Abstract
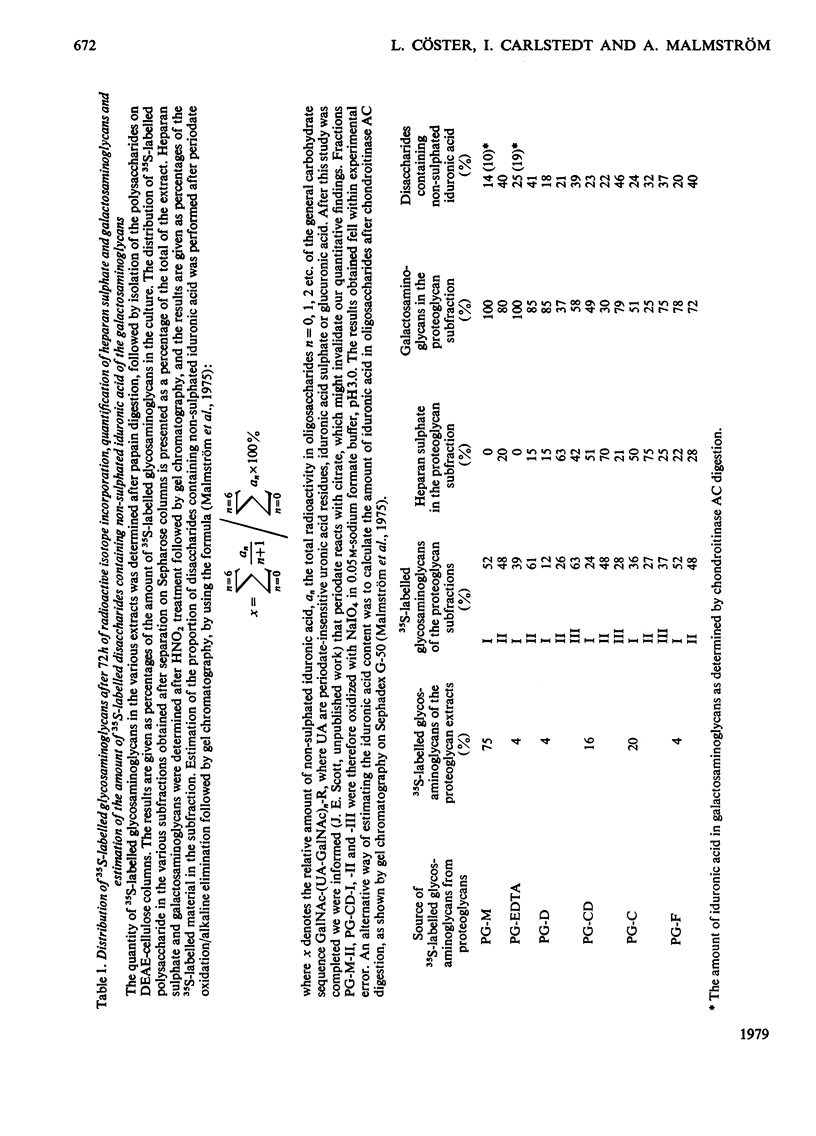
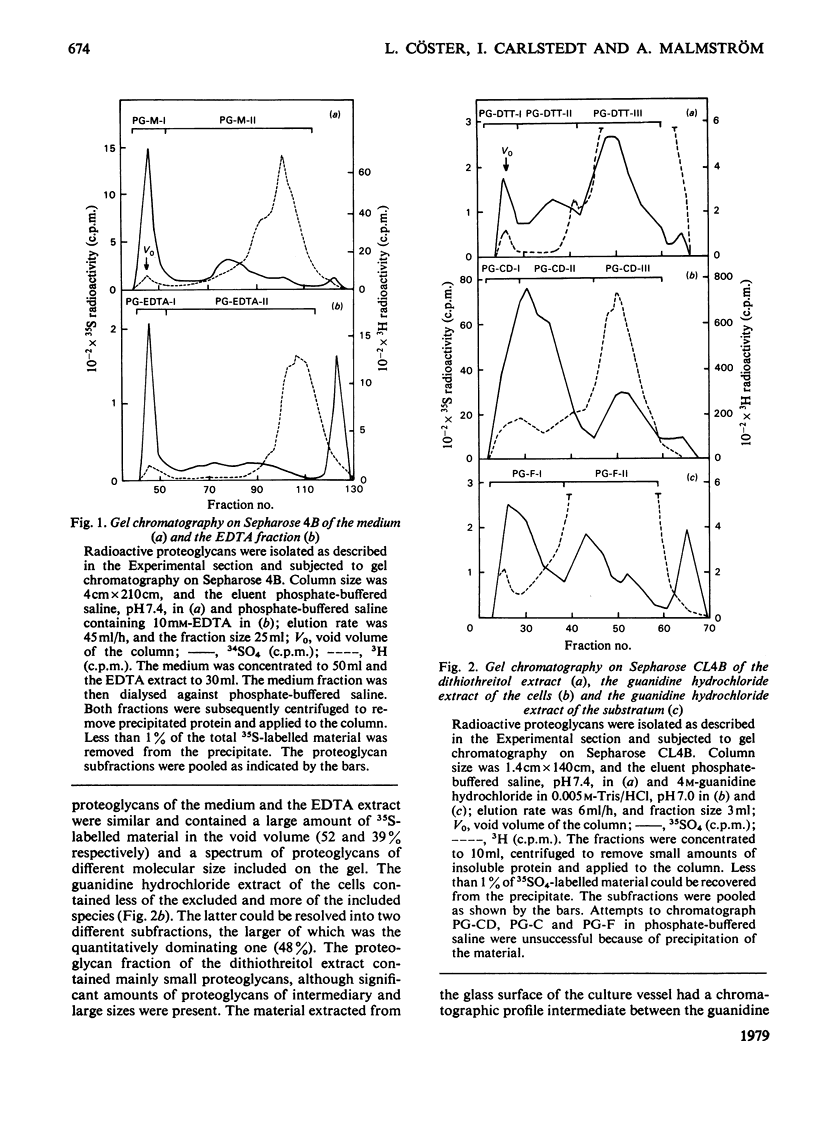
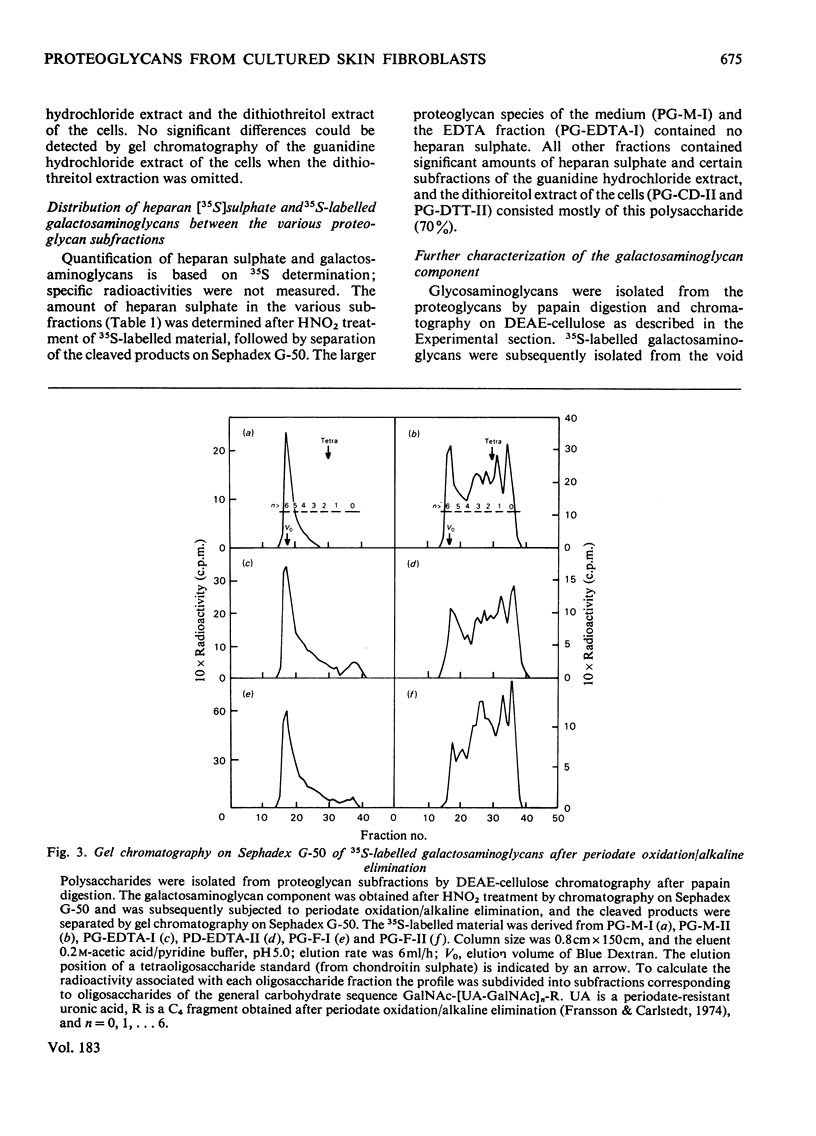
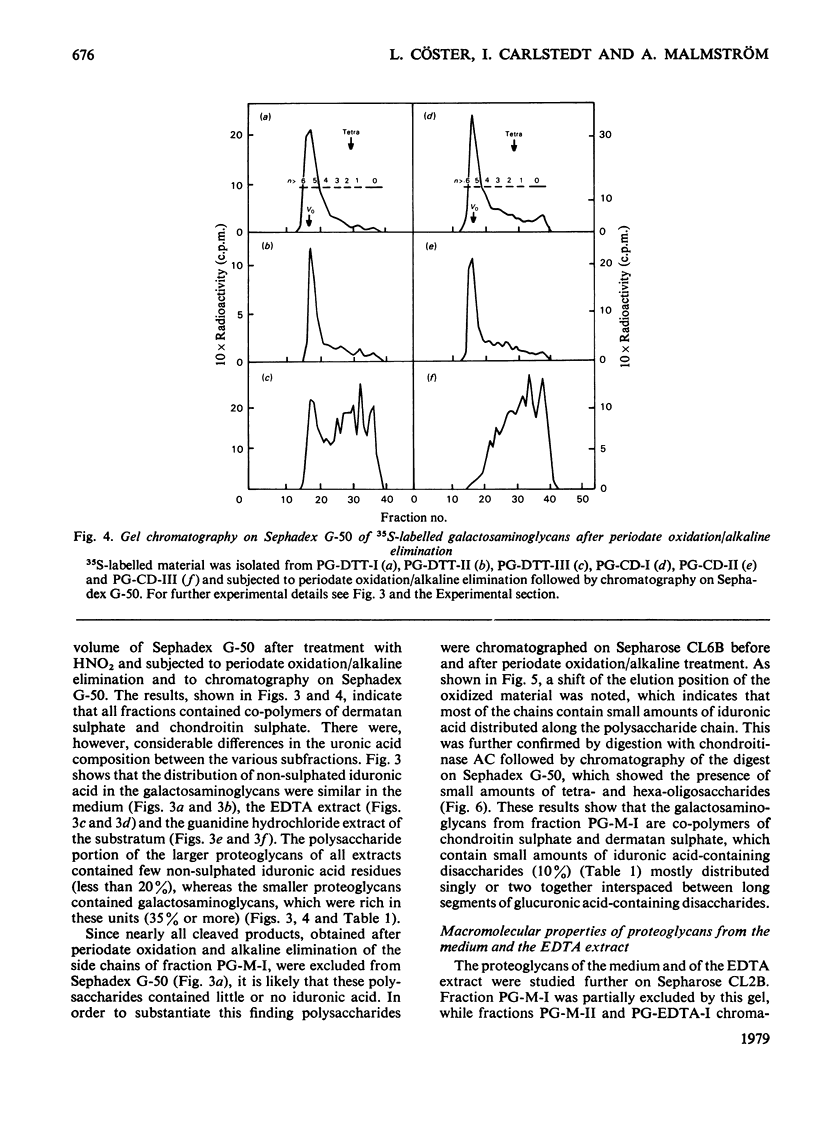
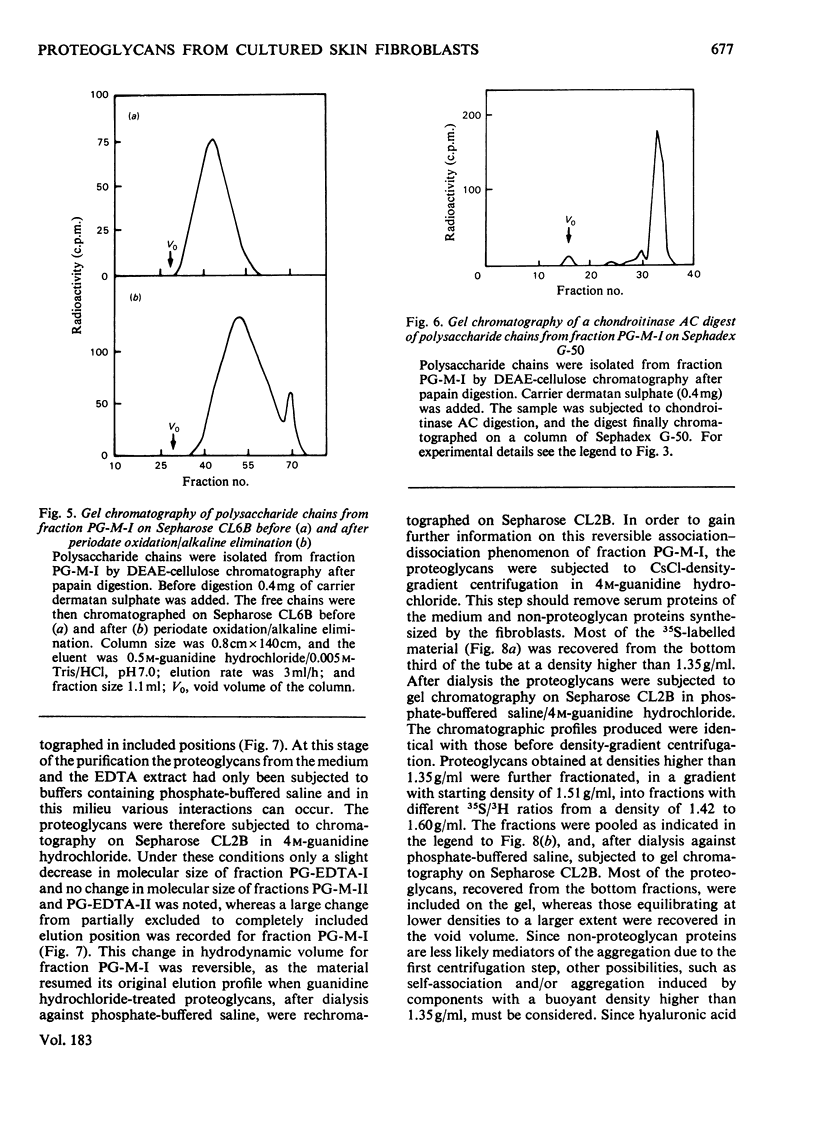
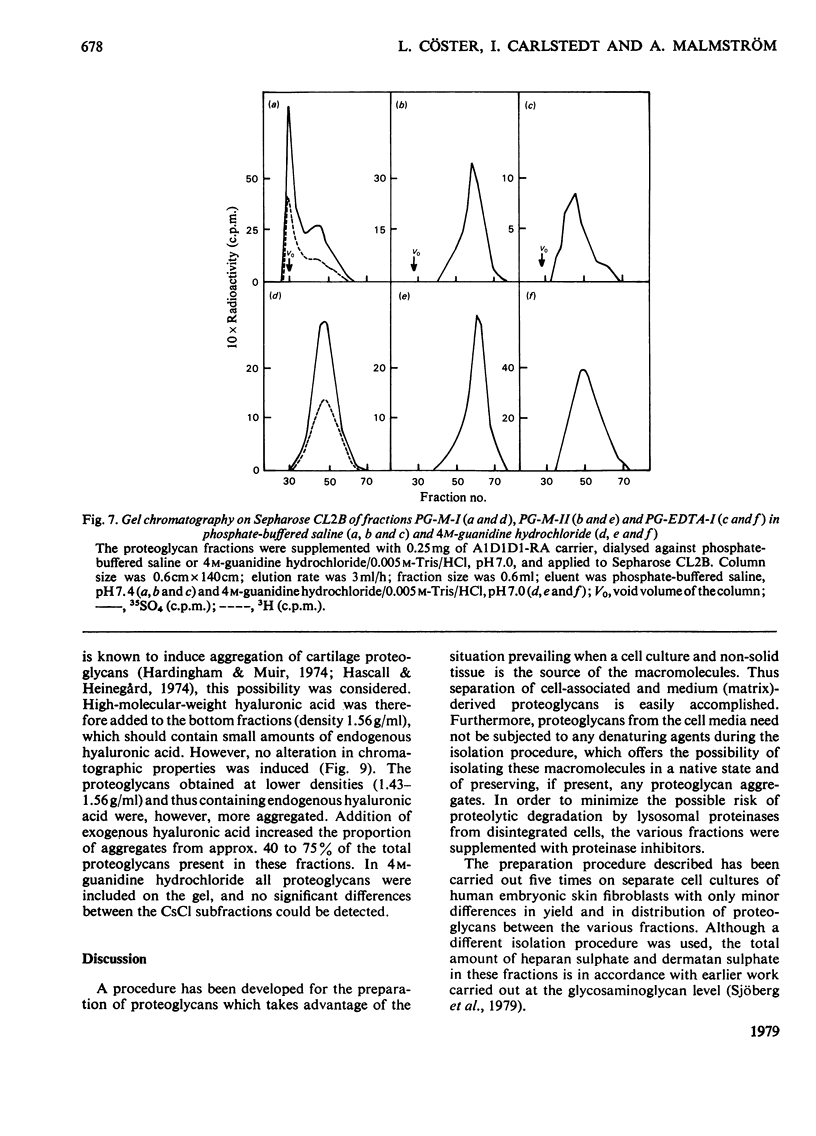
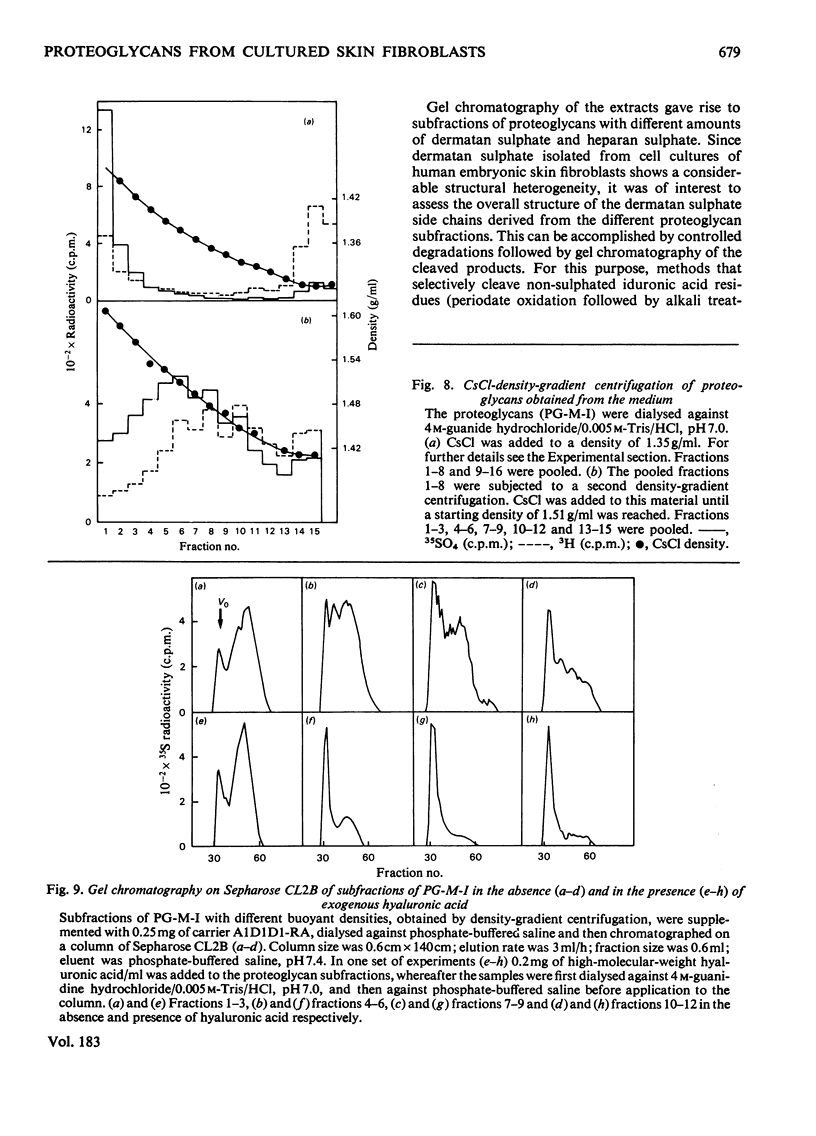
35SO42- - and [3H]-leucine-labelled proteoglycans were isolated from the medium of a fibroblast culture, from an EDTA extract of the monolayer, and from consecutive dithiothreitol and guanidine hydrochloride extracts of the cells. Proteoglycans of different sizes were isolated from the extracts by gel chromatography on Sepharose 4B. In the medium and the EDTA extract the largest proteoglycans contained only 35S-labelled galactosaminoglycan, whereas all other fractions contained in addition heparan [35S-labelled galactosaminoglycan, whereas all other fractions contained in addition heparin [35S]sulphate. The galactosaminoglycan-containing proteoglycans of the various extracts were separated into a larger component, containing chondroitin sulphate-like side chains, and a smaller component, containing dermatan sulphate. The larger proteoglycan of the medium showed reversible association-dissociation behaviour when chromatographed on Sepharose CL2B in phosphate-buffered saline and 4M-guanidine hydrochloride respectively. This property remained after removal of extraneous proteins by CsCl-density-gradient centrifugation in guanidine hydrochloride. The association was markedly increased by the addition of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conrad G. W., Hamilton C., Haynes E. Differences in glycosaminoglycans synthesized by fibroblast-like cells from chick cornea, heart, and skin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6861–6870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Carlstedt I. Alkaline and smith degradation of oxidized dermatan sulphate-chondroitin sulphate copolymers. Carbohydr Res. 1974 Sep;36(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A. Interaction between dermatan sulphate chains. I. Affinity chromatography of copolymeric galactosaminioglycans on dermatan sulphate-substituted agarose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 23;437(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A. Periodate oxidation of L-iduronic acid residues in dermatan sulphate. Carbohydr Res. 1974 Sep;36(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)83055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fratantoni J. C., Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. The defect in Hurler's and Hunter's syndromes: faulty degradation of mucopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):699–706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSFELD H., MEYER K., GODMAN G., LINKER A. Mucopolysaccharides produced in tissue culture. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 May 25;3(3):391–396. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.3.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Polydispersity of cartilage proteoglycans. Structural variations with size and buoyant density of the molecules. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1980–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer P. M. Heparan sulfates of cultured cells. II. Acid-soluble and -precipitable species of different cell lines. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1445–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresse H., von Figura K., Buddecke E., Fromme H. G. Metabolism of sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cultivated bovine arterial cells. I. Characterization of different pools of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Jun;356(6):929–941. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1975.356.s1.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAGUNOFF D., WARREN G. Determination of 2-deoxy-2-sulfoaminohexose content of mucopolysaccharides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Dec;99:396–400. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malström A., Carlstedt I., Aberg L., Fransson L. A. The copolymeric structure of dermatan sulphate produced by cultured human fibroblasts. Different distribution of iduronic acid and glucuronic acid-containing units in soluble and cell-associated glycans. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):477–489. doi: 10.1042/bj1510477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Dorfman A. Hurler's syndrome: biosynthesis of acid mucopolysaccharides in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1310–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurtrey J., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Dalferes E. R., Jr, Berenson G. S., Gregory J. D. Isolation of proteoglycan-hyaluronate complexes from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1621–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norling B., Glimelius B., Westermark B., Wasteson A. A chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan from human cultured glial cells aggregates with hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):914–921. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. Isolation and partial characterization of a dermatan sulphate proteoglycan from pig skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 21;264(2):354–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Eisenstein R. Characterization of bovine aorta proteoglycan extracted with guanidine hydrochloride in the presence of protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1312–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Uzman B. G. Production and secretion of chondroitin sulfates and dermatan sulfate by established mammalian cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 21;43(4):723–728. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90675-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg I., Carlstedt I., Cöster L., Malmström A., Fransson L. A. Structure and metabolism of sulphated glycosaminoglycans in cultures of human fibroblasts. Structural characteristics of co-polymeric galactosaminoglycans in sequential extracts of fibroblasts during pulse-chase experiments. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):257–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1780257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg I., Fransson L. A. Synthesis of glycosaminoglycans by human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Different distribution of heparan sulphate, chondroitin sulphate and dermatan sulphate in various fractions of cell culture. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):383–392. doi: 10.1042/bj1670383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Saito H., Yamagata T., Anno K., Seno N., Kawai Y., Furuhashi T. Formation of three types of disulfated disaccharides from chondroitin sulfates by chondroitinase digestion. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1543–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Lowther D. A. Dermatan sulfate-protein: isolation from and interaction with collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


