Abstract
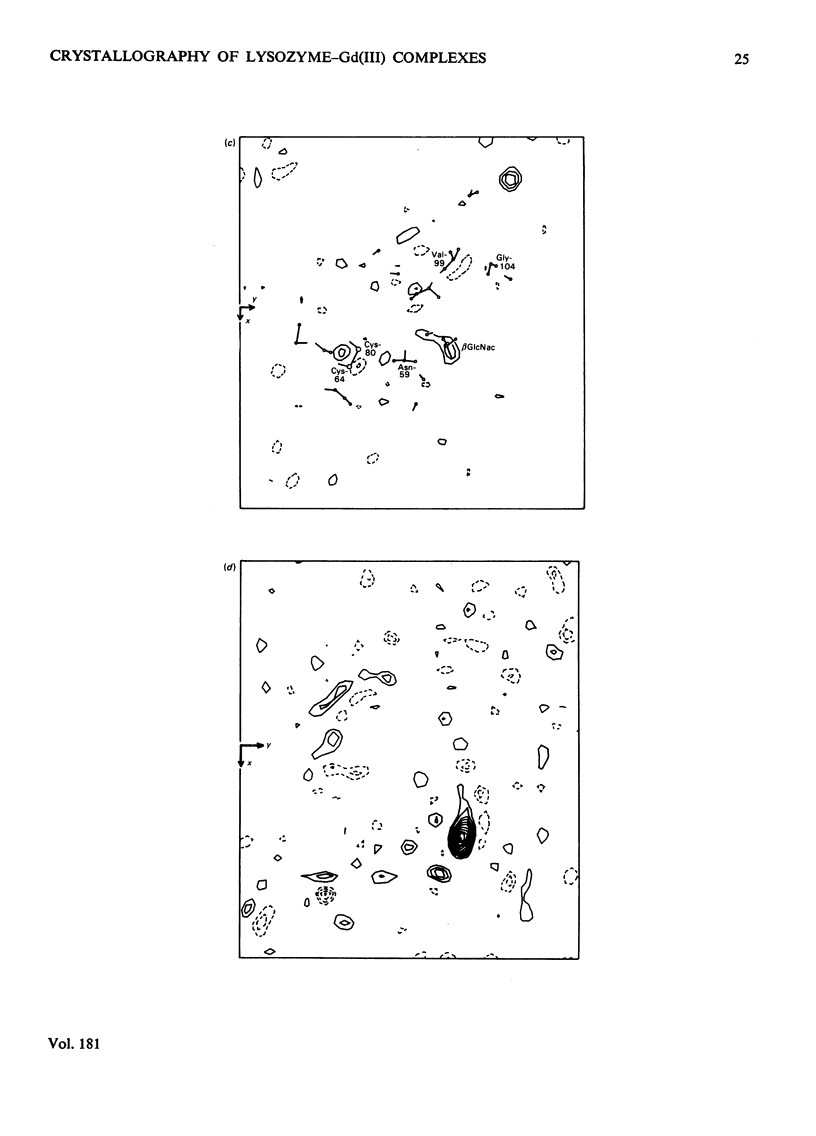
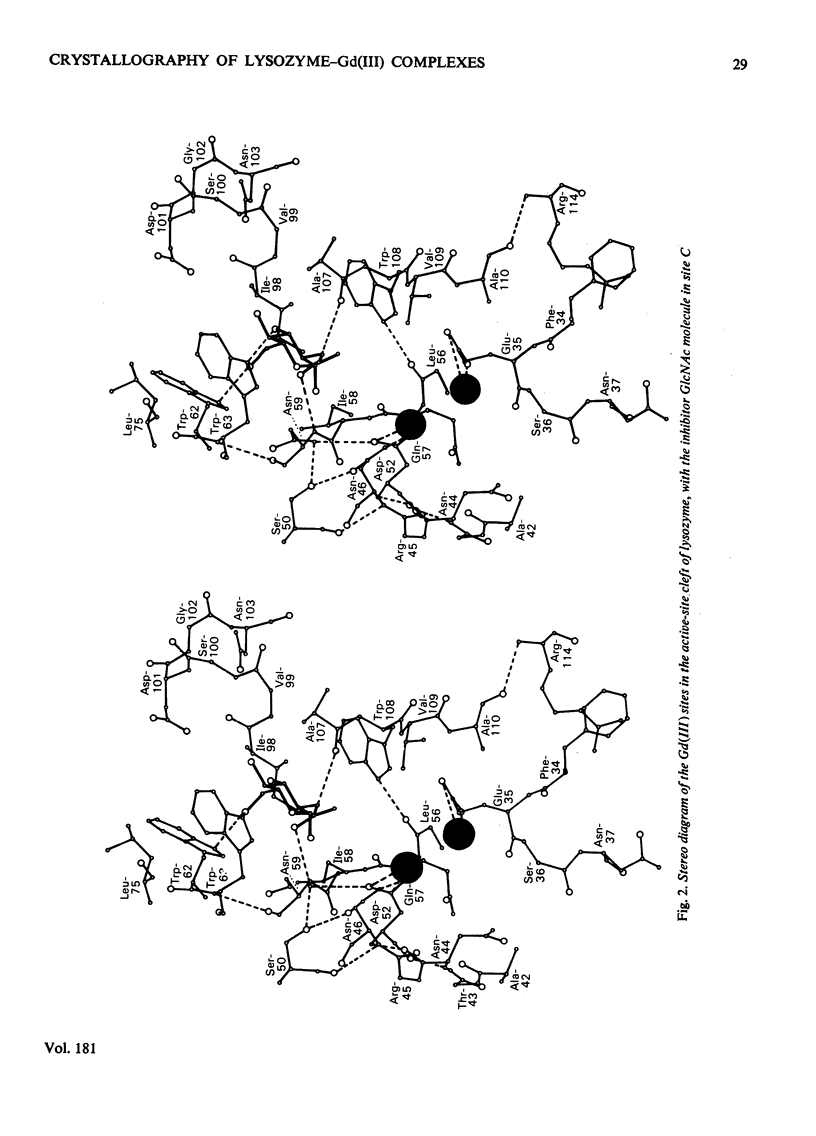
Analysis at 0.25 nm resolution of the crystal structures of lysozyme-Gd(III) and lysozyme-Gd(III)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNac), prepared by diffusion methods, show that there are two main binding positions for Gd(III), one of which is close to glutamic acid-35 and the other close to aspartic acid-52. The two sites are 0.36 nm part. There is no evidence for the weak binding of Gd(III) to any of the eight other carboxy groups of lysozyme. In the presence of Gd(III), the binding of GlcNac is similar to that observed for the binding of the beta-anomer in subsite C. There are numerous small conformational changes in the protein on binding (Gd(III) and the sugar, and these have been quantified to a first approximation by real-space refinement. These changes are similar in both structures, and involve, among other small movements, shifts of one of the disulphide bridges by up to 0.05 nm. The movement of residues 70--74 observed in the binary complex of lysozyme-GlcNac [Perkins, Johnson, Machin & Phillips (1978) Biochem. J. 173-617] is not observed in the ternary complex of lysozyme-Gd(III)-GlcNac. The nature of the lysozyme-Gd(III) complex is discussed in the light of evidence from other crystallographic studies and n.m.r. solution studies. Preliminary findings for a lysozyme-Gd(III) complex prepared by co-crystallization methods are reported.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agresti D. G., Lenkinski R. E., Glickson J. D. Lanthanide induced NMR perturbations of HEW lysozyme: evidence for nonaxial symmetry. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91558-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
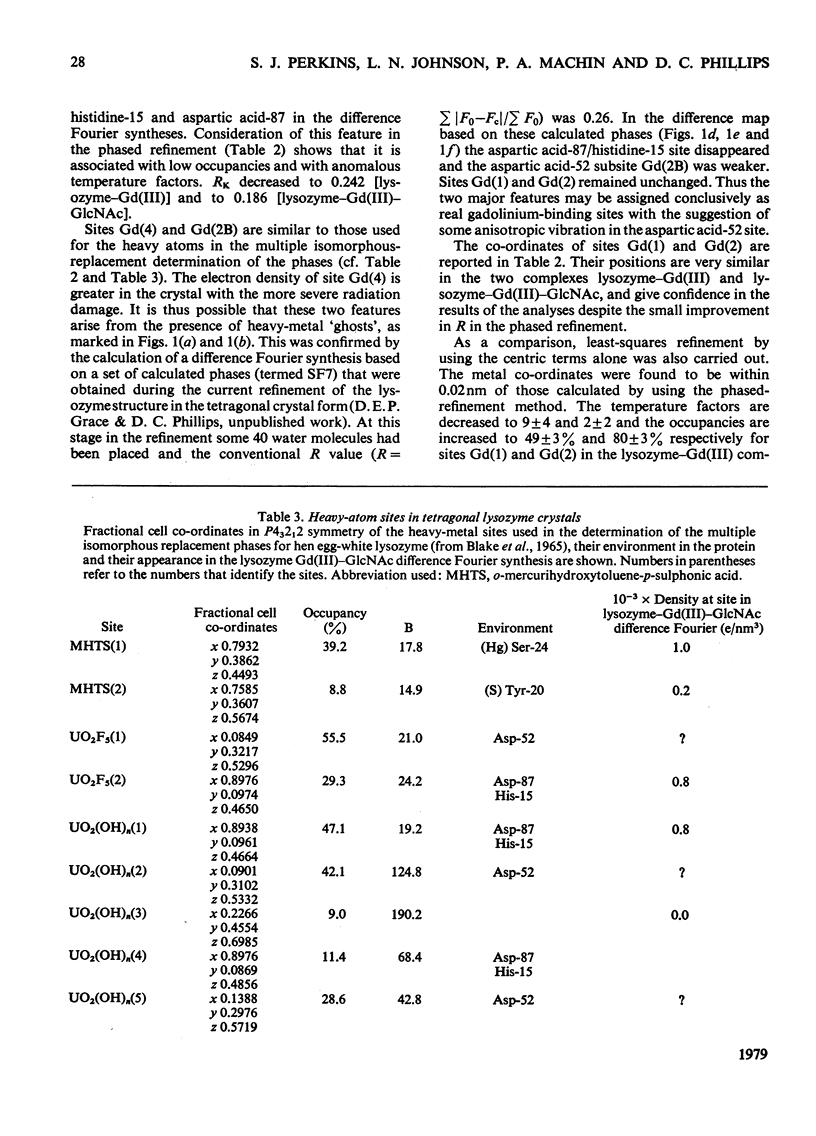
- Blake C. C., Koenig D. F., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. A three-dimensional Fourier synthesis at 2 Angstrom resolution. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):757–761. doi: 10.1038/206757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. Real-space refinement of the structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 25;82(3):371–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwek R. A., Richards R. E., Morallee K. G., Nieboer E., Williams R. J., Xavier A. V. The lanthanide cations as probes in biological systems. Proton relaxation enhancement studies for model systems and lysozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 29;21(2):204–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N. The crystal structure of N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine. Acta Crystallogr. 1966 Dec 10;21(6):885–891. doi: 10.1107/s0365110x66004146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Dwek R. A. The mechanism of water-proton relaxation in enzyme paramagnetic-ion complexes. 1. The Gd(3)-lysozyme complex. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):271–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Metal ion binding in triclinic lysozyme. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7663–7667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Structures of triclinic mono- and di-N-acetylglucosamine: lysozyme complexes--a crystallographic study. J Mol Biol. 1976 Feb 15;101(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu S., Ikeda K., Hamaguchi K., Fujio H., Amano T. Ionization constants of Glu 35 and Asp 52 in hen, turkey, and human lysozymes. J Biochem. 1974 Oct;76(4):671–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenkinski R. E., Agresti D. G., Chen D. M., Glickson J. D. An analysis of the Co2+-induced nuclear magnetic resonance perturbations of hen egg white lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1463–1468. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Johnson L. N., Machin P. A., Phillips D. C. Crystal structures of egg-white lysozyme of hen in acetate-free medium and of lysozyme complexes with N-acetylglucosamine and beta-methyl N-acetylglucosaminide. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):607–616. doi: 10.1042/bj1730607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secemski I. I., Lienhard G. E. The effect of gadolinium ion on the binding of inhibitors and substrates to lysozyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2932–2938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrake A., Rupley J. A. Environment and exposure to solvent of protein atoms. Lysozyme and insulin. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):351–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Kay L. M., Dickerson R. E. The structure of bovine trypsin: electron density maps of the inhibited enzyme at 5 Angstrom and at 2-7 Angstron resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Sharon N., Moult J., Smilansky A., Yonath A. Binding of divalent copper ions to aspartic acid residue 52 in hen egg-white lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 5;87(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


