Abstract
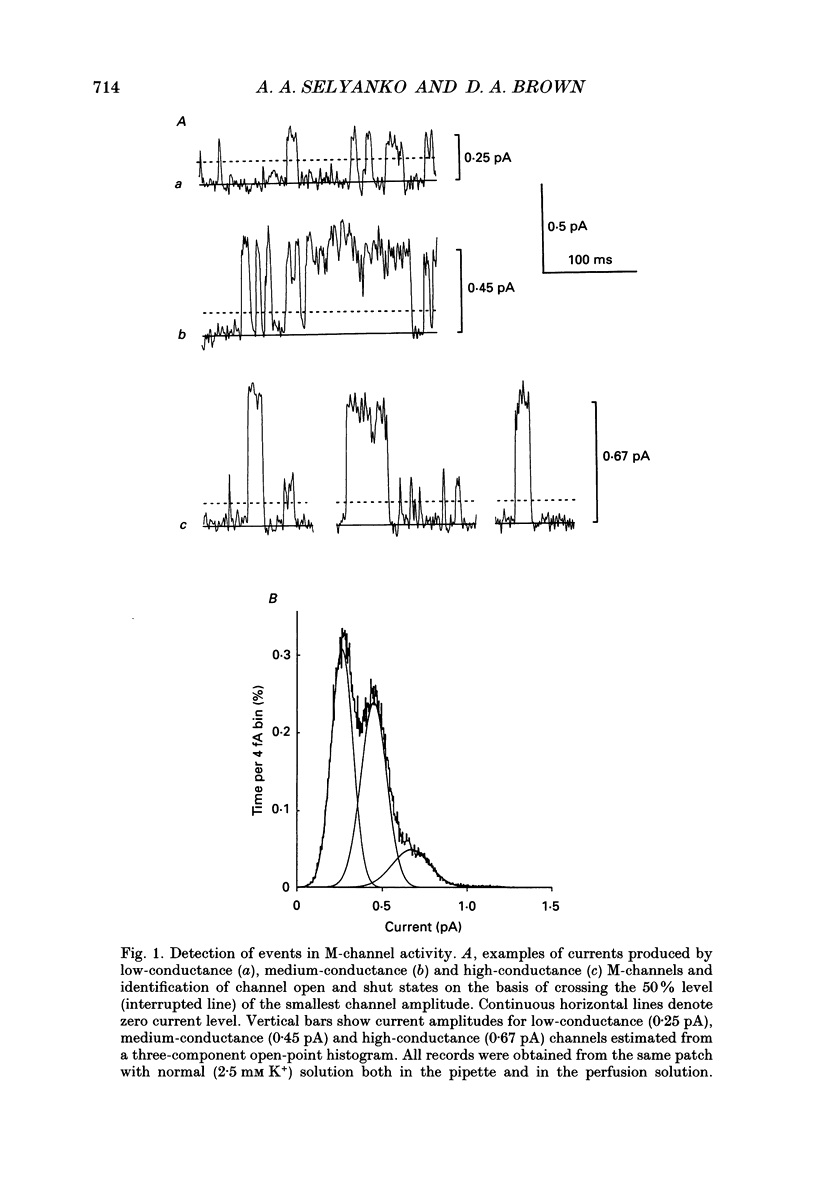
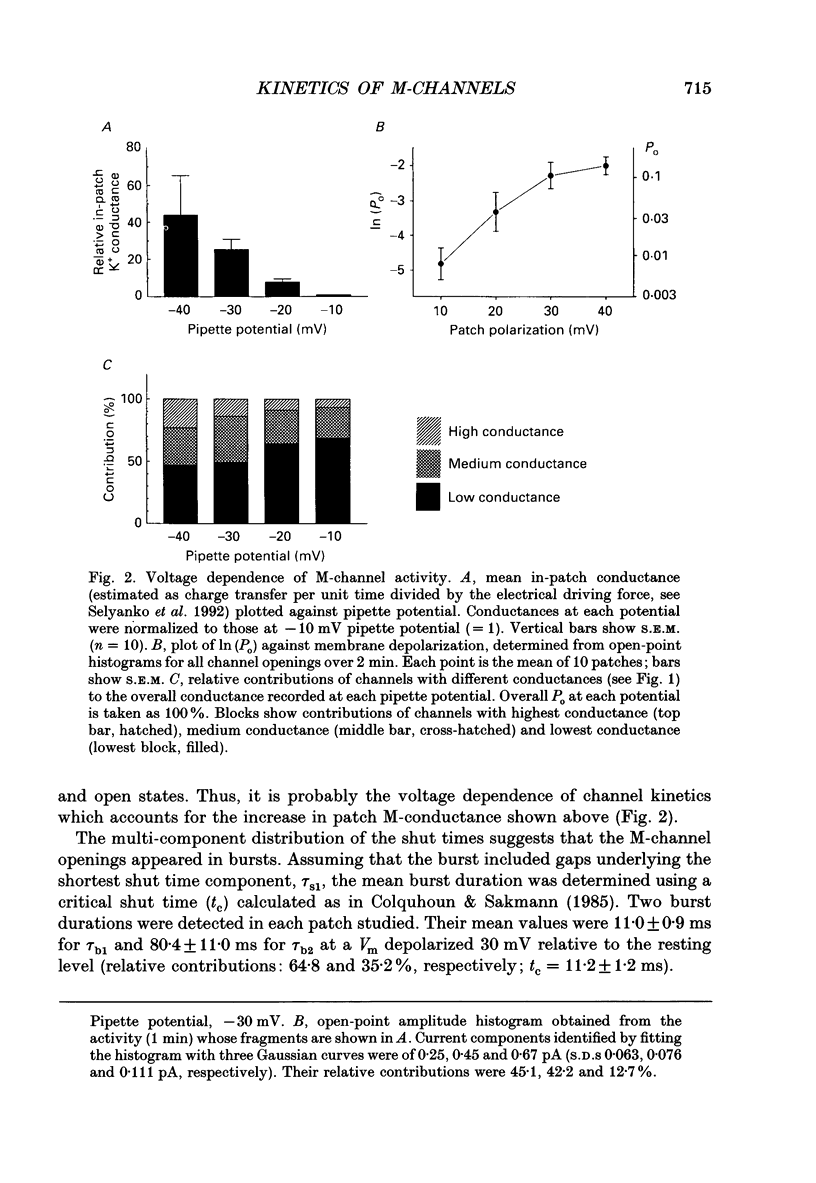
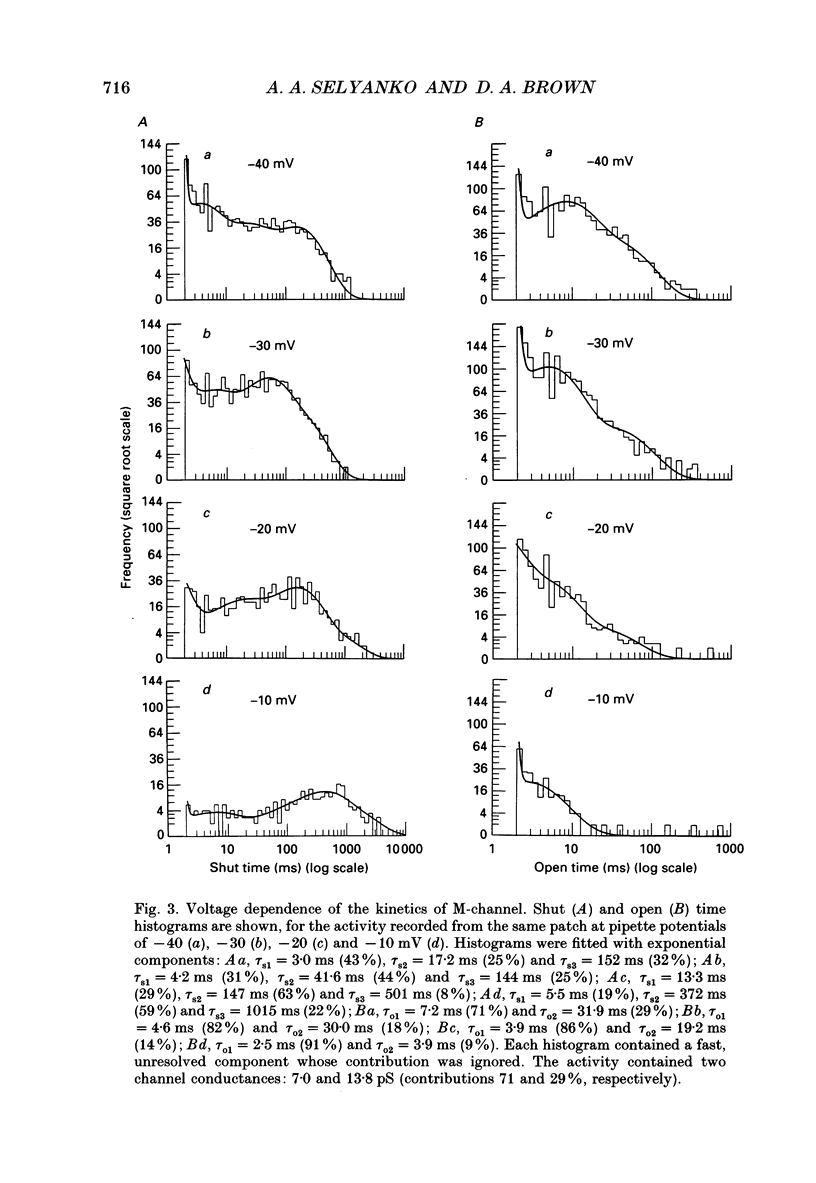
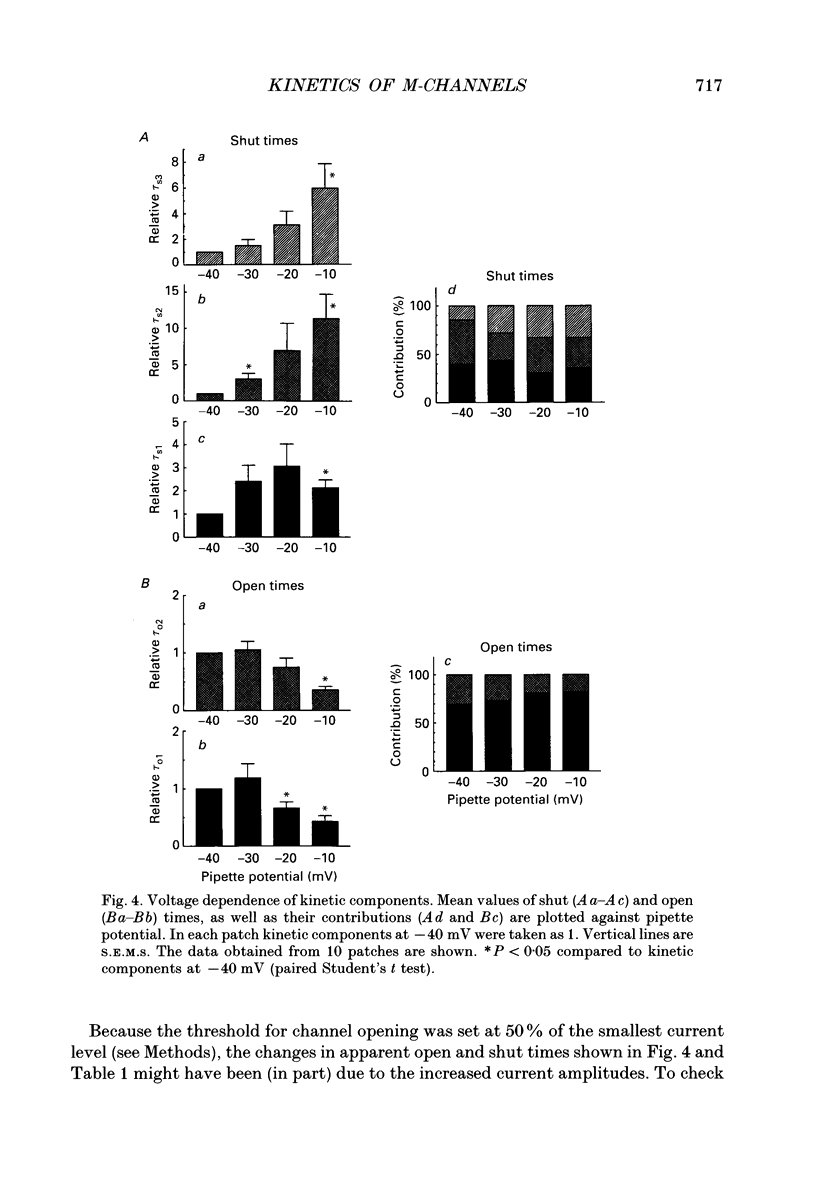
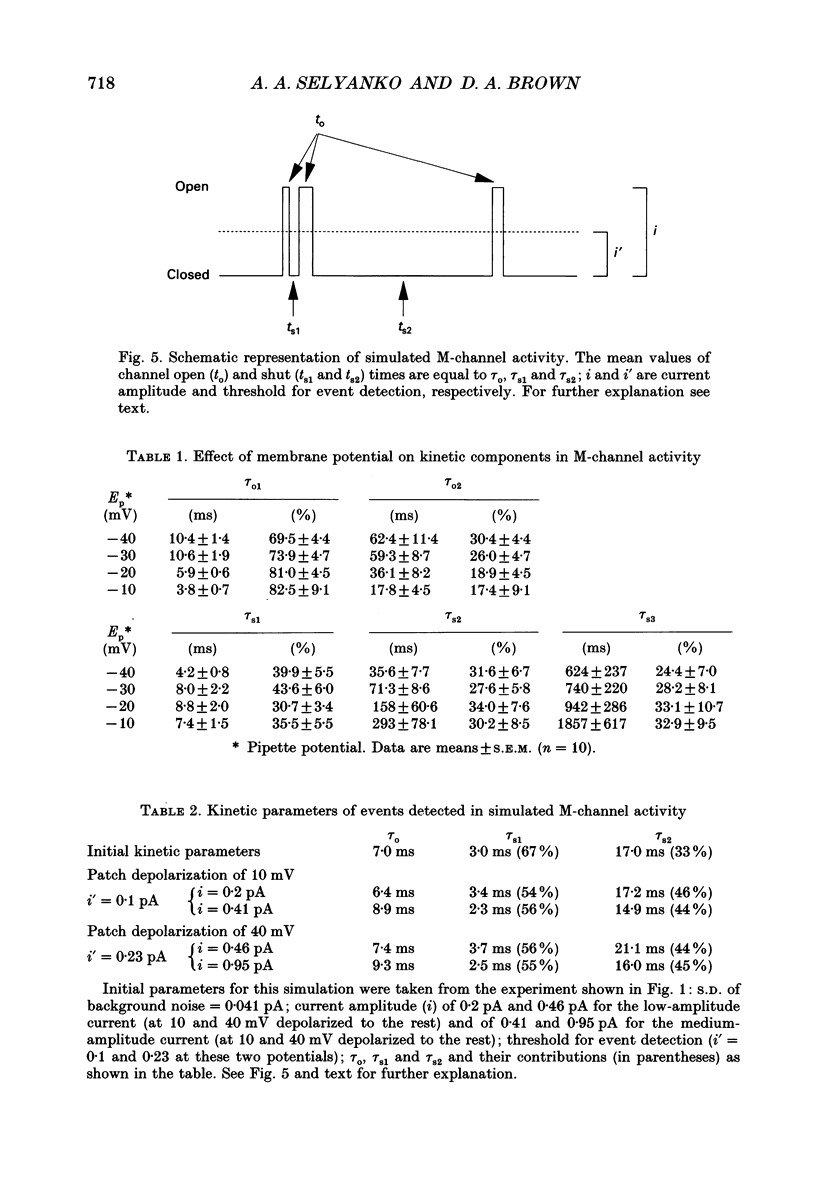
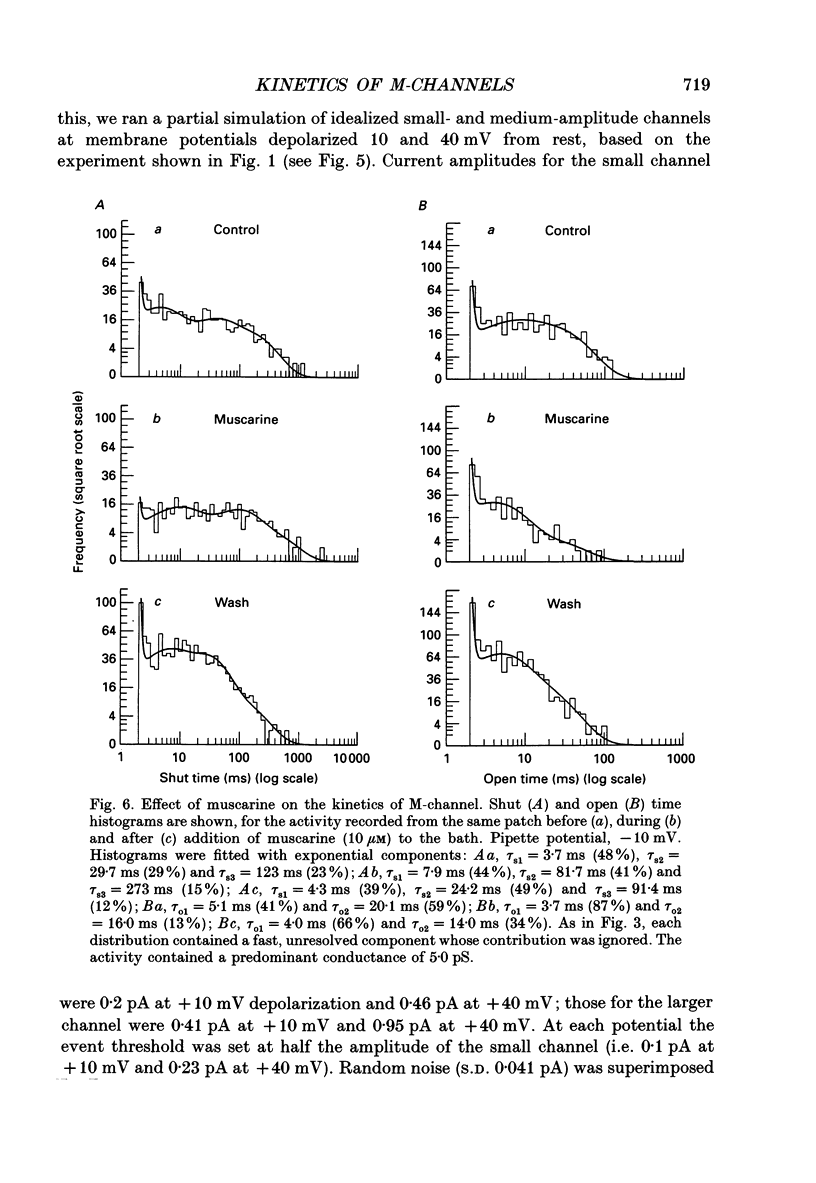
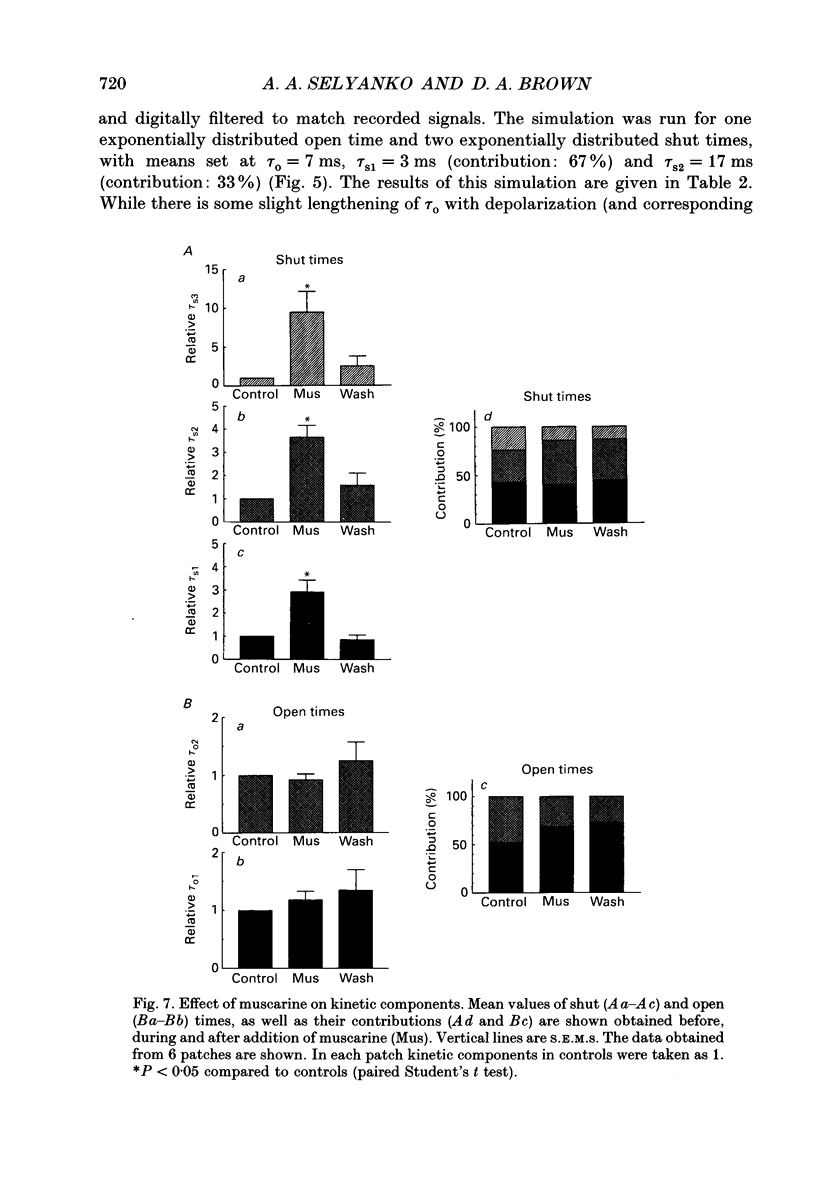
1. Using cell-attached patch pipettes, sustained activity of single potassium M-channels was recorded from dissociated rat superior cervical ganglion neurones. Previous results indicated that this activity, consisting of three main levels of open-channel conductance (congruent to 7, congruent to 12 and congruent to 19 pS) was activated by membrane depolarization and inhibited by muscarine added outside the patch. Consequently, a kinetic analysis was undertaken in order to identify M-channel states sensitive to muscarine and membrane potential. 2. Channel activity recorded at 30 mV positive to the resting membrane potential level (congruent to -60 mV) showed three shut and two open times. Mean shut times were: tau s1 = 8.0 +/- 2.2 ms; tau s2 = 71.3 +/- 8.6 ms and tau s3 = 740 +/- 220 ms. Mean open times were: tau o1 = 10.6 +/- 1.9 ms and tau o2 = 59.3 +/- 8.7 ms. When bursts of channel openings were determined as those including tau s1, two exponential components were evident in burst duration distributions (tau b1 = 11.0 +/- 0.9 ms and tau b2 = 80.4 +/- 11.0 ms). 3. Membrane hyperpolarization significantly lengthened all three shut times and shortened both open times. It also slightly enhanced the relative contribution of high-conductance channels and decreased the relative contribution of low-conductance channels to overall activity. 4. All three shut times of the M-channels were lengthened by 10 microM muscarine without significantly affecting their open times. 5. It is concluded that both open and shut states of the M-channel are voltage sensitive while only shut states are sensitive to muscarine.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. M-currents and other potassium currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Sep;330:537–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Constanti A. Pharmacological inhibition of the M-current. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:223–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Adams P. R. Muscarinic suppression of a novel voltage-sensitive K+ current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):673–676. doi: 10.1038/283673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. M currents. Ion Channels. 1988;1:55–94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7302-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Marrion N. V., Smart T. G. On the transduction mechanism for muscarine-induced inhibition of M-current in cultured rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:469–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. M-currents: an update. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Sakmann B. Fast events in single-channel currents activated by acetylcholine and its analogues at the frog muscle end-plate. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:501–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constanti A., Brown D. A. M-Currents in voltage-clamped mammalian sympathetic neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Jul 17;24(3):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez H. S., Adams P. R. A G Protein Mediates the Inhibition of the Voltage-Dependent Potassium M Current by Muscarine, LHRH, Substance P and UTP in Bullfrog Sympathetic Neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;1(5):529–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrion N. V., Adams P. R., Gruner W. Multiple kinetic states underlying macroscopic M-currents in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Jun 22;248(1323):207–214. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrion N. V., Smart T. G., Brown D. A. Membrane currents in adult rat superior cervical ganglia in dissociated tissue culture. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jun 1;77(1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90606-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A., Fukuda K., Kubo T., Numa S. Intracellular calcium release mediated by two muscarinic receptor subtypes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Nov 21;240(1-2):88–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. G., Marsh S. J., Brown D. A. M-current noise and putative M-channels in cultured rat sympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:269–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. Muscarine and t-LHRH suppress M-current by activating an IAP-insensitive G-protein. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3343–3353. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03343.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Trouslard J., Marsh S. J., Brown D. A. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of the M-current in rodent neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Physiol. 1992;451:159–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selyanko A. A., Stansfeld C. E., Brown D. A. Closure of potassium M-channels by muscarinic acetylcholine-receptor stimulants requires a diffusible messenger. Proc Biol Sci. 1992 Nov 23;250(1328):119–125. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1992.0139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld C. E., Marsh S. J., Gibb A. J., Brown D. A. Identification of M-channels in outside-out patches excised from sympathetic ganglion cells. Neuron. 1993 Apr;10(4):639–654. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90166-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


