Abstract
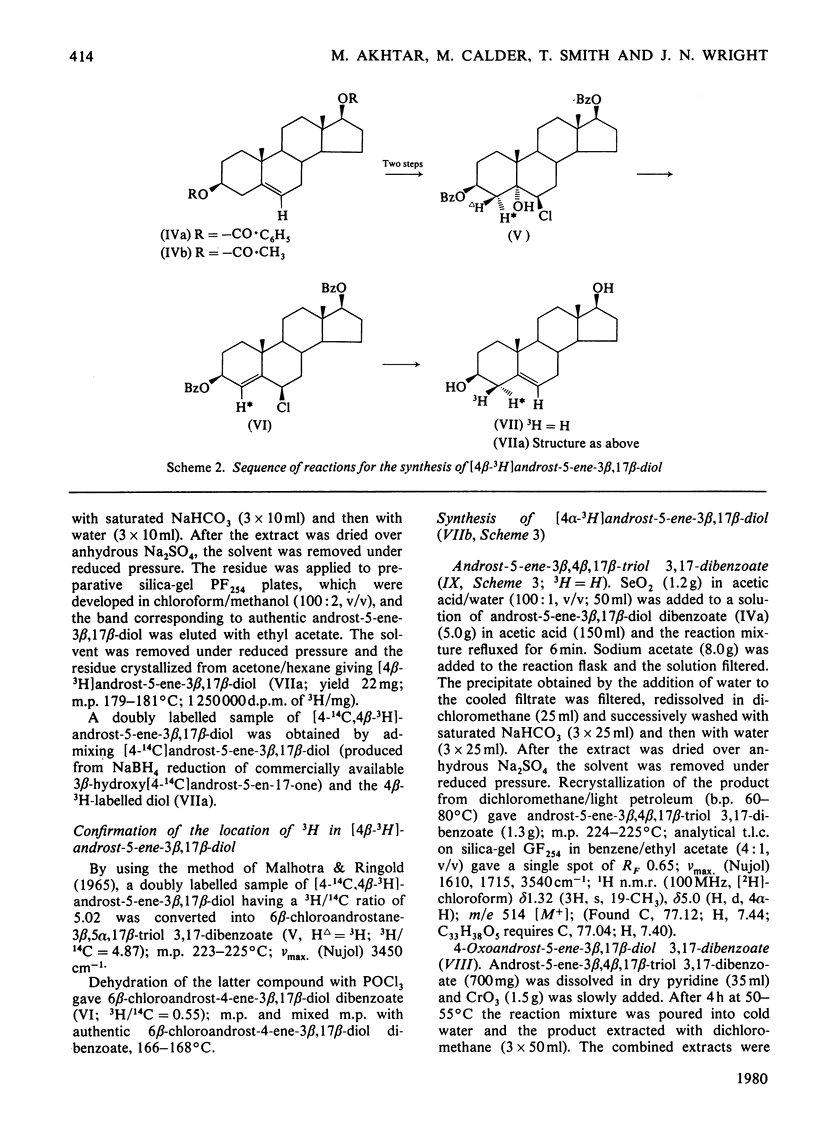
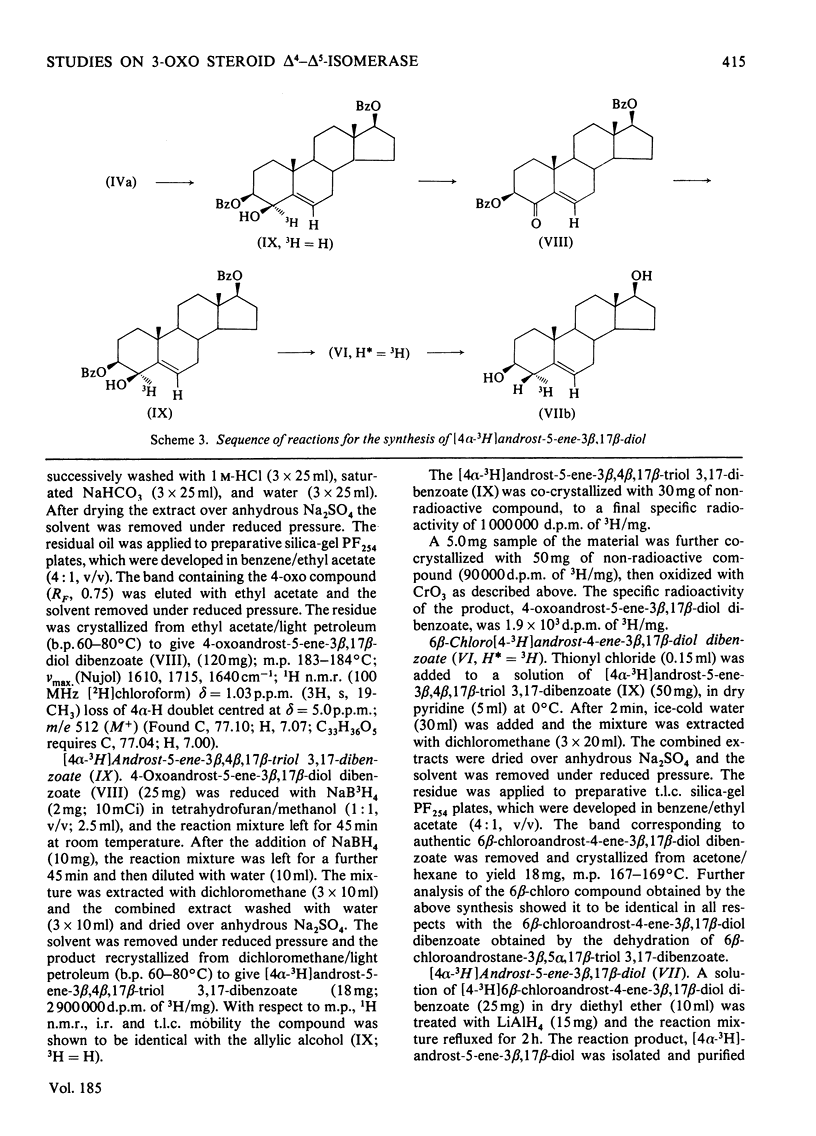
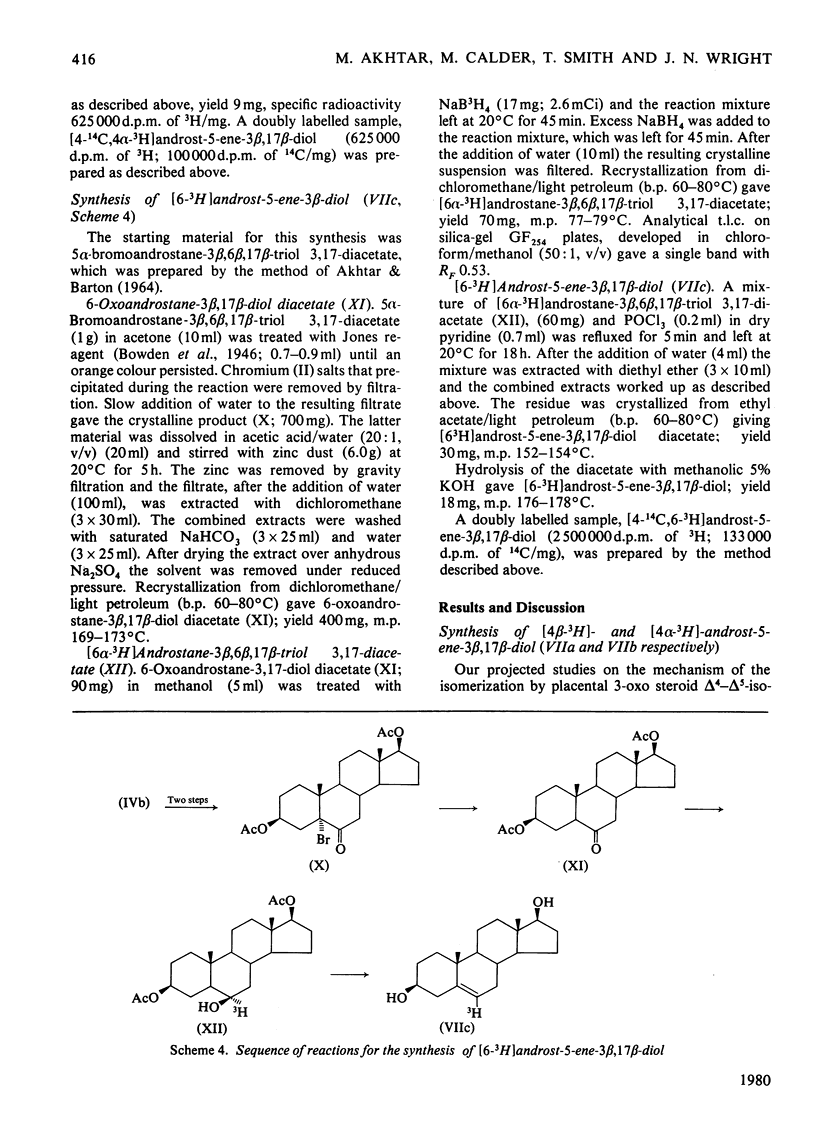
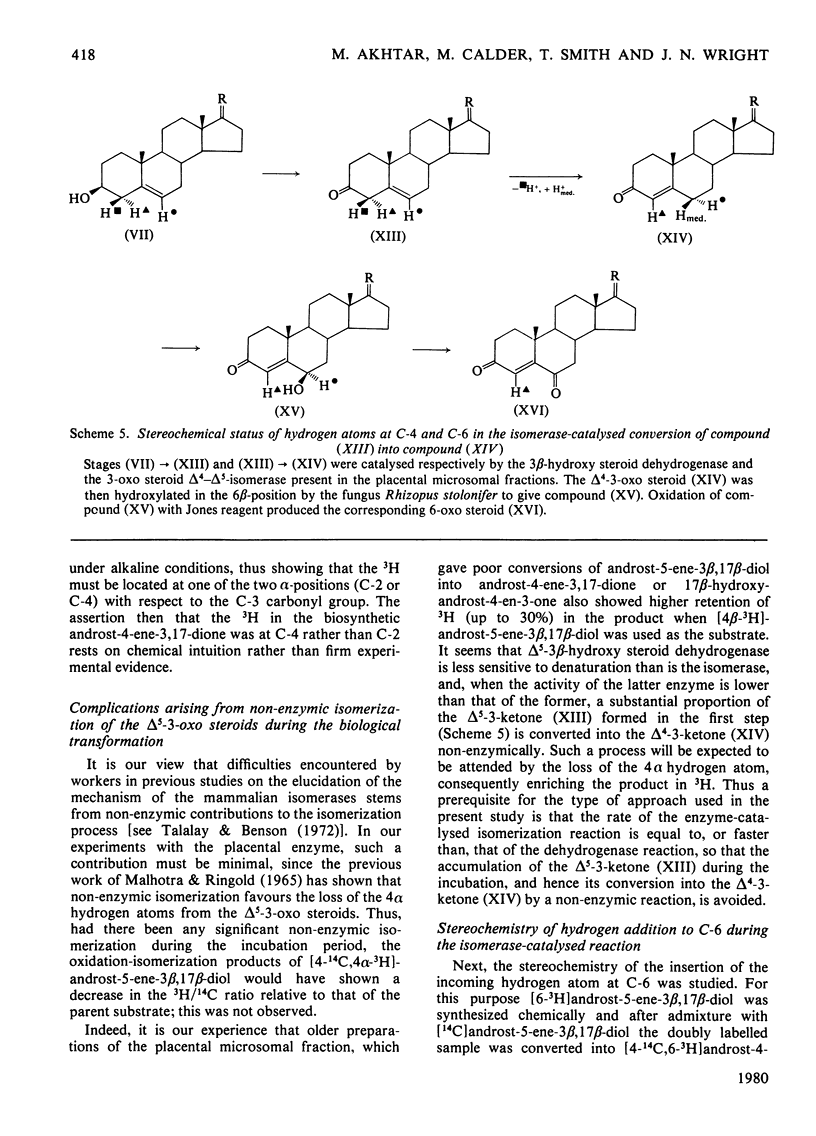
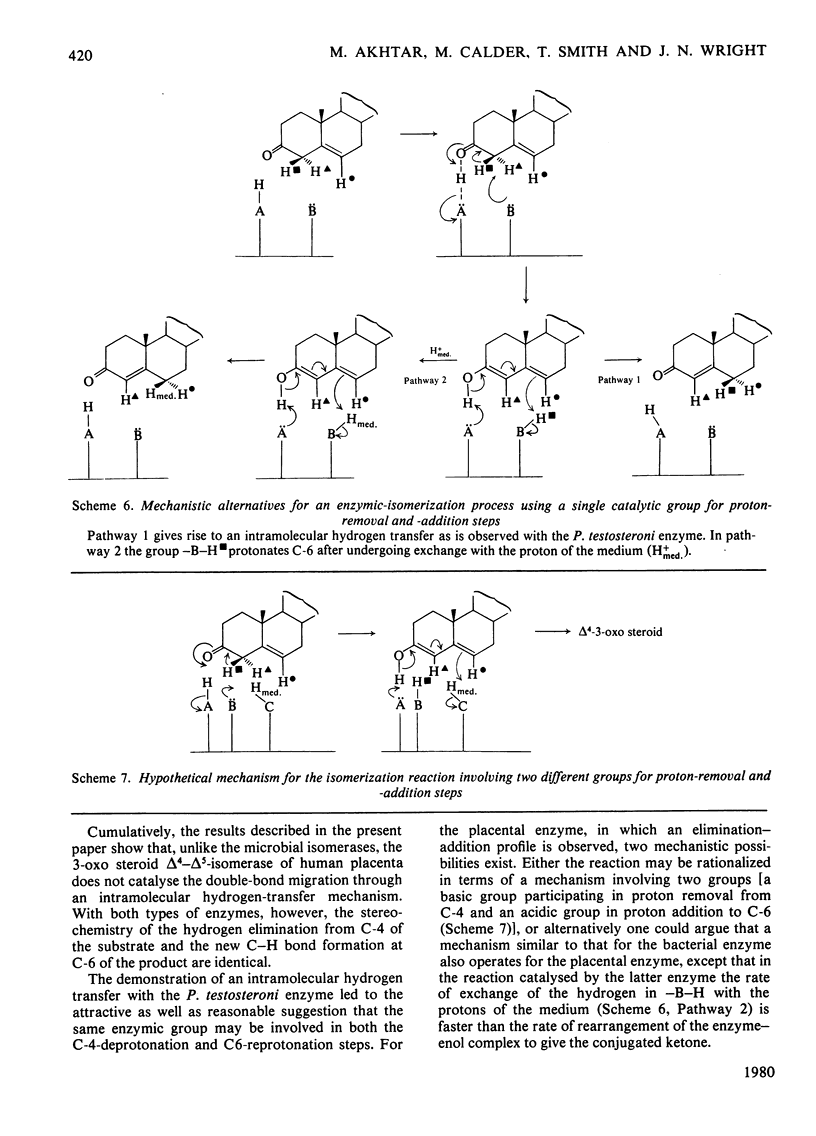
The mechanism of isomerization of delta 5-3-ox steroids to delta 4-3-oxo steroids was examined by using the membrane-bound 3-oxo steroid delta 4-delta 5-isomerase (EC 5.3.3.1) and the 3 beta-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase present in the microsomal fraction obtained from full-term human placenta. (1) Methods for the preparation of androst-5-ene-3 beta, 17 beta-diol specifically labelled at the 4 alpha-, 4 beta- or 6-positions are described. (2) Incubations with androst-5-ene-3 beta, 17 beta-diol stereospecifically 3H-labelled either in the 4 alpha- or 4 beta-position showed that the isomerization reaction occurs via a stereospecific elimination of the 4 beta hydrogen atom. In addition, the complete retention of 3H in the delta 4-3-oxo steroids obtained from [4 alpha-3H]androst-5-ene-3 beta, 17 beta-diol indicates that the non-enzymic contribution to these experiments was negligible. (3) To study the stereochemistry of the insertion of the incoming proton at C-6, the [6-3H]androst-4-ene-3, 17-dione obtained from the oxidation isomerization of [6-3H]androst-5-ene-3 beta, 17 beta-diol was enzymically hydroxylated in the 6 beta-position by the fungus Rhizopls stolonifer. Retention of 3H in the 6 alpha-position of the isolated 6 beta-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3, 17-dione indicates that in the isomerase-catalysed migration of the C(5) = C(6) double bond, the incoming proton from the acidic group on the enzyme must enter C-6 from the beta-face, forcing the existing 3H into the 6 alpha-position.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achmatowicz S., Barton D. H., Magnus P. D., Poulton G. A., West P. J. Photochemical transformations. XXX. Photolysis of thiobenzoic acid O-esters. I. Photolysis of O-cholesteryl thiobenzoate. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1973;15:1567–1570. doi: 10.1039/p19730001567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar M., Skinner S. J. The intermediary role of a 19-oxoandrogen in the biosynthesis of oestrogen. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(2):318–321. doi: 10.1042/bj1090318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN K. J. Biological aromatization of steroids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Feb;234(2):268–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose I. A. Mechanism of the aldose-ketose isomerase reactions. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:491–517. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. G., Brooks C. J. The substrate specificity and stereochemistry, reversibility and inhibition of the 3-oxo steroid delta 4-delta 5-isomerase component of cholesterol oxidase. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):121–129. doi: 10.1042/bj1670121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P., DOBSON M. M., TAPLEY D. F. Oxidative degradation of testosterone by adaptive enzymes. Nature. 1952 Oct 11;170(4328):620–621. doi: 10.1038/170620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P., WANG V. S. Enzymic isomerization of delta5-3-ketosteroids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Oct;18(2):300–301. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


