Abstract
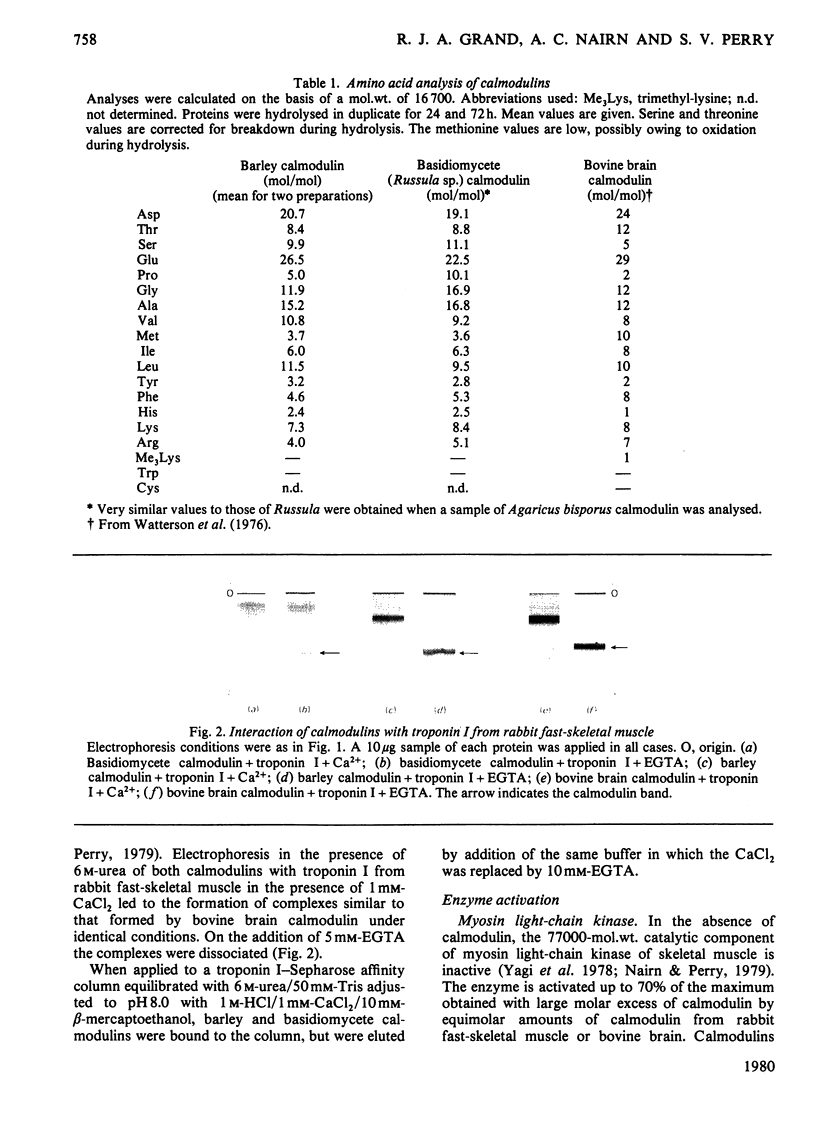
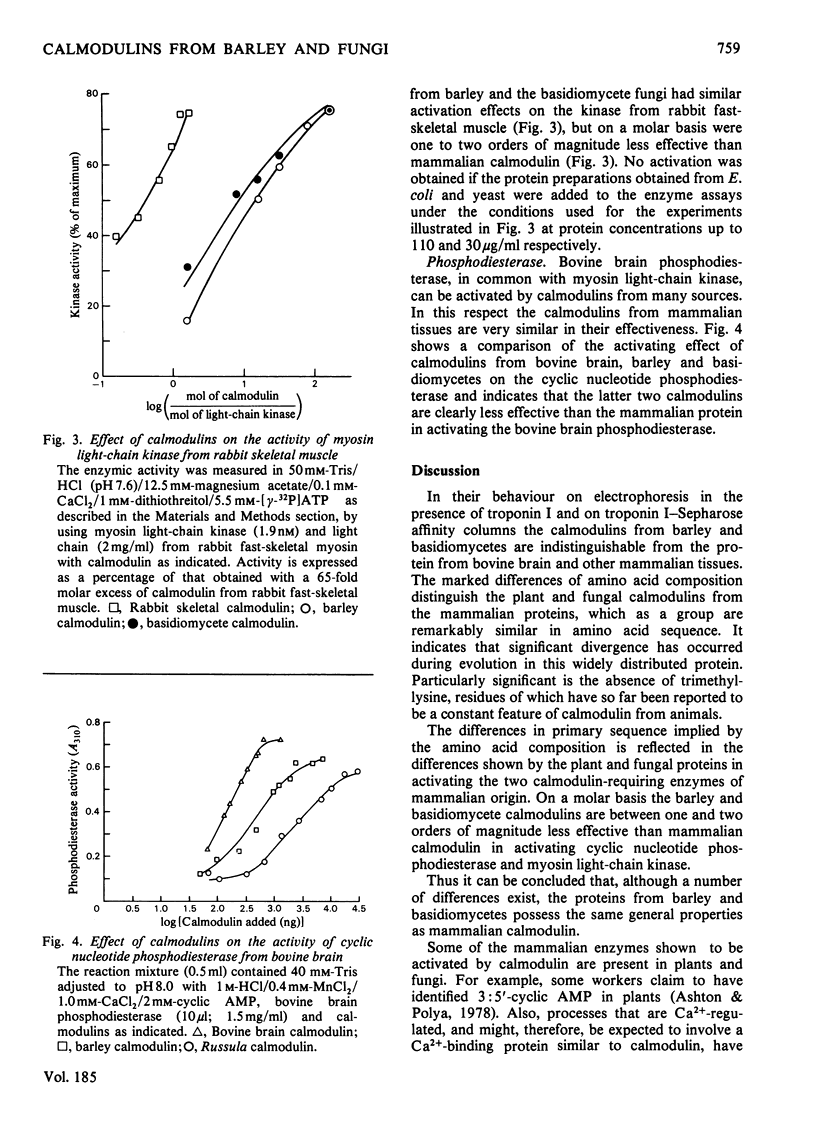
1. Calmodulin-like proteins were purified from the fruiting bodies of higher (basidiomycete) fungi and barley (Hordeum sp.) shoots. 2. These calmodulins have electrophoretic mobilities on 10% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels at pH 8.3 in the presence of 6 M-urea and at pH 8.3 in the presence of 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulphate similar to that of bovine brain calmodulin. They interacted with rabbit skeletal-muscle troponin I in the presence of Ca2+. 3. Barley and fungal calmodulins activated myosin light-chain kinase and phosphodiesterase in the presence of Ca2+, although the amounts needed were at least an order of magnitude greater than is required to produce the same effect with mammalian calmodulin. 4. Amino acid analyses indicated a number of differences from the mammalian protein, most notably the absence of trimethyl-lysine. 5. By using 125I-labelled calmodulin, a small amount of calmodulin-binding protein was detected in homogenates of barley and fungi. 6. No protein corresponding to calmodulin could be found in Escherichia coli or yeast, although a relatively high concentration of a protein that bound calmodulin was detected in E. coli by this technique.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Cormier M. J. Calcium-dependent regulation of NAD kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90747-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton A. R., Polya G. M. Cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in axenic rye grass endosperm cell cultures. Plant Physiol. 1978 May;61(5):718–722. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.5.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Demonstration of an activator. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 6;38(3):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90747-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Jackson R. L., Schreiber W. E., Means A. R. Sequence homology of the Ca2+-dependent regulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from rat testis with other Ca2+-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 25;253(2):343–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath R. M., Vincenzi F. F. Phosphodiesterase protein activator mimics red blood cell cytoplasmic activator of (Ca2+-Mg2+)ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 22;77(4):1203–1209. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V. Calmodulin-binding proteins from brain and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):285–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1830285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head J. F., Weeks R. A., Perry S. V. Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 1;161(3):465–471. doi: 10.1042/bj1610465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Yamazaki R. Calcium dependent phosphodiesterase activity and its activating factor (PAF) from brain studies on cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase (3). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H. Purification of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitory protein by affinity chromatography on activator protein coupled to Sepharose. Biochemistry. 1978 Jan 10;17(1):120–126. doi: 10.1021/bi00594a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Identification of epsilon-N-monomethyllysine and epsilon-N-trimethyllysine in rabbit skeletal myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Sep 24;37(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90880-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. Calmodulin and myosin light-chain kinase of rabbit fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):89–97. doi: 10.1042/bj1790089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of troponin and the effects of interactions between the components of the complex. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):733–743. doi: 10.1042/bj1410733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pires E. M., Perry S. V. Purification and properties of myosin light-chain kinase from fast skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1670137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanui H. Measurement of inorganic orthophosphate in biological materials: extraction properties of butyl acetate. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):489–504. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Stevens F. C., Wang J. H. Purification and characterization of a Ca2+-binding protein in Lumbricus terrestris. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D., Stevens F. C., Wang J. H. The distribution of the Ca++-dependent protein activator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase in invertebrates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):975–982. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80481-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Desai R. Modulator binding protein. Bovine brain protein exhibiting the Ca2+-dependent association with the protein modulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4175–4184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Harrelson W. G., Jr, Keller P. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. Structural similarities between the Ca2+-dependent regulatory proteins of 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and actomyosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4501–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V., Cole H. A., Trayer I. P. The regulatory proteins of the myofibril. Separation and biological activity of the components of inhibitory-factor preparations. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):215–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1270215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K., Yazawa M., Kakiuchi S., Ohshima M., Uenishi K. Identification of an activator protein for myosin light chain kinase as the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1338–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]