Abstract
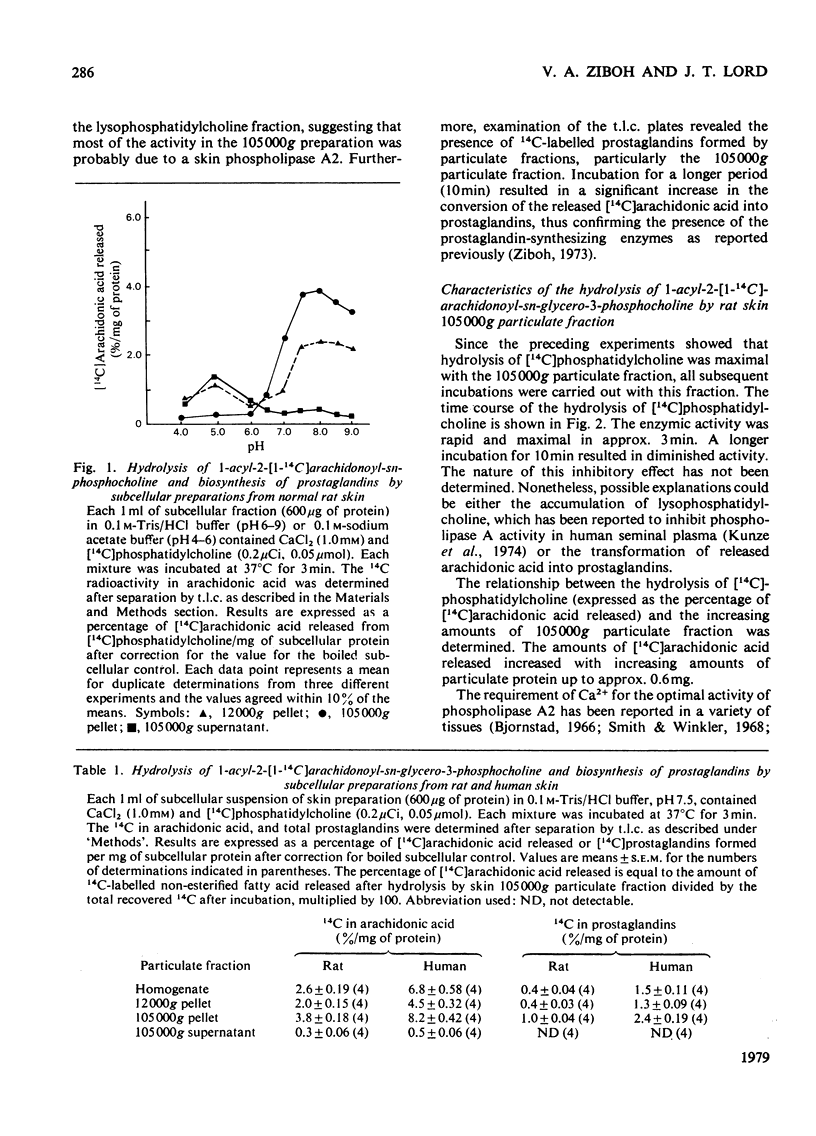
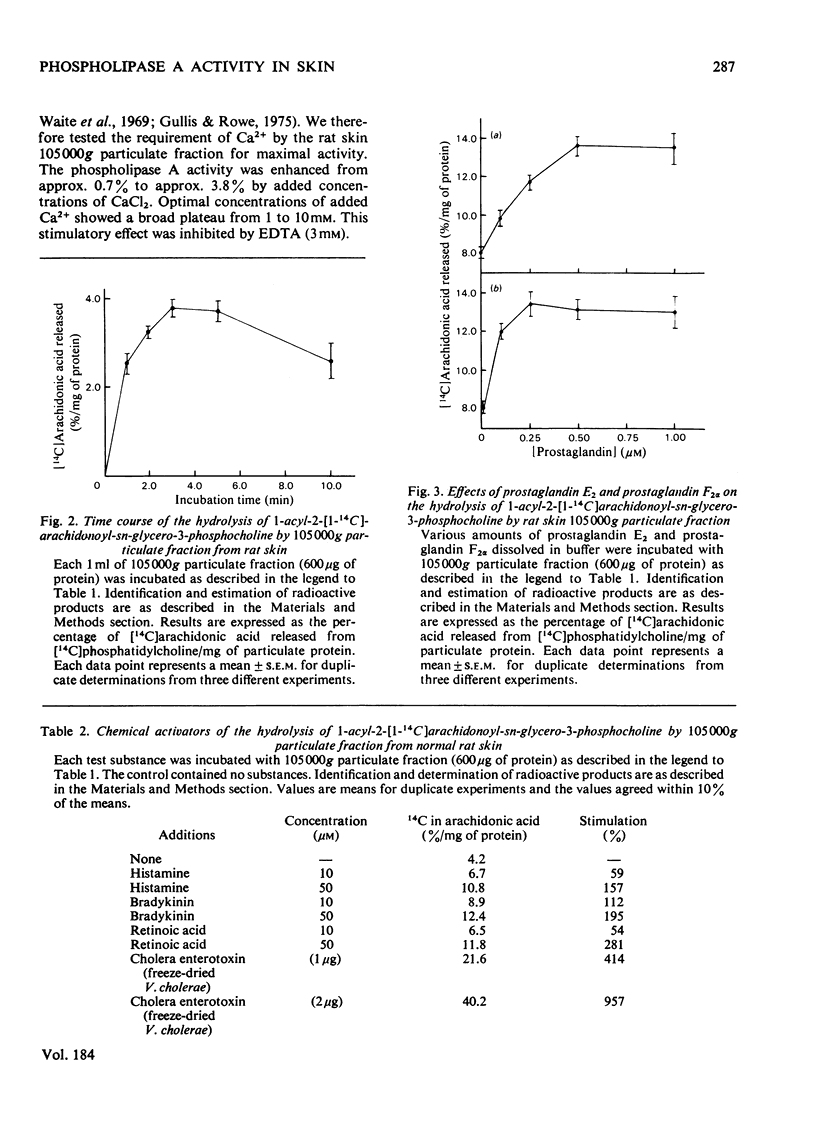
The distribution of the hydrolysis of 1-acyl-2-[1-14C]arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine and the simultaneous biosynthesis of prostaglandins by subcellular fractions from human and rat skin membrane preparations were determined. The phospholipase A2 activity was distributed among the subcellular particulate preparations with the highest specific activity in the 105000g particulate fraction. The activity was optimal at pH 7.5 in the presence of 1.0 mM-CaCl2 and was inhibited by EDTA. The hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine by the skin 105000g particulate fraction was inhibited by cortisol and triamcinolone acetonide and it was stimulated by histamine, bradykinin, retinoic acid and cholera enterotoxin (freeze-dried Vibrio cholerae). Furthermore hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine by the skin phospholipase A was also enhanced by low concentrations of prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2 alpha. These last results suggest that the amplication of the hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine by prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin F2 alpha, with the consequent release of arachidonic acid (the substrate of prostaglandin synthesis) is likely a positive-feedback regulation of the arachidonic acid-prostaglandin cascade.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjornstad P. Phospholipase activity in rat-liver microsomes studied by the use of endogenous substrates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 1;116(3):500–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsten M. E., Miller J. D. Effects of prostaglandins and oxytocin on calcium release from a uterine microsomal fraction. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1576–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finck A. D., Katz R. L. Prevention of cholera-induced intestinal secretion in the cat by aspirin. Nature. 1972 Aug 4;238(5362):273–274. doi: 10.1038/238273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. The importance of phospholipase-A2 in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Feb 1;25(3):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALLAI-HATCHARD J. J., THOMPSON R. H. PHOSPHOLIPASE-A ACTIVITY OF MAMMALIAN TISSUES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 1;98:128–136. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Panczenko B., Korbut R., Grodzinska L., Ocetkiewicz A. Corticosteroids inhibit prostaglandin release from perfused mesenteric blood vessels of rabbit and from perfused lungs of sensitized guinea pig. Prostaglandins. 1975 Aug;10(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullis R. J., Rowe C. E. The stimulation by transmitter substances and putative transmitter substances of the net activity of phospholipase A2 of synaptic membranes of cortex of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):197–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1480197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- HANAHAN D. J. The enzymatic degradation of phosphatidyl choline in diethyl ether. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B., Duell E. A., Stawiski M., Voorhees J. J. Increased concentrations of nonesterified arachidonic acid, 12L-hydroxy-5,8,10,14-eicosatetraenoic acid, prostaglandin E2, and prostaglandin F2alpha in epidermis of psoriasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5130–5134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze H., Nahas N., Wurl M. Phospholipases in human seminal plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 26;348(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze H., Vogt W. Significance of phospholipase A for prostaglandin formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:123–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDS W. E. Metabolism of glycerolipids. 2. The enzymatic acylation of lysolecithin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2233–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long V. J. Variations in lipid composition at different depths in the cow snout epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Oct;55(4):269–273. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin E-like substance from canine kidney by bradykinin. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):36–43. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and the oedema of inflammation. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):217–219. doi: 10.1038/246217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachbaur J., Colbeau A., Vignais P. M. Distribution of membrane-confined phospholipases A in the rat hepatocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):426–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp F. P., Flower R. J., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Partial purification of rabbit aorta contracting substance-releasing factor and inhibition of its activity by anti-inflammatory steroids. Nature. 1976 Oct 7;263(5577):479–482. doi: 10.1038/263479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Voglmayr J. K., White I. G. Phospholipid changes in spermatozoa during passage through the genital tract of the bull. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 24;306(2):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. F., LANDS W. E. Positional specificites in phospholipid hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman Y. E., Verhagen J. Evidence of a membrane-bound phospholipase A in rat liver lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):670–677. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90633-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherphof G., Westenberg H. Stimulation and inhibition of pancreatic phospholipase A2 by local anesthetics as a result of their interaction with the substrate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 19;398(3):442–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. D., Winkler H. Lysosomal phospholipases A1 and A2 of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1968 Aug;108(5):867–874. doi: 10.1042/bj1080867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonkeman H., van Dorp D. A. The action of prostaglandin synthetase on 2-arachidonyl-lecithin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):430–432. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M. Isolation of rat liver mitochondrial membrane fractions and localization of the phospholipase A. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2536–2542. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weglicki W. B., Waite M., Sisson P., Shohet S. B. Myocardial phospholipase A of microsomal and mitochondrial fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 4;231(3):512–519. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziboh V. A. Biosynthesis of prostaglandin E 2 in human skin: subcellular localization and inhibition by unsaturated fatty acids and anti-inflammatory drugs. J Lipid Res. 1973 Jul;14(4):377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziboh V. A., Hsia S. L. Effects of prostaglandin E 2 on rat skin: inhibition of sterol ester biosynthesis and clearing of scaly lesions in essential fatty acid deficiency. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):458–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziboh V. A., Price B., Fulton J. Effects of retinoic acid on prostaglandin biosynthesis in guinea-pig skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Oct;65(4):370–374. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12607622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziboh V. A., Vanderhoek J. Y., Lands W. E. Inhibition of sheep vesicular gland oxygenase by unsaturated fatty acids from skin of essential fatty acid deficient rats. Prostaglandins. 1974 Feb 10;5(3):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


