Abstract
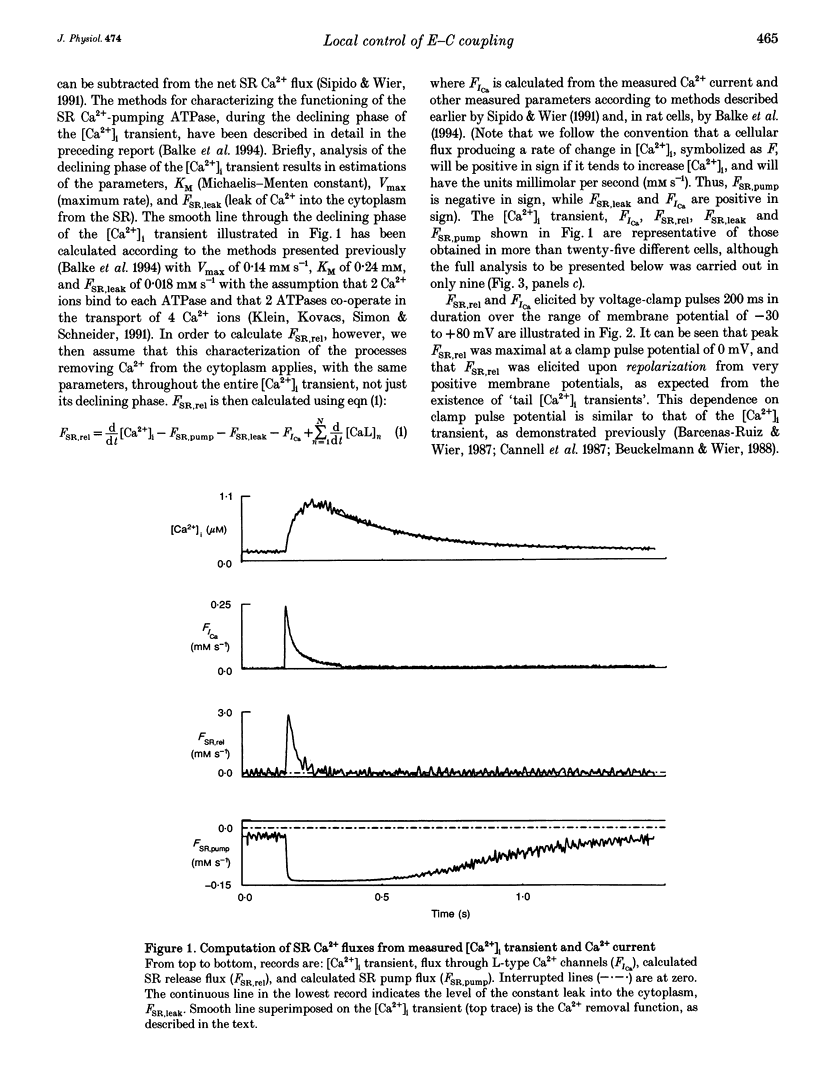
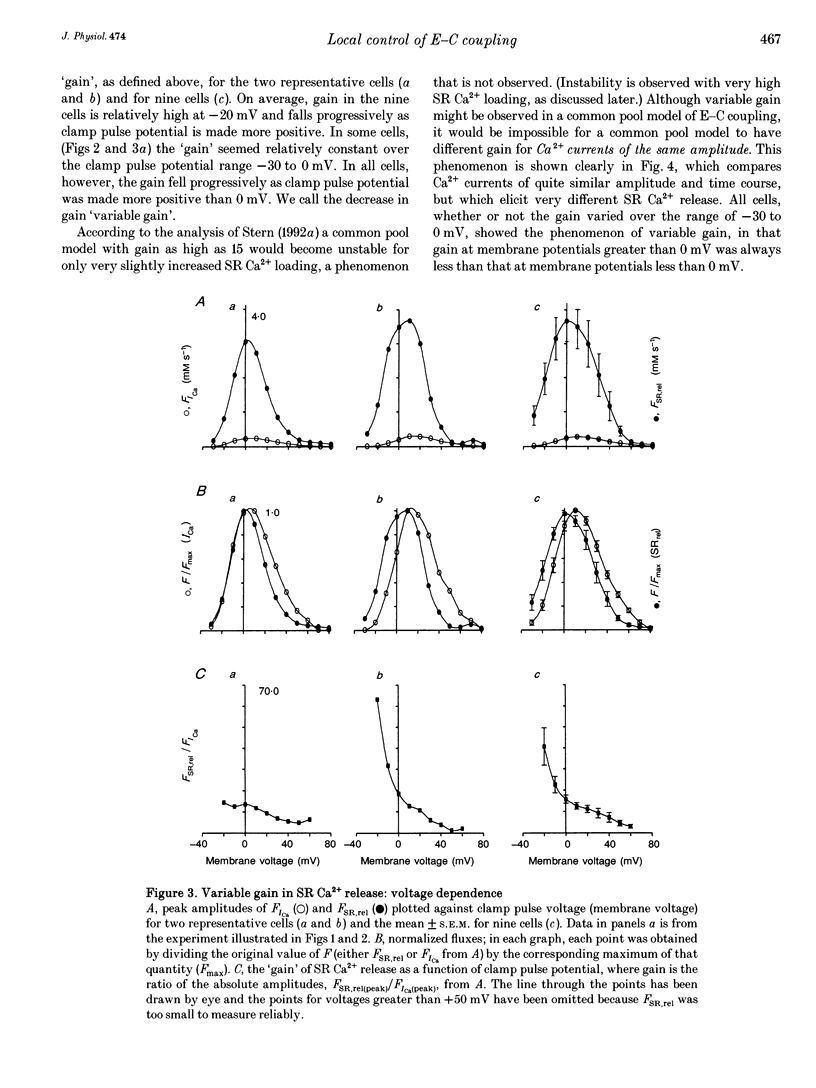
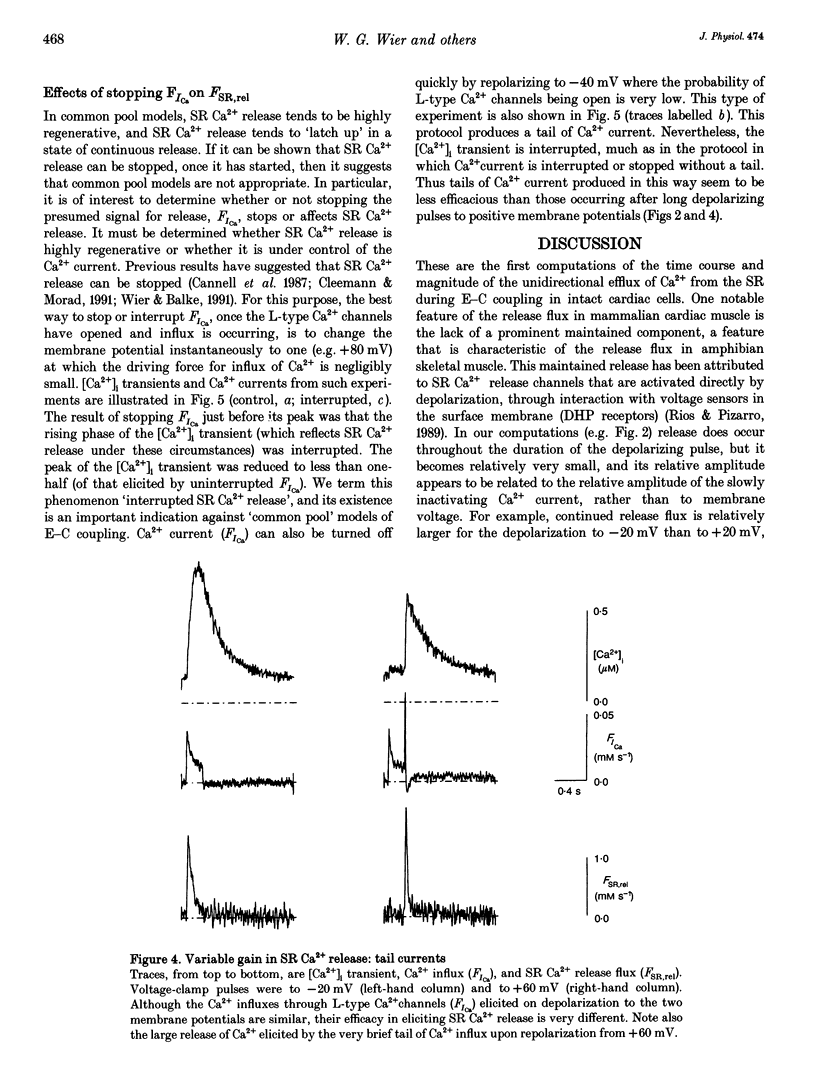
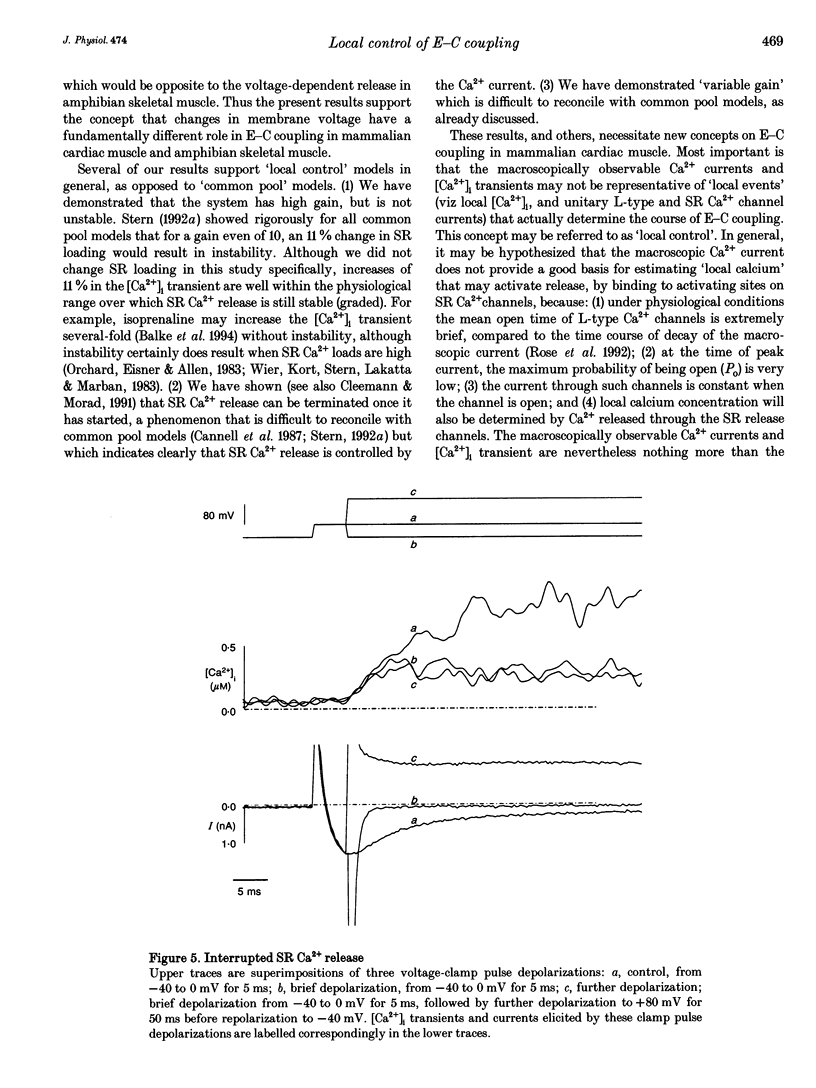
1. Cytosolic free calcium ion concentration ([Ca2+]i) and whole-cell L-type Ca2+ channel currents were measured during excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling in single voltage-clamped rat cardiac ventricular cells. The measurements were used to compute the total cellular efflux of calcium ions through sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ release channels (FSR,rel) and the influx of Ca2+ via L-type Ca2+ channels (FICa). 2. FSR,rel was elicited by depolarizing voltage-clamp pulses 200 ms in duration to membrane potentials from -30 to +80 mV. Over this range, peak FSR,rel had a bell-shaped dependence on clamp pulse potential. In all cells, the 'gain' of the system, measured as the ratio, FSR,rel(max)/FICa(max), declined from about 16, at 0 mV, to much lower values as clamp pulse voltage was made progressively more positive. We named this phenomenon of change in gain as a function of membrane potential, 'variable gain'. At clamp pulse potentials in the range -30 to 0 mV, the gain differed from cell to cell, being constant at about 16 in some cells, but decreasing from high values (approximately 65) at -20 mV in others. 3. At clamp pulse potentials at which Ca2+ influx (FICa) was maintained, FSR,rel also had a small maintained component. When macroscopic Ca2+ influx was brief (1-2 ms, during 'tails' of FICa), FSR,rel rose rapidly to a peak after repolarization and then declined with a half-time of about 9 ms (typically). 4. The rising phase of [Ca2+]i transients could be interrupted by stopping Ca2+ influx rapidly (by voltage clamp). We therefore termed this phenomenon 'interrupted SR Ca2+ release'.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley R. H., Williams A. J. Divalent cation activation and inhibition of single calcium release channels from sheep cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1990 May;95(5):981–1005. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.5.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke C. W., Egan T. M., Wier W. G. Processes that remove calcium from the cytoplasm during excitation-contraction coupling in intact rat heart cells. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 1;474(3):447–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke C. W., Rose W. C., Marban E., Wier W. G. Macroscopic and unitary properties of physiological ion flux through T-type Ca2+ channels in guinea-pig heart cells. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:247–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcenas-Ruiz L., Wier W. G. Voltage dependence of intracellular [Ca2+]i transients in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 1987 Jul;61(1):148–154. doi: 10.1161/01.res.61.1.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Peskoff A. Diffusion around a cardiac calcium channel and the role of surface bound calcium. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):703–721. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82284-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beuckelmann D. J., Wier W. G. Mechanism of release of calcium from sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1988 Nov;405:233–255. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Berlin J. R., Lederer W. J. Effect of membrane potential changes on the calcium transient in single rat cardiac muscle cells. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1419–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2446391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleemann L., Morad M. Role of Ca2+ channel in cardiac excitation-contraction coupling in the rat: evidence from Ca2+ transients and contraction. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:283–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Simulated calcium current can both cause calcium loading in and trigger calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):291–320. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Feb;85(2):247–289. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Kovacs L., Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Decline of myoplasmic Ca2+, recovery of calcium release and sarcoplasmic Ca2+ pump properties in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:639–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc N., Hume J. R. Sodium current-induced release of calcium from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):372–376. doi: 10.1126/science.2158146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzanti M., DeFelice L. J. Ca channel gating during cardiac action potentials. Biophys J. 1990 Oct;58(4):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82448-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Henderson J. S. Rapid calcium release from cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles is dependent on Ca2+ and is modulated by Mg2+, adenine nucleotide, and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3065–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli E., Lederer W. J. Voltage-independent calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):565–568. doi: 10.1126/science.2173135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näbauer M., Callewaert G., Cleemann L., Morad M. Regulation of calcium release is gated by calcium current, not gating charge, in cardiac myocytes. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):800–803. doi: 10.1126/science.2543067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näbauer M., Morad M. Ca2(+)-induced Ca2+ release as examined by photolysis of caged Ca2+ in single ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):C189–C193. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.1.C189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill S. C., Mill J. G., Eisner D. A. Local activation of contraction in isolated rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1165–C1168. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orchard C. H., Eisner D. A., Allen D. G. Oscillations of intracellular Ca2+ in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):735–738. doi: 10.1038/304735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose W. C., Balke C. W., Wier W. G., Marban E. Macroscopic and unitary properties of physiological ion flux through L-type Ca2+ channels in guinea-pig heart cells. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:267–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sham J. S., Cleemann L., Morad M. Gating of the cardiac Ca2+ release channel: the role of Na+ current and Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1311127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipido K. R., Wier W. G. Flux of Ca2+ across the sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells during excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Buffering of calcium in the vicinity of a channel pore. Cell Calcium. 1992 Mar;13(3):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90046-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Theory of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):497–517. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81615-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdeolmillos M., O'Neill S. C., Smith G. L., Eisner D. A. Calcium-induced calcium release activates contraction in intact cardiac cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Apr;413(6):676–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00581820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G. Cytoplasmic [Ca2+] in mammalian ventricle: dynamic control by cellular processes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:467–485. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Kort A. A., Stern M. D., Lakatta E. G., Marban E. Cellular calcium fluctuations in mammalian heart: direct evidence from noise analysis of aequorin signals in Purkinje fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7367–7371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Yue D. T. Intracellular calcium transients underlying the short-term force-interval relationship in ferret ventricular myocardium. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


