Abstract
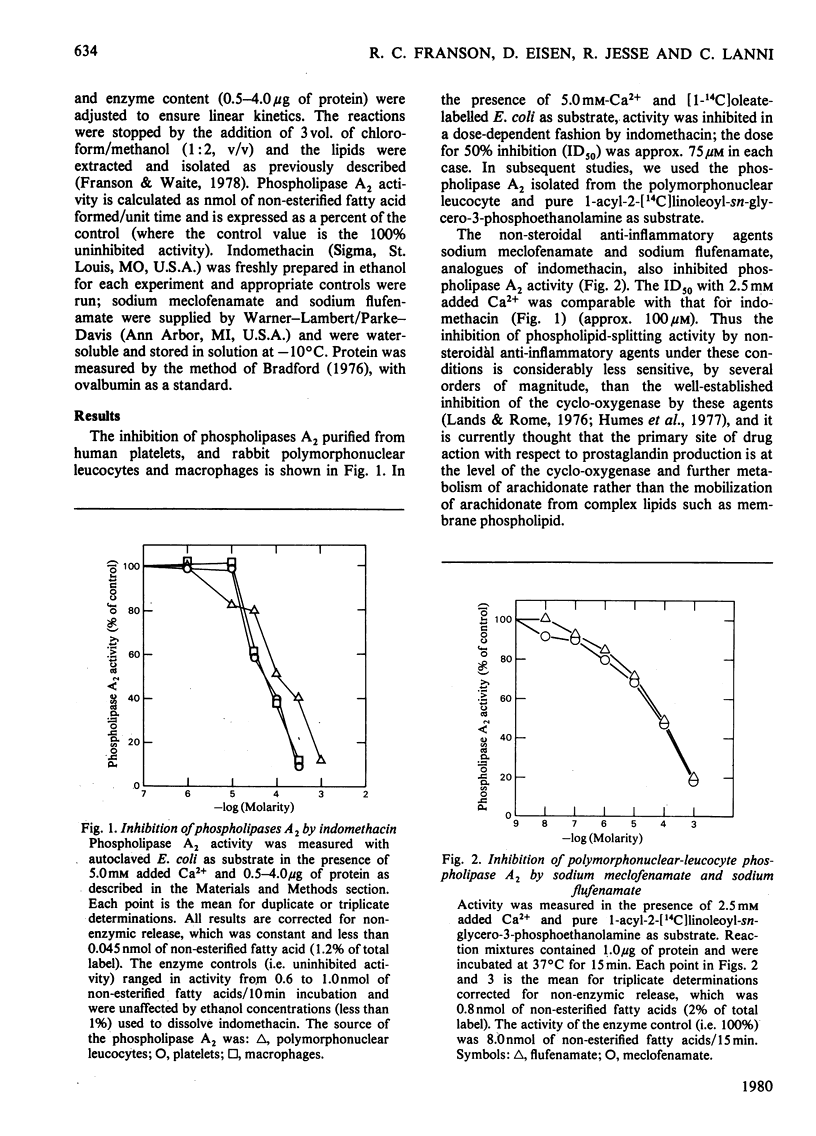
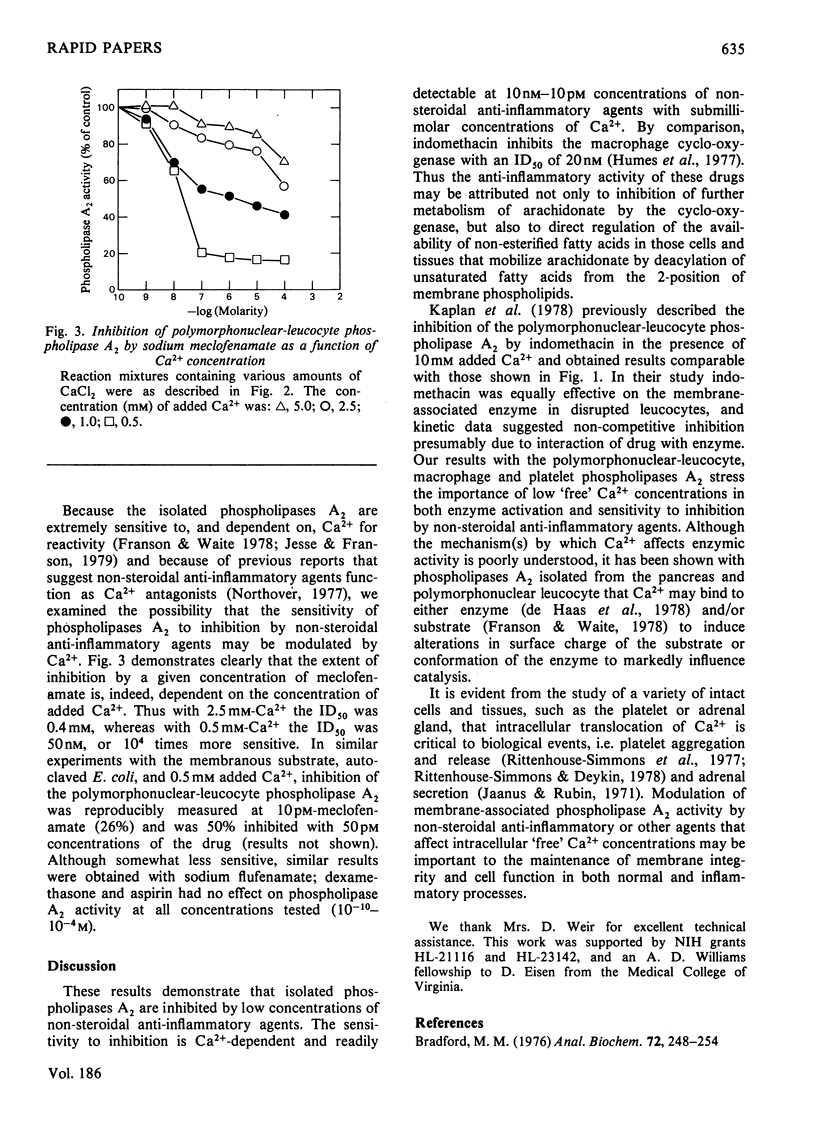
Highly purified Ca2+-dependent phospholipases A2 that were isolated from human platelets, rabbit alveolar macrophages and peritoneal polymorphonuclear leucocytes and were active in the neutral-to-alkaline pH range were inhibited 50% by 75 microM-indomethacin in the presence of 5.0 mM added Ca2+. Sodium meclofenamate and sodium flufenamate were also inhibitory; the sensitivity to inhibition was a function of Ca2+ concentration. The dose for 50% inhibition (ID50) with meclofenamate was 0.4 mM in the presence of 2.5 mM added Ca2+, but 50nM in the presence of 0.5 mM added Ca2+. Thus, inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents via Ca2+ antagonism may significantly contribute to the mechanism of drug action.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson R., Waite M. Relation between calcium requirement, substrate charge, and rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte phospholipase A2 activity. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4029–4033. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Bonney R. J., Pelus L., Dahlgren M. E., Sadowski S. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Davies P. Macrophages synthesis and release prostaglandins in response to inflammatory stimuli. Nature. 1977 Sep 8;269(5624):149–151. doi: 10.1038/269149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaanus S. D., Rubin R. P. The effect of ACTH on calcium distribution in the perfused cat adrenal gland. J Physiol. 1971 Mar;213(3):581–598. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L., Weiss J., Elsbach P. Low concentrations of indomethacin inhibit phospholipase A2 of rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2955–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northover B. J. Indomethacin--a calcium antagonist. Gen Pharmacol. 1977;8(5-6):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(77)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Deykin D. The activation by Ca2+ of platelet phospholipase A2. Effects of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate and 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 1;543(4):409–422. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S., Russell F. A., Deykin D. Mobilization of arachidonic acid in human platelets. Kinetics and Ca2+ dependency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):370–380. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite S., Schmeidler K., Elsbach P. Partial characterization and purification of a rabbit granulocyte factor that increases permeability of Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):33–42. doi: 10.1172/JCI107915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haas G. H., Slotboom A. J., Verheij H. M., Jansen E. H., de Araujo P. S., Vidal J. C. Interaction of phospholipase A2 with lipid-water interfaces. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1978;3:11–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


