Abstract
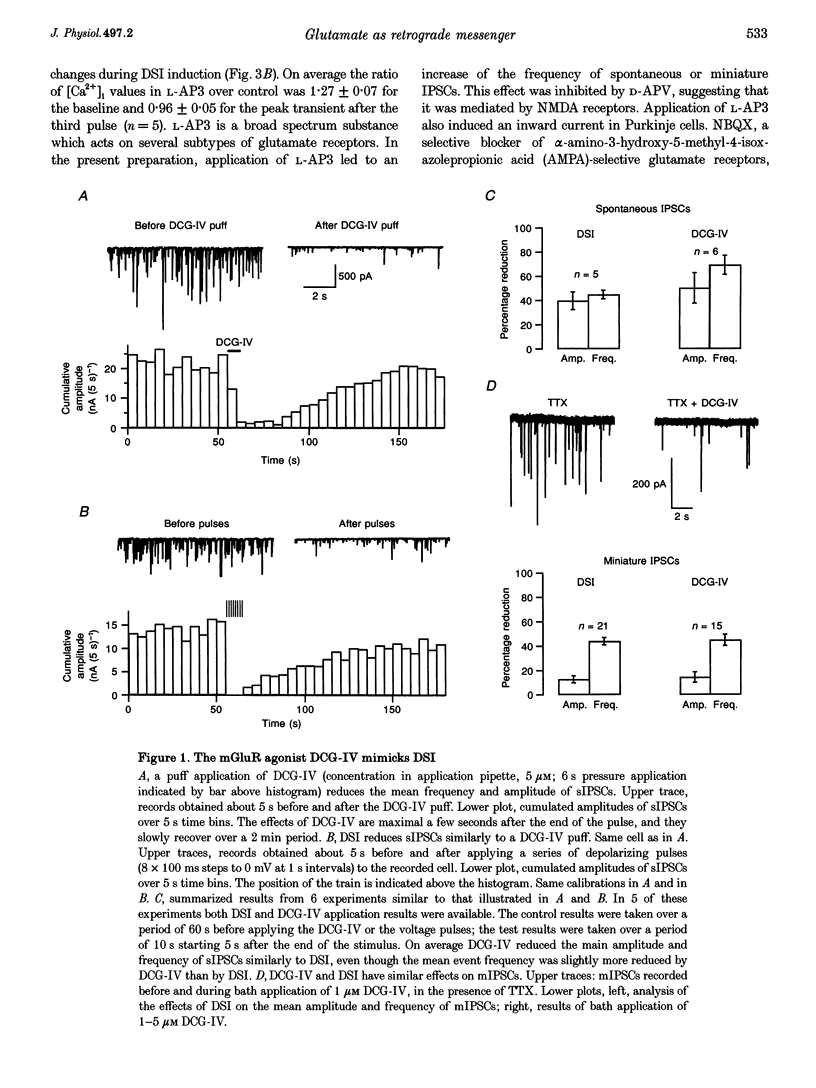
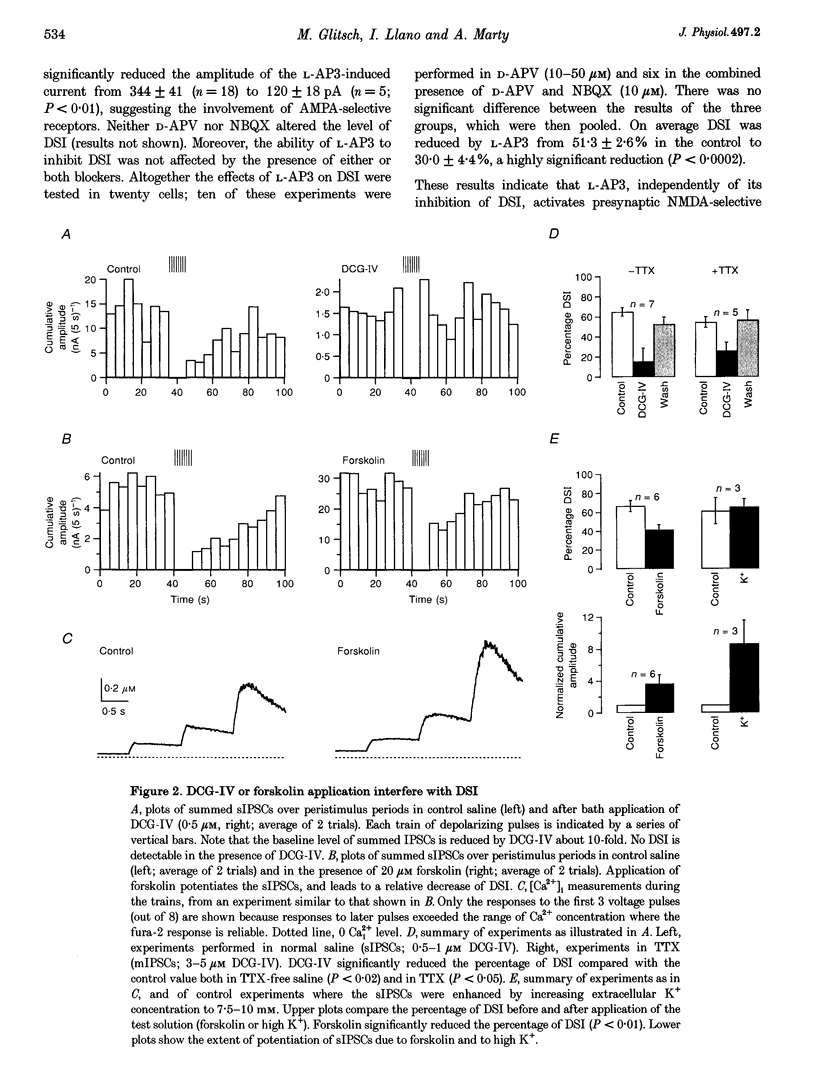
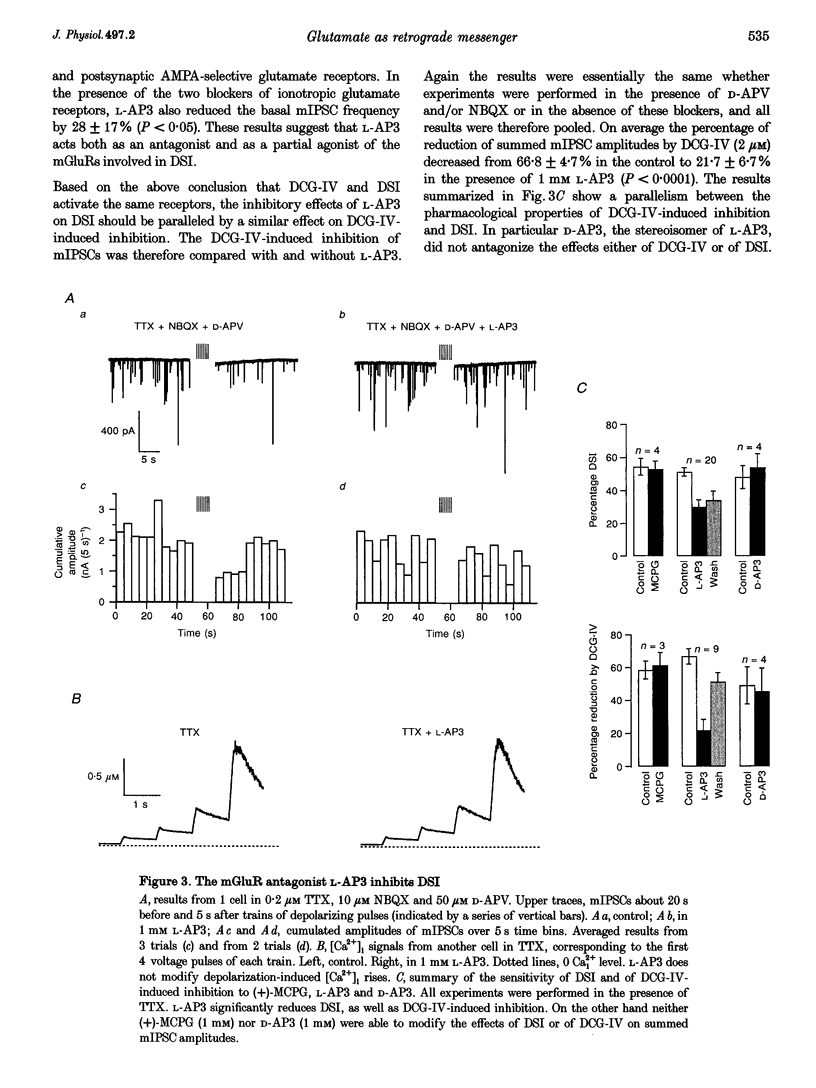
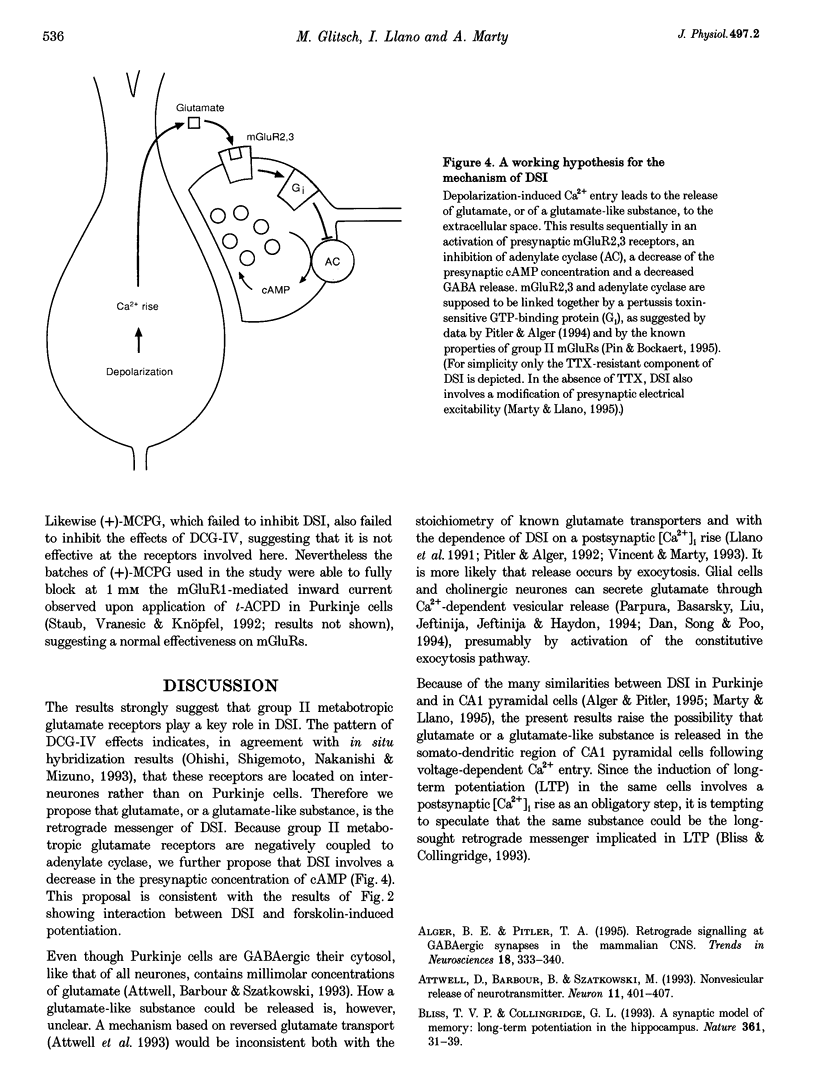
1. Depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI) is a form of synaptic plasticity which involves a retrograde messenger. We have performed experiments in Purkinje cells of rat cerebellar slices to determine the nature of this messenger. 2. DSI is mimicked by 2-(2,3-dicarboxycyclopropyl)-glycine (DCG-IV), a specific agonist of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). 3. DSI is reduced if transmitter release is inhibited by saturating doses of DCG-IV. 4. Both DSI and DCG-IV-induced inhibition are inhibited by L-2-amino-3-phosphonopropionic acid (L-AP3), a drug which interferes with several subtypes of mGluRs. 5. DSI is reduced if synaptic activity is enhanced by application of forskolin. 6. We propose that glutamate or a glutamate-like substance is the retrograde messenger implicated in DSI, and that the inhibition resulting from presynaptic glutamate binding is mediated by a decrease in the presynaptic concentration of cAMP.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger B. E., Pitler T. A. Retrograde signaling at GABAA-receptor synapses in the mammalian CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1995 Aug;18(8):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(95)93923-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwell D., Barbour B., Szatkowski M. Nonvesicular release of neurotransmitter. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90145-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Collingridge G. L. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):31–39. doi: 10.1038/361031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dan Y., Song H. J., Poo M. M. Evoked neuronal secretion of false transmitters. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierro L., Llano I. High endogenous calcium buffering in Purkinje cells from rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1996 Nov 1;496(Pt 3):617–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Momiyama A., Takahashi T., Ohishi H., Ogawa-Meguro R., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Role of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in synaptic modulation in the accessory olfactory bulb. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):687–690. doi: 10.1038/366687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Gerschenfeld H. M. Beta-adrenergic enhancement of inhibitory synaptic activity in rat cerebellar stellate and Purkinje cells. J Physiol. 1993 Aug;468:201–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Leresche N., Marty A. Calcium entry increases the sensitivity of cerebellar Purkinje cells to applied GABA and decreases inhibitory synaptic currents. Neuron. 1991 Apr;6(4):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., Marty A. Presynaptic metabotropic glutamatergic regulation of inhibitory synapses in rat cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1995 Jul 1;486(Pt 1):163–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A., Llano I. Modulation of inhibitory synapses in the mammalian brain. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Jun;5(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohishi H., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S., Mizuno N. Distribution of the mRNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR3) in the rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Sep 8;335(2):252–266. doi: 10.1002/cne.903350209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpura V., Basarsky T. A., Liu F., Jeftinija K., Jeftinija S., Haydon P. G. Glutamate-mediated astrocyte-neuron signalling. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):744–747. doi: 10.1038/369744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Bockaert J. Get receptive to metabotropic glutamate receptors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Jun;5(3):342–349. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Depolarization-induced suppression of GABAergic inhibition in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells: G protein involvement in a presynaptic mechanism. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1447–1455. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Postsynaptic spike firing reduces synaptic GABAA responses in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4122–4132. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncer J. C., Shinozaki H., Miles R. Dual modulation of synaptic inhibition by distinct metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1995 May 15;485(Pt 1):121–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub C., Vranesic I., Knöpfel T. Responses to Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Activation in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells: Induction of an Inward Current. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(9):832–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P., Armstrong C. M., Marty A. Inhibitory synaptic currents in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells: modulation by postsynaptic depolarization. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:453–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent P., Marty A. Neighboring cerebellar Purkinje cells communicate via retrograde inhibition of common presynaptic interneurons. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90118-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]