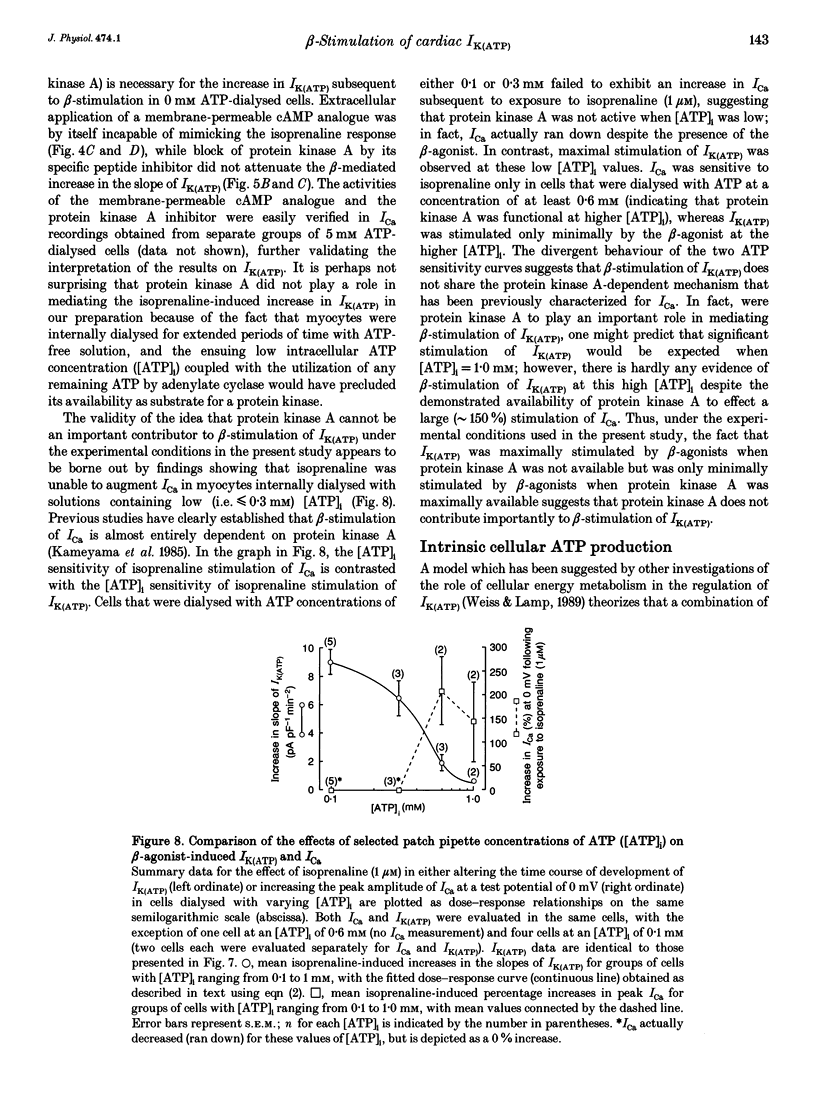
1. To address the questions of whether beta-adrenoreceptor stimulation can augment ATP-sensitive potassium current (IK(ATP)), and what the mechanism of such an effect might be, action potentials and whole-cell ionic currents were recorded from adult cat cardiac ventricular myocytes using a conventional whole-cell patch technique. 2. An outwardly directed, ohmic, non-inactivating, glyburide (10 microM)-sensitive current reversing near the reversal potential for potassium (EK) developed slowly (10-25 min) in cells dialysed with an ATP-free pipette (intracellular) solution. During this time, action potential duration markedly decreased while the resting membrane potential hyperpolarized closer to EK. Extended (> 30 min) periods of internal dialysis with ATP-free solution eventually resulted in run-down of the outward current. 3. Externally applied isoprenaline (1 microM) caused a rapidly developing (< or = 60 s), sustained enhancement of a glyburide (10 microM)-sensitive IK(ATP) in cells internally dialysed with ATP-free solution. IK(ATP) remained elevated even after the isoprenaline was removed, and subsequent applications of the beta-agonist failed to increase IK(ATP) further. Half-maximal isoprenaline stimulation of IK(ATP) occurred at a concentration of approximate of 1.5 nM. 4. Pretreatment with propranolol (1 microM) prevented the enhancement of IK(ATP) by a beta-agonist. 5. Isoprenaline-induced IK(ATP) could be blocked by either internal application of GDP-beta-S (2-5 mM) or pretreatment with cholera toxin (1-10 microgram ml-1, > 18 h). Pretreatment with pertussis toxin (1-2 microgram ml-1, > 18 h) did not attenuate the isoprenaline response, whereas internally applied GTP-gamma-S (100 microM) or F- (20 mM) caused IK(ATP) to increase rapidly in the absence of the beta-agonist. 6. Although externally applied forskolin (10 microM) also stimulated IK(ATP), neither 1,9-dideoxyforskolin (10 microM) nor 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-cAMP (200 microM) had any effect on the current. Internal application of the adenylate cyclase inhibitor 2'-deoxyadenosine-3'-monophosphate (100 microM) resulted in a reduction in the response to isoprenaline, while internal application of a protein kinase A inhibitor (PKI5-24, 22.5 microM) did not attenuate the response to the beta-agonist. 7. IK(ATP) developed slowly during internal dialysis with ATP-free solution.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
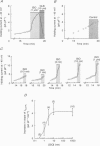
PDF

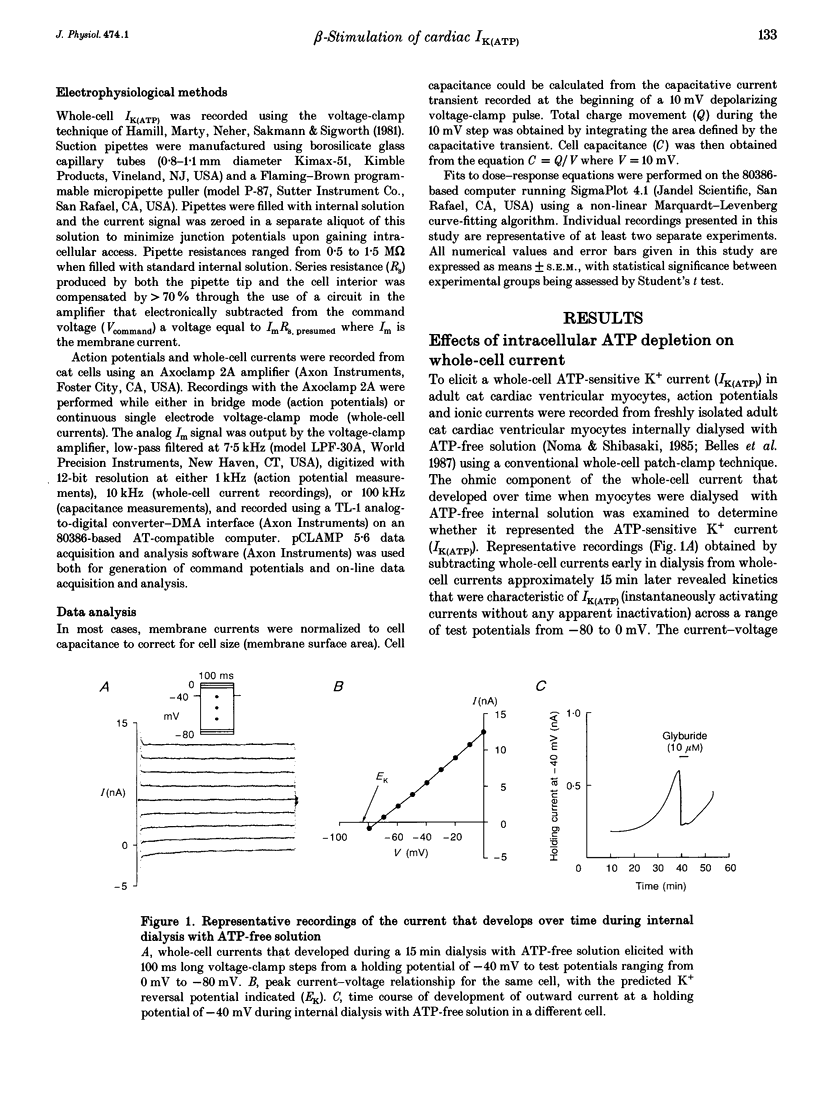






Images in this article
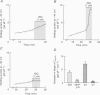
Selected References
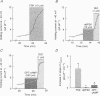
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belles B., Hescheler J., Trube G. Changes of membrane currents in cardiac cells induced by long whole-cell recordings and tolbutamide. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):582–588. doi: 10.1007/BF00584657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. A cellular logic for G protein-coupled ion channel pathways. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2175–2179. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.8.1708737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushfield M., Johnson R. A. Regulation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine: characterization of the P-site. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Apr;18(2):150–151. doi: 10.1042/bst0180150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Methods Enzymol. 1988;157:378–417. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)57093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faivre J. F., Findlay I. Action potential duration and activation of ATP-sensitive potassium current in isolated guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 2;1029(1):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90450-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. ATP4- and ATP.Mg inhibit the ATP-sensitive K+ channel of rat ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Jul;412(1-2):37–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00583729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I. Effects of ADP upon the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in rat ventricular myocytes. J Membr Biol. 1988;101(1):83–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01872823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay I., Faivre J. F. ATP-sensitive K channels in heart muscle. Spare channels. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka M., Fan Z. Activation of ATP-sensitive outward K+ current by nicorandil (2-nicotinamidoethyl nitrate) in isolated ventricular myocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):278–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohl C. M., Li Q. A. Compartmentation of cAMP in adult canine ventricular myocytes. Relation to single-cell free Ca2+ transients. Circ Res. 1991 Nov;69(5):1369–1379. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.5.1369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse M. J., Wit A. L. Electrophysiological mechanisms of ventricular arrhythmias resulting from myocardial ischemia and infarction. Physiol Rev. 1989 Oct;69(4):1049–1169. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.4.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Noma A., Shibasaki T. Properties of adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:441–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyama M., Hofmann F., Trautwein W. On the mechanism of beta-adrenergic regulation of the Ca channel in the guinea-pig heart. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Oct;405(3):285–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00582573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Coupling of ATP-sensitive K+ channels to A1 receptors by G proteins in rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H820–H826. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer W. J., Nichols C. G. Nucleotide modulation of the activity of rat heart ATP-sensitive K+ channels in isolated membrane patches. J Physiol. 1989 Dec;419:193–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. J., Jr, Sanguinetti M. C., Kimura S., Bassett A. L. Therapeutic potential of modulating potassium currents in the diseased myocardium. FASEB J. 1992 Aug;6(11):2952–2960. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.11.1386585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J. The regulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channel activity in intact and permeabilized rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol. 1990 Apr;423:91–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A. ATP-regulated K+ channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):147–148. doi: 10.1038/305147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noma A., Shibasaki T. Membrane current through adenosine-triphosphate-regulated potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol. 1985 Jun;363:463–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribalet B., Ciani S., Eddlestone G. T. ATP mediates both activation and inhibition of K(ATP) channel activity via cAMP-dependent protein kinase in insulin-secreting cell lines. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Oct;94(4):693–717. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripoll C., Lederer W. J., Nichols C. G. Modulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channel activity and contractile behavior in mammalian ventricle by the potassium channel openers cromakalim and RP49356. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):429–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinetti M. C., Scott A. L., Zingaro G. J., Siegl P. K. BRL 34915 (cromakalim) activates ATP-sensitive K+ current in cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8360–8364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen W. K., Tung R. T., Machulda M. M., Kurachi Y. Essential role of nucleotide diphosphates in nicorandil-mediated activation of cardiac ATP-sensitive K+ channel. A comparison with pinacidil and lemakalim. Circ Res. 1991 Oct;69(4):1152–1158. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.4.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. H., Hemwall E. L., Marino T. A., Houser S. R. Isolation and morphology of calcium-tolerant feline ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1983 Nov;245(5 Pt 1):H891–H896. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1983.245.5.H891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTWEIN W., GOTTSTEIN U., DUDEL J. Der Aktionsstrom der Myokardfaser im Sauerstoffmangel. Pflugers Arch. 1954;260(1):40–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00363778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano M., Qin D. Y., Noma A. ATP-dependent decay and recovery of K+ channels in guinea pig cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):H45–H50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.1.H45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuringer D., Escande D. Apparent competition between ATP and the potassium channel opener RP 49356 on ATP-sensitive K+ channels of cardiac myocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;36(6):897–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Hescheler J. Inward-rectifying channels in isolated patches of the heart cell membrane: ATP-dependence and comparison with cell-attached patches. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Jun;401(2):178–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00583879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng G. N., Hoffman B. F. Actions of pinacidil on membrane currents in canine ventricular myocytes and their modulation by intracellular ATP and cAMP. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Jan;415(4):414–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00373618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Giebisch G. Dual modulation of renal ATP-sensitive K+ channel by protein kinases A and C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9722–9725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. N., Lamp S. T. Cardiac ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Evidence for preferential regulation by glycolysis. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Nov;94(5):911–935. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.5.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]