Abstract
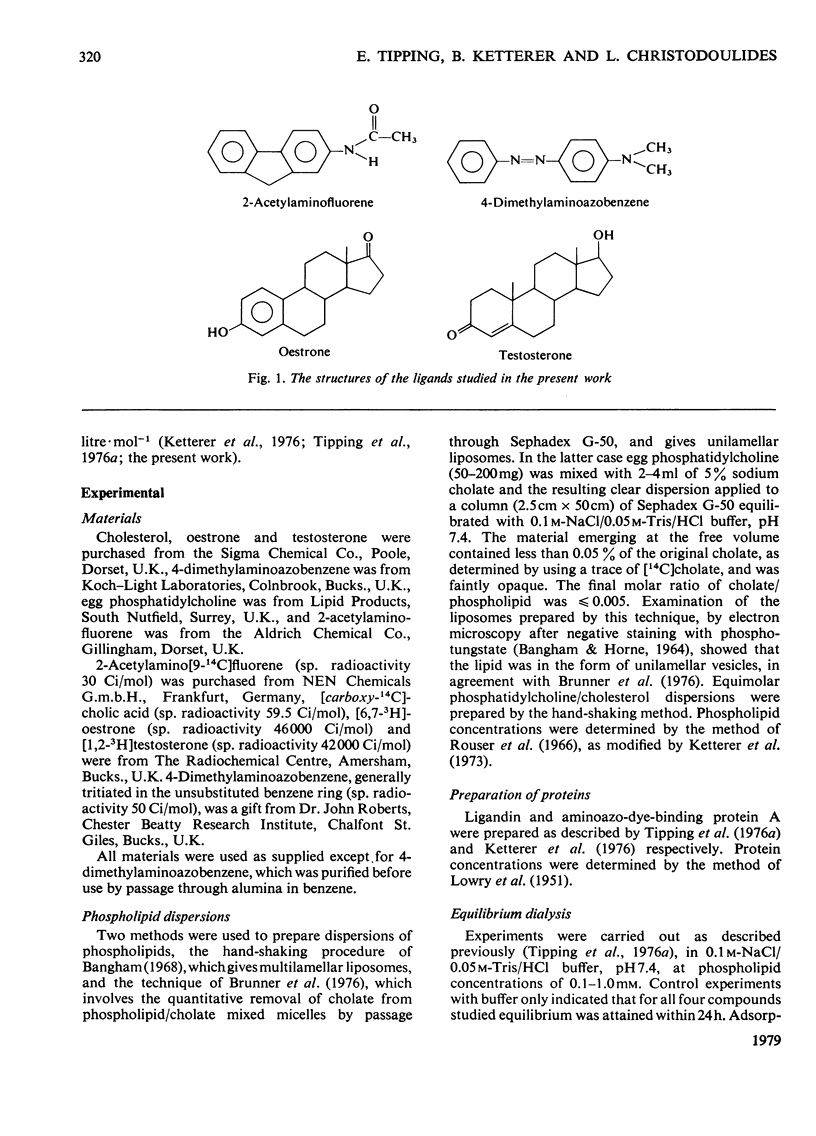
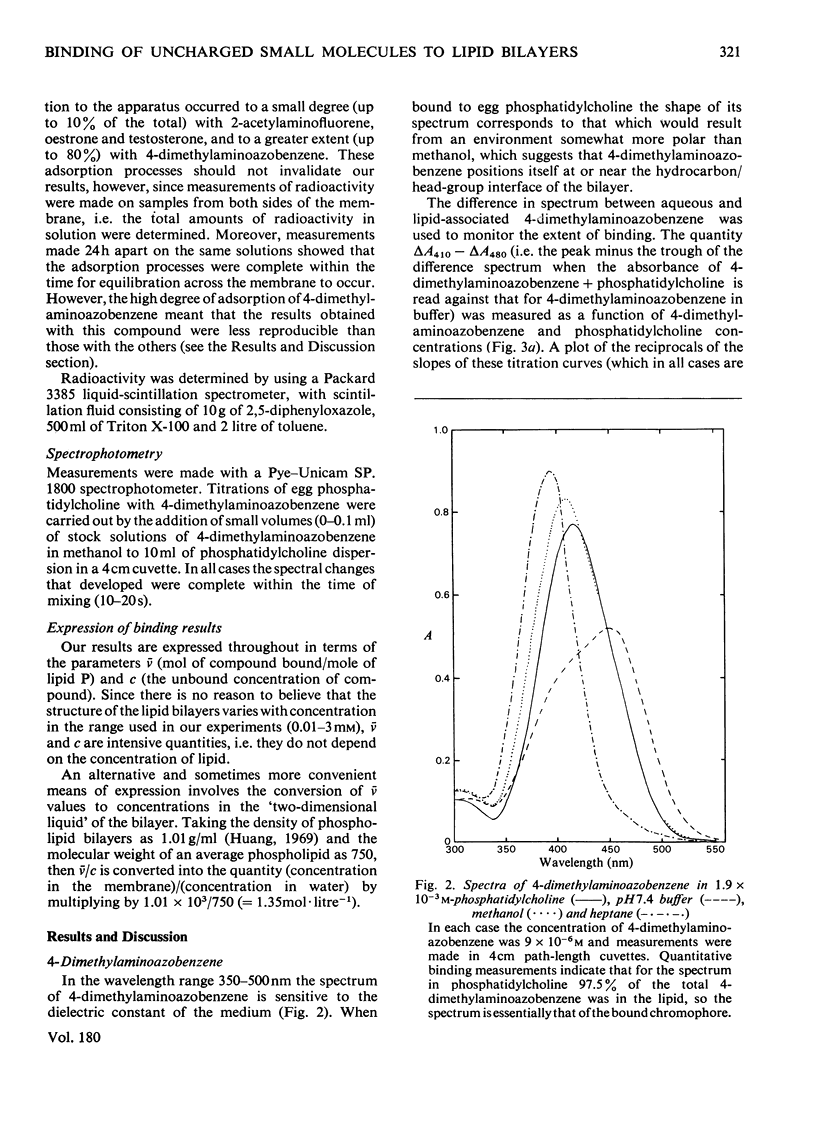
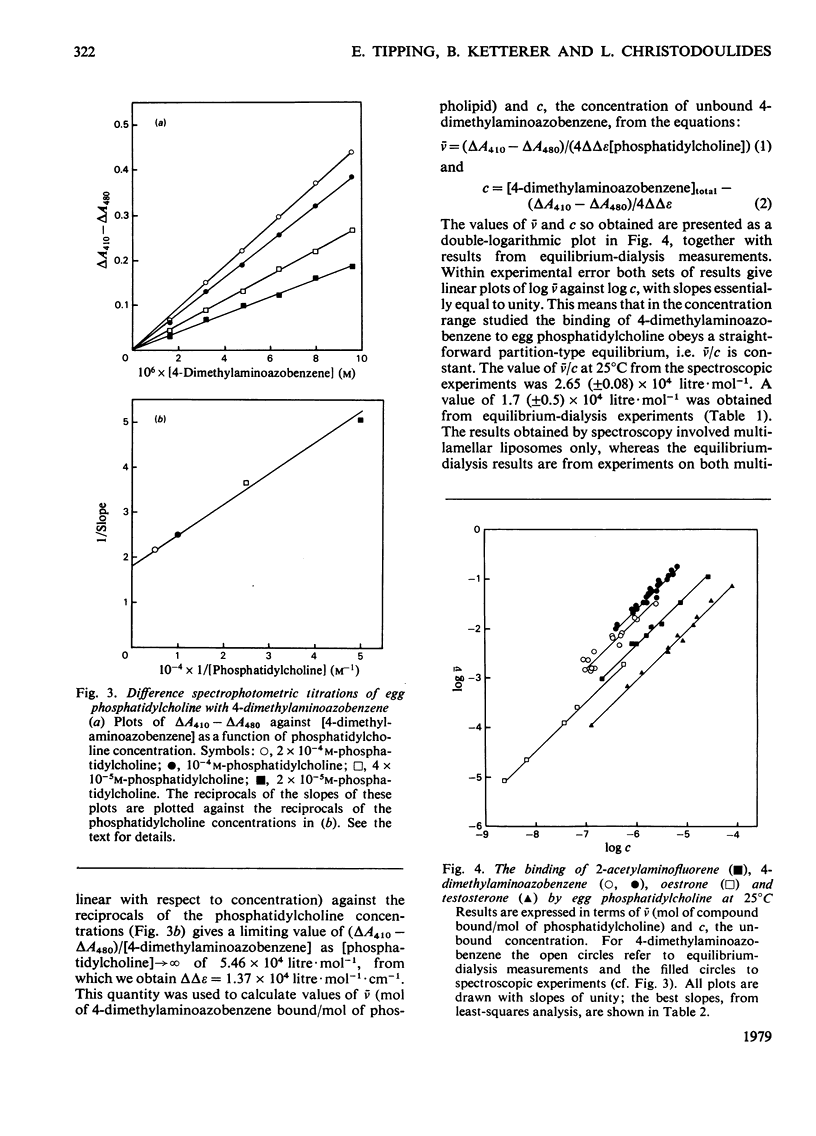
1. To assess the possible involvement of ligandin and aminoazo-dye-binding protein A in intracellular transport it is necessary to know how their ligands, most of which are molecules with hydrophobic moieties, interact with cellular membranes. To obtain such information we have examined the interactions of 2-acetylaminofluorene, 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene, oestrone and testosterone with aqueous dispersions of egg phosphatidylcholine and egg phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol (1:1, molar ratio) by equilibrium dialysis and spectrophotometry. 2. At 25°C and pH7.4, the partition coefficients for binding to phosphatidylcholine [expressed as (mol of ligand bound/mol of phosphatidylcholine)/unbound ligand concentration] were: for 2-acetylaminofluorene, 5.0×103 litre·mol−1; for 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene, 2.1×104 litre·mol−1; for oestrone, 3.1×103 litre·mol−1; and for testosterone, 4.2×102 litre·mol−1. In the ranges studied these values were independent of concentration. The results for the two steroids confirm those of Heap, Symons & Watkins [(1970) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 218, 482–495]. 3. The introduction of cholesterol into the lipid bilayers caused large decreases in the partition coefficients of oestrone and testosterone, but had relatively little effect on the binding of 2-acetylaminofluorene and 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene. 4. By assuming that the interactions with egg phosphatidylcholine bilayers resemble those with the phospholipid components of mammalian intracellular membranes the phosphatidylcholine partition coefficients, together with data for binding to the intracellular proteins ligandin and aminoazo-dye-binding protein A, enable the subcellular distributions of the four compounds to be estimated. For the rat hepatocyte up to 98, 99, 89 and 58% of the total 2-acetylaminofluorene, 4-dimethylaminoazobenzene, oestrone and testosterone respectively may be membrane-bound.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM A. D., HORNE R. W. NEGATIVE STAINING OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS AND THEIR STRUCTURAL MODIFICATION BY SURFACE-ACTIVE AGENTS AS OBSERVED IN THE ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:660–668. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley R. A., Martin W. G., Schneider H. Dynamic behavior of fluorescent probes in lipid bilayer model membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):268–275. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth C. A., Freedman R. B., Rabin B. R. Sex specific binding of steroid hormones to microsomal embranes of rat liver. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 31;230(13):137–139. doi: 10.1038/newbio230137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner J., Skrabal P., Hauser H. Single bilayer vesicles prepared without sonication. Physico-chemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):322–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depierre J. W., Dallner G. Structural aspects of the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 29;415(4):411–472. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M. Rotational and translational diffusion in membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):179–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heap R. B., Symons A. M., Watkins J. C. Steroids and their interactions with phospholipids: solubility, distribution coefficient and effect on potassium permeability of liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 15;218(3):482–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. Studies on phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Formation and physical characteristics. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):344–352. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamisaka K., Listowsky I., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Interactions of bilirubin and other ligands with ligandin. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2175–2180. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketley J. N., Habig W. H., Jakoby W. B. Binding of nonsubstrate ligands to the glutathione S-transferases. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8670–8673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Hicks R. M., Christodoulides L., Beale D. Studies of the chemistry of the luminal plasma membrane of rat bladder epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 22;311(2):180–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Tipping E., Hackney J. F., Beale D. A low-molecular-weight protein from rat liver that resembles ligandin in its binding properties. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):511–521. doi: 10.1042/bj1550511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketterer B., Tipping E., Meuwissen J., Beale D. Ligandin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(5):626–630. doi: 10.1042/bst0030626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litwack G., Ketterer B., Arias I. M. Ligandin: a hepatic protein which binds steroids, bilirubin, carcinogens and a number of exogenous organic anions. Nature. 1971 Dec 24;234(5330):466–467. doi: 10.1038/234466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNCK A. The interfacial activity of steroid hormones and synthetic estrogens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snart R. S., Wilson M. J. Uptake of steroid hormones into artificial phospholipid-cholesterol membranes. Nature. 1967 Aug 26;215(5104):964–964. doi: 10.1038/215964a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stier A., Sackmann E. Spin labels as enzyme substrates. Heterogeneous lipid distribution in liver microsomal membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 6;311(3):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping E., Ketterer B., Christodoulides L., Enderby G. Spectroscopic studies of the binding of bilirubin by ligandin and aminoazo-dye-binding protein A. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):211–216. doi: 10.1042/bj1570211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping E., Ketterer B., Christodoulides L., Enderby G. The interactions of haem with ligandin and aminoazo-dye-binding protein A. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):461–467. doi: 10.1042/bj1570461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping E., Ketterer B., Christodoulides L., Enderby G. The non-convalent binding of small molecules by ligandin. Interactions with steroids and their conjugates, fatty acids, bromosulphophthalein carcinogens, glutathione and realted compounds. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):583–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping E., Ketterer B., Christodoulides L. Interactions of small molecules with phospholipid bilayers. Binding to egg phosphatidylcholine of some organic anions (bromosulphophthalein, oestrone sulphate, haem and bilirubin) that bind to ligandin and aminoazo-dye-binding protein A. Biochem J. 1979 May 15;180(2):327–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1800327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping E., Ketterer B., Koskelo P. The binding of porphyrins by ligandin. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):509–516. doi: 10.1042/bj1690509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Callis J. B. Pyrene. A probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 10;13(19):4000–4006. doi: 10.1021/bi00716a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakim D., Vessey D. A. Membrane-bound estrone as substrate for microsomal UDP-glucuronyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7534–7537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


