Abstract
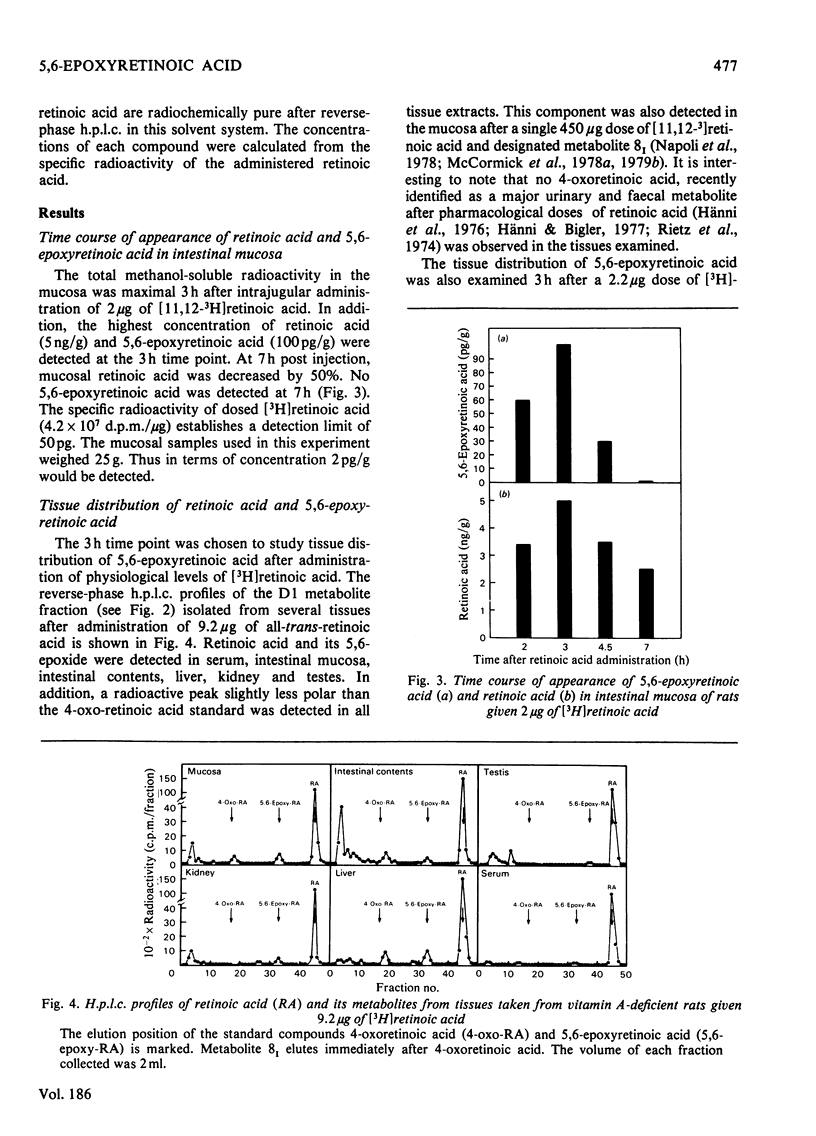
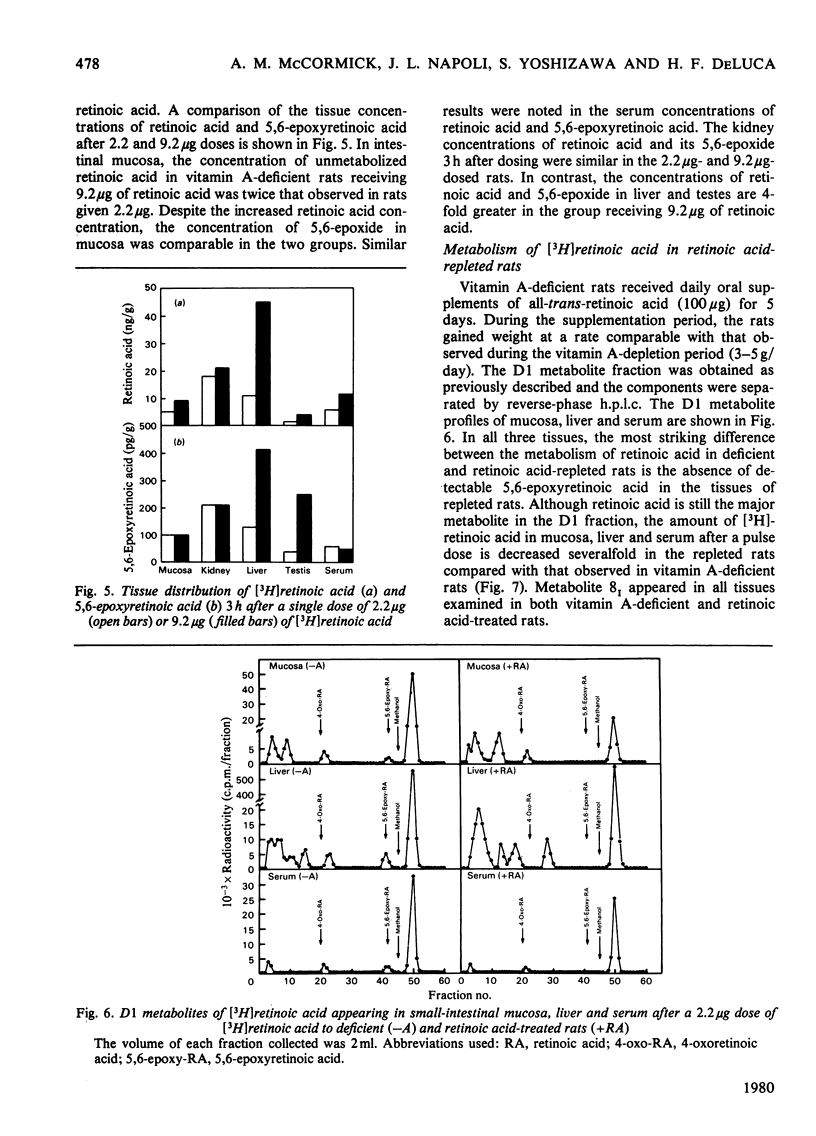
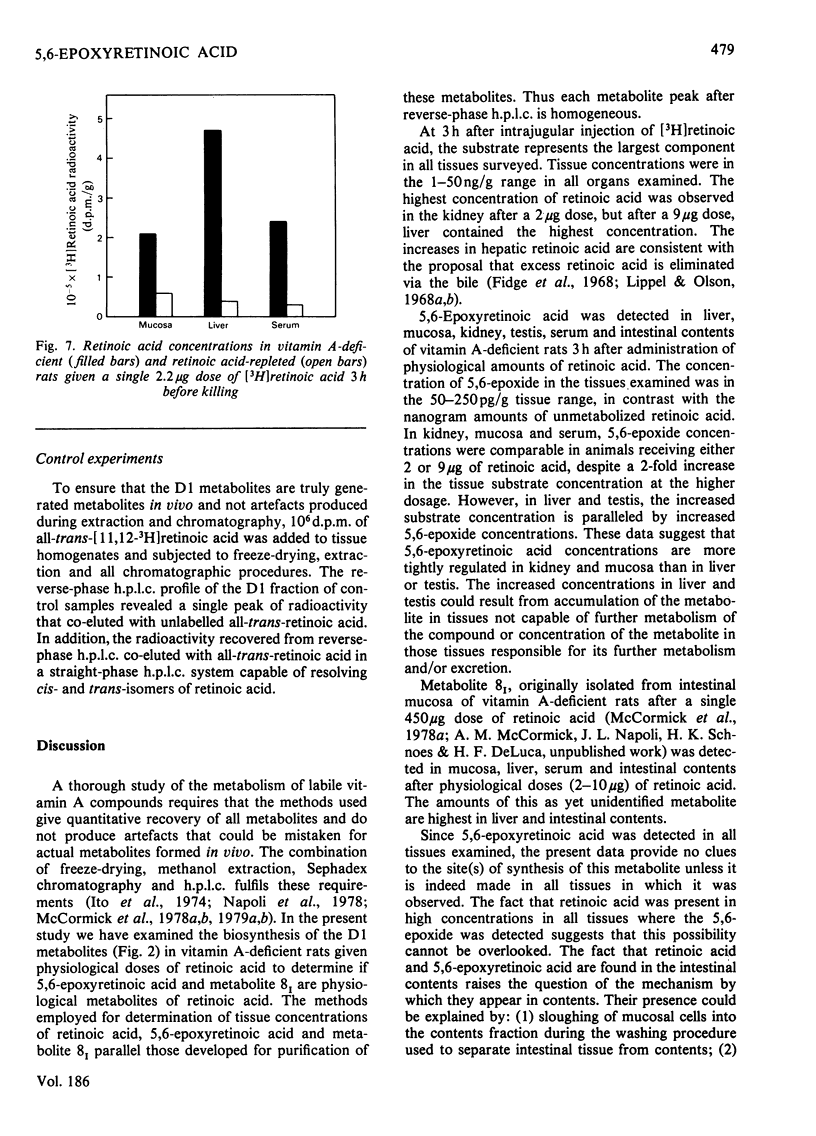
5,6-Epoxyretinoic acid was detected in small intestine, kidney, liver, testes and serum of vitamin A-deficient rats 3 h after a single physiological dose of [3H]retinoic acid. The maximum concentration of 5,6-epoxide in intestinal mucosa was observed 3 h after intrajugular administration of retinoic acid. However, at 7 h post administration, no 5,6-epoxyretinoic acid was detected in mucosa, demonstrating the rapid intestinal metabolism or excretion of this metabolite. No 5,6-epoxy[3H]retinoic acid was detected in mucosa, liver or serum of retinoic acid-repleted rats 3 h after administration of 2 micrograms of [3H]retinoic acid.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Luca L., Little E. P., Wolf G. Vitamin A and protein synthesis by rat intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):701–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Shiratori T., Ganguly J., Goodman D. S. Pathways of absorption of retinal and retinoic acid in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):103–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geison R. L., Johnson B. C. Studies on the in vivo metabolism of retinoic acid in the rat. Lipids. 1970 Apr;5(4):371–378. doi: 10.1007/BF02532101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänni R., Bigler F. Isolation and identification of three major metabolites of retinoic acid from rat feces. Helv Chim Acta. 1977 Apr 20;60(3):881–887. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19770600317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänni R., Bigler F., Meister W., Englert G. Isolation and identification of three urinary metabolites of retinoic acid in the rat. Helv Chim Acta. 1976 Sep 29;59(6):2221–2227. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19760590636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. L., Zile M., Ahrens H., DeLuca H. F. Liquid-gel partition chromatography of vitamin A compounds; formation of retinoic acid from retinyl acetate in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1974 Sep;15(5):517–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNGALWALA F. B., CAMA H. R. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF 5,6-MONOEPOXYVITAMIN A ACETATE, 5,6-MONOEPOXYVITAMIN A ALCOHOL, 5,6-MONOEPOXYVITAMIN A ALDEHYDE AND THEIR CORRESPONDING 5,8-MONOEPOXY (FURANOID) COMPOUNDS. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:17–26. doi: 10.1042/bj0950017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John K. V., Lakshmanan M. R., Cama H. R. Preparation, properties and metabolism of 5,6-monoepoxyretinoic acid. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):539–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1030539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. C., Kennedy M., Chiba N. Vitamin A and nuclear RNA synthesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Aug;22(8):1048–1058. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.8.1048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKSHMANAN M. R., JUNGALWALA F. B., CAMA H. R. METABOLISM AND BIOLOGICAL POTENCY OF 5,6-MONOEPOXYVITAMIN A ALDEHYDE IN THE RAT. Biochem J. 1965 Apr;95:27–34. doi: 10.1042/bj0950027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippel K., Olson J. A. Biosynthesis of beta-glucuronides of retinol and of retinoic acid in vivo and in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):168–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippel K., Olson J. A. Origin of some derivatives of retinoic acid found in rat bile. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):580–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A. M., Napoli J. L., Deluca H. F. High-pressure liquid chromatographic resolution of vitamin A compounds. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A. M., Napoli J. L., Schnoes H. K., DeLuca H. F. Isolation and identification of 5, 6-epoxyretinoic acid: a biologically active metabolite of retinoic acid. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4085–4090. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A. M., Napoli J. L., Schnoes H. K., DeLuca H. F. Isolation of 5,8-oxyretinoic acid from rat intestinal mucosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Feb;192(2):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan B., Thompson J. N. The preparation and biological activity of methyl 5,6-epoxy-retinoate. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):835–842. doi: 10.1042/bj1010835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli J. L., McCormick A. M., Schnoes H. K., DeLuca H. F. Identification of 5,8-oxyretinoic acid isolated from small intestine of vitamin A-deficient rats dosed with retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2603–2605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietz P., Wiss O., Weber F. Metabolism of vitamin A and the determination of vitamin A status. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:237–249. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zile M., DeLuca H. F. Retinoic acid: some aspects of growth-promoting activity in the albino rat. J Nutr. 1968 Mar;94(3):302–308. doi: 10.1093/jn/94.3.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zile M., Deluca H. F. Vitamin A and ribonucleic acid synthesis in rat intestine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Sep;140(1):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


