Abstract
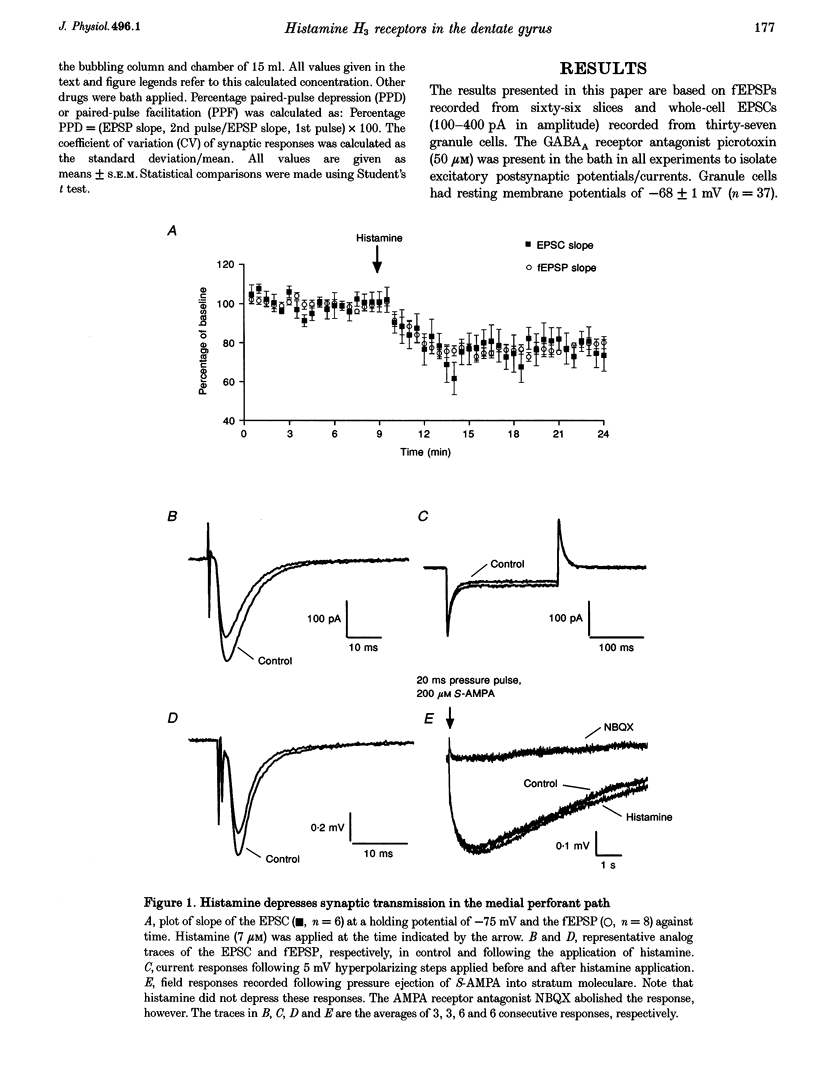
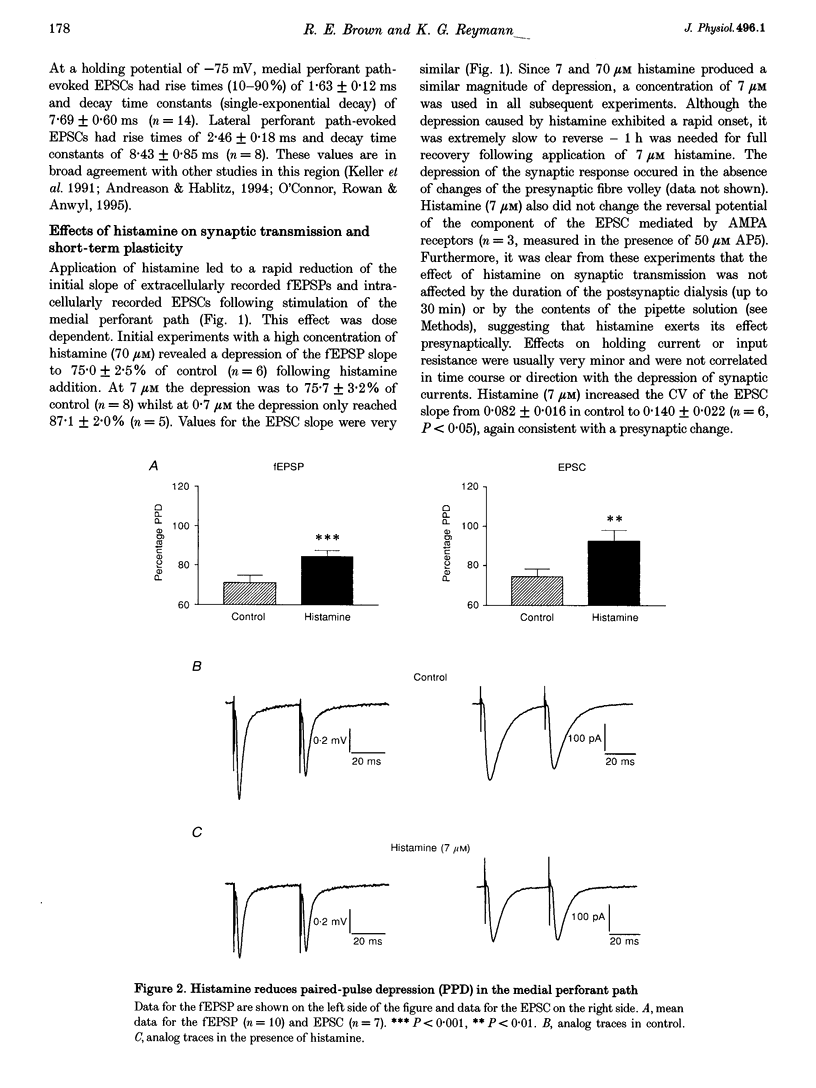
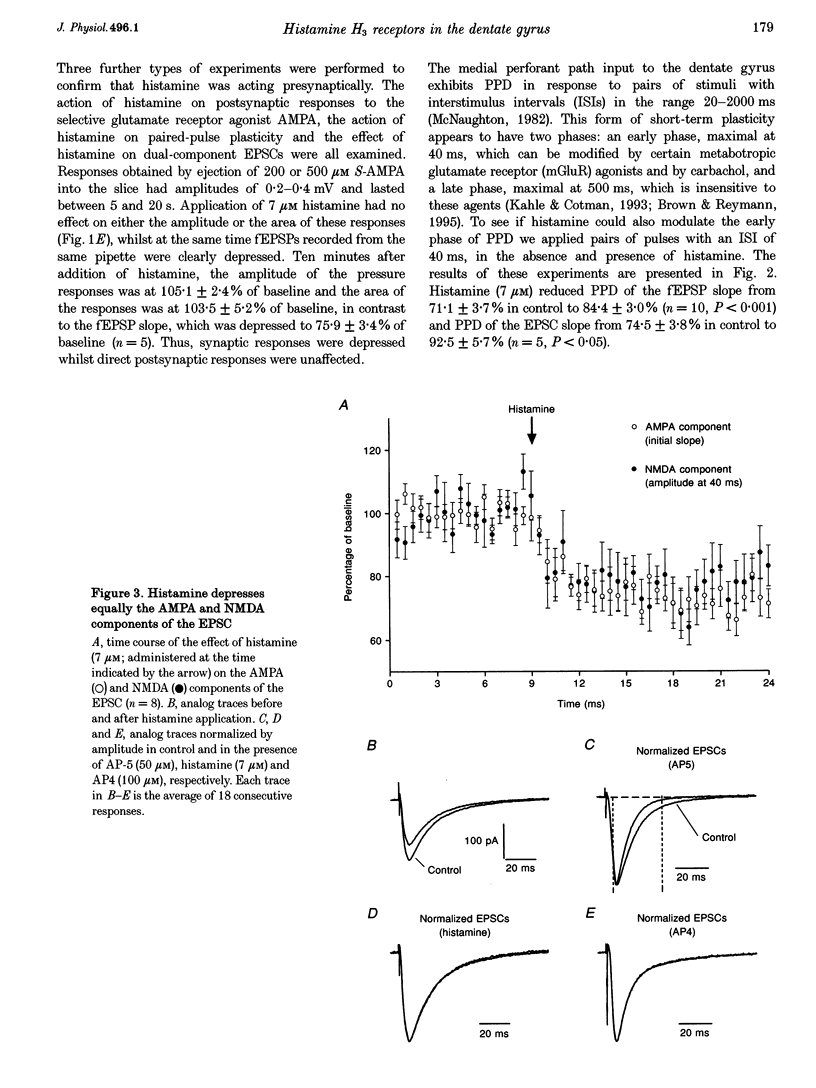
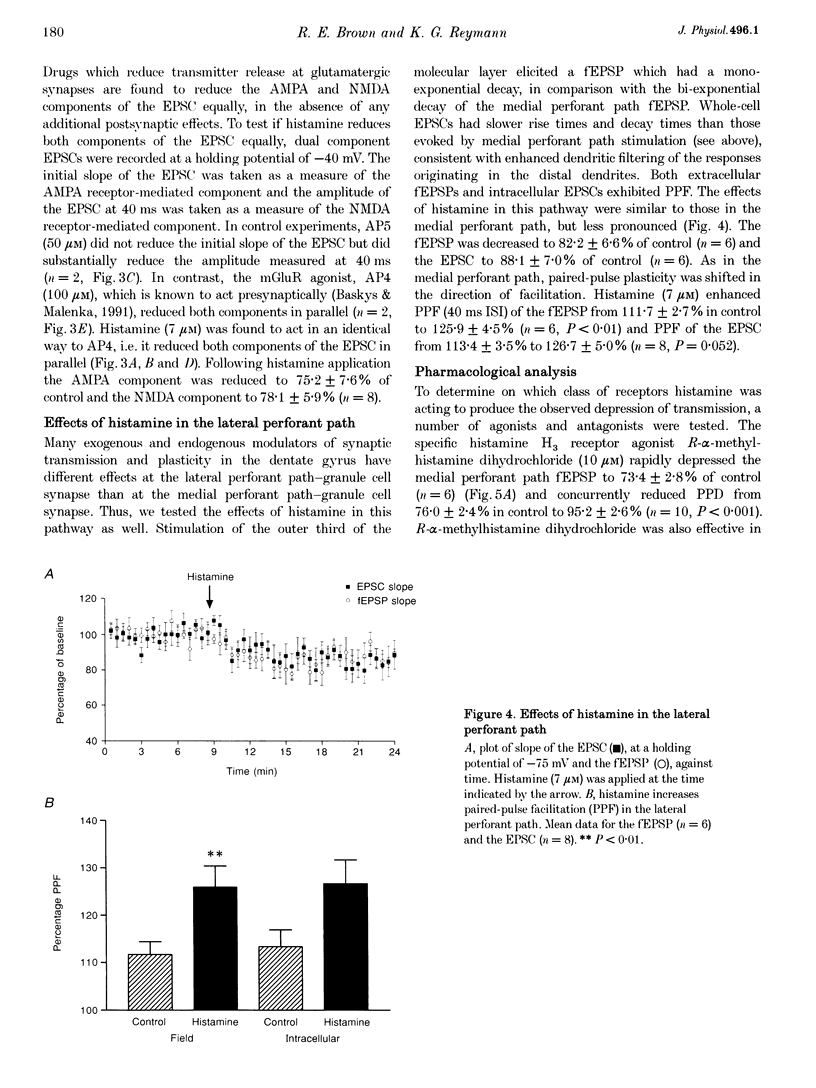
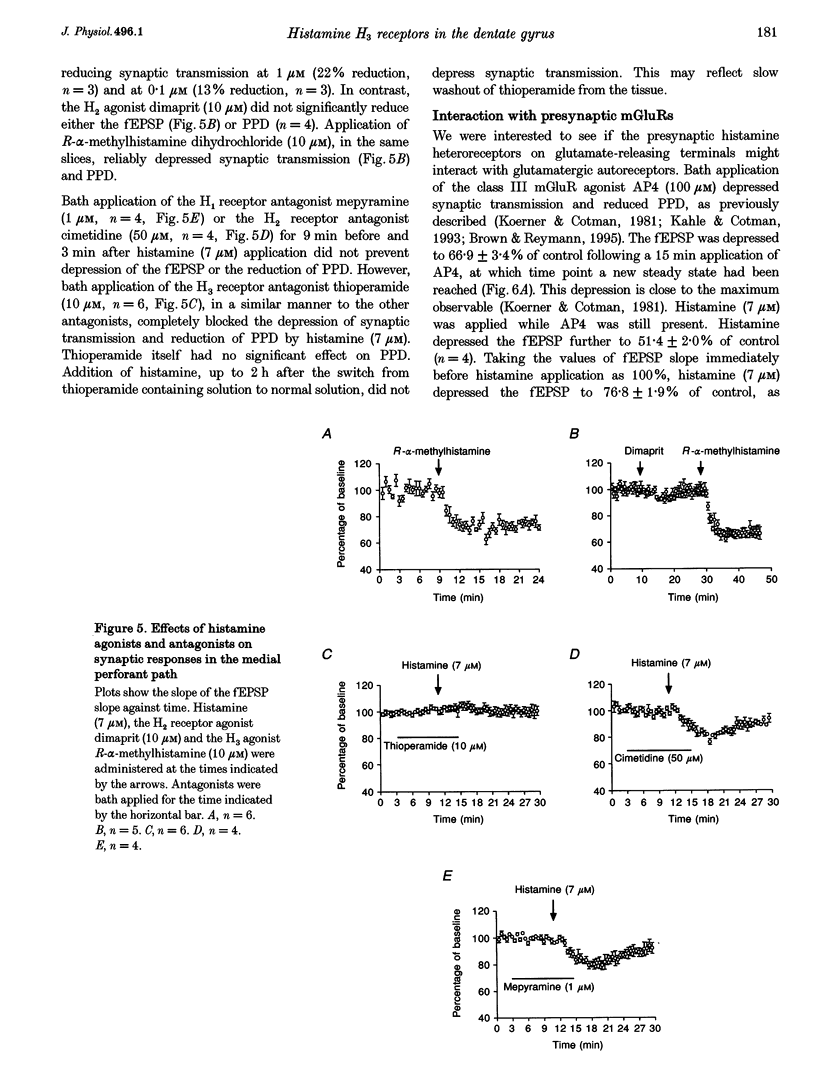
1. The effects of histamine on excitatory synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus region of rat hippocampal slices were examined using extracellular and whole-cell patch-clamp recording techniques. The GABAA receptor antagonist picrotoxin (50 microM) was present in the bath in all experiments. 2. Histamine (0.7-70 microM) reversibly depressed field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) or excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) recorded intracellularly by up to 30%. The presynaptic fibre volley and EPSC reversal potential were unaffected by histamine, as were responses following pressure ejection of the glutamate receptor agonist S-alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (S-AMPA) into the slice. 3. Histamine (7 microM) depressed equally the AMPA and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) components of the dual-component EPSC, recorded at -40 mV. 4. In addition to depressing synaptic transmission, histamine also reduced the magnitude of paired-pulse depression (PPD; 40 ms interpulse interval) of the medial perforant path EPSC. 5. Histamine depressed medial perforant path EPSCs more strongly than lateral perforant path EPSCs. Paired-pulse facilitation (PPF; 40 ms interpulse interval) in the lateral perforant path was enhanced by histamine. 6. The effects of histamine on synaptic transmission and PPD were mimicked by the selective H3 receptor agonist R-alpha-methylhistamine (0.1-10 microM) but not by the selective H2 receptor agonist dimaprit (10 microM). Similarly, the H3 receptor antagonist thioperamide (10 microM) blocked the effect of histamine whereas the H1 antagonist mepyramine (1 microM) and the H2 receptor antagonist cimetidine (50 microM) were ineffective. 7. Histamine actions on synaptic transmission and PPD were not occluded by application of the metabotropic glutamate agonist L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (AP4). 8. The results indicate that histamine depresses synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus by binding to histamine H3 receptors located on perforant path terminals. The mechanism by which histamine depresses transmission is independent of that used by class III metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R. Blockade of neurotransmitter-activated K+ conductance by QX-314 in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 25;199(2):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
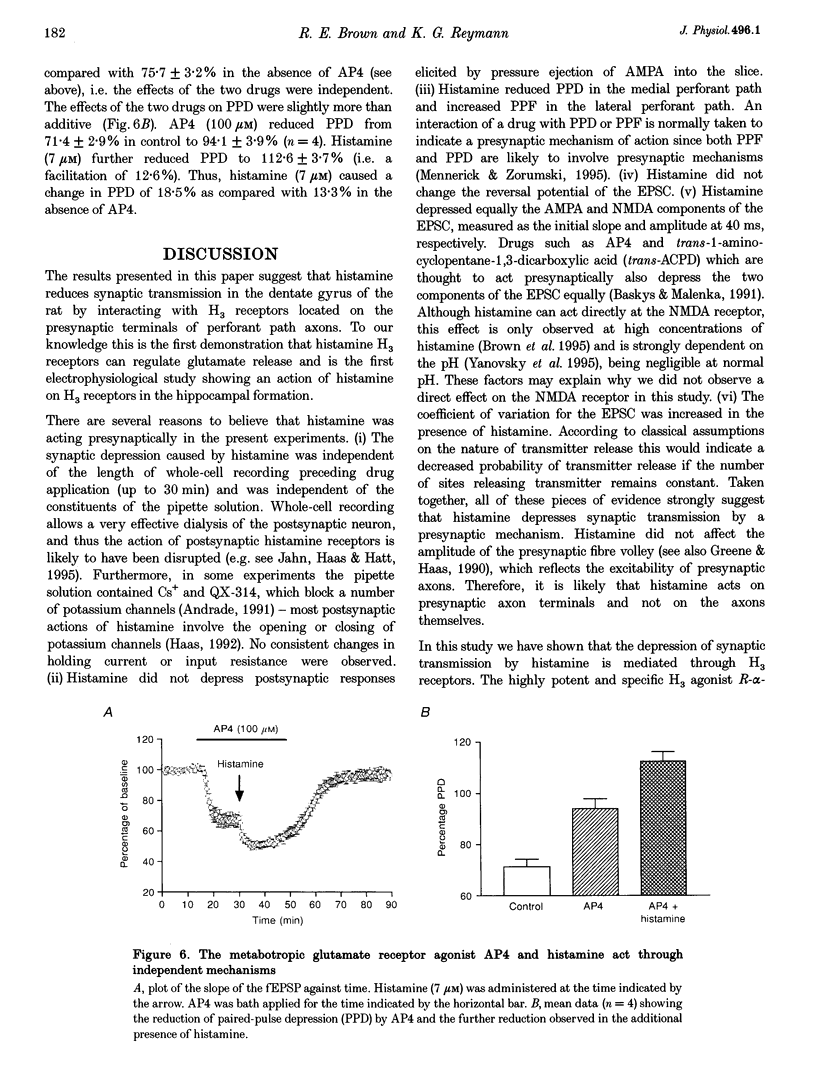
- Andreasen M., Hablitz J. J. Paired-pulse facilitation in the dentate gyrus: a patch-clamp study in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Jul;72(1):326–336. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.1.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Drutel G., Schwartz J. C. Characterization of histamine H3 receptors regulating acetylcholine release in rat entorhinal cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr;114(7):1518–1522. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13379.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Lancelot J. C., Lecomte J. M., Pollard H., Robba M., Schunack W., Schwartz J. C. Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):117–123. doi: 10.1038/327117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin K. B., Bronzino J. D., Morgane P. J. Paired-pulse facilitation and inhibition in the dentate gyrus is dependent on behavioral state. Exp Brain Res. 1989;77(3):594–604. doi: 10.1007/BF00249612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Malenka R. C. Agonists at metabotropic glutamate receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSCs in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:687–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. E., Reymann K. G. Metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists reduce paired-pulse depression in the dentate gyrus of the rat in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Aug 18;196(1-2):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11825-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Sarvey J. M. Norepinephrine induces pathway-specific long-lasting potentiation and depression in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov N. B., Reymann K. G. Simultaneous local pressure microejection of excitatory amino acids and field potential recording with a single micropipette in the hippocampal slice. J Neurosci Methods. 1993 Oct;50(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(93)90058-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. W., Haas H. L. Effects of histamine on dentate granule cells in vitro. Neuroscience. 1990;34(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90140-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanse Eric, Gustafsson Bengt. Long-term Potentiation and Field EPSPs in the Lateral and Medial Perforant Paths in the Dentate Gyrus In Vitro: a Comparison. Eur J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;4(11):1191–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough L. B. Cellular localization and possible functions for brain histamine: recent progress. Prog Neurobiol. 1988;30(6):469–505. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(88)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn K., Haas H. L., Hatt H. Patch clamp study of histamine activated potassium currents on rabbit olfactory bulb neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Oct;352(4):386–393. doi: 10.1007/BF00172775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. S. Entorhinal-hippocampal connections: a speculative view of their function. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Feb;16(2):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90018-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahle J. S., Cotman C. W. Carbachol depresses synaptic responses in the medial but not the lateral perforant path. Brain Res. 1989 Mar 13;482(1):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahle J. S., Cotman C. W. L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid and 1S,3R-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid reduce paired-pulse depression recorded from medial perforant path in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):207–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller B. U., Konnerth A., Yaari Y. Patch clamp analysis of excitatory synaptic currents in granule cells of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:275–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner J. F., Cotman C. W. Micromolar L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid selectively inhibits perforant path synapses from lateral entorhinal cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 6;216(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. S., Sakai K., Jouvet M. Evidence for histaminergic arousal mechanisms in the hypothalamus of cat. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Feb;27(2):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor J. J., Rowan M. J., Anwyl R. Tetanically induced LTP involves a similar increase in the AMPA and NMDA receptor components of the excitatory postsynaptic current: investigations of the involvement of mGlu receptors. J Neurosci. 1995 Mar;15(3 Pt 1):2013–2020. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-03-02013.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panula P., Pirvola U., Auvinen S., Airaksinen M. S. Histamine-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1989;28(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Duvoisin R. The metabotropic glutamate receptors: structure and functions. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Jan;34(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00129-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., Moreau J., Arrang J. M., Schwartz J. C. A detailed autoradiographic mapping of histamine H3 receptors in rat brain areas. Neuroscience. 1993 Jan;52(1):169–189. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90191-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Betz R., Göthert M. Histamine H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonin release in the rat brain cortex. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 May;337(5):588–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00182737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicker E., Fink K., Hinterthaner M., Göthert M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rat brain cortex via presynaptic H3 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6):633–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00717738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Pollard H., Ruat M. Histaminergic transmission in the mammalian brain. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):1–51. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley K. J., Otis T. S., Mody I. Membrane properties of dentate gyrus granule cells: comparison of sharp microelectrode and whole-cell recordings. J Neurophysiol. 1992 May;67(5):1346–1358. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.67.5.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorobjev V. S., Sharonova I. N., Walsh I. B., Haas H. L. Histamine potentiates N-methyl-D-aspartate responses in acutely isolated hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):837–844. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Inagaki N., Yamatodani A., Watanabe T. Is the histaminergic neuron system a regulatory center for whole-brain activity? Trends Neurosci. 1991 Sep;14(9):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90034-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winson J., Abzug C. Neuronal transmission through hippocampal pathways dependent on behavior. J Neurophysiol. 1978 May;41(3):716–732. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.3.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanovsky Y., Reymann K., Haas H. L. pH-dependent facilitation of synaptic transmission by histamine in the CA1 region of mouse hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Oct 1;7(10):2017–2020. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


