Abstract
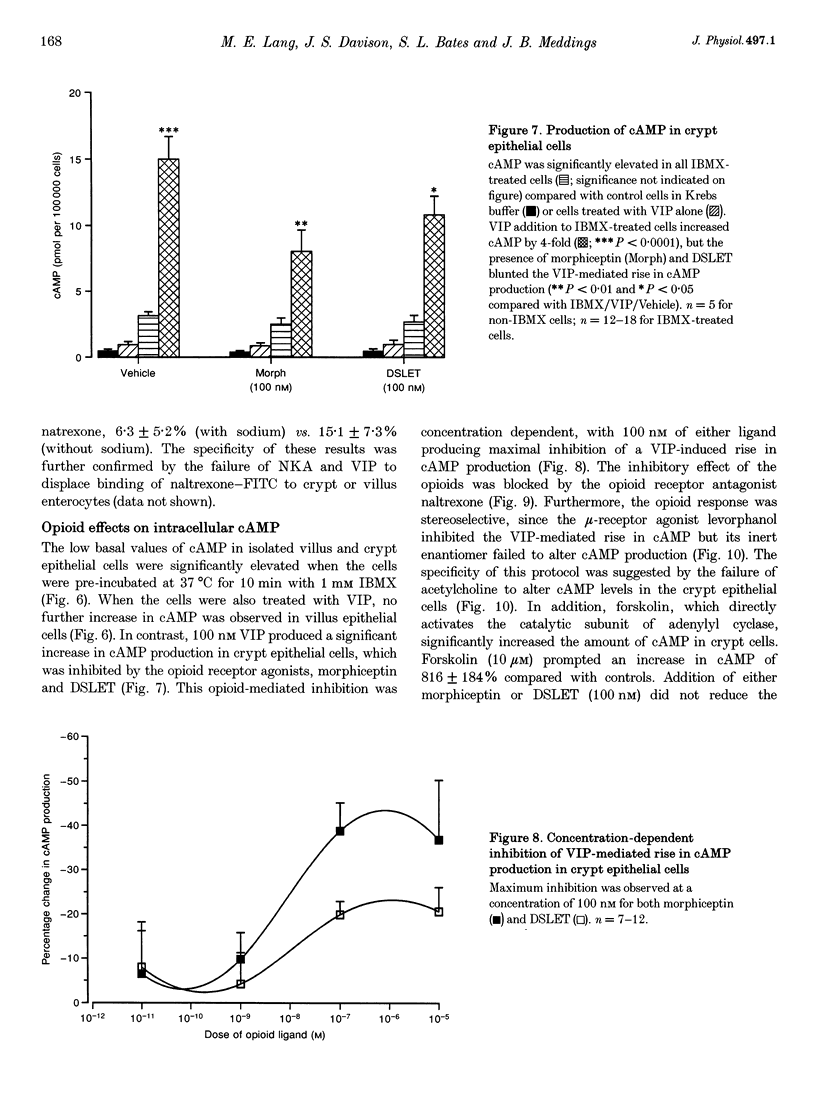
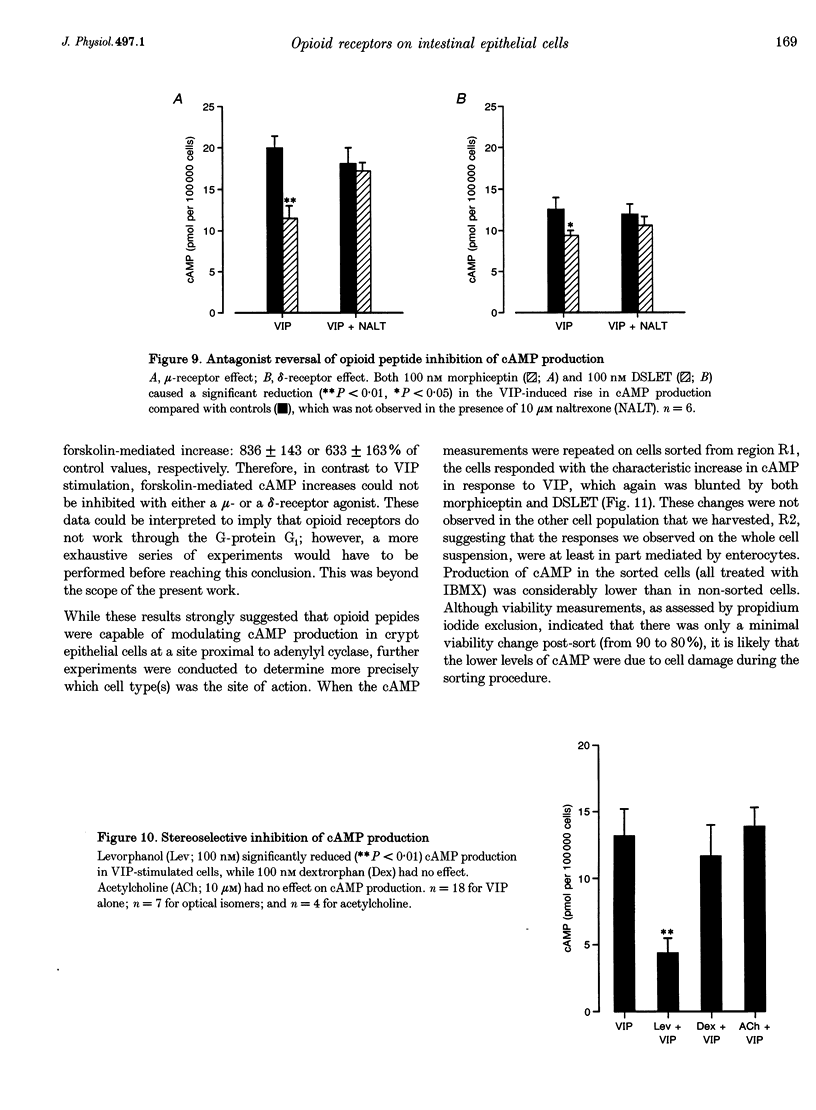
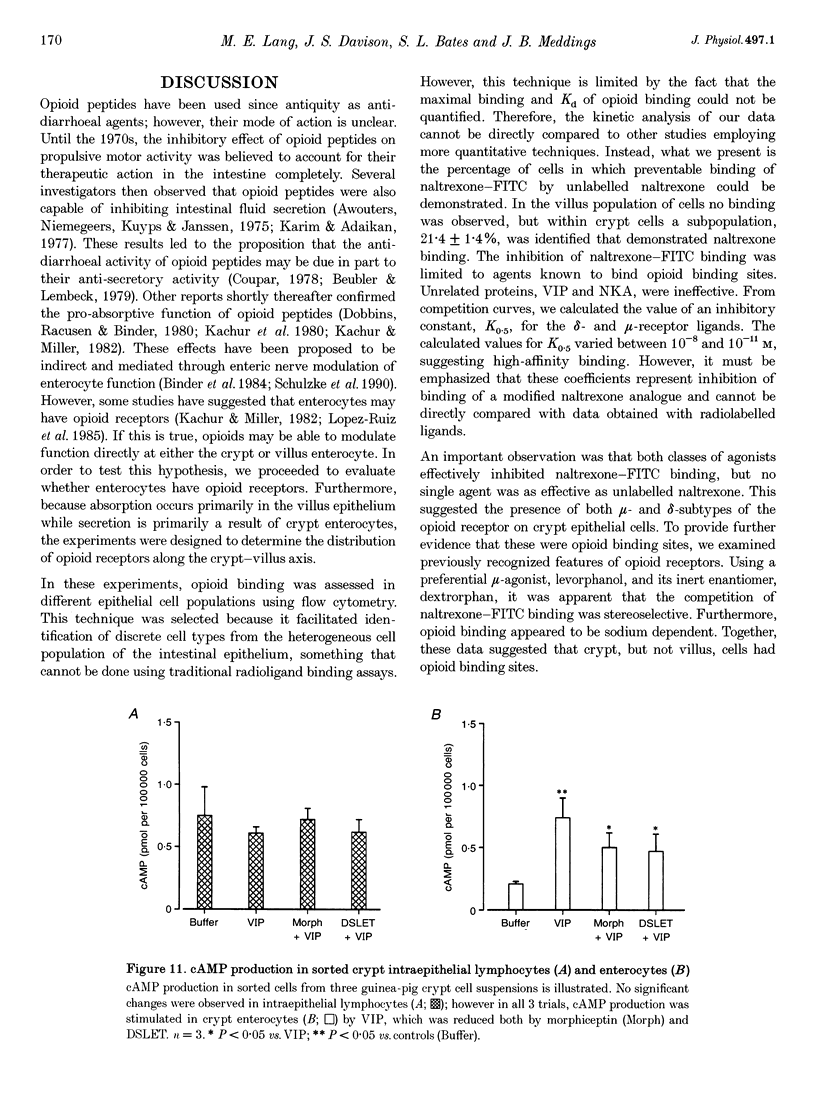
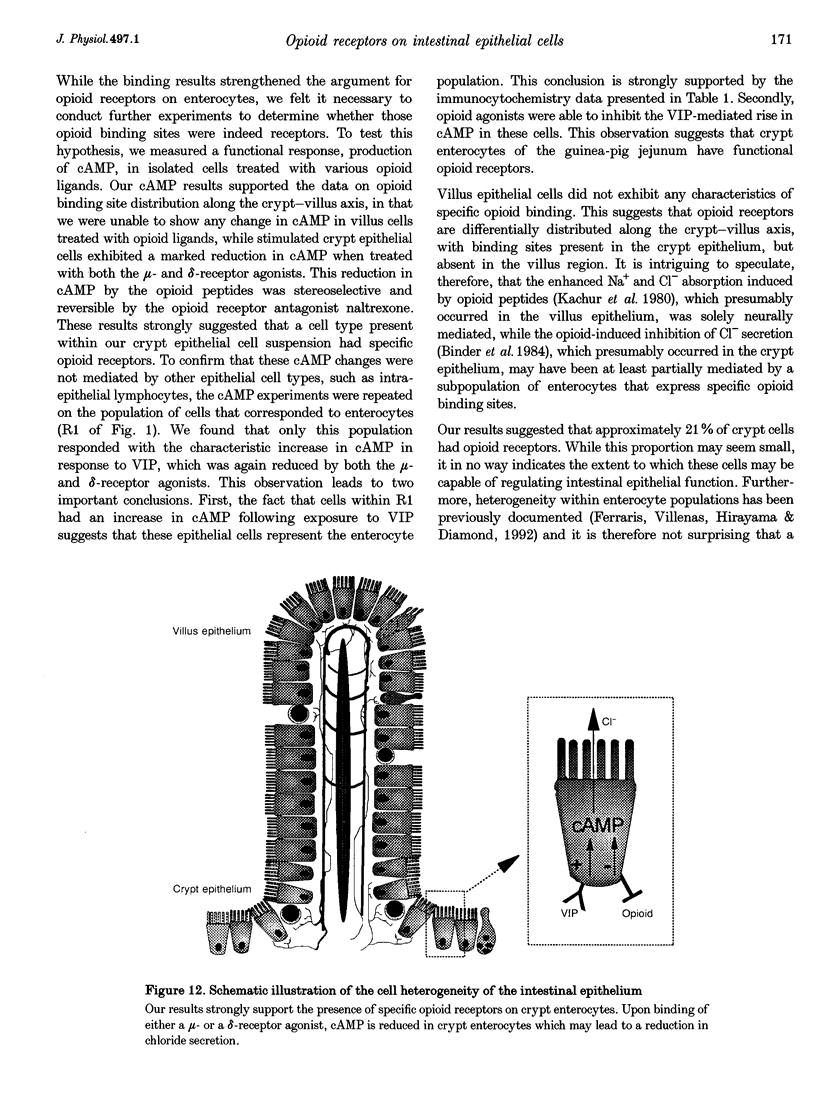
1. Opioid peptides promote net intestinal absorption via two mechanisms: stimulation of Na+ and Cl- absorption and inhibition of Cl- secretion. Although these transport changes are predominantly mediated by submucosal neurones, it is currently unclear whether opioid peptides can regulate enterocyte function directly. We therefore tested the hypothesis that enterocytes have specific opioid receptors. 2. Villus and crypt jejunal epithelial cells were isolated by the distended sac method from anaesthetized guinea-pigs. Flow cytometry was used to resolve enterocytes from other cell types and to determine whether binding of a fluorescently labelled opioid antagonist, naltrexone-FITC, could be prevented by unlabelled mu- and delta-opioid receptor agonists. A population of crypt enterocytes (approximately 21%) exhibited high-affinity naltrexone-FITC binding to both mu- and delta-type binding sites that was stereoselective and sodium dependent. Villus enterocytes did not exhibit any of these characteristics. 3. Basal cAMP production was elevated in both villus and crypt cells treated with IBMX (3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine). Villus cells did not respond to 100 nM vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), nor were they affected by opioid peptides. In contrast, 100 nM VIP significantly increased cAMP production in crypt epithelial cells, which was significantly reduced by both morphiceptin and D-Ser2-Leu-Enk-Thr. This opioid-mediated effect was stereoselective and blocked by the opioid receptor antagonist naltrexone. 4. These experiments suggest that enterocytes isolated from the crypt epithelium of guineapigs have both mu- and delta-types of opioid receptors. It is possible that these cells participate in opioid-mediated regulation of intestinal secretion.
Full text
PDF


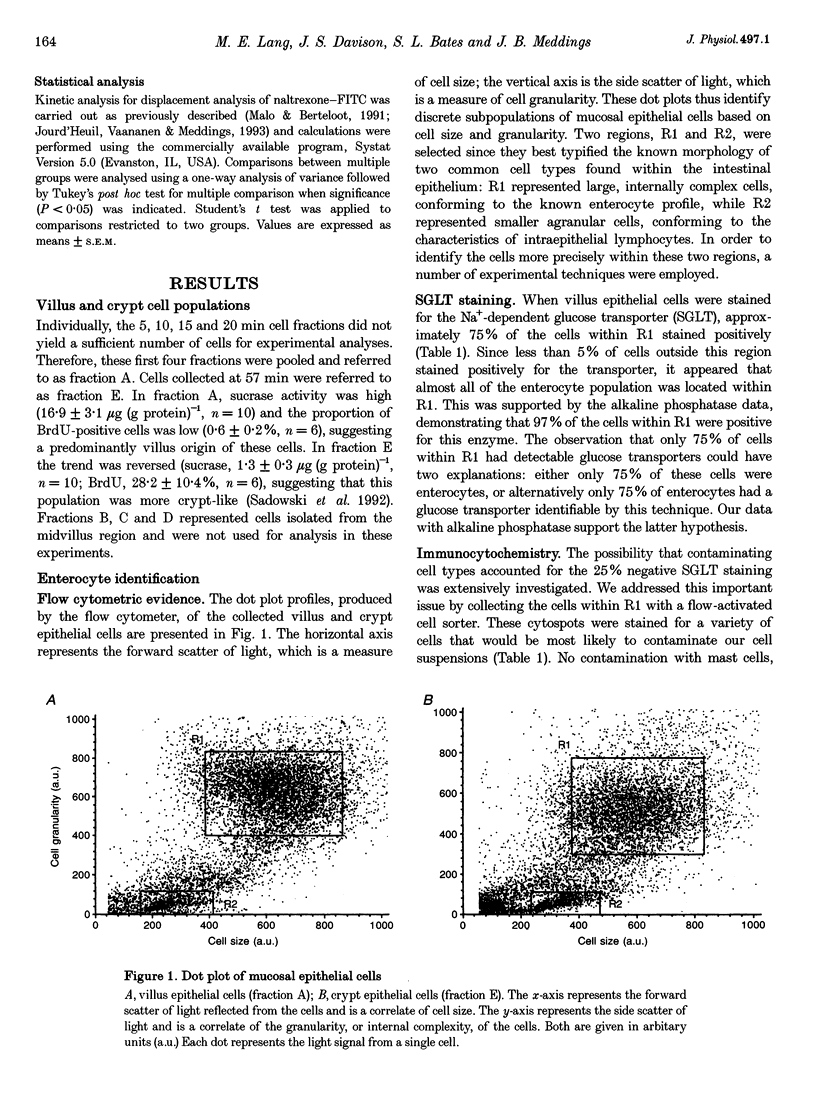
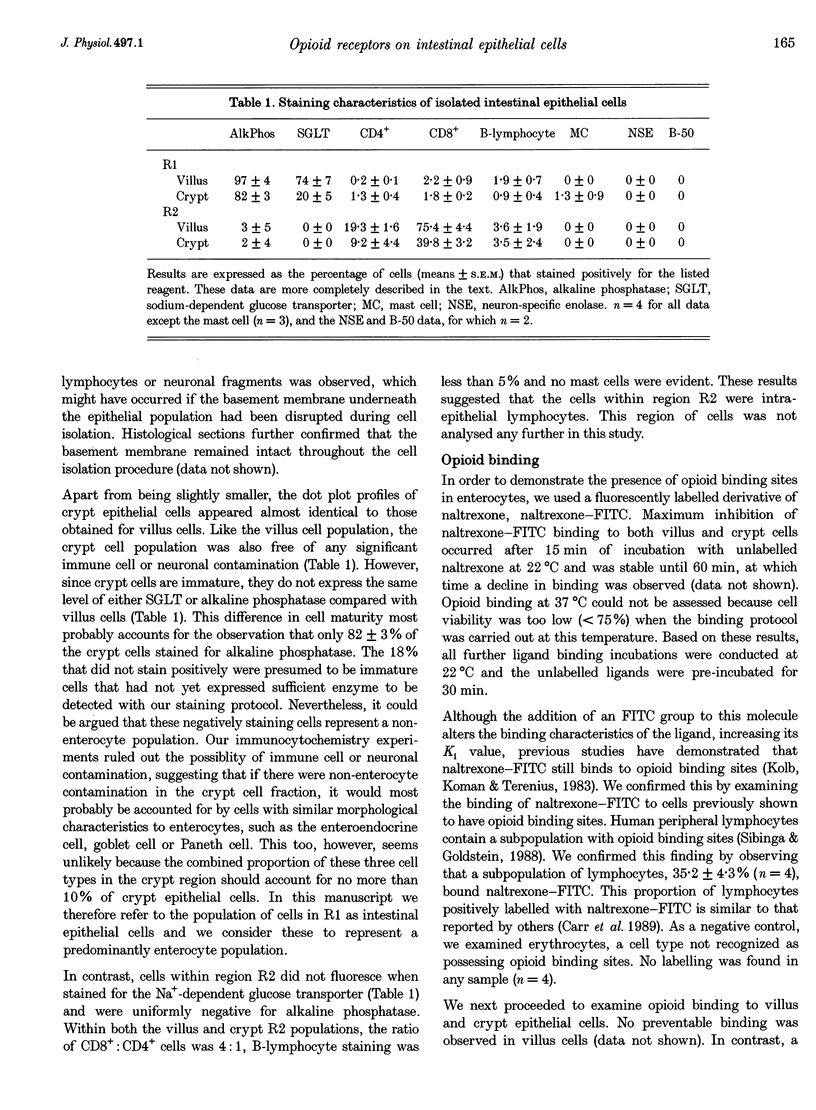
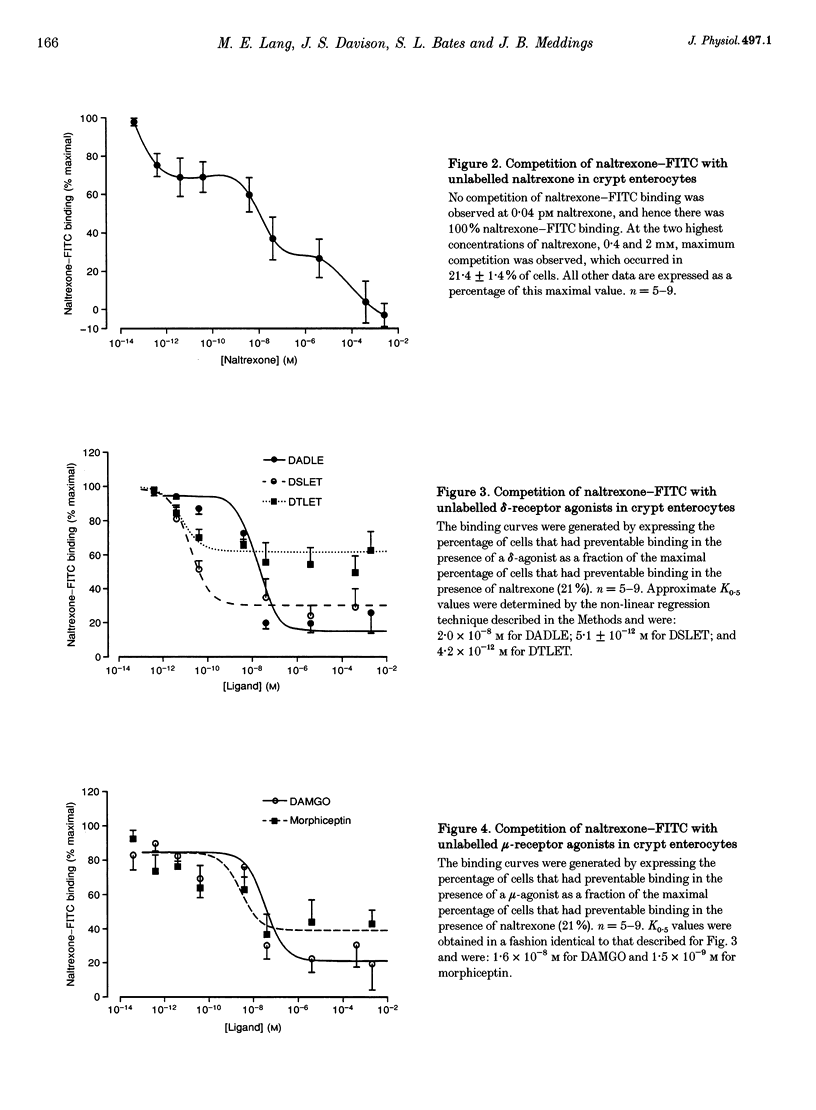



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awouters F., Niemegeers C. J., Kuyps J., Janssen P. A. Loperamide antagonism of castor oil-induced diarrhea in rats: a quantitative study. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975 Sep;217(1):29–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beubler E., Lembeck F. Inhibition of stimulated fluid secretion in the rat small and large intestine by opiate agonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;306(2):113–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00498980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Laurenson J. P., Dobbins J. W. Role of opiate receptors in regulation of enkephalin stimulation of active sodium and chloride absorption. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):G432–G436. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.4.G432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. J., DeCosta B. R., Kim C. H., Jacobson A. E., Guarcello V., Rice K. C., Blalock J. E. Opioid receptors on cells of the immune system: evidence for delta- and kappa-classes. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):161–168. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Roy A. C. Morphine-like drugs inhibit the stimulation of E prostaglandins of cyclic AMP formation by rat brain homogenate. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):24–27. doi: 10.1038/248024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupar I. M. Inhibition by morphine of prostaglandin-stimulated fluid secretion in rat jejunum. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07774.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Harms V., Yamashiro D. J., Hughes R. J., Binder H. J., Wright E. M. Preferential binding of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide to basolateral membrane of rat and rabbit enterocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):27–35. doi: 10.1172/JCI110748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake V. U., Hunter J. C., Hill R. G., Hughes J. Characterization of kappa-opioid receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 21;182(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90494-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J., Racusen L., Binder H. J. Effect of D-alanine methionine enkephalin amide on ion transport in rabbit ileum. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):19–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI109830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris R. P., Villenas S. A., Hirayama B. A., Diamond J. Effect of diet on glucose transporter site density along the intestinal crypt-villus axis. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):G1060–G1068. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.6.G1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Rimele T. J., Wietecha M. Studies on rat intestinal epithelial cell receptors for serotonin and opiates. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:101–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I. C., Perrin D., Penman E., Yaseen A., Ray K., Howell S. L. Effect of dynorphin on insulin and somatostatin secretion, calcium uptake, and c-AMP levels in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1983 Aug;32(8):685–690. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.8.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green I. C., Ray K., Perrin D. Opioid peptide effects on insulin release and c-AMP in islets of Langerhans. Horm Metab Res. 1983 Mar;15(3):124–128. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle J., Hardcastle P. T., Read N. W., Redfern J. S. The action of loperamide in inhibiting prostaglandin-induced intestinal secretion in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;74(3):563–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10465.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchin B. W., Dobson P. R., Brown B. L., Hardcastle J., Hardcastle P. T., Taylor C. J. Measurement of intracellular mediators in enterocytes isolated from jejunal biopsy specimens of control and cystic fibrosis patients. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):893–899. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jourd'Heuil D., Vaananen P., Meddings J. B. Lipid peroxidation of the brush-border membrane: membrane physical properties and glucose transport. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jun;264(6 Pt 1):G1009–G1015. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.6.G1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachur J. F., Miller R. J. Characterization of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig ileal mucosa. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M. Control of guinea pig intestinal electrolyte secretion by a delta-opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2753–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. M., Adaikan P. G. The effect of loperamide on prostaglandin induced diarrhoea in rat and man. Prostaglandins. 1977 Feb;13(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M. Opiate receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1869–1874. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90293-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb V. M., Koman A., Terenius L. Fluorescent probes for opioid receptors. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Ruiz M. P., Arilla E., Gómez-Pan A., Prieto J. C. Interaction of Leu-enkephalin with isolated enterocytes from guinea pig: binding to specific receptors and stimulation of cAMP accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90620-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo C., Berteloot A. Analysis of kinetic data in transport studies: new insights from kinetic studies of Na(+)-D-glucose cotransport in human intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles using a fast sampling, rapid filtration apparatus. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jun;122(2):127–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01872636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura E., Buchan A. M., McIntosh C. H. Autoradiographic localization of mu- and delta-type opioid receptors in the gastrointestinal tract of the rat and guinea pig. Gastroenterology. 1986 Nov;91(5):1084–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(86)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peerce B. E., Wright E. M. Examination of the Na+-induced conformational change of the intestinal brush border sodium/glucose symporter using fluorescent probes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4272–4279. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
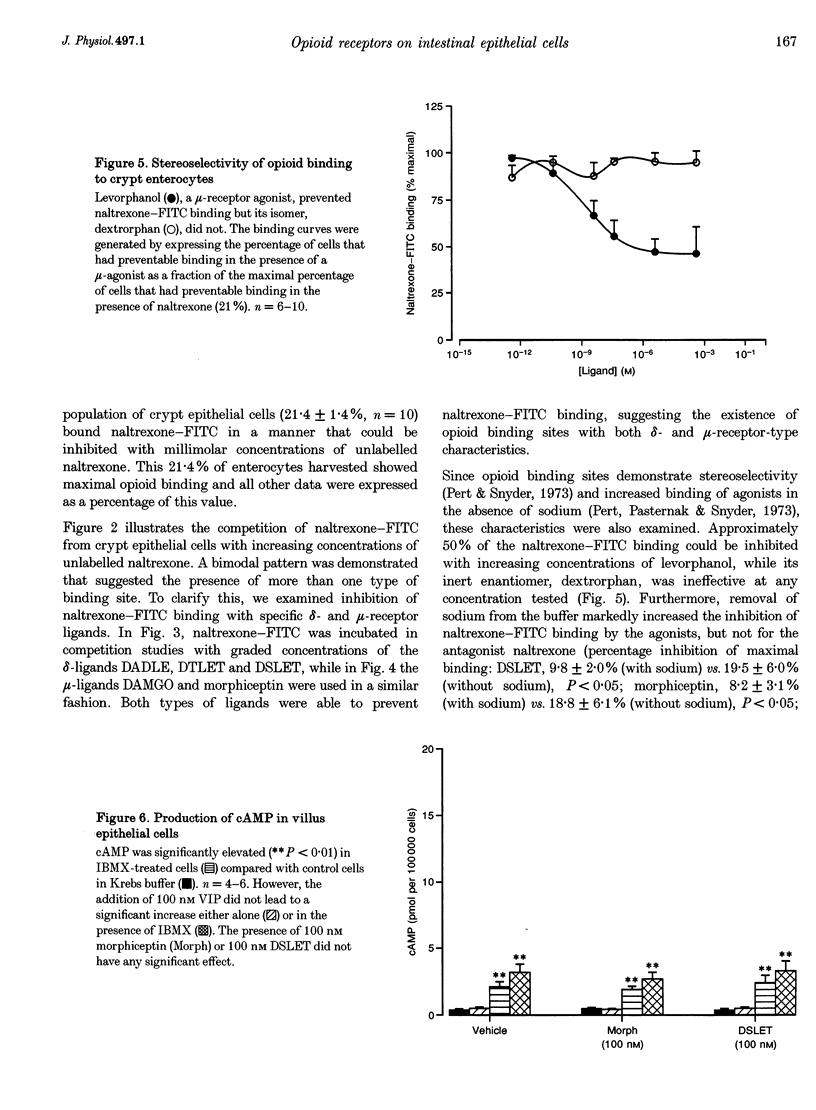
- Pert C. B., Pasternak G., Snyder S. H. Opiate agonists and antagonists discriminated by receptor binding in brain. Science. 1973 Dec 28;182(4119):1359–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4119.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Properties of opiate-receptor binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2243–2247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quito F. L., Seybold V. S., Brown D. R. Opiate binding sites in mucosa of pig small intestine. Life Sci. 1991;49(25):PL219–PL222. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90297-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski D. C., Gibbs D. J., Meddings J. B. Proline transport across the intestinal microvillus membrane may be regulated by membrane physical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 23;1105(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90164-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulzke J. D., Fromm M., Riecken E. O., Reutter W. Enkephalin affects ion transport via the enteric nervous system in guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;20(2):182–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1990.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey K. A., Sutherland L. R., Davison J. S., Zwiers H., Gill M. J., Church D. L. Peptides in the gastrointestinal tract in human immunodeficiency virus infection. The GI/HIV Study Group of the University of Calgary. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jul;103(1):18–28. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91090-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. Opiate-dependent modulation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibinga N. E., Goldstein A. Opioid peptides and opioid receptors in cells of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:219–249. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber P. G., Gumucio D. L., Wang W. Isolation of intestinal epithelial cells for the study of differential gene expression along the crypt-villus axis. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jun;260(6 Pt 1):G895–G903. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.260.6.G895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voisin T., Rouyer-Fessard C., Laburthe M. Distribution of common peptide YY-neuropeptide Y receptor along rat intestinal villus-crypt axis. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):G753–G759. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.5.G753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]