Abstract
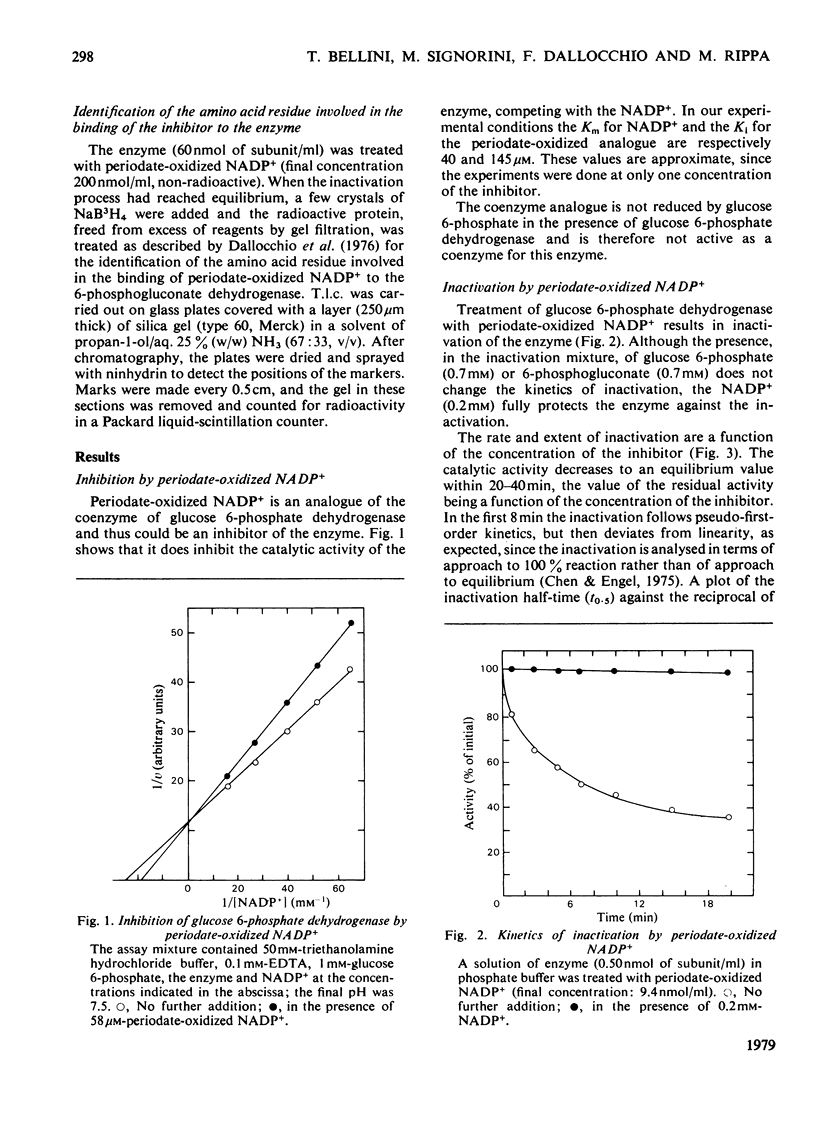
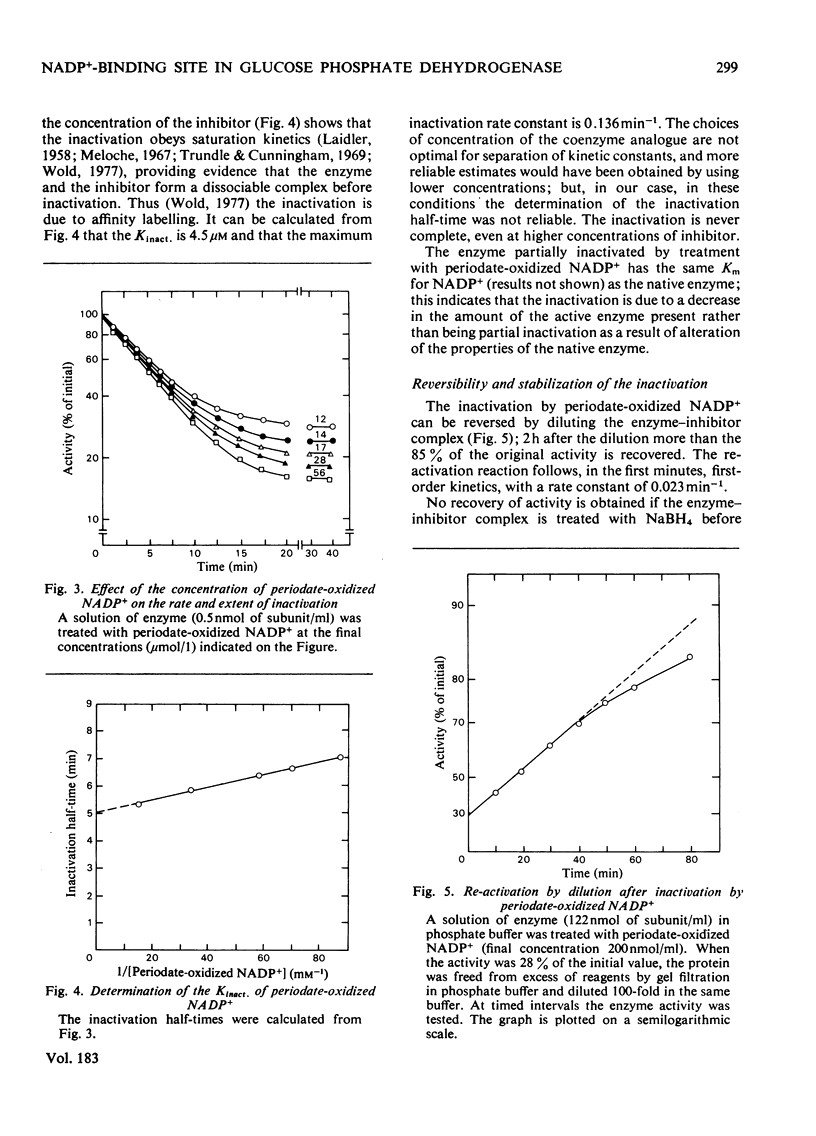
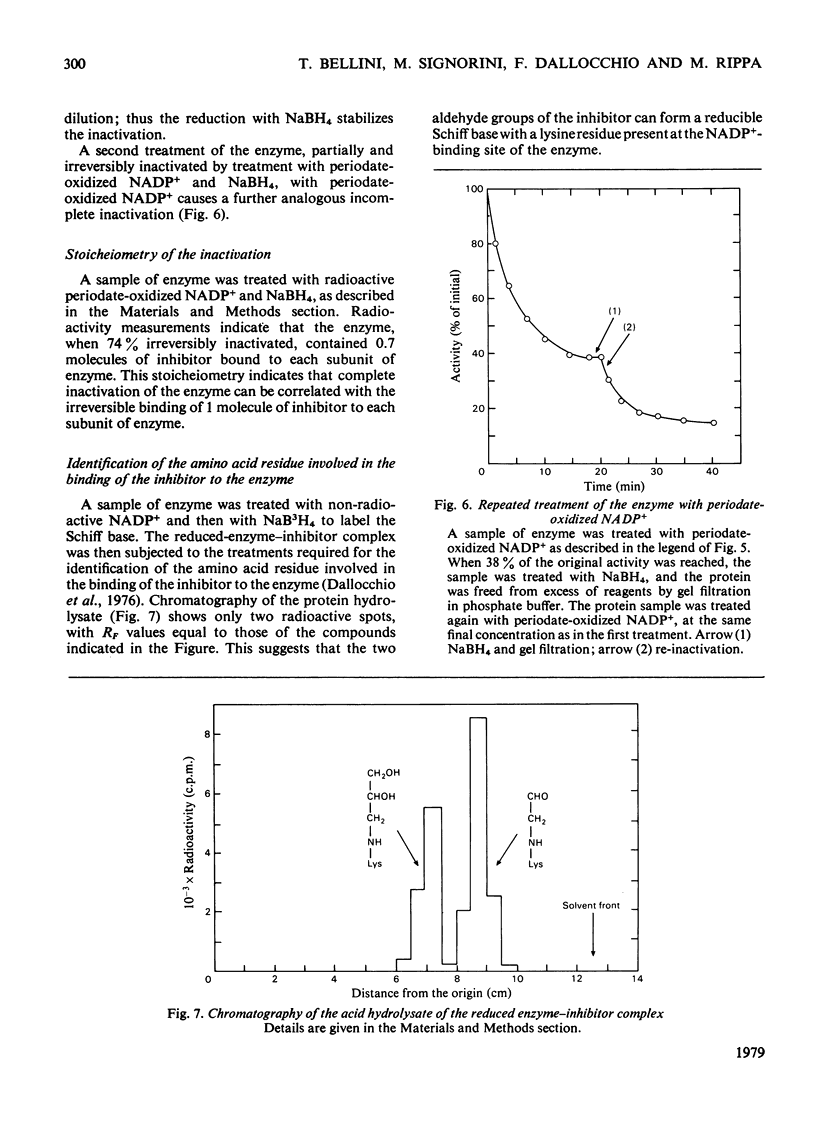
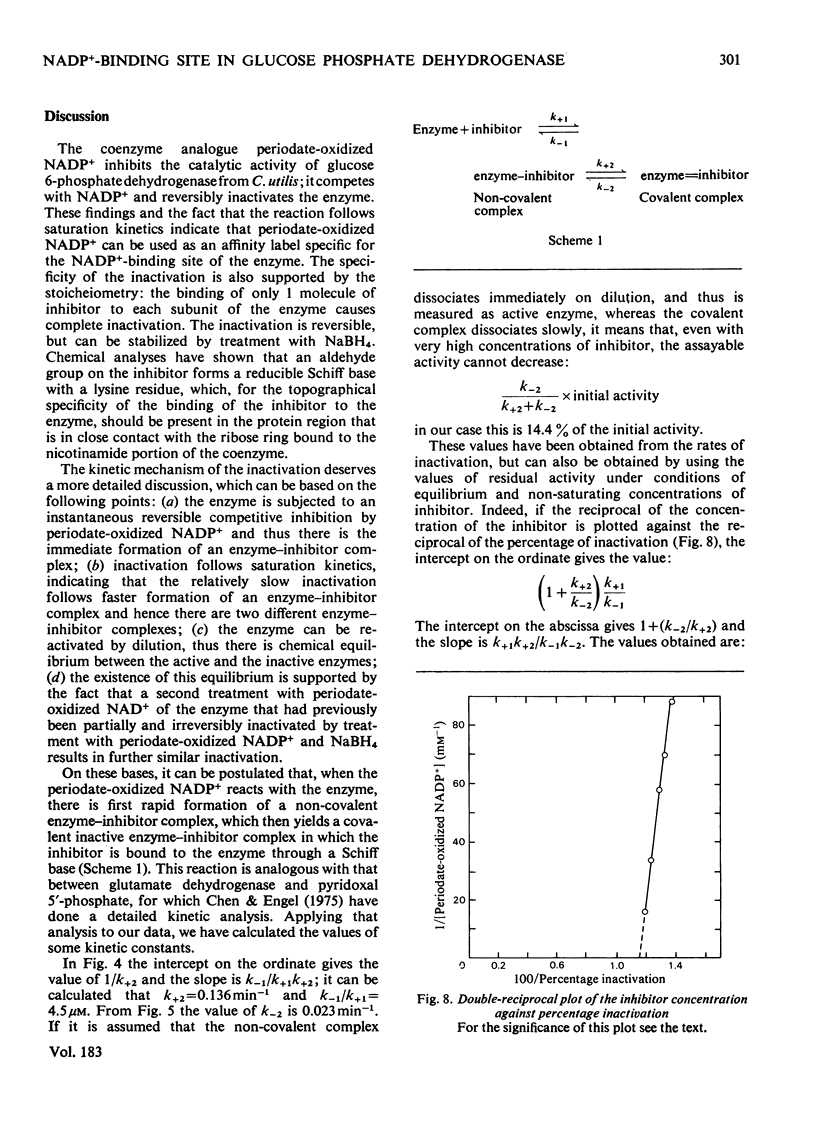
1. Periodate-oxidized NADP+ inhibits the catalytic activity of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Candida utilis, competing with NADP+. 2. Incubation of the enzyme with the coenzyme analogue causes partial reversible inactivation of the enzyme as a result of affinity labelling of the coenzyme-binding site. 3. Some kinetic values of the reaction were calculated. 4. The inactivation can be made irreversible by treatment with NaBH4, which reduces a Schiff base formed between an aldehyde group on the coenzyme analogue and a lysine residue on the enzyme. 5. Complete inactivation can be correlated with the binding of only one inhibitor to each enzyme subunit. 6. The lysine residue involved in the binding of the inhibitor is present at the coenzyme-binding site.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang G. G., Huang T. Oxidized NADP as a potential active-site-directed reagent of pigeon liver malic enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91787-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. S., Engel P. C. The equilibrium position of the reaction of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase with pyridoxal5'-phosphate. A demonstration that covalent modification with this reagent completely abolishes catalytic activity. Biochem J. 1975 May;147(2):351–358. doi: 10.1042/bj1470351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilla R., Doering K. M., Domagk G. F., Rippa M. A simplified procedure for the isolation of a highly active crystalline glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Candida utilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallocchio F., Negrini R., Signorini M., Rippa M. Identification of the chemical groups involved in the binding of periodate-oxidized NADP+ to 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloche H. P. Bromopyruvate inactivation of 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconic aldolase. I. Kinetic evidence for active site specificity. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2273–2280. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippa M., Signorini M., Signori R., Dallocchio F. A new powerful inhibitor specific for the TPN binding site of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):281–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80907-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trundle D., Cunningham L. W. Iodine oxidation of the sulfhydryl groups of creatine kinase. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):1919–1925. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold F. Affinity labeling--an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:3–14. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


