Abstract
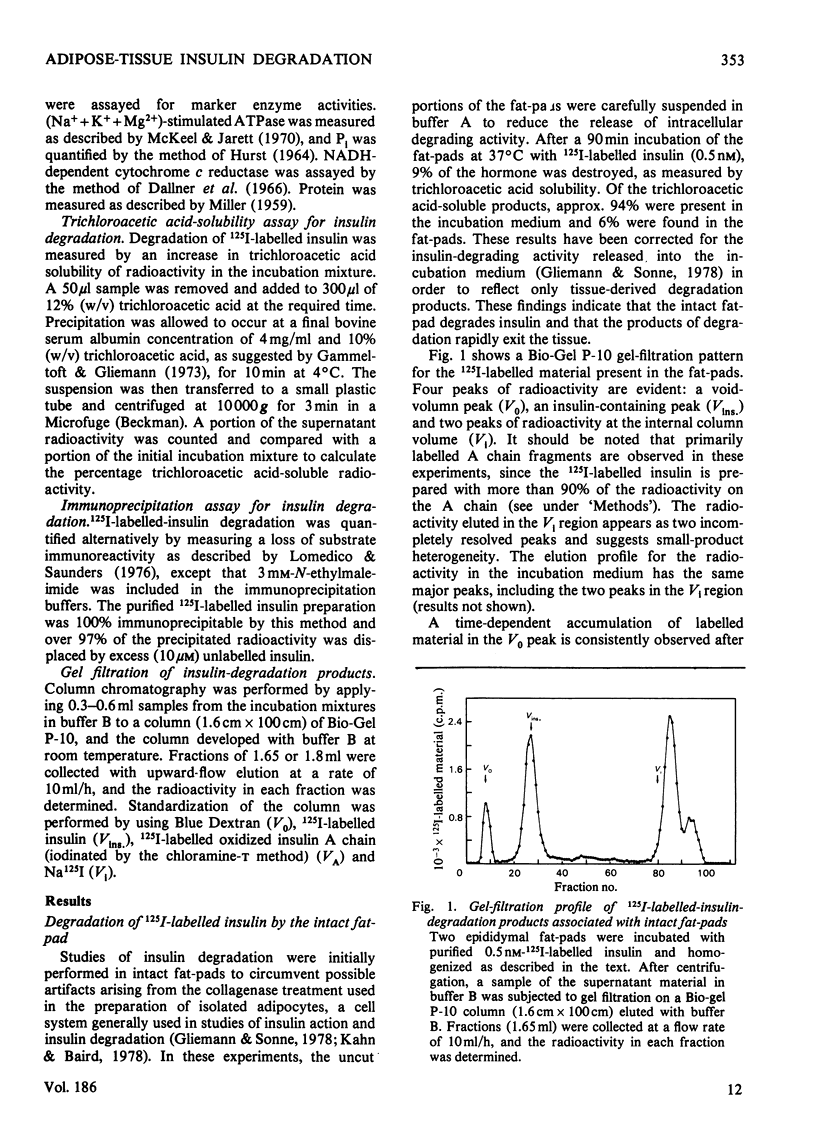
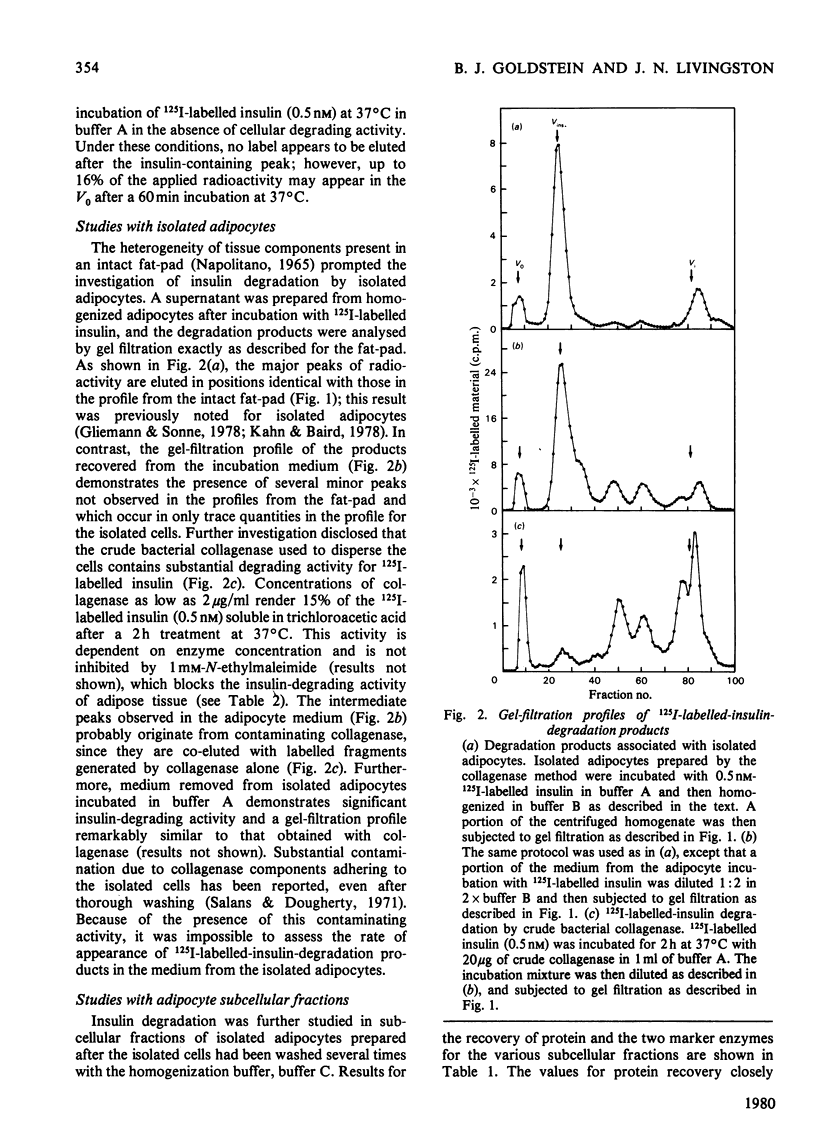
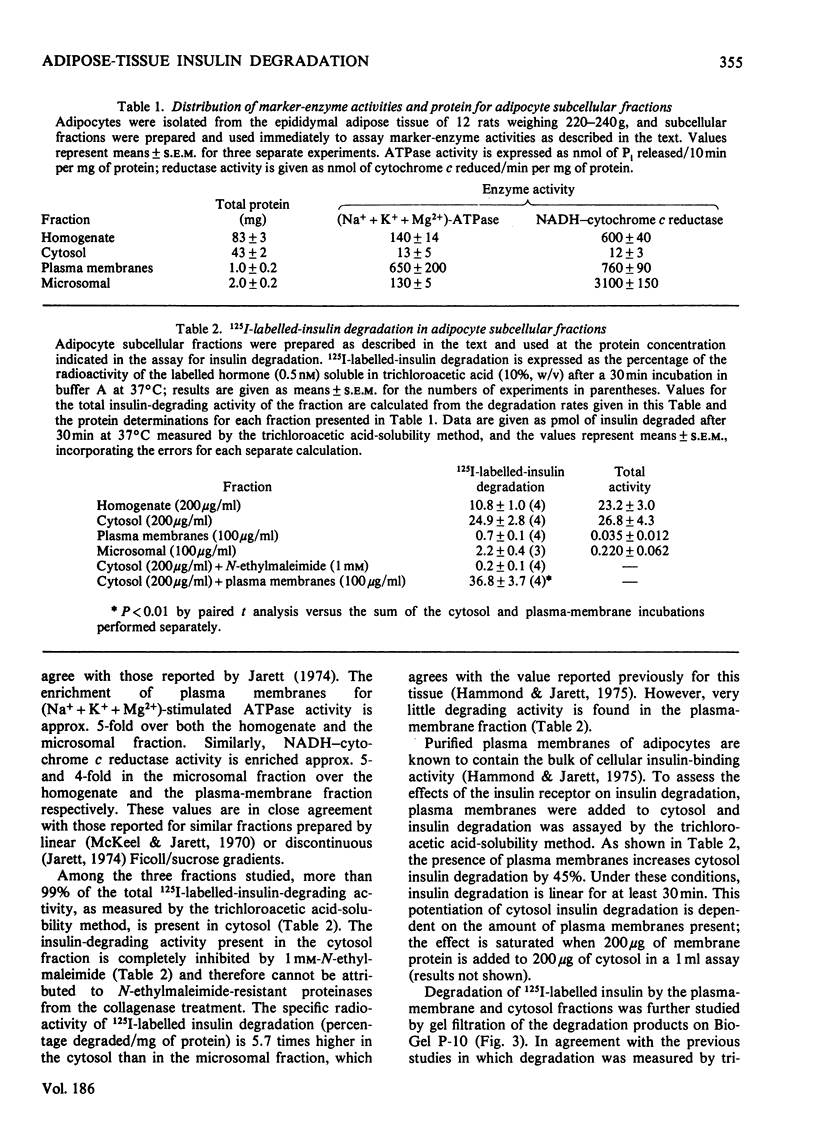
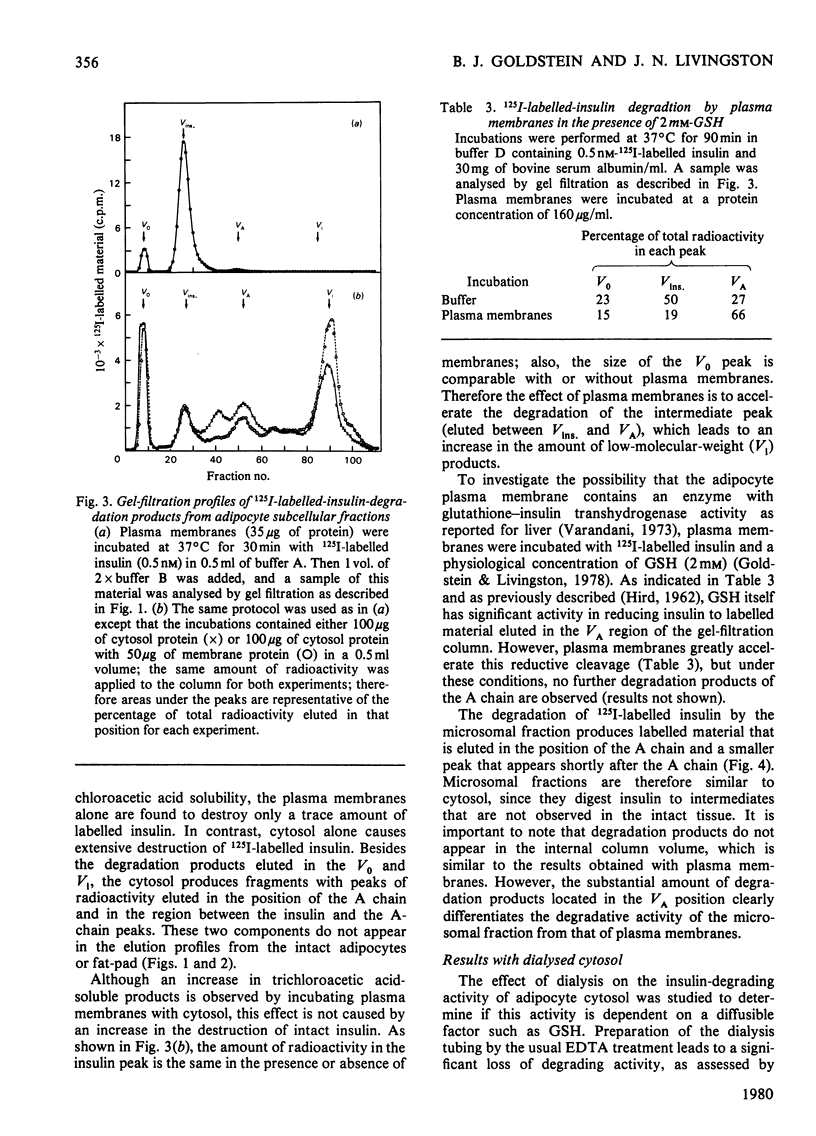
A systematic study of the degradation of physiological concentrations of 125I-labelled insulin was performed in intact fat-pads, isolated adipocytes and subcellular fractions of isolated adipocytes. The findings indicate that insulin is rapidly degraded to low-molecular-weight peptides and/or amino acids by the intact tissue and isolated cells. Of the total insulin-degradation products present after incubation with an intact fat-pad, 94% is recovered in the medium, indicating that these products are not retained by the cells or tissue. The plasma membranes do not degrade insulin significantly in the absence of reduced glutathione, and over 99% of the cellular degradative capacity is found in the postmicrosomal supernatant (cytosol). The cytosol degrades insulin to several labelled fragments that are intermediate in size between insulin and insulin A chain, as well as to the low-molecular-weight tissue degradation products. Inclusion of plasma membranes with cytosol accelerates the cleavage of the intermediate fragments to the size of the small products seen with the intact tissue. However, plasma membranes do not increase the initial step in the degradation of insulin when incubated with cytosol, suggesting that the insulin receptor is not involved with the direct cleavage of insulin. This study supports the hypothesis that the bulk of insulin degradation occurs in the adipocyte cytosol, where intermediate-sized fragments are generated and rapidly cleaved to smaller products by the plasma membrane and quickly released into the surrounding medium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniades H. N., Stathakos D., Simon J. D. Conversion of (125I)insulin and (125I)proinsulin into high molecular weight forms in vivo. Endocrinology. 1974 Dec;95(6):1543–1553. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-6-1543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRNETT R. J., BALL E. G. Metabolic and ultrastructural changes induced in adipose tissue by insulin. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Sep;8:83–101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J. Intracellular protein degradation. Essays Biochem. 1977;13:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Regulation of the D-glucose transport system in isolated fat cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Mar 26;11(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01792833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallner G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. II. Synthesis of constitutive microsomal enzymes in developing rat hepatocyte. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):97–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C. Insulin and glucagon degradation by the kidney. II. Characterization of the mechanisms at neutral pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 21;437(2):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujino M., Wakimasu M., Taketomi S., Iwatsuka H. Insulin-like activities and insulin-potentiating actions of a modified insulin B21-26 fragment: beta-Ala-Arg-Gly-Phe-Phe-Tyr-NH2. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):360–364. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Gammeltoft S., Vinten J. Time course of insulin-receptor binding and insulin-induced lipogenesis in isolated rat fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3368–3374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Sonne O. Binding and receptor-mediated degradation of insulin in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7857–7863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B. J., Livingston J. N. Effects in adipocytes of diamide on GSH levels, glucose uptake and cell integrity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 19;513(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Carpentier J. L., Freychet P., LeCam A., Orci L. Intracellular translocation of iodine-125-labeled insulin: direct demonstration in isolated hepatocytes. Science. 1978 May 19;200(4343):782–785. doi: 10.1126/science.644321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRD F. J. The reduction of serum albumin, insulin and some simple disulphides by glutathione. Biochem J. 1962 Nov;85:320–326. doi: 10.1042/bj0850320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURST R. O. THE DETERMINATION OF NUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHORUS WITH A STANNOUS CHLORIDE-HYDRAZINE SULPHATE REAGENT. Can J Biochem. 1964 Feb;42:287–292. doi: 10.1139/o64-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond J. M., Jarett L. Insulin degradation by isolated fat cells and their subcellular fractions. Diabetes. 1975 Nov;24(11):1011–1019. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.11.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L. Subcellular fractionation of adipocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:60–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. The fate of insulin bound to adipocytes. Evidence for compartmentalization and processing. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4900–4906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. Membrane receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):261–286. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katunuma N., Kominami E., Banno Y., Kito K., Aoki Y., Urata G. Concept on mechanism and regulation of intracellular enzyme degradation in mammalian tissues. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1976;14:325–345. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(76)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Insulin binding to solubilized material from fat cell membranes: evidence for two binding species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Effect of glucocorticoids on the glucose transport system of isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8353–8360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Saunders G. F. Preparation of pancreatic mRNA: cell-free translation of an insulin-immunoreactive polypeptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):381–391. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahbouba M., Smith H. J. Thiolation and disulphide cross-linking of insulin to form macromolecules of potential therapeutic value. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;86A:247–260. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3282-4_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minemura T., Lacy W. W., Crofford O. B. Regulation of the transport and metabolism of amino acids in isolated fat cells. Effect of insulin and a possible role for adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3872–3881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudman D., Garcia L. A., DiGirolamo M., Shank P. W. Cleavage of bovine insulin by rat adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1966 Jan;78(1):169–185. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salans L. B., Dougherty J. W. The effect of insulin upon glucose metabolism by adipose cells of different size. Influence of cell lipid and protein content, age, and nutritional state. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1399–1410. doi: 10.1172/JCI106623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner K., Doisy R. J. Degradation of insulin by a particulate fraction from adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;116(5):825–831. doi: 10.1042/bj1160825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T. Insulin degradation. X. Identification of insulin degrading activity of rat liver plasma membrane as glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varandani P. T., Shroyer L. A., Nafz M. A. Sequential degradation of insulin by rat liver homogenates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1681–1684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzel G., Eisele K., Guglielmi H., Stock W., Renner R. Structure and activity of insulin. XI. Biologically active synthetic peptides of the insulin sequence B22-25. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Dec;352(12):1735–1738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzel G., Eisele K., Schulz V., Stock W. Structure and activity of insulin. XII. Further studies on biologically acitve synthetic fragments of the B-chain. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Mar;354(3):321–330. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


